Abstract
The present study aimed to identify microRNAs (miRNAs) involved in regulating retinal neovascularization and retinopathy of prematurity (ROP). A total of 80 healthy C57BL/6 neonatal mice were randomly divided into the oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR) group (n=40), in which 7-day-old mice were maintained in 75% oxygen conditions for 5 days, or the control group (n=40). Following collection of retinal tissue, retinal angiography and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining were performed. Total RNA was also extracted from retinal tissue, and miRNA microarrays and reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) were performed to identify differentially expressed miRNAs in the two groups. Retinal angiography and H&E staining revealed damage to retinas in the OIR group. Compared with the control group, 67 miRNAs were differentially expressed in the OIR group, of which 34 were upregulated and 33 were downregulated. Of these differentially expressed miRNAs, 32 exhibited a fold change ≥2, of which 21 were upregulated and 11 were downregulated. The results of RT-qPCR for miR-130a-3p and miR-5107-5p were in accordance with those of the miRNA microarray. The newly identified miRNAs may be important in the development of ROP, and may provide a basis for future research into the mechanisms of ROP.
Keywords: retinopathy of prematurity, microRNA, mice, oxygen-induced retinopathy, animal model
Introduction
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) is a vascular proliferative disease that primarily occurs in preterm infants, causing disorganized growth of retinal blood vessels, which results in scarring, retinal detachment and occasionally blindness (1). ROP is associated with low gestational age and birth weight; although advances in neonatal care have resulted in improved survival rates for premature infants, the incidence of ROP has increased (2,3). Numerous studies have been undertaken to examine the pathophysiological mechanisms of ROP (4,5); however, these currently remain unclear.
Animal models of oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR) have previously been used to reveal mechanisms of ROP development, including oxidant stress, the functions of growth factors including insulin-like growth factor (IGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and structure-functional anomalies (6,7). Bioinformatic strategies have also been widely used to investigate ROP mechanisms; a study by Sato et al (8) investigated gene-expression profiles in murine oxygen-induced retinopathy as early as 2009.
microRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs of 18–26 nucleotides in length that regulate gene expression through sequence-specific base pairing with target mRNAs. Numerous miRNAs have been identified through molecular cloning and bioinformatics strategies (9,10). miRNAs generally inhibit mRNA translation of their target genes (11), and have been reported to be important in biological processes including vascular angiogenesis, cell growth, embryonic development, cell proliferation, tissue differentiation and apoptosis (12–15).
It is well documented that miRNAs regulate vascular angiogenesis (16) and the regulation of VEGF, IGF-2 and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) by miRNA (miR)-126 is associated with retinal vascular angiogenesis under conditions of OIR (17). However, whether other miRNAs are involved in the pathological process of angiogenesis in OIR conditions currently remains unclear. Therefore, the present study aimed to screen for miRNA candidates affecting retinal neovascularization using an OIR mouse model.
Materials and methods
Establishment of oxygen-induced retinopathy mouse model
A total of 80 (36 female; 44 male) 7-day-old healthy C57BL/6 neonatal mice (weight, 3±0.3 g) were provided by the Animal Center of Nanjing University (Nanjing, China). All procedures in the study followed the protocols approved by the Animal Care and Use Committees of Nanjing Medical University (Nanjing, China). The mice were maintained in specific-pathogen-free conditions at the Animal Center of Nanjing Medical University. The mice were reared in a clean grade animal room, at 23±2°C and 50±10% humidity. The light did not exceed 350 lux and the light/dark cycle was 12-h. Food, water and bedding were replaced every two days. The oxygen concentration was monitored with an oxygen concentration detector. The mice were randomly divided into the OIR group (n=40) or the control group (n=40). For OIR modeling, 7-day-old mice were maintained in 75% oxygen condition for 5 days, then in normal room air for a further 5 days. Mice in the control group were maintained in normal room air for the duration of the experiment. The present study was approved by the ethics review board of Nanjing Children's Hospital of Nanjing Medical University.
Retinal angiography
On postnatal day 17 (P17), 50 mg high molecular weight fluorescein isothiocyanate dextrans (catalog no. 75005; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany) were dissolved in 1 ml phosphate buffer containing 4% polyformaldehyde and directly perfused through the left ventricle of the heart following an intraperitoneal injection of 10% chloral hydrate (3 ml/kg; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck Millipore). The eyes were then enucleated and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde at 4°C for 2 h. The retina was separated and mounted on a microscope slide. The vasculature was examined under a fluorescent microscope (Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) at an original magnification of ×40. In total, 30 sections were counted, and 3 fields of view were assessed for each slide.
Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining
Paraformaldehyde-fixed retinal tissue was embedded in paraffin and sliced into 6 µm sections. The sections were stained with HE and examined by routine light microscopy (Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). Briefly, sections were dried, followed by xylene dewaxing and rehydration with decreasing concentrations of alcohol. The slides were then stained with hematoxylin for 15 min and differentiated with hydrochloric acid alcohol for 30 sec. Following staining with 1% ammonia, sections were stained with 1% eosin for 2 min, followed by dehydration in alcohol and mounting. The number of vascular endothelial cells with nuclei breaking through the internal limiting membrane (ILM) was counted. In total, 30 sections were counted, and 3 fields of view were assessed for each slide.
Extraction and quantification of total RNA
For total RNA extraction, retinal tissue was frozen at −80°C and crushed using a BioPulverizer (Aoran Technology Ltd., Shanghai, China). Homogenization was performed by adding 1 ml TRIzol® reagent (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) to the tissue fragments, according to the manufacturer's protocol. Extracted RNA was dissolved in RNAse-free water and incubated at 60°C for 10 min.
Absorbance at 260, 280 and 230 nm was measured using an ultraviolet spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Wilmington, DE, USA). The purity of the extracted RNAs was determined by calculating the A260/A280 and A260/A230 ratios.
miRNA microarray
Following isolation of total RNA from retinal tissue, microarray was performed by LC Sciences (Houston, TX, USA). Each detection probe on the microfluidic chips consisted of a chemically modified nucleotide coding segment complementary to target a total of 25,141 miRNAs (from miRBase version 19.0, www.mirbase.org/) or other RNA (control or customer-defined sequences) and a spacer segment of polyethylene glycol to extend the coding segment away from the substrate. The detection probes were made by in situ synthesis using photogenerated reagent chemistry. The hybridization melting temperatures were balanced by chemical modifications of the detection probes. Hybridization used 100 µl 6X saline sodium phosphate EDTA buffer (0.90 M NaCl, 60 mM Na2HPO4, 6 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, pH 6.8) containing 25% formamide at 34°C. Following RNA hybridization, tag-conjugating Cyanine3 dye was circulated through the microfluidic chip at 34°C overnight. Fluorescence images were collected using a GenePix 4000B microarray scanner (Molecular Devices LLC, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) and visualized using Array-Pro image analysis software version 6.3 (Media Cybernetics, Inc., Rockville, MD, USA). Data were analyzed by subtracting the background, and then normalizing the signals using a LOWESS filter (locally-weighted regression).
Following normalization, differentially expressed miRNAs were identified through fold-change filtering (fold change ≥2). Hierarchical clustering was performed using MeV software version 4.6 (The Institute for Genomic Research, J. Craig Venter Institute, Rockville, MA, USA).
Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
Following isolation of total RNA, 1 µg total RNA was used for RT using the TaqMan® MicroRNA Reverse Transcription kit (Applied Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) according to the manufacturer's protocol. The cDNA obtained was used for qPCR, with probes for Mus musculus (mmu)-miR-130a-3p and mmu-miR-5107-5p, listed in Table I. The hot start method was used for fluorescent qPCR and the standard internal reference [U6 spliceosomal RNA (snRNA)] coupled with the control group was amplified for each sample. qPCR was performed in a 20-µl reaction mixture, with each tube containing 10 µl 2X TaqMan Universal Master Mix II, 1 µl TaqMan MicroRNA assays (Applied Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), 1.33 µl cDNA template and 7.67 µl RNase-free water. The cycling conditions were as follows: An initial denaturation step at 50°C for 2 min and 95°C for 2 min, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 15 sec, and annealing/extension at 60°C for 1 min. The U6 snRNA was used as an internal control for normalization. The relative quantitative (RQ) value, obtained using the 2−ΔΔCq method (18), was used for statistical analysis. Briefly, the cycle threshold (Cq) values were calculated using automatic baseline settings. The ΔCq value between internal control U6 and the corresponding Cq value for the target gene was used for the relative quantification of miRNA expression.
Table I.
