Abstract
Developing the Wnt pathway inhibitors has been considered as a therapeutic approach for cancers and other Wnt-related diseases. Previously we found that the G-rich sequence of WNT1 promoter is capable of forming G-quadruplex structure and stabilizing agents for Wnt1-mediated signaling pathway. Using a established cell-based drug screen system that enabled the evaluation of WNT1 expression activity in a G-quadruplex structure dependent manner, we evaluated a series of 6-substituted 9-chloro-11H-indeno[1,2-c]quinolin-11-one derivatives that potentially inhibit the Wnt1-mediated signaling pathway. The most potent compound SJ26 showed repression of WNT1 activity in a G-quadruplex structure-dependent manner. Moreover, compound SJ26 inhibited the WNT1-mediated downstream signaling pathway and suppressed migration activity of cancer cells. Thus, we have identified a tetracyclic azafluorenone, SJ26, that is capable of binding to G-quadruplex DNA structure, repressing WNT1 expression, and inhibiting cell migration.
Keywords: Wnt1-mediated signaling pathway, G-quadruplex, 6-substituted 9-chloro-11H-indeno[1, 2-c]quinolin-11-ones, reporter assay
INTRODUCTION
Tumor metastasis is the most common cause of cancer related-death. Targeting metastasis is considered as one of the highest priorities for researches in antitumor agents [1]. The Wnt-mediated signal pathway regulates various cellular functions, including proliferation, survival, migration, and development by trigger downstream signaling cascades [2]. Many of the Wnt-targeted genes are involved in tumorigenesis and metastasis. For example, myc and cyclin D1 are involved in proliferation and WISP1 is involved in angiogenesis [3, 4]. Wrch1 and MMP7 are also known to be involved in migration and invasion of cancer cells [5, 6]. Clinically, aberrant activation of Wnt signaling is observed in a variety of tumors. Previous studies reported that high levels of WNT1 expression in patients are associated with advanced metastasis [7–9]. and the overall survival is lower in patients with Wnt1-positive cancer. Thus, developing the Wnt pathway inhibitors has been considered as a therapeutic approach for the treatment of patients with cancers and other Wnt-related diseases [10, 11].
Small molecule inhibitors of the Wnt signaling pathways have been designed to target mediators of Wnt-signaling pathway [11]. These compounds mainly aim to decrease the levels of β-catenin [12–16]. Agents targeting Wnt directly have also been developed. For example, the anti-Wnt1 antibody was used to block the stimulation of Wnt1 downstream signaling pathway. Treatment of anti-Wnt1 antibody was shown to reduce the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma and colorectal cancer both in vivo and in vitro [17, 18].
Previous our study reported that the G-rich sequence of WNT1 promoter is capable of forming both hairpin and G-quadruplex structures in the presence of potassium ion [19, 20]. Significantly, the Wnt1-mediated signaling pathway can be repressed upon the addition of G-quadruplex stabilizing agents in cancer cells. Consequently, the migration and invasion activities of cancer cells were also decreased [19]. Thus, it is likely that suppression of tumor metastasis can be achieved through stabilizing the G-quadruplex forming sequence located at the WNT1 promoter.
Diverse anthracycline derivatives (e.g. doxorubicin, daunorubicin, mitoxantrone and ametantrone) have been shown to have anti-proliferative (or cytostatic) properties. We and others showed that the structurally related anthraquinone compounds can stabilize G-quadruplex structure formed by telomeric DNA sequences and inhibit telomerase or topoisomerase activity [21–33]. Camptothecin (CPT) and TAS-103 are also cytotoxic quinoline alkaloid derivatives that show potent topoisomerase (topo) I and/or topo II inhibition activities [34–37]. Two related CPT family members, irinotecan and topotecan, are currently used clinically as anticancer chemotherapy drugs [38, 39]. Based on the structures of anthracycline, here we design and synthesize a series of 6-substituted 9-chloro-11H-indeno[1,2-c]quinolin-11-one derivatives by varying the side chains with heterocyclic amine moieties and lipophilic alkyl chains (Figure 1). We have also integrated the pharmocophore of camptothecin (CPT) and TAS-103 into our drug design [40, 41]. The synthesis and results of these series of compounds against various cell lines and other SAR evaluation will be reported in a separate paper. In this study, the G-quadruplex structure-dependent WNT1 repression activities of these newly synthesized compounds were analyzed by a cell-based assay system. We found that compound SJ26 showed potent inhibitory effects to the Wnt1-mediated downstream signaling pathway in a G-quadruplex structure dependent manner and inhibited the migration activity of cancer cells. Our results suggested the tetracyclic azafluorenones are potent WNT1 repressors.
