Abstract
Background
Long-term treatment with antibiotics containing pivalic acid may decrease serum carnitine concentration and can sometimes be associated with severe hypoglycemia and encephalopathy in infants. Little has been reported, however, on severe hypocarnitinemia induced by acute administration in older children.
Case presentation
We describe a 6-year-old Japanese girl with Fukuyama-type congenital muscular dystrophy who lost consciousness after 3 days of treatment with an antibiotic containing pivalic acid (cefditoren pivoxil). Investigations at the onset of unconsciousness revealed hypoglycemia (free plasma glucose concentration: 31 mg/dL) and hypocarnitinemia (serum free carnitine concentration: 6.2 μmol/L). Intravenous administration of glucose rapidly improved her symptoms without any complications. Serum free carnitine concentration was 29.0 μmol/L immediately prior to the initiation of cefditoren pivoxil. Computed tomography scanning showed severe peripheral skeletal muscle atrophy, indicating the likelihood of decreased carnitine stores in skeletal muscle.
Conclusions
Although serum carnitine concentration can appear deceptively normal, skeletal muscle carnitine stores can be reduced in patients with severe muscular atrophy. Even a short course of a pivalate-containing antibiotic can lead to life-threatening hypocarnitinemia in older children with severe muscular dystrophy.
Keywords: Carnitine, Fukuyama-type congenital muscular dystrophy, Antibiotics, Pivalic acid, Hypoglycemia
Background
Carnitine, a water-soluble quaternary amine, is responsible for the intracellular transport of long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria, facilitating fatty acid oxidation. Severe carnitine deficiency impairs β-oxidation, and thereby the ability to produce glucose, which may result in hypoglycemia. Although most patients with carnitine deficiency are asymptomatic, it can cause muscle weakness, hypotonia, nausea and vomiting, fatigue, recurrent infection, failure to thrive, poor appetite, poor concentration, apathy, and headaches. Furthermore, carnitine deficiency can occasionally cause severe and life-threatening complications, including hypoglycemic encephalopathy and dilated cardiomyopathy [1, 2].
Carnitine deficiency may be classified as primary or secondary; the primary form is associated with genetically determined metabolic errors whereas the secondary form is associated with acquired diseases or iatrogenic factors such as drug administration. Recent studies have reported that severe secondary carnitine deficiency induced by long-term administration of pivalate-containing antibiotics, particularly for more than 14 days, causes hypoketotic hypoglycemia and acute encephalopathy in infants [3–6]. However, there have been few reports to date of carnitine deficiency provoked by short-term antibiotics in older children. Here, we report the case of a 6-year-old girl with Fukuyama-type congenital muscular dystrophy (FCMD) who developed severe hypoglycemia caused by carnitine deficiency after a 3-day oral course of cefditoren pivoxil (CDTR-PI), an antibiotic containing pivalic acid.
Case presentation
A 6-year-old Japanese girl with FCMD was admitted to our hospital with sudden-onset impaired consciousness. She had been diagnosed with FCMD by genetic testing at 9 months of age, having a homo-retrotransposon insertional mutation of the fukutin gene. Her height was 108 cm (−1.0 SD) and weight was 13.0 kg (−2.0 SD). She was able to sit but not stand, and could eat only a soft diet. Her Gross Motor Function Classification System score was level five [7]. She had previously been admitted to hospital for treatment of acute pharyngitis, for which she was prescribed CDTR-PI (8.5 mg/kg/day orally). During this time, she could consume half of her usual calorific intake without weight loss or dehydration. After 3 days of treatment, her level of consciousness declined. On physical examination, her Glasgow Coma Scale score was 9 out of 15 (E3V2M4), core temperature was 36.6 °C, blood pressure was 108/68 mmHg, and heart rate was 130 beats/min. Laboratory investigations revealed a serum creatine kinase concentration of 588 IU/L and hypoglycemia (free plasma glucose concentration of 31 mg/dL). Hepatic and renal function, serum electrolyte and ammonia concentrations, and acid-base balance were all within the normal range, but serum free carnitine concentration was markedly reduced (6.2 μmol/L) (Table 1).
Table 1.
