Abstract
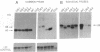
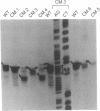
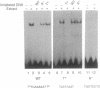
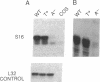
All of the mammalian ribosomal protein (rp) genes examined to date initiate transcription with high precision despite the fact that they do not contain a well-defined TATA box. The initiation sites are situated within polypyrimidine tracts that are flanked by both upstream and intragenic promoter elements. In the TATA-box region of each rp promoter, there is a functionally critical element with nuclear factor binding specificity that is distinct from that of a conventional TATA box. To understand how the various elements contribute to rp promoter function, we have used site-specific mutagenesis-transfection protocols and factor binding analyses to evaluate the significance of the polypyrimidine initiator and the TATA-box counterpart for efficient and accurate transcription of the rpS16 gene. Our results indicate (i) that the polypyrimidine initiator sequence critically defines the position of the transcriptional start site, whereas a much less specific sequence is sufficient to satisfy the efficiency requirement; (ii) that an uninterrupted stretch of pyrimidines in the initiator region is not necessary for efficient transcription of rpS16 gene; and (iii) that the TATA-box counterpart or even a substituted conventional TATA box primarily influences promoter efficiency. The great diversity of promoter design, which is becoming evident as more RNA polymerase II promoters are being carefully dissected, suggests that the requirements for building a functional initiation complex may be much more flexible than was previously appreciated.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayer D. E., Dynan W. S. Simian virus 40 major late promoter: a novel tripartite structure that includes intragenic sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2021–2033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I. T., Roufa D. J. The transcriptionally active human ribosomal protein S17 gene. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Struhl K. Saturation mutagenesis of a yeast his3 "TATA element": genetic evidence for a specific TATA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2691–2695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S., Perry R. P. Importance of introns for expression of mouse ribosomal protein gene rpL32. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2075–2082. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Buratowski S., Sharp P. A., Guarente L. Yeast TATA-binding protein TFIID binds to TATA elements with both consensus and nonconsensus DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5718–5722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Equipotent mouse ribosomal protein promoters have a similar architecture that includes internal sequence elements. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1789–1800. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Perry R. P. A characterization of the elements comprising the promoter of the mouse ribosomal protein gene RPS16. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5323–5337. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Luciw P. A., Duchange N. Structural arrangements of transcription control domains within the 5'-untranslated leader regions of the HIV-1 and HIV-2 promoters. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1101–1114. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. E., Coleclough C., Perry R. P. Functional significance and evolutionary development of the 5'-terminal regions of immunoglobulin variable-region genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):681–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. F., Concino M. F., Weinmann R. Genetic profile of the transcriptional signals from the adenovirus major late promoter. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90657-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tilly K., Maniatis T. Fine structure genetic analysis of a beta-globin promoter. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):613–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3457470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Multiple mRNAs for 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase determined by multiple transcription initiation sites and intron splicing sites in the 5'-untranslated region. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10369–10377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. C., Fisch T. M., Benecke B. J., Nevins J. R., Heintz N. Definition of multiple, functionally distinct TATA elements, one of which is a target in the hsp70 promoter for E1A regulation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):723–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90410-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga K., Hirose S., Suzuki Y. In monkey COS cells only the TATA box and the cap site region are required for faithful and efficient initiation of the fibroin gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1543–1558. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M., Perry R. P. Characterization of the multigene family encoding the mouse S16 ribosomal protein: strategy for distinguishing an expressed gene from its processed pseudogene counterparts by an analysis of total genomic DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3560–3576. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B. Transcription elements and factors of RNA polymerase B promoters of higher eukaryotes. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1988;23(2):77–120. doi: 10.3109/10409238809088317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]