Figure 1. Chemical structures of several known tetracyclic quinoline derivatives, topoisomerase I inhibitors and Wnt modulators.
RESULTS
Cell-based system for expression repressors of WNT1 gene
Functional analysis of human WNT1 proximal promoter using reporter assays revealed that the 277-bp upstream sequence of WNT1 is sufficient for the control of developmentally regulated expression [42, 43]. Sequence analysis of the 277-bp sequence identified two TATA boxes and a stretch of extremely G-rich sequence. Significantly, the G-rich sequence of the WNT1 promoter contains four runs of at least three contiguous guanines that are capable of forming G-quadruplex structures under physiological conditions [19, 20].
To facilitate the analysis of WNT1 expression, we ligated downstream to the WNT1 promoter a reporter gene, SEAP, to generate a WNT1 promoter-driven reporter construct, pWNT1-SEAP. We have also constructed two mutants that failed to form G-quadruplex structure, m1 and m6 (Figure 2A). The expression of SEAP can then be used as the criterion for the measurement of wild-type and mutant WNT1 expression efficiency. Stable human lung carcinoma cell (H1299) lines carrying wild-type or mutant plasmids were selected. Although reporter analysis using transient transfection method to introduce reporter plasmids into cells produces better results in general, the approach is not suitable for drug screening because it needs additional steps for the analysis. These additional steps are prone to introduce variations in the screens. Moreover, transfection step requires additional reagents that are not economic for large-scale screens. Thus, stable clones were employed in drug screens.
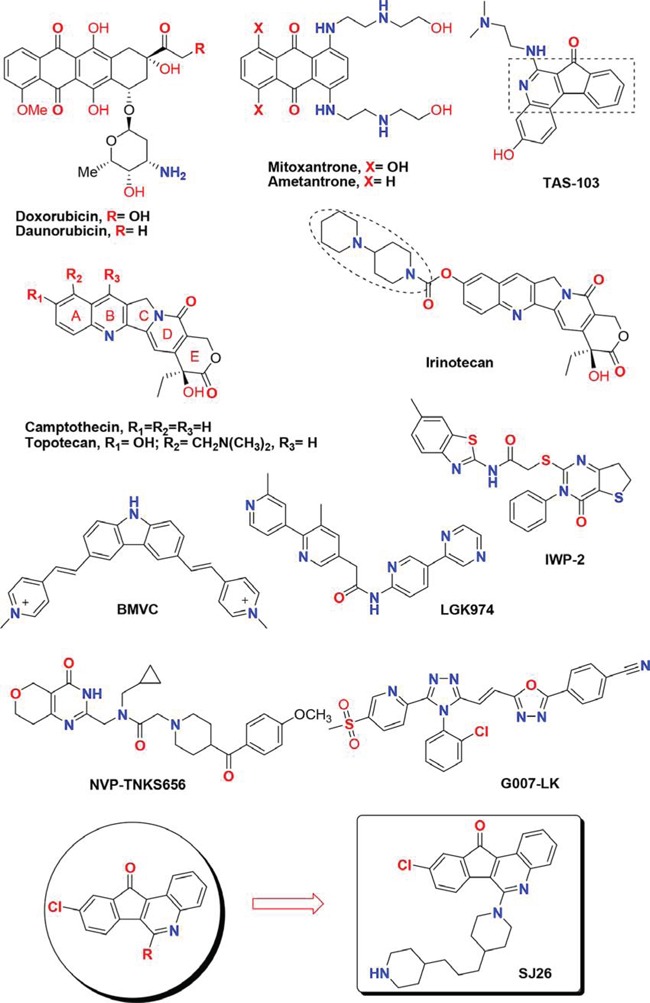
Figure 2. Establishing a cell-based assay system that inhibits WNT1 expression through stabilizing the G-quadruplex structure formed at its promoter.