Context sequences of the probes of mmu-miR-130a-3p, mmu-miR-5107-5p and the internal control U6 snRNA used in the present study.
| Assay name | Context sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| mmu-miR-130a | CAGUGCAAUGUUAAAAGGGCAU |
| mmu-miR-5107 | UGGGCAGAGGAGGCAGGGACA |
| U6 snRNA | GTGCTCGCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAATTGGAACGATACAGAGAAGATTAGCATGGCCCCTGCGCAAGGATGACACGCAAATTCGTGAAGCGTTCCATATTTT |
hsa, Homo sapiens; miR, microRNA; mmu, Mus musculus; snRNA, spliceosomal RNA.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 13.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Comparisons of retinal endothelial cell nucleus between the OIR and control groups were performed using the means t-test. RT-qPCR data were evaluated by one-way analysis of variance and independent sample t-test. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. To evaluate miRNA expression profiles, t-tests were performed, and P<0.01 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Result of retinal angiography
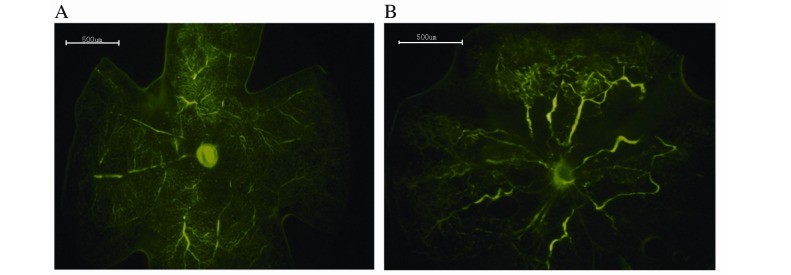
Retinal angiography was performed to detect differences between the control and OIR groups, and thus determine whether the murine model was successfully established. The retinal vasculature of the control group extended from the optic nerve to the periphery, with the vessels forming a fine radial branching pattern (Fig. 1A). The retinal vascular pattern in the OIR group was characterized by decreased central perfusion, which was particularly notable in the central retina (Fig. 1B). The murine OIR model was, therefore, successfully established.
Figure 1.
Retinal angiography with high-molecular-weight fluorescein-dextran. (A) Retina of the control group. No neovascularization was observed in the peripheral perfusion area. (B) Retina of the oxygen-induced retinopathy group. Decreased vascular plexus and vascular tortuosity was visible in the peripheral perfusion area. Original magnification, ×40; scale bars=500 µm.
Histological changes
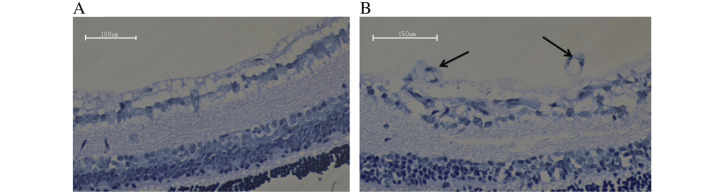
Histology was conducted to examine differences in retinal tissue between the control and OIR groups. Vascular cells in the control group did not extend from the internal limiting membrane into the vitreous (Fig. 2A), while vascular cells in the OIR group extended from the internal limiting membrane into the vitreous (Fig. 2B). The degree of hyperoxia-induced neovascularization was quantified by counting the number of vascular cell nuclei on the vitreal side of the internal limiting membrane of the retina. There was an average of 0.89±0.71 nuclei extending into the internal limiting membrane in the control group, compared with 30.17±7.43 nuclei in the OIR group (P=0.00006; Fig. 3). The retinal tissue in the OIR model was, therefore demonstrated to be damaged, further confirming the successful establishment of the OIR model.
Figure 2.
Hematoxylin and eosin staining of (A) control group and (B) oxygen-induced retinopathy group retinas. Arrows indicate the enlarged intraretinal vessel profiles. Original magnification, ×400; scale bar=150 µm.
Figure 3.
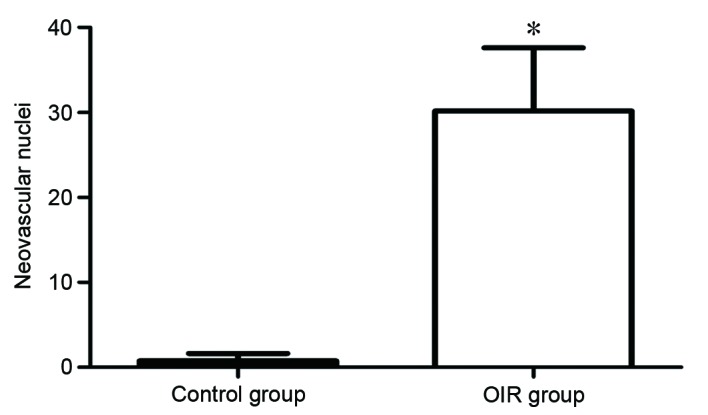
Quantification of proliferative neovascular response to OIR. The total number of vascular nuclei extending from the internal limiting membrane into the vitreous per section was counted. Values are presented as the mean number of nuclei ± standard deviation. *P<0.0001 vs. control group. OIR, oxygen-induced retinopathy.
