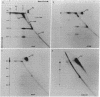
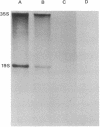
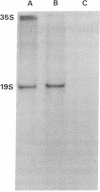
Abstract
The DNA genome of cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) replicates in the cytoplasm of infected plant cells by reverse transcription of an RNA template. Viral RNA is generated in the nucleus by transcription of an episomal minichromosome containing supercoiled DNA. We have assessed the relative activities of the nuclear and cytoplasmic phases of the CaMV multiplication cycle by monitoring unencapsidated viral DNA forms and polyadenylylated RNAs in different organs of one host plant and in different host species. Systemically infected leaves of a highly susceptible host, turnip (Brassica rapa), contained abundant 35S RNA and 19S RNA transcripts and unencapsidated reverse transcription products but relatively little supercoiled DNA. In contrast, supercoiled DNA accumulated in roots and other tissues of turnip plants but without significant amounts of steady-state viral RNA. Infected but asymptomatic leaves of a less susceptible CaMV host, kohlrabi (Brassica oleracea), contained supercoiled DNA almost exclusively but negligible viral RNA and DNA products of reverse transcription. An allotetraploid species, rape (Brassica napus), exhibited infection characteristics and minichromosome expression levels intermediate between the other two species from which it was derived. We conclude that expression of the CaMV minichromosome is a key phase of the virus multiplication cycle, which is regulated differentially in organs of a highly susceptible host species. Furthermore, this regulation exhibits genetic variation among different Brassica species and controls host susceptibility to CaMV infection.
Full text
PDF

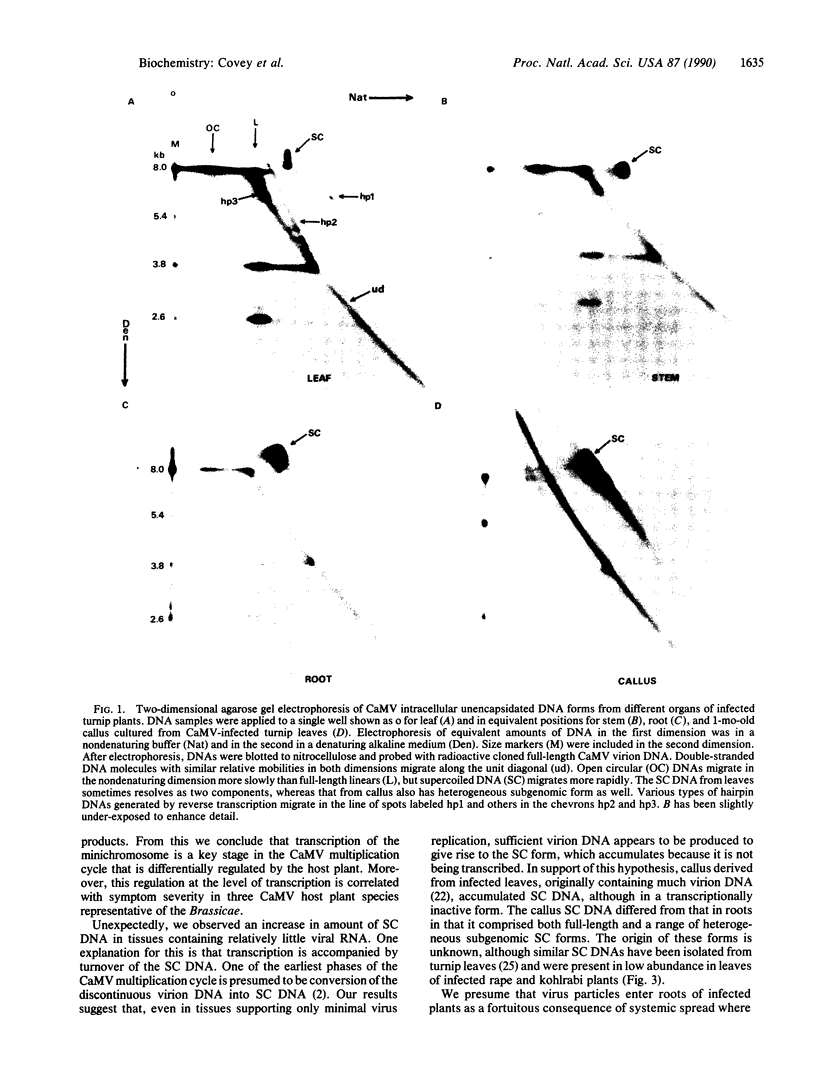

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benfey P. N., Chua N. H. Regulated genes in transgenic plants. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):174–181. doi: 10.1126/science.244.4901.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfey P. N., Ren L., Chua N. H. The CaMV 35S enhancer contains at least two domains which can confer different developmental and tissue-specific expression patterns. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2195–2202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08342.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey S. N., Lomonossoff G. P., Hull R. Characterisation of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA sequences which encode major polyadenylated transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6735–6747. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey S. N., Turner D. S. Hairpin DNAs of cauliflower mosaic virus generated by reverse transcription in vivo. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2763–2768. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey S. N., Turner D., Mulder G. A small DNA molecule containing covalently-linked ribonucleotides originates from the large intergenic region of the cauliflower mosaic virus genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):251–264. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilley H., Dudley R. K., Jonard G., Balàzs E., Richards K. E. Transcription of Cauliflower mosaic virus DNA: detection of promoter sequences, and characterization of transcripts. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):763–773. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilley H., Richards K. E., Jonard G. Observations concerning the discontinuous DNAs of cauliflower mosaic virus. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):277–282. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01417.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. H., Hull R. Replication of cauliflower mosaic virus and transcription of its genome in turnip leaf protoplasts. Virology. 1978 May 15;86(2):468–481. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R., Covey S. N. Characterisation of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA forms isolated from infected turnip leaves. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1881–1895. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R., Covey S. N., Maule A. J. Structure and replication of caulimovirus genomes. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;7:213–229. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1987.supplement_7.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Kavanagh T. A., Bevan M. W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3901–3907. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marco Y., Howell S. H. Intracellular forms of viral DNA consistent with a model of reverse transcriptional replication of the cauliflower mosaic virus genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1517–1528. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olszewski N. E., Guilfoyle T. J. Nuclei purified from cauliflower mosaic virus-infected turnip leaves contain subgenomic, covalently closed circular cauliflower mosaic virus DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8901–8914. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olszewski N., Hagen G., Guilfoyle T. J. A transcriptionally active, covalently closed minichromosome of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA isolated from infected turnip leaves. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):395–402. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90156-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant A. L., Covey S. N., Grierson D. Detection of a subgenomic mRNA for gene V, the putative reverse transcriptase gene of cauliflower mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8305–8321. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. H., Hill C. B. Rapid-cycling populations of brassica. Science. 1986 Jun 13;232(4756):1385–1389. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4756.1385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]