A. Schematic diagrams showed the mutation sites of WNT1 in reporter assays. The G-quadruplex-forming sequences of Wnt1 (wild-type), Wnt1-m1, or Wnt1-m6 (Wnt1 mutations) were indicated. B. Wnt1-m1 and m6 mutations did not affect the basal expression level of WNT1. The H1299 cells harboring wild-type, WNT1-m1, and Wnt1-m6 reporters were analyzed for their basal expression activity. The relative phosphatase activities of wild-type, WNT1-m1, and WNT1-m6 mutant were presented using the wild-type level as 100%. C. BMVC repressed WNT1 expression required G-quadruplex structure formation. The H1299 cells harboring wild-type, WNT1-m1, and WNT1-m6 reporters were incubated with the indicated concentrations of BMVC for 2 days. The phosphatase activities were then analyzed using the activity of DMSO-treated cells as 100%. Asterisks indicate p < 0.05.
The basal phosphatase activities under the control of wild-type or mutants promoters were first analyzed. We detected similar phosphatase activities for wild-type, the Wnt1-m1, and the Wnt1-m6 promoters, suggesting that the mutation did not affect the general transcriptional activity of the WNT1 promoter (Figure 2B). To test if our reporter system is capable of differentiate G-quadruplex structure-mediated repression of WNT1 expression, the SEAP expression was monitored in the presence of 3,6-bis(1-methyl-4-vinylpyridinium) carbazole diiodide (BMVC) because it was shown to bind and stabilize the G-quadruplex structure at WNT1 promoter [19]. Upon treatment with BMVC, the expressions of SEAP from the wild-type promoter were reduced (Figure 2C). In contrast, the expression efficiency of mutant promoters did not respond to BMVC treatments. Thus, formation of G-quadruplex structure is required for suppressing WNT1 expression by BMVC. This result indicated that our reporter construct is capable of monitoring the expression of WNT1. Moreover, addition of WNT1-m1 and -m6 mutation enables the evaluation of whether the repression requires G-quadruplex structure. Thus, the cells harboring pWNT1-SEAP or its mutants could be used as a tool to monitor the expression of WNT1 in a G-quadruplex structure dependent manner.
Inhibitory effect of compound SJ26 on the WNT1 expression of G-quadruplex dependent manner
The expression of SEAP in H1299 cells harboring these reporters were used as the criterion to evaluate if the 6-substituted 9-chloro-11H-indeno[1,2-c]quinolin-11-one derivatives repressed the expression of WNT1 in cancer cells. To facilitate effective identification of compounds that selectively repress WNT1 activity, we established a screening strategy that was adopted and modified from the NCI-60 Human Tumor Cell Lines Screen (https://dtp.cancer.gov/discovery_development/nci-60/methodology.htm). The relative WNT1 expressions by these compounds at one-dose (10 μM) were first determined in these cells. We reasoned that an effective inhibitor should give good inhibitory effect at this concentration. The numbers reported (values between 0 and 100) for the one-dose assays represented the WNT1 promoter activities relative to the no-drug control that were determined by SEAP assays (Table 1). To rule out compounds that showed apparent SEAP repression activities by inhibiting cell growth, MTT assays were also introduced into our screen. It is to eliminate compounds that showed WNT1 repressing activities non-selectively. Compounds that exhibited significant WNT1 promoter inhibition and did not show grow inhibitory activity in the one-dose screen are selected and further evaluated.
