Abstract
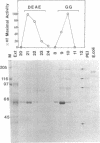
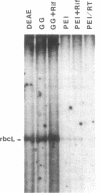
Prominent polypeptides with apparent molecular masses of 180, 120, 85, and 38 kDa are found in an extensively purified preparation of maize chloroplast DNA-dependent RNA polymerase that retains the capacity to initiate transcription of the cloned chloroplast gene rbcL correctly and the requirement for a supercoiled DNA template for specific and active transcription. Amino-terminal amino acid sequences of the 180-, 120-, and 38-kDa polypeptides have been determined and found to correspond precisely to the sequences deduced from the 5' ends of the maize chloroplast rpoC2, rpoB, and rpoA genes, respectively. These experiments show that these chloroplast rpo genes encode the prominent polypeptides in the highly enriched maize chloroplast RNA polymerase preparation and support the conclusion that these polypeptides are functional components of the enzyme. The rpoB, rpoC1, and rpoC2 genes have been mapped on the maize chloroplast chromosome.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Audren H., Bisanz-Seyer C., Briat J. F., Mache R. Structure and transcription of the 5S rRNA gene from spinach chloroplasts. Curr Genet. 1987;12(4):263–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00435288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley W., Smith H. J., Bogorad L. RNA polymerases of maize: partial purification and properties of the chloroplast enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D., Gatenby A. A. Mutational analysis of the maize chloroplast ATPase-beta subunit gene promoter: the isolation of promoter mutants in E. coli and their characterization in a chloroplast in vitro transcription system. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3641–3648. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04129.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozens A. L., Walker J. E. Pea chloroplast DNA encodes homologues of Escherichia coli ribosomal subunit S2 and the beta'-subunit of RNA polymerase. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):453–460. doi: 10.1042/bj2360453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossland L. D., Rodermel S. R., Bogorad L. Single gene for the large subunit of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase in maize yields two differentially regulated mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4060–4064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiratsuka J., Shimada H., Whittier R., Ishibashi T., Sakamoto M., Mori M., Kondo C., Honji Y., Sun C. R., Meng B. Y. The complete sequence of the rice (Oryza sativa) chloroplast genome: intermolecular recombination between distinct tRNA genes accounts for a major plastid DNA inversion during the evolution of the cereals. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):185–194. doi: 10.1007/BF02464880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson G. S., Holton T. A., Whitfield P. R., Bottomley W. Spinach chloroplast rpoBC genes encode three subunits of the chloroplast RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 20;200(4):639–654. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90477-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly S. O., Bogorad L. Preferential transcription of cloned maize chloroplast DNA sequences by maize chloroplast RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):822–826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd G. H., Bogorad L. A facile procedure for purifying maize chloroplast RNA polymerase from whole cell homogenates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 26;609(1):14–30. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerbs S., Bräutigam E., Parthier B. Polypeptides of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of spinach chloroplasts: characterization by antibody-linked polymerase assay and determination of sites of synthesis. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1661–1666. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03834.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little M. C., Hallick R. B. Chloroplast rpoA, rpoB, and rpoC genes specify at least three components of a chloroplast DNA-dependent RNA polymerase active in tRNA and mRNA transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14302–14307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinke A., Igloi G. L., Kössel H. Nucleotide sequence of tDNA(Cys)GCA and its flanking regions from Zea mays chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5696–5696. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purton S., Gray J. C. The plastid rpoA gene encoding a protein homologous to the bacterial RNA polymerase alpha subunit is expressed in pea chloroplasts. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 May;217(1):77–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00330945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruf M., Kössel H. Structure and expression of the gene coding for the alpha-subunit of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from the chloroplast genome of Zea mays. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):5741–5754. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.5741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D., Bogorad L. Transcription analysis of the maize chloroplast gene for the ribosomal protein S4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1853–1867. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Ohme M., Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Hayashida N., Matsubayashi T., Zaita N., Chunwongse J., Obokata J., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2043–2049. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sijben-Müller G., Hallick R. B., Alt J., Westhoff P., Herrmann R. G. Spinach plastid genes coding for initiation factor IF-1, ribosomal protein S11 and RNA polymerase alpha-subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):1029–1044. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. J., Bogorad L. The polypeptide subunit structure of the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of Zea mays chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4839–4842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirdivant S. M., Crossland L. D., Bogorad L. DNA supercoiling affects in vitro transcription of two maize chloroplast genes differently. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4886–4890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaitlin D., Hu J., Bogorad L. Binding and transcription of relaxed DNA templates by fractions of maize chloroplast extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):876–880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]