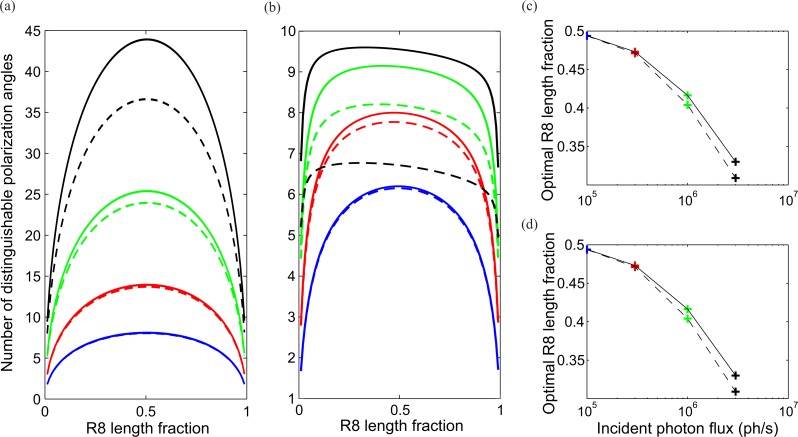
Figure 8. Optimum division of CRP between R7 and R8 maximizes two measures of coding ability, number of discriminable polarization angles and mutual information.
Optima depend on light intensity (incident photon flux, Ni) and presence of intrinsic noise. (A) Discriminable polarization angles versus R8 length fraction in the absence of intrinsic noise, without transduction unit saturation (solid curves) and with saturation (dashed curves). Four light intensities Ni; 1 × 105 (blue), 3 × 105 (red), 1 × 106 (green) and 3 × 106 (black) photons s−1. (B) As in (A) but in the presence of intrinsic noise. Note the optimum division shifts to shorter R8 at higher intensities. (C) Optimum R8 length fractions from (B) versus incident photon flux without transduction unit saturation (solid curve) and with saturation (dashed curve). (D) As in (C), but R8 length optimizes mutual information. Degree of polarization d = 0.1.