Table 1. Effect of tetracyclic azafluorenone derivatives on repressing WNT1 expression.
| Compd SJ | R | H1299a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEAP (% ± SD)b | MTT (% ± SD) | ||||||
| Wnt1 | m1c | m6 | Wnt1 | m1 | m6 | ||
| 2 | −Cl | 94.7 ± 34.9 | 96.22 ± 21.4 | 157.8 ± 20.6 | 114.5 ± 3.0 | 101.0 ± 17.2 | 132.9 ± 7.5 |
| 3 | −NHCH3 | 17.1 ± 10.0 | 49.0 ± 10.8 | 32.6 ± 17.4 | 92.9 ± 4.9 | 139.2 ± 20.5 | 90.9 ± 5.5 |
| 4 | −N(CH3)2 | 17.4 ± 9.1 | 79.4 ± 14.9 | 35.3 ± 21.5 | 101.2 ± 2.3 | 137.5 ± 16.2 | 83.8 ± 3.2 |
| 5 | −NHCH2CH2N(CH2CH3)2 | 23.0 ± 2.4 | 25.7 ± 12.4 | 45.5 ± 26.3 | 97.1 ± 4. 6 | 113.9 ± 18.9 | 76.8 ± 5.5 |
| 6 | −N(CH2CH2)2 | 33.3 ± 11.5 | 76.5 ± 18.6 | 34.2 ± 21.2 | 104.9 ± 1.0 | 102.9 ± 6.6 | 81.9 ± 8.3 |
| 7 | −N(CH2CH2)2CH2 | 34.0 ± 14.7 | 75.1 ± 19.8 | 53.6 ± 15.7 | 113.8 ± 11.1 | 151.1 ± 1.0 | 92.0 ± 14.7 |
| 8 | −N(CH2CH2)2CHCH3 | 57.6 ± 7.1 | 98.7 ± 31.1 | 58.1 ± 17.4 | 105.3 ± 10.9 | 163.8 ± 7.0 | 104.3 ± 14.1 |
| 9 | −N(CH2CH2CH2)2 | 55.8 ± 13.9 | 85.8 ± 37.0 | 57.4 ± 15.8 | 118.2 ± 7.0 | 148.7 ± 1.0 | 96.6 ± 6.8 |
| 10 | −N(CH2CH2)2O | 30.1 ± 9.5 | 79.1 ± 18.1 | 46.7 ± 15.5 | 98.0 ± 9.0 | 119.6 ± 16.4 | 95.9 ± 3.6 |
| 11 | −N(CH2CH2)2S | 55.7 ± 14.7 | 115.5 ± 21.9 | 53.8 ± 13.4 | 109.0 ± 5.6 | 154.2 ± 15.2 | 110.8 ± 3.5 |
| 12 | −N(CH2CH2)2NH | 76.2 ± 13.4 | 103.5 ± 4.8 | 63.5 ± 13.1 | 88.8 ± 13.1 | 131.6 ± 23.1 | 105.4 ± 9.0 |
| 13 | −N[CH(CH3)CH2](CH2CH2)NH | 60.7 ± 0.9 | 115.3 ± 2.8 | 64.6 ± 3.0 | 120.1 ± 8.3 | 161.0 ± 0.3 | 100.3 ± 9.2 |
| 14 | −N(CH2CH2)2NCH3 | 73.1 ± 7. 9 | 64.7 ± 22.1 | 50.1 ± 19.1 | 99.8 ± 1.2 | 145.3 ± 3.7 | 92.4 ± 1.1 |
| 15 | −N(CH2CH2)2NCH2CH3 | 78.7 ± 11.4 | 110.3 ± 9.8 | 48.6 ± 17.0 | 112.5 ± 0.0 | 153.6 ± 21.0 | 113.8 ± 5.2 |
| 16 | −N(CH2CH2)2NCH(CH2CH2)2 | 57.3 ± 14.0 | 131.8 ± 30.4 | 76.3 ± 7.8 | 121.0 ± 6.6 | 169.7 ± 14.0 | 120.0 ± 4.6 |
| 17 | −N(CH2CH2)2CHN (CH2CH2)2CH2 | 38.4 ± 19.5 | 20.8 ± 14.0 | 51.3 ± 19.6 | 112.9 ± 3.9 | 157.8 ± 8.3 | 115.8 ± 9.8 |
| 18 | −N(CH2CH2)2NC6H5 | 34.5 ± 13.8 | 49.4 ± 7.8 | 74.2 ± 12.9 | 98.5 ± 9.3 | 152.5 ± 6.9 | 94.6 ± 0.6 |