Blood examination, chest X-ray, and echocardiographic findings on admission
| Hematological examination | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complete blood count | Biochemistry | Blood gas (vein) | ||||
| WBC | 1.8 × 103/μl | TP | 7.1 g/dl | pH | 7.428 | |
| RBC | 3.5 × 106/μl | AST | 65 U/l | pO2 | 46.4 mmHg | |
| Hb | 12.9 g/dl | ALT | 38 U/l, | pCO2 | 39.9 mmHg | |
| Plt | 38.9 × 105/μl | Na | 135 mEq/l | HCO3- | 26.3 mmol/l | |
| K | 4.2 mEq/l | BE | 1.8 mmol/l | |||
| Cl | 97 mEq/l | Lac | 9.0 mmol/l | |||
| BUN | 13 mg/dl | |||||
| Creatinine | <0.10 mg/dl | |||||
| CK | 588 IU/l | |||||
| CRP | 0.24 mg/dl | |||||
| NH3 | 52 μg/dl | |||||
| Glucose | 31 mg/dl | |||||
| Serum carnitine | Serum carnitine (just 3 days before cefditoren pivixil was started) | |||||
| Total Carnitine | 14.1 μmol/l | Total Carnitine | 33.7 μmol/l | |||
| Free Carnitine | 6.2 μmol/l | Free Carnitine | 29.0 μmol/l | |||
| Acyl Carnitine | 4.7 μmol/l | Acyl Carnitine | 7.9 μmol/l | |||
| Chest X-ray | Echocardiographic study | |||||
| Cardiothoracic ratio | 50% | IVC diameter 11 mm | ||||
| Lungs | normal | Caval/Ao ratio 0.9 (normal value: 0.8–1.0) | ||||
We diagnosed the patient with hypoglycemia originating from a carnitine deficiency induced by CDTR-PI, as the serum free carnitine concentration was 29.0 μmol/L when measured retrospectively in a sample taken 3 days before CDTR-PI treatment was initiated. The patient was immediately administered intravenous glucose and her level of consciousness rapidly improved without any complications. We discontinued CDTR-PI treatment and initiated l-carnitine supplementation. One month later, the patient’s serum free carnitine concentration lay within the normal range with no relapse of symptoms, hypoglycemia, or side effects reported (Fig. 1a).
Fig. 1.
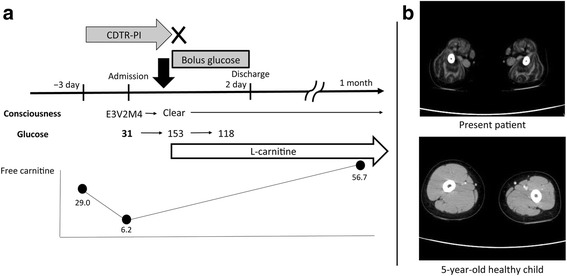
Clinical course and computed tomography (CT) scanning of the central part of the femoral muscles. a Clinical course of the patient from the onset of coma 3 days after initiation of treatment with cefditoren pivoxil (CDTR-PI) to follow-up 1 month later. Serum l-carnitine and glucose concentrations are shown. b CT scans of the femur acquired to assess skeletal muscle volume, which was markedly less than would be expected in a healthy child
Computed tomography (CT) scanning undertaken to evaluate skeletal muscle volume showed severe atrophy of the peripheral muscles compared with an age-matched healthy child who had undergone CT to investigate left leg pain (Fig. 1b). We also calculated the renal reabsorption rate of free carnitine (RRFC) using the following equation: RRFC (%) = 1 − (urine free carnitine × serum creatinine)/(serum free carnitine × urine creatinine). An RRFC of 98% (normal value: >95%) indicated that renal carnitine malabsorption was not responsible for the patient’s episode of hypocarnitinemia [8]. Serum creatinine concentration was <0.1 mg/dL in this case; therefore, we substituted 0.1 mg/dL and considered that the true RRFC value must have been above 98%.