Quality assessment of total retinal RNA
In order to determine the quality of the extracted retinal tissue RNA, total RNA quality assessment was performed. RNA with A260/A280 ratio close to 2.0 is regarded as pure RNA: A260/A280 ratio <1.8 indicates sample contamination, while a ratio >2.0 suggests RNA hydrolysis. An A260/A280 ratio in the range of 1.8–2.1 is acceptable. In addition, for pure RNA samples, the A260/A230 ratio should be >1.8. As presented in Table II, the A260/A280 ratios of the extracted RNA were ~2.0 and the 260/A230 ratios were all >2.2. The quality of the extracted RNA was therefore good.
Table II.
RNA purity from retinal tissue RNA extractions.
| Sample group | Concentration (µg/µl) | UV A260/A280 | UV A260/A230 | Quantity (µg) | 28S/18Sa | Bioanalyzer result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen-induced retinopathy | 0.25 | 2.00 | 2.21 | 10.72 | 2.5 | Pass |
| Control | 0.34 | 2.03 | 2.28 | 14.59 | 2.4 | Pass |
The 28S/18S ribosomal RNA ratio was used to assess the quality of the RNA. Ratios >2 indicate that the total RNA is high quality.
miRNA expression profile
To examine changes in miRNA expression levels in mice in the OIR group, a microarray analysis was performed to evaluate miRNA expression profiles. There were 67 differentially expressed miRNAs in the OIR group compared with the control group, of which, 34 were upregulated and 33 were downregulated. There were 32 differentially expressed miRNAs with a fold change ≥2.0, of which, 21 were upregulated (Table III) and 11 were downregulated (Table IV). Of these miRNAs, 6 miRNAs that were upregulated in the OIR group compared with the control group (miR-1907, miR-3970, miR-5107-5p, miR-133b-5p, miR-3962 and miR-145b; Table III) and 11 miRNAs that were downregulated in the OIR group compared with the control group (miR-495-3p, miR-677-3p, miR-let-7d-3p, miR-328-3p, miR-301a-3p, miR-128-3p, miR-872-5p, miR-181c-5p, miR-744-5p, miR-130a-3p and miR-377-3p; Table IV) were statistically significantly different (P<0.05), with a ≥2-fold change. Of the upregulated miRNAs in the OIR group, mmu-miR-1907 had the greatest fold-change compared with the control group, and of the downregulated miRNAs, mmu-miR-495-3p had the greatest difference compared with the control group. Hierarchical clustering revealed distinguishable miRNA expression profiles between the two groups, with S01 as the control group and S03 as the experimental group (Fig. 4). Thus, modulation of oxygen conditions resulted in differential miRNA expression.
Table III.
Differentially expressed microRNAs upregulated (>2-fold) in the oxygen-induced retinopathy group compared with the control group, listed and arranged according to magnitude of change.
| Name | Fold-change | P-value |
|---|---|---|
| mmu-miR-1907 | 14.389 | 0.000108 |
| mmu-miR-3970 | 12.300 | 0.000069 |
| mmu-miR-5107-5p | 9.714 | 0.000632 |
| mmu-miR-133b-5p | 7.753 | 0.000973 |
| mmu-miR-3962 | 7.068 | 0.000009 |
| mmu-miR-145b | 5.077 | 0.000924 |
| mmu-miR-3072-5p | 3.690 | 0.002920 |
| mmu-miR-129-2-3p | 3.074 | 0.001340 |
| mmu-miR-714 | 3.000 | 0.004800 |
| mmu-miR-29c-3p | 2.833 | 0.001420 |
| mmu-miR-145a-5p | 2.500 | 0.003340 |
| mmu-miR-100-5p | 2.425 | 0.000081 |
| mmu-miR-3107-5p | 2.385 | 0.005480 |
| mmu-miR-30c-1-3p | 2.172 | 0.004510 |
| mmu-miR-96-5p | 2.157 | 0.009780 |
| mmu-miR-6236 | 2.148 | 0.006500 |
| mmu-miR-3473b | 2.122 | 0.005810 |
| mmu-miR-214-3p | 2.093 | 0.006740 |
| mmu-miR-9-5p | 2.089 | 0.000624 |
| mmu-miR-181d-5p | 2.070 | 0.002950 |
| mmu-miR-3473e | 2.045 | 0.005690 |
mmu, Mus musculus; miR, microRNA.
Table IV.
