Figure 1. CUG2 induces EMT, in which NT of CUG2 is more important than CT of CUG2.
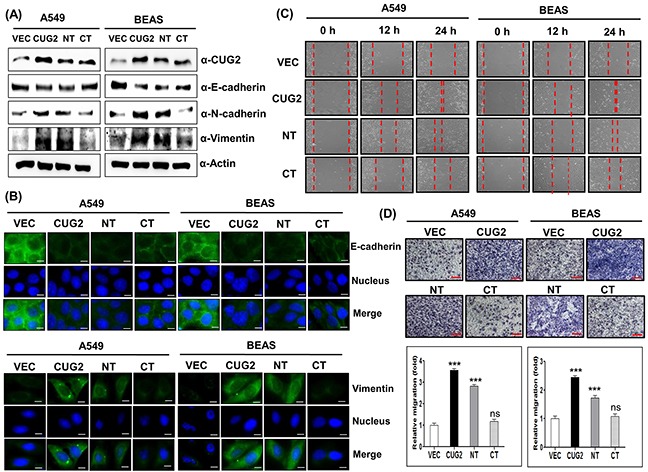
A. Expression of CUG2, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and vimentin was detected by immunoblotting using the corresponding antibodies. NT indicates N-terminal domain of CUG2 and CT indicates C-terminal domain of CUG2. B. Expression of E-cadherin and vimentin was detected by immunofluorescence using Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (green) and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated donkey anti-goat IgG (green), respectively. For nuclear staining, DAPI was added prior to mounting in glycerol. Scale bar indicates 10 μm. C. Cell migration was measured by a wound healing assay. The wound closure areas were monitored by phase-contrast microscopy at a magnification of 100×. The assays were repeated twice. D. An invasion assay was performed using 48-well Boyden chambers. The chamber was assembled using polycarbonate filters coated with Matrigel. Scale bar indicates 100 μm. The assays were repeated twice. Each assay was performed in triplicate and error bars indicate standard deviation (SD) (ns; not significant, p> 0.05, ***; p< 0.001)
