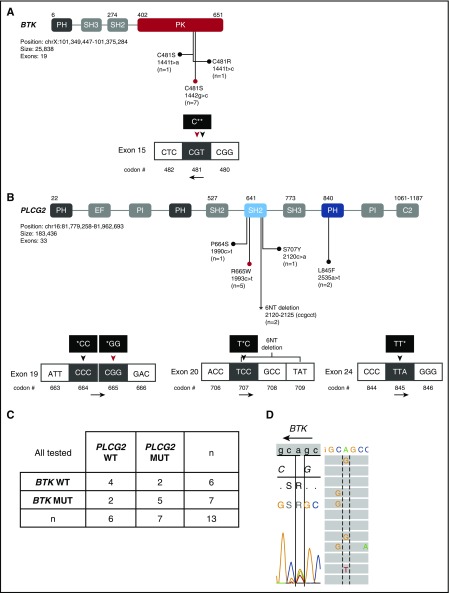
Figure 2.
BTK and PLCG2 mutations at disease progression. Schematic representation of functional domains of (A) BTK and (B) PLCG2 with amino acid substitutions due to nonsynonymous mutations or deletion indicated. (A) BTK gene domains and nucleotide changes. Mutations in exon 15 of BTK affect C481 in the protein tyrosine kinase (PK) domain. BTK c.1442G>C (red circle and red triangle) and c.1441T>A mutations lead to C481S. BTK c.1441T>C mutation leads to C481R substitution. (B) PLCG2 gene domains and nucleotide changes. Mutations in PLCG2 exons 19 and 20 affect the N-terminal SH2 domain and mutations in exon 24 the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. The P664S mutation and the 6-nucleotide deletion in PLCG2 exon 20 (*), have not been previously described in CLL. (C) Number of patients with BTK and/or PLCG2 mutations at progression. (D) Sanger sequencing and NGS of patient PD9 reveals 3 different types of nucleotide changes in BTK exon 15. Shown is the sense DNA strand. BTK is encoded on the antisense strand; the black arrow indicates the read direction. Dotted and solid lines are aligned at BTK nucleotide position 1441. Left panel, The result of Sanger sequencing showing c.1442G>T (C481S), c.1441T>C (C481R), and c.1441T>A (C481S). Right panel, The result of NGS showing c.1441T>C (C481R) and c.1441T>A (C481S). EF, EF-hand domain; MUT, mutated; PI, phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C X domain; WT, wild-type.