Differentially expressed microRNAs downregulated (>2-fold) in the oxygen-induced retinopathy group compared with the control group, listed and arranged according to magnitude of change.
| Name | Fold-change | P-value |
|---|---|---|
| mmu-miR-495-3p | 3.354 | 0.000002 |
| mmu-miR-677-3p | 3.255 | 0.000206 |
| mmu-miR-let-7d-3p | 2.606 | 0.002650 |
| mmu-miR-328-3p | 2.465 | 0.001420 |
| mmu-miR-301a-3p | 2.462 | 0.003470 |
| mmu-miR-128-3p | 2.149 | 0.002440 |
| mmu-miR-872-5p | 2.076 | 0.008250 |
| mmu-miR-181c-5p | 2.070 | 0.006170 |
| mmu-miR-744-5p | 2.065 | 0.004720 |
| mmu-miR-130a-3p | 2.000 | 0.000412 |
| mmu-miR-377-3p | 2.000 | 0.006950 |
mmu, Mus musculus; miR, microRNA.
Figure 4.
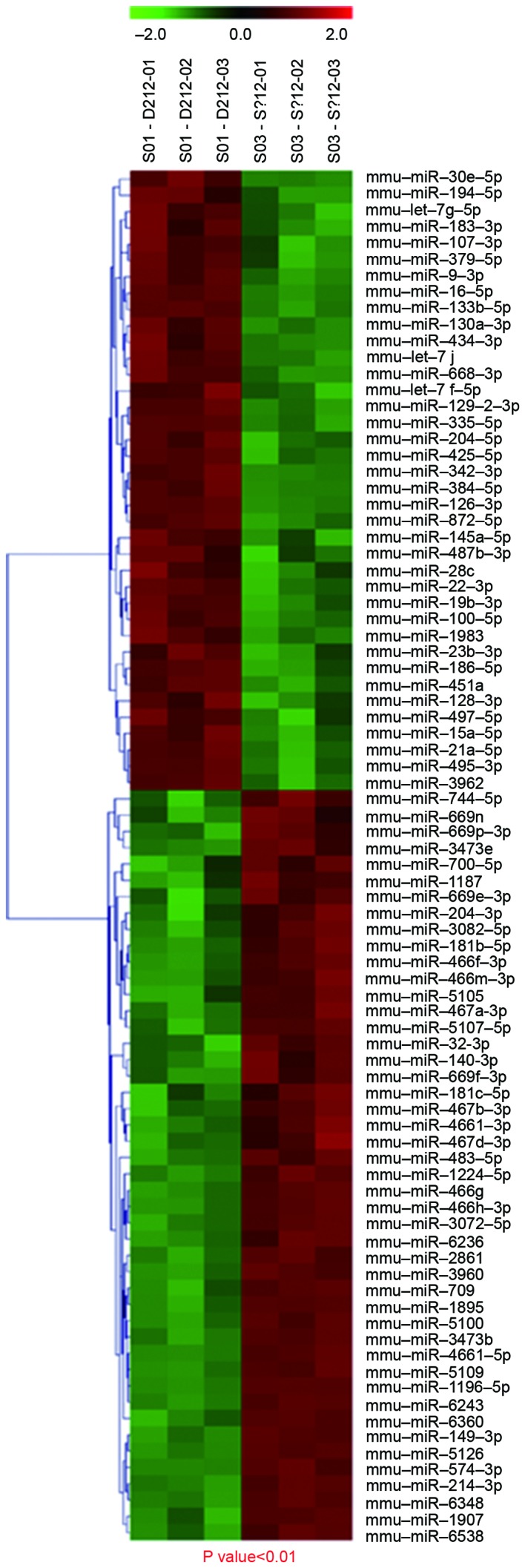
Hierarchical clustering of miRNAs in the control (S01) and oxygen-induced retinopathy (S03) groups. Two-way hierarchical cluster heat map presents all significantly expressed miRNAs: Each row displays the relative expression level of a single miRNA; each column displays the expression level of a single sample. Red, high relative expression; green, low relative expression; and black, zero. mmu, Mus musculus; miR, microRNA.
Confirmation of differentially expressed miRNAs by RT-qPCR
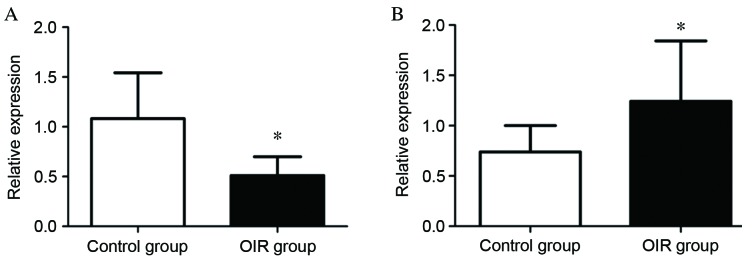
To validate the differential expression profiles of miRNAs indicated by microarray analysis, RT-qPCR analysis of miRNAs was performed for mmu-miR-130a-3p and mmu-miR-5107-5p. These miRNAs were selected for confirmatory testing by RT-qPCR as they exhibited large fold-changes, large mean values and small P-values. The relative expression level of mmu-miR-130a-3p was significantly lower in the OIR group compared with the control group (P=0.00239; Fig. 5A), while that of mmu-miR-5107-5p was significantly higher in the OIR group compared with the control group (P=0.0352; Fig. 5B). The data from this confirmatory RT-qPCR analysis was, therefore, consistent with that of the microarray analysis.