Discussion
Our patient suffered severe carnitine deficiency induced by 3-day oral administration of CDTR-PI. Pivalic acid is released as a result of the metabolism of the prodrug CDTR-PI, and combines with serum free carnitine to form pivaloylcarnitine, which is excreted by the kidneys. Consequently, long-term treatment with an antibiotic containing pivalic acid may provoke hypocarnitinemia [3–6, 9], especially in patients at risk of carnitine deficiency such as those with inherited causes of carnitine metabolism, severe epilepsy, renal disorders or severe neurologic disability, infants less than 2 years old, and patients fed parenterally or taking multiple antiepileptic drugs [10, 11]. However, a case has been reported of a 1-year-old Japanese patient with hypoglycemia associated with hypocarnitinemia induced by 2 days of cefcapene pivoxil treatment [12]. Additionally, Ito et al. reported that treatment with cefteram pivoxil significantly decreased the level of serum free carnitine in both children and adults, even in short-term therapy, and advised that carnitine supplementation may be necessary for patients who are taking these antibiotics, particularly those vulnerable to carnitine deficiency [13]. Although our patient was an older child who could usually receive adequate calories orally (1200 kcal/day, appropriate for her body weight and activity level), she did not receive enough to eat for 3 days (about half of her usual calorific intake) after antibiotic treatment was initiated because of her acute pharyngitis.
We judge, however, that even if our patient’s diet had been marginally deficient in carnitine, her most important risk factor for carnitine deficiency was severe muscular dystrophy. Large quantities of carnitine can be stored in skeletal muscle; in a healthy patient, the proportion stored in skeletal muscle exceeds 95% [1]. Consequently, severe muscle atrophy such as that seen in patients with Duchenne or Becker muscular dystrophy [14, 15] reduces the capacity to store carnitine and replenish serum free carnitine when it is suddenly depleted, even when the renal reabsorption of carnitine is normal. As far as we are aware, there have been no previous reports of carnitine deficiency in FCMD, but our patient’s skeletal muscle volume was markedly lower than that of a healthy child. We suggest that the patient’s reduced muscle bulk would have further predisposed her to hypoglycemia, which was likely to the result of a lack of glycogen and glycogenic amino acid storage in skeletal muscle as well as β-oxidation impairment. Fever would also have induced a hypercatabolic state that would have markedly elevated glucose consumption.
We did not measure blood and urine ketone bodies, a diagnostic limitation for hypoketotic hypoglycemia in this patient, because we imitated prompt emergency treatment for severe hypoglycemia to prevent permanent central nervous system damage. However, the normal venous blood gas test results arguably preclude the possibility of ketotic hypoglycemia. Early diagnosis and rapid, appropriate treatment for severe hypoglycemia resolved our patient’s symptoms without any complications.
The rapid fall in serum free carnitine from 29.0 μmol/L to 6.2 μmol/L observed in this girl with FCMD after just 3 days of treatment with CDTR-PI underlines the speed at which potentially life-threatening symptoms can develop in patients at risk of carnitine deficiency. It is important to note that pivalate antibiotics are not the only type of antibiotic that can influence serum free carnitine; β-lactam antibiotics are reported to competitively block the binding of organic cation/carnitine transporter 2 (OCTN2) and inhibit reabsorption in the kidney [16, 17]. As far as we are aware, however, there have been no reports of β-lactam antibiotics causing adverse events such as those seen in this case.
Conclusions
This case shows that even short-term administration of antibiotics containing pivalic acid in older children with severe musculoskeletal disorders requires careful monitoring for carnitine deficiency to avoid serious adverse effects. Alternative antibiotics should therefore be administered to children at risk. Supplementation with l-carnitine is recommended so that complications can be avoided if alternative antibiotics cannot be identified.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Edanz (http://www.edanzediting.co.jp) for the English language review.
Funding
No funding was obtained for this study.
Availability of data and materials
The data from this study are available from the corresponding author upon requests.
Authors’ contributions
MI and YS provided the emergency report for the patient at the outpatient clinic and wrote the manuscript. MF performed the medical care and wrote and revised the manuscript. HW and EI both helped with the acquisition of data, data analysis and interpretation, and critical review of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient’s parents for the publication of this case report, images, and all information contained in it.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All examinations and investigations in this case were approved by the ethics committee of Ehime University Graduate School of Medicine. Written informed consent was obtained from the parents of the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations
- CDTR-PI
Cefditoren pivoxil
- CT
Computed tomography
- FCMD
Fukuyama-type congenital muscular dystrophy
- OCTN2
Organic cation/carnitine transporter 2
- RRFC
Renal reabsorption rate of free carnitine
Contributor Information
Masanori Ito, Phone: +81-89-960-5320, Email: multiple.pd@gmail.com.
