Abstract
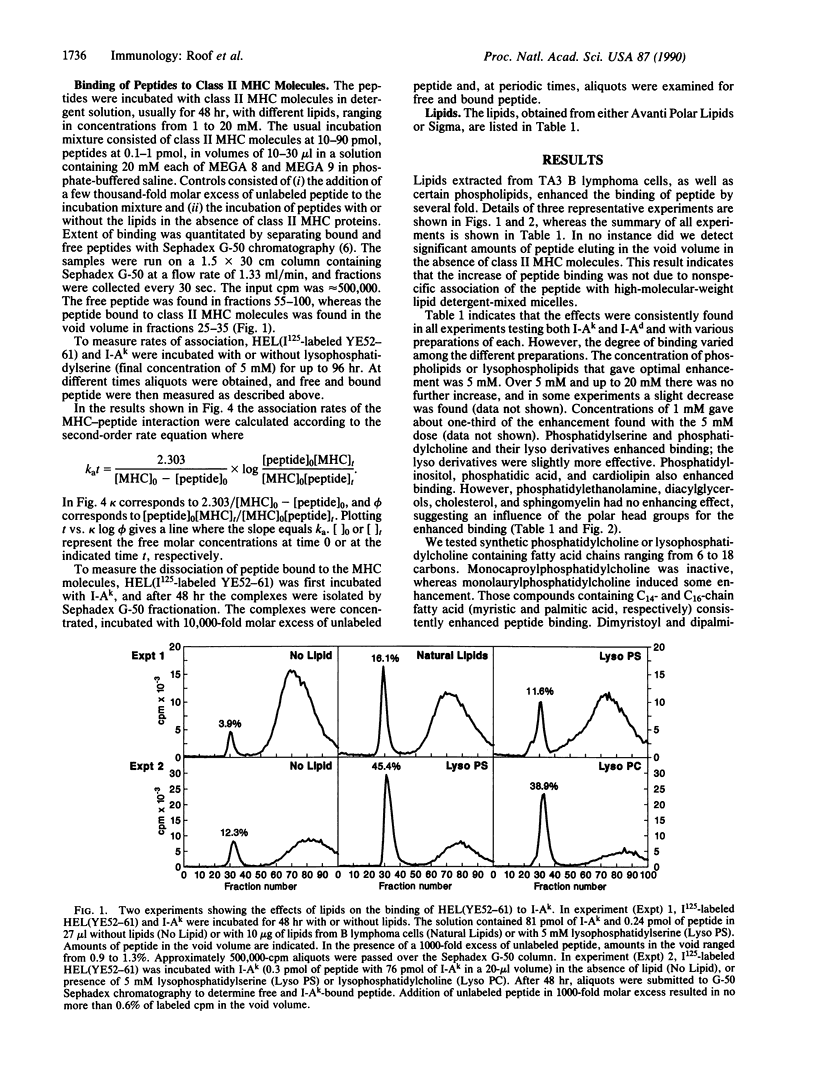
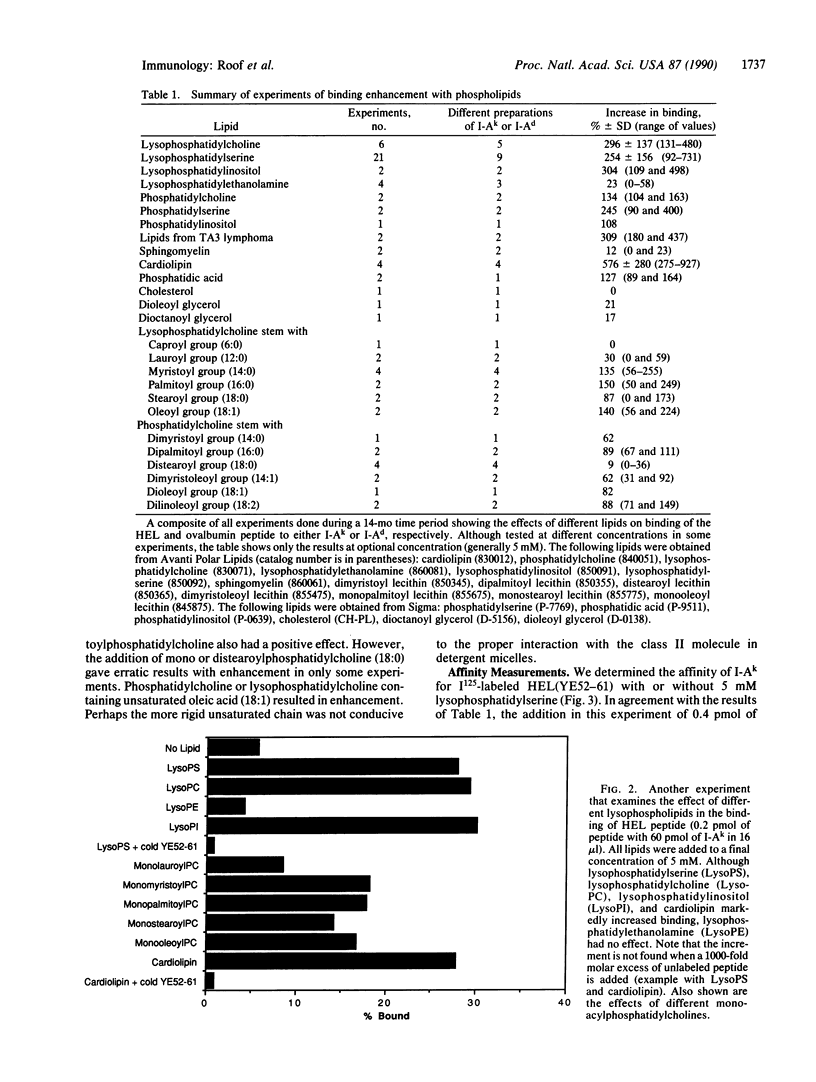
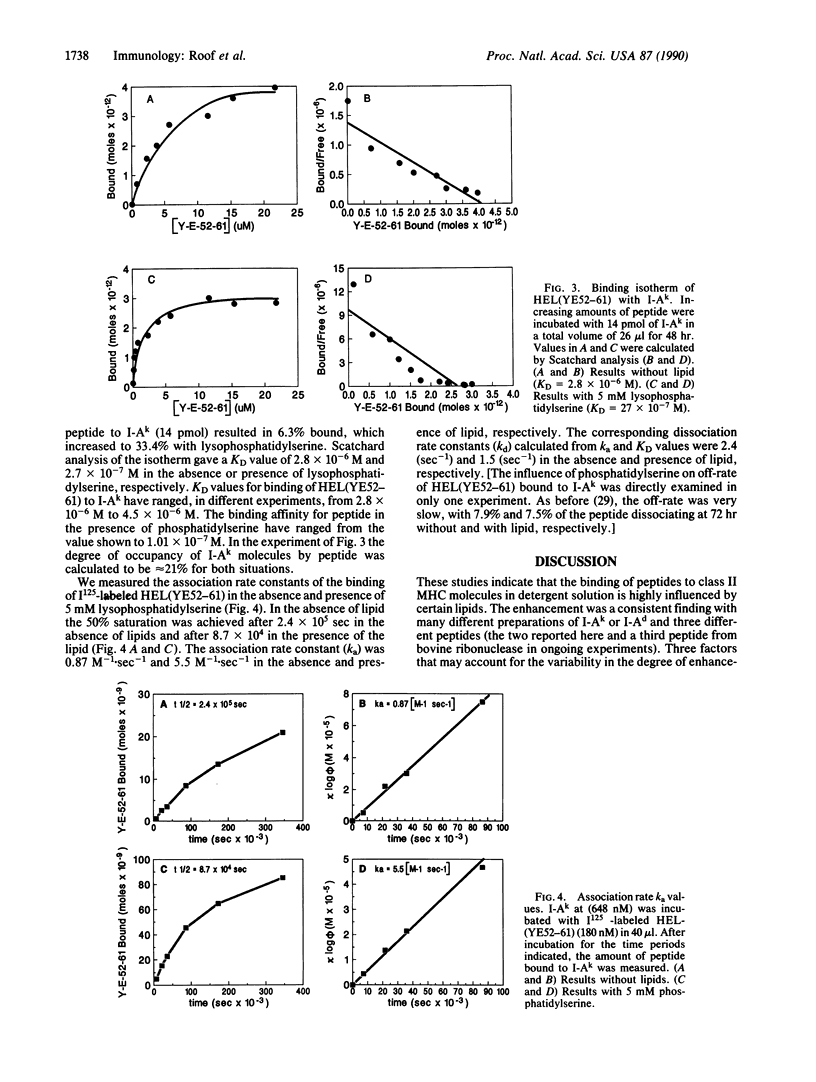
The binding of a lysozyme and ovalbumin peptide to purified class II major histocompatibility molecules in detergents was increased by the addition of certain lipids. Natural lipids from B lymphoma cells enhanced the binding and so did phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylinositol, and cardiolipin. Phosphatidylethanolamine, sphingomyelin, and cholesterol had no effect. There was no major difference between the effects of a phospholipid and its lyso derivative. As studied with phosphatidylcholine, the increase in peptide binding was also dependent on the fatty acid composition of the lipid. The binding affinity was increased 10- to 50-fold in the presence of lipid as a result of an increase in the association rate while the off-rate remained essentially unchanged. Our results suggest that lipids, directly or indirectly, induce conformational changes in class II molecules that favor their peptide-binding property.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen P. M., Matsueda G. R., Adams S., Freeman J., Roof R. W., Lambert L., Unanue E. R. Enhanced immunogenicity of a T cell immunogenic peptide by modifications of its N and C termini. Int Immunol. 1989;1(2):141–150. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.2.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babbitt B. P., Allen P. M., Matsueda G., Haber E., Unanue E. R. Binding of immunogenic peptides to Ia histocompatibility molecules. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):359–361. doi: 10.1038/317359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batenburg A. M., Demel R. A., Verkleij A. J., de Kruijff B. Penetration of the signal sequence of Escherichia coli PhoE protein into phospholipid model membranes leads to lipid-specific changes in signal peptide structure and alterations of lipid organization. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 26;27(15):5678–5685. doi: 10.1021/bi00415a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):512–518. doi: 10.1038/329512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Jardetzky T., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bjorkman P. J., Wiley D. C. A hypothetical model of the foreign antigen binding site of class II histocompatibility molecules. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):845–850. doi: 10.1038/332845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Colon S., Smith C., Freed J. H., Miles C., Grey H. M. Interaction between a "processed" ovalbumin peptide and Ia molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3968–3971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Sette A., Colon S. M., Jenis D. M., Grey H. M. Isolation and characterization of antigen-Ia complexes involved in T cell recognition. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1071–1077. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90822-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Sette A., Colon S. M., Miles C., Grey H. M. The relation between major histocompatibility complex (MHC) restriction and the capacity of Ia to bind immunogenic peptides. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1353–1358. doi: 10.1126/science.2435001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceppellini R., Frumento G., Ferrara G. B., Tosi R., Chersi A., Pernis B. Binding of labelled influenza matrix peptide to HLA DR in living B lymphoid cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):392–394. doi: 10.1038/339392a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datema K. P., Wolfs C. J., Marsh D., Watts A., Hemminga M. A. Spin-label electron spin resonance study of bacteriophage M13 coat protein incorporation into mixed lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7571–7574. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmann M., Marsh D. Spin-label studies on the origin of the specificity of lipid-protein interactions in Na+,K+-ATPase membranes from Squalus acanthias. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3572–3578. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmann M., Watts A., Marsh D. Spin-label studies of lipid-protein interactions in (Na+,K+)-ATPase membranes from rectal glands of Squalus acanthias. Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 12;24(6):1386–1393. doi: 10.1021/bi00327a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falo L. D., Jr, Benacerraf B., Rothstein L., Rock K. L. Cerulenin is a potent inhibitor of antigen processing by antigen-presenting cells. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):3918–3923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falo L. D., Jr, Haber S. I., Herrmann S., Benacerraf B., Rock K. L. Characterization of antigen association with accessory cells: specific removal of processed antigens from the cell surface by phospholipases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):522–526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong T. M., McNamee M. G. Stabilization of acetylcholine receptor secondary structure by cholesterol and negatively charged phospholipids in membranes. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 30;26(13):3871–3880. doi: 10.1021/bi00387a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Roof R. W., Unanue E. R. Turnover of Ia-peptide complexes is facilitated in viable antigen-presenting cells: biosynthetic turnover of Ia vs. peptide exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4230–4234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. E., Deepe G. S., Jr Requirements for histoplasmin presentation by accessory cells to a Histoplasma capsulatum-reactive T-cell line. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Feb;45(2):105–113. doi: 10.1002/jlb.45.2.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo C. Lipid-protein interactions and the function of the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1987;21(4):319–347. doi: 10.3109/10409238609113615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles P. F., Watts A., Marsh D. Spin-label studies of head-group specificity in the interaction of phospholipids with yeast cytochrome oxidase. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 29;20(20):5888–5894. doi: 10.1021/bi00523a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird D. M., Parce J. W., Montgomery R. I., Cunningham C. C. Effect of phospholipids on the catalytic subunits of the mitochondrial F0.F1-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14851–14856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luescher I. F., Allen P. M., Unanue E. R. Binding of photoreactive lysozyme peptides to murine histocompatibility class II molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):871–874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. Selectivity of lipid-protein interactions. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1987 Dec;19(6):677–689. doi: 10.1007/BF00762302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandi J., Wright M. V., Ray T. K. Effects of phospholipase A2 on gastric microsomal H+, K+-ATPase system: role of "boundary lipids" and the endogenous activator protein. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 6;22(25):5814–5821. doi: 10.1021/bi00294a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell G. L., Knowles P. F., Marsh D. Spin-label studies on the specificity of interaction of cardiolipin with beef heart cytochrome oxidase. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8138–8145. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quill H., Carlson L., Fox B. S., Weinstein J. N., Schwartz R. H. Optimization of antigen presentation to T cell hybridomas by purified Ia molecules in planar membranes. Ia molecule polymorphism determines the antigenic fine specificity of the response to cytochrome c peptides. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Apr 2;98(1):29–41. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90432-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R. Regulation of protein kinase C activity by lipids. FASEB J. 1988 May;2(8):2348–2355. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.8.3282960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivnay B., Fischer G. Phospholipid distribution in the microenvironment of the immunoglobulin E-receptor from rat basophilic leukemia cell membrane. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 23;25(19):5686–5693. doi: 10.1021/bi00367a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivnay B., Metzger H. Reconstitution of the receptor for immunoglobulin E into liposomes. Conditions for incorporation of the receptor into vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12800–12808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roosnek E., Demotz S., Corradin G., Lanzavecchia A. Kinetics of MHC-antigen complex formation on antigen-presenting cells. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4079–4082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadegh-Nasseri S., McConnell H. M. A kinetic intermediate in the reaction of an antigenic peptide and I-Ek. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):274–276. doi: 10.1038/337274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandermann H., Jr, McIntyre J. O., Fleischer S. Site-site interaction in the phospholipid activation of D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6201–6208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sette A., Buus S., Appella E., Smith J. A., Chesnut R., Miles C., Colon S. M., Grey H. M. Prediction of major histocompatibility complex binding regions of protein antigens by sequence pattern analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3296–3300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. D., Stubbs C. D. Modulation of membrane protein function by bilayer lipids. Basic Res Cardiol. 1987;82 (Suppl 1):93–97. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-08390-1_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugarova N. N., Dukhovich A. F., Shvets S. V., Philippova N. Y., Berezin I. V. Kinetics of the inactivation of the protein-lipid complex, firefly luciferase, by sodium deoxycholate and its reactivation by phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 17;921(3):465–472. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Allen P. M. The basis for the immunoregulatory role of macrophages and other accessory cells. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):551–557. doi: 10.1126/science.2437650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsunomiya N., Nakanishi M., Arata Y., Yasuda T., Saito S., Koyama K., Tadakuma T. T cell-mediated recognition of foreign antigen and the Ia molecule observed by stopped-flow fluorometry. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1471–1475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts A., Volotovski I. D., Marsh D. Rhodopsin-lipid associations in bovine rod outer segment membranes. Identification of immobilized lipid by spin-labels. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):5006–5013. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeagle P. L. Lipid regulation of cell membrane structure and function. FASEB J. 1989 May;3(7):1833–1842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meer G. Lipid traffic in animal cells. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:247–275. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