Figure 5.
Verification of miRNA differential expression. Expression levels of (A) mmu-miR-130a-3p and (B) mmu-miR-5107-5p identified by miRNA microarray were examined by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of one representative experiment and three independent experiments per sample (n=40) were performed for each miRNA. *P<0.05 vs. control group. miRNA, microRNA; mmu, Mus musculus; OIR, oxygen-induced retinopathy.
Discussion
In the present study, a mouse model of OIR was constructed and subsequently used to identify differentially expressed miRNAs via microarray. Two of the differentially expressed miRNAs identified by microarray were confirmed by RT-qPCR. Hyperoxia was, therefore, demonstrated to result in the dysregulation of miRNAs in murine retinal tissue, suggesting that miRNAs are important in the development and progression of oxygen-induced ROP.
The OIR mouse model was first developed in 1994 (7) and is commonly used for studies of retinal neovascularization in ROP and other vasculopathologies. Subsequent studies have demonstrated its utility in investigating the pathogenesis of retinal neovascularization and medical interventions for ROP and other retinal angiopathies (8,19). The model has also proven to be reproducible and quantifiable, making it a favorable model for microarray analysis.
In the present study, a miRNA microarray was used to analyze miRNA expression profiles and to identify differentially expressed miRNAs in the retinal tissues of mice subjected to OIR: 67 differentially expressed miRNAs were identified in the OIR group compared with the control group. The functions of the majority of the upregulated miRNAs identified in the present study, including miR-1907, miR-3970, miR-5107-5p, miR-3962 and miR-145b, have not previously been reported. As a result, the effects of these miRNAs and potential applications of their functions require further investigations.
In the present study, the expression of miR-133b-5p was revealed to be up to 7.753-fold higher in the OIR group compared with the control group, indicating a potential role for this miRNA in the development of ROP. miR-133b-5p regulates the expression of heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) during gp120 V3 loop peptide-induced rat neuronal cell apoptosis (20). Hsp70 is a chaperone protein that inhibits key effectors of the apoptotic machinery at the pre- and postmitochondrial level (21). In addition, miR-133b, the precursor of miR-133b-5p, is downregulated in human osteosarcoma cells, resulting in increased apoptosis, and potentially acting as a tumor suppressor gene (22). The expression of miR-133b-5p may, therefore, regulate programmed cell apoptosis pathways and be involved in the development of ROP.
In contrast to the largely uncharacterized upregulated miRNAs, some of the downregulated miRNAs identified in the present study have been demonstrated to be involved in numerous diseases. The miR-1et-7 family is widely distributed in vertebrates and invertebrates, and participates in numerous biological processes, including reticulocytes (23), T-cell generation, angiogenesis (24) and the Fas-mediated apoptotic process in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (25,26). It is, therefore, unsurprising that the expression of miR-let-7d-3p is decreased in a disease such as ROP, which is caused by abnormal blood vessel development. miR-328 expression has been demonstrated to be elevated in numerous lung adenocarcinoma subtypes, which may affect the degree of malignancy of tumor progression by inhibiting the proliferation of GBM cells in gliomas (27–30). A known target of miR-328 is RTP801, which is also a target of miR-181b-5p, which had an effect on the cancer stem cells fraction and neurosphere formation as surrogate marker (31). RTP801 expression is induced in the retina following hyperoxia treatment, while the development of retinopathy is significantly attenuated in an RTP801-knockout mouse model of ROP (32). These findings suggest important roles of miR-328 and miR-181b-5p in the pathogenesis of ROP by regulating the expression of RTP801.
The potential targets of other miRNAs are also related to ROP. One of the miR-872-5p targets is insulin-like growth factor 1, which acts upstream of retinal VEGF and is important in ROP (33). Angiopoietin 2, a potential target of miR-128-3p, induces endothelial cell apoptosis and is involved in ROP (31). miR-301a and miR-130a are miRNAs that have been suggested to bind to conserved sites of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) 3′ untranslated region (34). PPARγ is widely expressed in the eye, is involved in the pathogenesis of OIR (35), and provides a pharmacological target for treating ocular angiogenesis (36). Furthermore, miR-130a contributes to angiogenesis by inhibiting the expression of two antiangiogenic homeobox transcription factors, homeobox A5 (HOXA5) and mesenchyme homeobox 2 (MEOX2; also termed GAX) (11). However, further research is required to establish whether these miRNAs (miR-872-5p, miR-128-3p, miR-301a and miR-130a) regulate ROP development.