Mitsumasa Fukuda, Email: fukumits@m.ehime-u.ac.jp.
Yuka Suzuki, Email: yusuzuki777@gmail.com.
Hiroyuki Wakamoto, Email: hirwaka@hotmail.com.
Eiichi Ishii, Email: ishiei@m.ehime-u.ac.jp.
References
- 1.Stanley CA. Carnitine deficiency disorders in children. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1033:42–51. doi: 10.1196/annals.1320.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wang SS, Rao J, Li YF, Zhang ZW, Zeng GH. Primary carnitine deficiency cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol. 2014;174:171–3. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.03.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Makino Y, Sugiura T, Ito T, Sugiyama N, Koyama N. Carnitine-associated encephalopathy caused by long-term treatment with an antibiotic containing pivalic acid. Pediatrics. 2007;120:e739–41. doi: 10.1542/peds.2007-0339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Okumura A, Morita M, Ikeno M, Abe S, Shimizu T. Acute encephalopathy in a child with secondary carnitine deficiency due to pivalate-conjugated antibiotics. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011;30:92. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3181fe3953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nakajima Y, Ito T, Maeda Y, Ichiki S, Sugiyama N, Mizuno M, et al. Detection of pivaloylcarnitine in pediatric patients with hypocarnitinemia after long-term administration of pivalate-containing antibiotics. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2010;221:309–13. doi: 10.1620/tjem.221.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Melegh B, Kerner J, Bieber LL. Pivampicillin-promoted excretion of pivaloylcarnitine in humans. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;36:3405–9. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90318-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Palisano R, Rosenbaum P, Walter S, Russell D, Wood E, Galuppi B. Development and reliability of a system to classify gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1997;39:214–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1997.tb07414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ohtani Y, Nishiyama S, Matsuda I. Renal handling of free and acyl-carnitine in secondary carnitine deficiency. Neurology. 1984;34:977–9. doi: 10.1212/WNL.34.8.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Holme E, Greter J, Jacobson CE, Lindstedt S, Nordin I, Kristiansson B, et al. Carnitine deficiency induced by pivampicillin and pivmecillinam therapy. Lancet. 1989;2:469–73. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(89)92086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Takeda Y, Kubota M, Sato H, Nagai A, Higashiyama Y, Kin H, et al. Carnitine in severely disabled patients: relation to anthropometric, biochemical variables, and nutritional intake. Brain Dev. 2015;37:94–100. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2014.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fukuda M, Kawabe M, Takehara M, Iwano S, Kuwabara K, Kikuchi C, et al. Carnitine deficiency: risk factors and incidence in children with epilepsy. Brain Dev. 2015;37:790–6. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2014.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Serious hypocarnitinemia and hypoglycaemia in children treated with antibacterials with a pivoxil group. In: Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) Alert for Proper Use of Drugs. 2012. http://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000153551.pdf#page=2. Accessed 21 Nov 2016.
- 13.Ito T, Sugiyama N, Kobayashi M, Kidouchi K, Itoh T, Uemura O, et al. Alteration of ammonia and carnitine levels in short-term treatment with pivalic acid-containing prodrug. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1995;175(1):43–53. doi: 10.1620/tjem.175.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Berthillier G, Eichenberger D, Carrier HN, Guibaud P, Got R. Carnitine metabolism in early stages of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Clin Chim Acta. 1982;122:369–75. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90140-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Le Borgne F, Guyot S, Logerot M, Beney L, Gervais P, Demarquoy J. Exploration of lipid metabolism in relation with plasma membrane properties of Duchenne muscular dystrophy cells: influence of L-carnitine. PLoS One. 2012;7:e49346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ohashi R, Tamai I, Nezu Ji J, Nikaido H, Hashimoto N, Oku A, et al. Molecular and physiological evidence for multifunctionality of carnitine/organic cation transporter OCTN2. Mol Pharmacol. 2001;59:358–66. doi: 10.1124/mol.59.2.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ganapathy ME, Huang W, Rajan DP, Carter AL, Sugawara M, Iseki K, et al. β-lactam antibiotics as substrates for OCTN2, an organic cation/carnitine transporter. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:1699–707. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.3.1699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data from this study are available from the corresponding author upon requests.


