Abstract
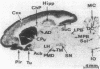
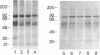
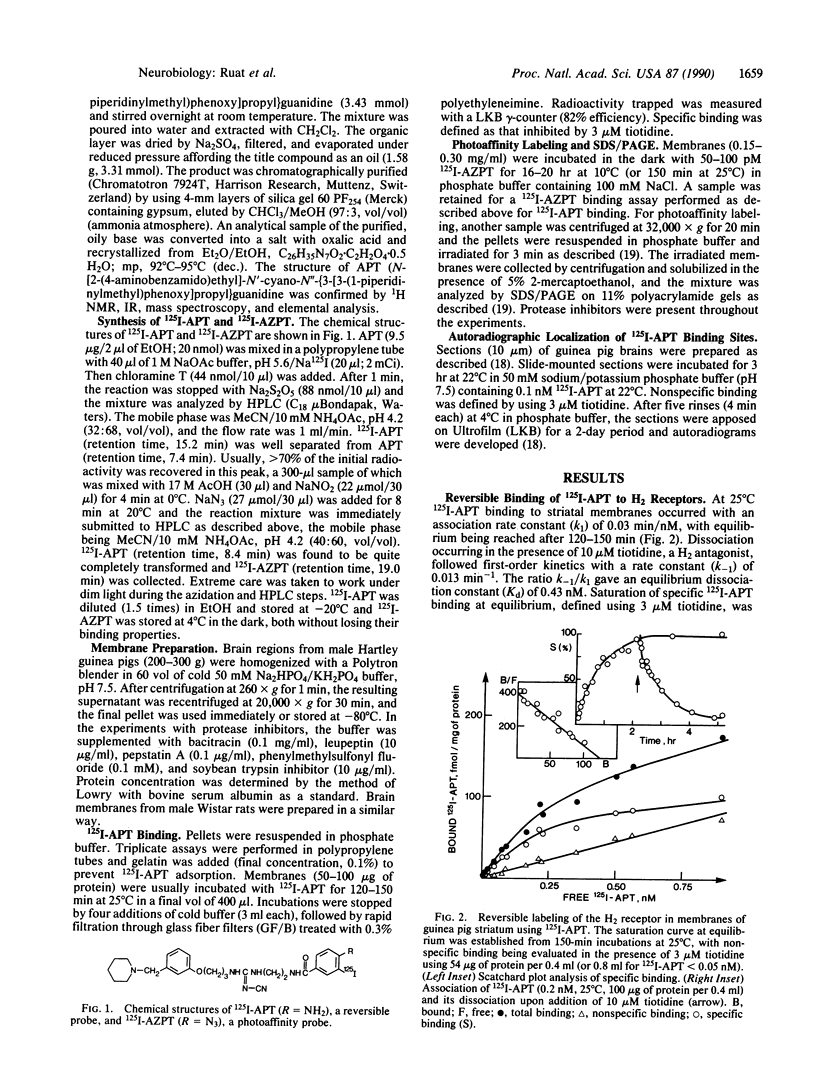
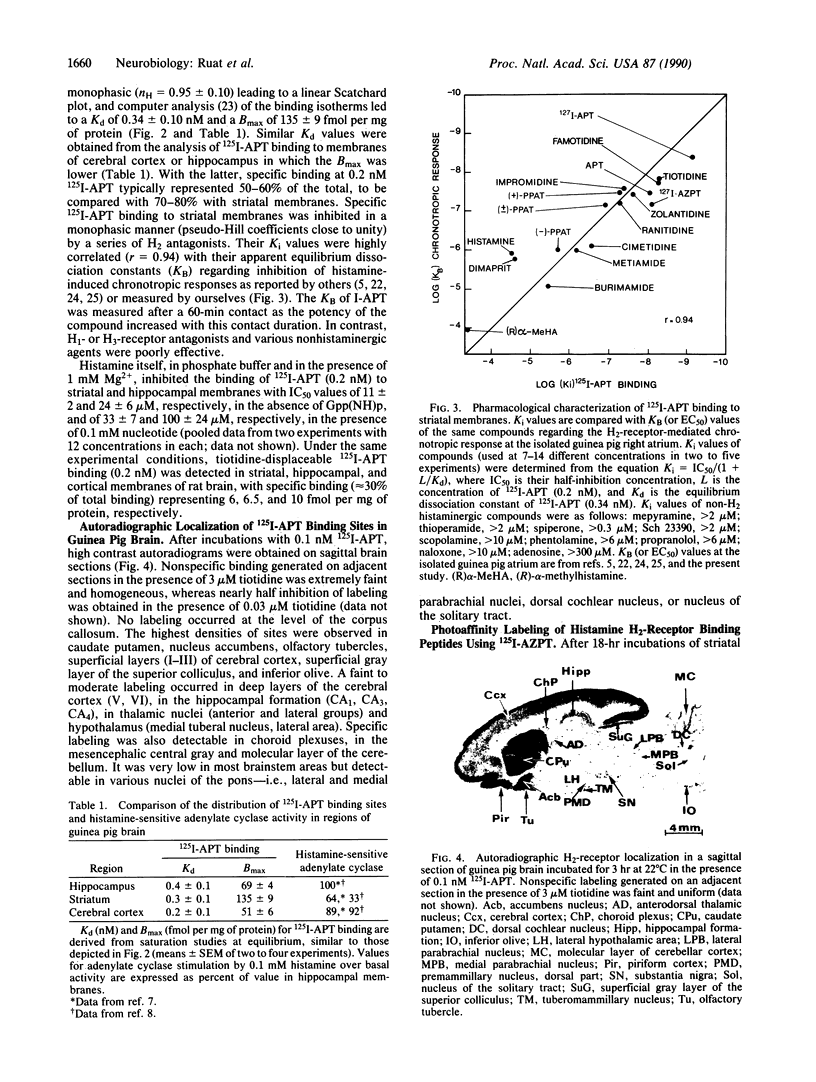
Iodoaminopotentidine (I-APT)--i.e., N-[2-(4-amino-3-iodobenzamido)ethyl]-N'-cyano-N''-(3-[3- (1-piperidinylmethyl)phenoxy]propyl)guanidine--represents one of the most potent H2-receptor antagonists known so far. In membranes of guinea pig brain 125I-APT bound reversibly, selectively, and with high affinity (Kd = 0.3 nM) to a homogeneous population of sites unambiguously identified as H2 receptors by inhibition studies conducted with a large panel of antagonists. 125I-APT binding was also inhibited by histamine, and the effect was modulated by a guanyl nucleotide, which is consistent with the association of the H2 receptor with a guanine nucleotide binding regulatory protein. The low nonspecific binding of 125I-APT generated high contrast autoradiographic pictures in brain sections and established the precise distribution of H2 receptors. Their highly heterogeneous distribution and laminated pattern in some areas--e.g., cerebral and hippocampal cortices--suggest their major association with neuronal elements. These localizations were more consistent than those of H1 receptors with the distribution of histaminergic projections, indicating that H2 receptors mediate a larger number of postsynaptic actions of histamine--e.g., in striatum. Colocalizations of H1 and H2 receptors in some areas account for their known synergistic interactions in cAMP formation induced by histamine. The distribution of 125I-APT binding sites did not strictly parallel that of the H2-receptor-linked adenylate cyclase activity, which may reflect heterogeneity among H2 receptors. After UV irradiation and SDS/PAGE analysis, [125I]iodoazidopotentidine (125I-AZPT), a photoaffinity probe derived from 125I-APT, was covalently incorporated in several peptides, among which the labeling of two peptides of 59 and 32 kDa was prevented by H2 antagonists, suggesting that they correspond to H2-receptor binding peptides or proteolysis products of the latter. These probes should be useful for sensitive radioassays, localization, purification, and molecular studies of the H2 receptor, which were previously impracticable.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Airaksinen M. S., Panula P. The histaminergic system in the guinea pig central nervous system: an immunocytochemical mapping study using an antiserum against histamine. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Jul 8;273(2):163–186. doi: 10.1002/cne.902730204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Lancelot J. C., Lecomte J. M., Pollard H., Robba M., Schunack W., Schwartz J. C. Highly potent and selective ligands for histamine H3-receptors. Nature. 1987 May 14;327(6118):117–123. doi: 10.1038/327117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry M., Martres M. P., Schwartz J. C. H1 and H2 receptors in the histamine-induced accumulation of cyclic AMP in guinea pig brain slices. Nature. 1975 Jan 31;253(5490):362–364. doi: 10.1038/253362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandina P., Knott P. J., Leung L. K., Green J. P. Stimulation of histamine H2 receptor in rat hypothalamus releases endogenous norepinephrine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Apr;249(1):44–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouthenet M. L., Ruat M., Sales N., Garbarg M., Schwartz J. C. A detailed mapping of histamine H1-receptors in guinea-pig central nervous system established by autoradiography with [125I]iodobolpyramine. Neuroscience. 1988 Aug;26(2):553–600. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90167-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calcutt C. R., Ganellin C. R., Griffiths R., Leigh B. K., Maguire J. P., Mitchell R. C., Mylek M. E., Parsons M. E., Smith I. R., Young R. C. Zolantidine (SK&F 95282) is a potent selective brain-penetrating histamine H2-receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jan;93(1):69–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajtkowski G. A., Norris D. B., Rising T. J., Wood T. P. Specific binding of 3H-tiotidine to histamine H2 receptors in guinea pig cerebral cortex. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):65–67. doi: 10.1038/304065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbarg M., Barbin G., Palacios J. M., Schwartz J. C. Effects of kainic acid on histaminergic systems in guinea pig hippocampus. Brain Res. 1978 Jul 21;150(3):638–641. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90829-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Konnerth A. Histamine and noradrenaline decrease calcium-activated potassium conductance in hippocampal pyramidal cells. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):432–434. doi: 10.1038/302432a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegstrand L. R., Kanof P. D., Greengard P. Histamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in mammalian brain. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):163–165. doi: 10.1038/260163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris D. B., Gajtkowski G. A., Rising T. J. Histamine H2-binding studies in the guinea-pig brain. Agents Actions. 1984 Apr;14(3-4):543–545. doi: 10.1007/BF01973867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa K., Nomura Y., Segawa T. Histamine acting on H2 receptors stimulates phospholipid methylation in synaptic membranes of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1987 May;48(5):1392–1398. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J. M., Garbarg M., Barbin G., Schwartz J. C. Pharmacological characterization of histamine receptors mediating the stimulation of cyclic AMP accumulation in slices from guinea-pig hippocampus. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;14(6):971–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J. M., Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of H1-histamine receptors in brain using 3H-mepyramine: preliminary studies. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct 1;58(3):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90478-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruat M., Körner M., Garbarg M., Gros C., Schwartz J. C., Tertiuk W., Ganellin C. R. Characterization of histamine H1-receptor binding peptides in guinea pig brain using [125I]iodoazidophenpyramine, an irreversible specific photoaffinity probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2743–2747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran V. T., Chang R. S., Snyder S. H. Histamine H1 receptors identified in mammalian brain membranes with [3H]mepyramine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6290–6294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venter J. C., Fraser C. M., Kerlavage A. R., Buck M. A. Molecular biology of adrenergic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors. A perspective. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Apr 15;38(8):1197–1208. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90325-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waud D. R., Parker R. B. Pharmacological estimation of drug-receptor dissociation constants. Statistical evaluation. II. Competitive antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Apr;177(1):13–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]