In summary, the present study has identified the differential expression of miRNAs in a murine model of OIR some of whose functions, or those of their known targets, are associated with the development of ROP. These findings are useful to understand the molecular basis of ROP and suggest that miRNAs are involved in the progression of ROP. However, further studies are required to confirm the involvement of the miRNAs identified in the present study in the development of ROP, and their molecular mechanisms.
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81260106).
References
- 1.McGregor ML, Bremer DL, Cole C, McClead RE, Phelps DL, Fellows RR, Oden N. HOPE-ROP Multicenter Group. High Oxygen Percentage in Retinopathy of Prematurity study: Retinopathy of prematurity outcome in infants with prethreshold retinopathy of prematurity and oxygen saturation >94% in room air: The high oxygen percentage in retinopathy of prematurity study. Pediatrics. 2002;110:540–544. doi: 10.1542/peds.110.3.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sola A, Chow L, Rogido M. Retinopathy of prematurity and oxygen therapy: A changing relationship. An Pediatr (Barc) 2005;62:48–63. doi: 10.1157/13070182. (In spanish) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chamney S, McGrory L, McCall E, Twaij S, Napier M, Rollins R, Marshall AH, Craig S, McLoone E. Treatment of retinopathy of prematurity in Northern Ireland, 2000–2011: A population-based study. J AAPOS. 2015;19:223–227. doi: 10.1016/j.jaapos.2015.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Levesque BM, Kalish LA, Winston AB, Parad RB, Hernandez-Diaz S, Phillips M, Zolit A, Morey J, Gupta M, Mammoto A, et al. Low urine vascular endothelial growth factor levels are associated with mechanical ventilation, bronchopulmonary dysplasia and retinopathy of prematurity. Neonatology. 2013;104:56–64. doi: 10.1159/000351040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Patel S Jivabhai, Bany-Mohammed F, McNally L, Valencia GB, Lazzaro DR, Aranda JV, Beharry KD. Exogenous superoxide dismutase mimetic without scavenging H2O2 causes photoreceptor damage in a rat model for oxygen-induced retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56:1665–1677. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-15321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Penn JS, Tolman BL, Henry MM. Oxygen-induced retinopathy in the rat: Relationship of retinal nonperfusion to subsequent neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994;35:3429–3435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Smith LE, Wesolowski E, McLellan A, Kostyk SK, D'Amato R, Sullivan R, D'Amore PA. Oxygen-induced retinopathy in the mouse. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994;35:101–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sato T, Kusaka S, Hashida N, Saishin Y, Fujikado T, Tano Y. Comprehensive gene-expression profile in murine oxygen-induced retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009;93:96–103. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2008.142646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R, Gilad S, Barad O, Barzilai A, Einat P, Einav U, Meiri E, et al. Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat Genet. 2005;37:766–770. doi: 10.1038/ng1590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Xie M, Zhang S, Yu B. microRNA biogenesis, degradation and activity in plants. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015;72:87–99. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1728-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Doench JG, Sharp PA. Specificity of microRNA target selection in translational repression. Genes Dev. 2004;18:504–511. doi: 10.1101/gad.1184404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kuhnert F, Mancuso MR, Hampton J, Stankunas K, Asano T, Chen CZ, Kuo CJ. Attribution of vascular phenotypes of the murine Egfl7 locus to the microRNA miR-126. Development. 2008;135:3989–3993. doi: 10.1242/dev.029736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen Y, Gorski DH. Regulation of angiogenesis through a microRNA (miR-130a) that down-regulates antiangiogenichomeobox genes GAX and HOXA5. Blood. 2008;111:1217–1226. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-07-104133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kuehbacher A, Urbich C, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S. Role of Dicer and Drosha for endothelial microRNA expression and angiogenesis. Circ Res. 2007;101:59–68. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.153916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Johnson CD, Esquela-Kerscher A, Stefani G, Byrom M, Kelnar K, Ovcharenko D, Wilson M, Wang X, Shelton J, Shingara J, et al. The let-7 microRNA represses cell proliferation pathways in human cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67:7713–7722. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Shen J, Yang X, Xie B, Chen Y, Swaim M, Hackett SF, Campochiaro PA. MicroRNAs regulate ocular neovascularization. Mol Ther. 2008;16:1208–1216. doi: 10.1038/mt.2008.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bai Y, Bai X, Wang Z, Zhang X, Ruan C, Miao J. MicroRNA-126 inhibits ischemia-induced retinal neovascularization via regulating angiogenic growth factors. Exp Mol Pathol. 