Figure 3. Time course for melflufen's accumulation and cytotoxic effect in CCRF-CEM leukemia cells.
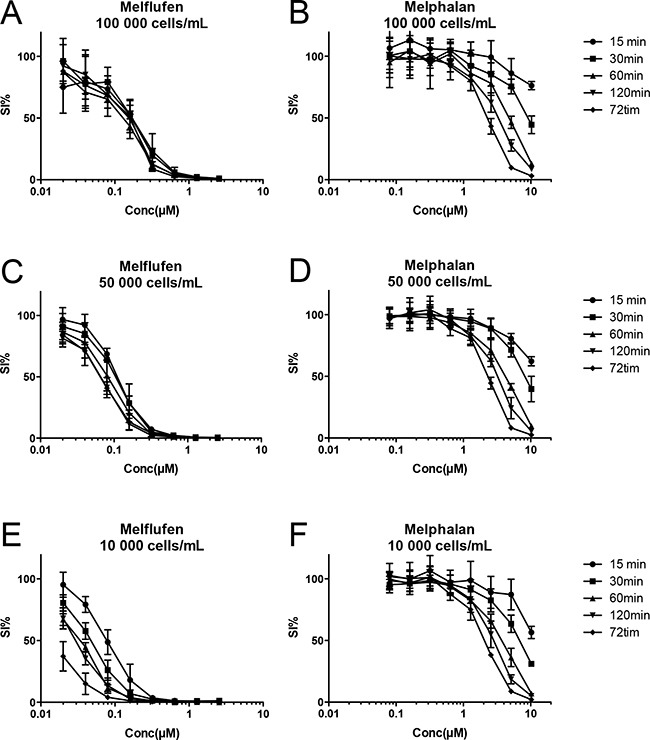
The peptidase-potentiated effect results in a rapid accumulation of the active drug, and with decreasing cell densities A-C-E. there are more drug molecules per cell, and activity increases (curves shifts to the left). The rapid accumulation results in a competition for melflufen, and with high cell densities (A) maximum effect is obtained already after 15 minutes, i.e. cells have taken up all melflufen from the medium. When the cell number is lower (C and E) there is a time course for the accumulation, and longer exposure yields higher activity (i.e. lower IC50). For melphalan the situation is completely different as the absorption of the drug is slow; longer exposure time results in higher activity regardless if the cell density is high or low, suggesting rather slow absorption and a concentration equilibrium B-D-F.
