Figure 1. Identification and characterization of human CD56brightNKG2A+ NK cells and restriction of EBV in B cells.
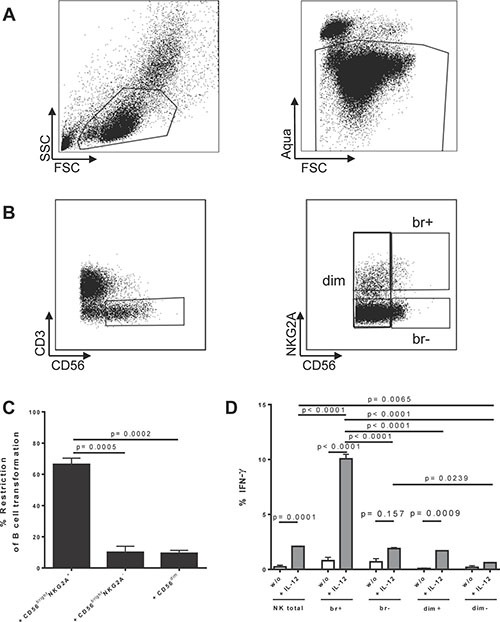
(A) Basic gating for all tonsillar and peripheral samples throughout this manuscript (representative example of PBMCs is shown); (B) Gating for CD56brightNKG2A+ and compared NK cell subsets (representative example of PBMCs is shown); (C) Restriction of EBV transformation of B cells after established EBV infection in B cells by tonsillar CD56brightNKG2A+ NK cells compared to other subsets (6 donors); (D) IFNγ production induced by overnight cytokine stimulation in different tonsillar NK subsets (3 donors); Restriction = (100 − (% transformed B cells in co-culture/% transformed B cells without NK) ×100); Data represent three independent experiments. All error bars represent SEM. p values depicted were calculated with two-tailed student's t test, or (1D) regular ANOVA corrected for multiple comparison testing by Tukey correction.