2011;91:471–477. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2011.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C (T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25:402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wang W, Li Z, Sato T, Oshima Y. Tenomodulin inhibits retinal neovascularization in a mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:15373–15386. doi: 10.3390/ijms131115373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Xia C, Cai Y, Lin Y, Guan R, Xiao G, Yang J. MiR-133b-5p regulates the expression of the heat shock protein 70 during rat neuronal cell apoptosis induced by the gp120 V3 loop peptide. J Med Virol. 2015;88:437–447. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rérole AL, Jego G, Garrido C. Hsp70: Anti-apoptotic and tumorigenic protein. Methods. 2011;787:205–230. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-295-3_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhao H, Li M, Li L, Yang X, Lan G, Zhang Y. MiR-133b is down-regulated in human osteosarcoma and inhibits osteosarcoma cells proliferation, migration, and invasion and promotes apoptosis. PLoS One. 2013;8:e83571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Noh SJ, Miller SH, Lee YT, Goh SH, Marincola FM, Stroncek DF, Reed C, Wang E, Miller JL. Let-7 microRNAs are developmentally regulated in circulating human erythroid cells. J Transl Med. 2009;7:98. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-7-98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Landskroner-Eiger S, Moneke I, Sessa WC. miRNAs as modulators of angiogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2013;3:a006643. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vaz F, Hanenberg H, Schuster B, Barker K, Wiek C, Erven V, Neveling K, Endt D, Kesterton I, Autore F, et al. Mutation of the RAD51C gene in a Fanconi anemia-like disorder. Nat Genet. 2010;42:406–409. doi: 10.1038/ng.570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wang S, Tang Y, Cui H, Zhao X, Luo X, Pan W, Huang X, Shen N. Let-7/miR-98 regulate Fas and Fas-mediated apoptosis. Genes Immun. 2011;12:149–154. doi: 10.1038/gene.2010.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ulivi P, Foschi G, Mengozzi M, Scarpi E, Silvestrini R, Amadori D, Zoli W. Peripheral Blood mir-328 expression as a potential biomarker for the early diagnosis of NSCLC. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:10332–10342. doi: 10.3390/ijms140510332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Arora S, Ranade AR, Tran NL, Nasser S, Sridhar S, Korn RL, Ross JT, Dhruv H, Foss KM, Sibenaller Z, et al. MicroRNA-328 is associated with (non-small) cell lung cancer (NSCLC) brain metastasis and mediates NSCLC migration. Int J Cancer. 2011;129:2621–2631. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Okumus NO, Gursel B, Meydan D, Ozdemir O, Odabas E, Gonullu G. Prognostic significance of concomitant radiotherapy in newly diagnosed glioblastomamultiforme: A multivariate analysis of 116 patients. Ann Saudi Med. 2012;32:250–255. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2012.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Delic S, Lottmann N, Stelzl A, Liesenberg F, Wolter M, Götze S, Zapatka M, Shiio Y, Sabel MC, Felsberg J, et al. MiR-328 promotes glioma cell invasion via SFRP1-dependent Wnt-signaling activation. Neuro Oncol. 2014;16:179–190. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/not164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S. miRBase: Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:D68–D73. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Brafman A, Mett I, Shafir M, Gottlieb H, Damari G, Gozlan-Kelner S, Vishnevskia-Dai V, Skaliter R, Einat P, Faerman A, et al. Inhibition of oxygen-induced retinopathy in RTP801-deficient mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004;45:3796–3805. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-0052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Nidadavolu LS, Niedernhofer LJ, Khan SA. Identification of microRNAs dysregulated in cellular senescence driven by endogenous genotoxicstress. Aging (Albany NY) 2013;5:460–473. doi: 10.18632/aging.100571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Huang JY, Chou SF, Lee JW, Chen HL, Chen CM, Tao MH, Shih C. MicroRNA-130a can inhibit hepatitis B virus replication via targeting PGC1α and PPARγ. RNA. 2015;21:385–400. doi: 10.1261/rna.048744.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tawfik A, Sanders T, Kahook K, Akeel S, Elmarakby A, Al-Shabrawey M. Suppression of retinal peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in experimental diabetes and oxygen-induced retinopathy: Role of NADPH oxidase. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009;50:878–884. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Simpson-Haidaris PJ, Pollock SJ, Ramon S, Guo N, Woeller CF, Feldon SE, Phipps RP. Anticancer role of PPARgamma agonists in hematological malignancies found in the vasculature, marrow and eyes. PPAR Res. 2010;2010:814609. doi: 10.1155/2010/814609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]