| 19 | −N(CH2CH2)2NCH2C6H5 | 52.8 ± 11.9 | 101.6 ± 7.2 | 59.2 ± 4.2 | 140.37 ± 0.0 | 155.1 ± 6.2 | 111.2 ± 2.2 |
| 20 | −N(CH2CH2)2NC6H4F(o) | 82.5 ± 11.9 | 94.7 ± 16.9 | 66.4 ± 2.6 | 119.9 ± 9.0 | 145.8 ± 8.2 | 122.7 ± 5.1 |
| 21 | −N(CH2CH2)2 NC6H4OCH3 (o) | 24.7 ± 8.5 | 39.5 ± 11.2 | 63.3 ± 7.0 | 128.9 ± 16.7 | 165.3 ± 15.9 | 118.8 ± 17.4 |
| 22 | −N(CH2CH2)2 NC6H4OCH3 (m) | 47.1 ± 0.6 | 79.1 ± 8.6 | 63.9 ± 6.8 | 98.6 ± 4.4 | 110.7 ± 10.7 | 102.1 ± 11.4 |
| 23 | −N(CH2CH2)2NCH (CH2CH2)2NCH3 | 49.2 ± 22.4 | 112.2 ± 26.7 | 55.6 ± 14.2 | 110.5 ± 3.2 | 135.6 ± 3.1 | 103.9 ± 12.1 |
| 24 | −N(CH2CH2)2C(OCH2)2 | 54.8 ± 19.0 | 122.0 ± 12.8 | 65.4 ± 4.7 | 103.1 ± 1.9 | 131.0 ± 34.2 | 114.6 ± 4.3 |
| 25 | −N(CH2CH2)2N(CO)N (CH2CH2)2CH2 | 65.7 ± 27.6 | 113.2 ± 20.7 | 63.5 ± 4.4 | 98.2 ± 14.9 | 146.5 ± 7.6 | 114.0 ± 6.8 |
| 26 | −N(CH2CH2)2CH(CH2)3 CH(CH2CH2)2NH | 42.7 ± 1.9 | 99.6 ± 22.7 | 83.7 ± 15.7 | 88.3 ± 8.5 | 127.6 ± 0.4 | 98.4 ± 5.2 |
| 27 | −SCH2CH2OH | 42.0 ± 7.6 | 96.8 ± 14.3 | 63.4 ± 1.7 | 97.0 ± 10.8 | 127.4 ± 12.9 | 79.1 ± 9.3 |
Non-small lung cancer cells H1299 were grown in RPMI 1640 media supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 units/mL penicillin and 100 mg/mL streptomycin in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 at 37°C.
SD, standard derivation; all experiments were independently performed at least three times.
The G-quadruplex-forming sequences of WNT1 (wild-type), WNT1-m1, or WNT1-m6 (WNT1 mutations) were indicated.
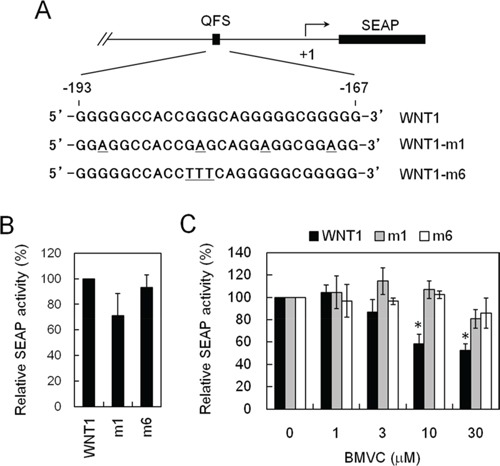
As shown in Table 1, more than half [13 out of 25 including: SJ3 (17.1%), SJ4 (17.4%), SJ5 (23.0%), SJ6 (33.3%), SJ7 (34.0%), SJ10 (30.1%), SJ17 (38.4%), SJ18 (34.5%), SJ21 (24.7%), SJ22 (47.1%), SJ23 (49.2%), SJ26 (42.7%), and SJ27 (42.0%)] of the tested compounds repressed more than 50% of the SEAP activity in wild-type WNT1 promoter, suggesting that this series of analogs are potent repressors of WNT1 expression. At 10 μM concentration, none of the synthesized derivatives showed potent cytotoxicity, indicating that the observed WNT1 repressing activities were not due to cellular toxicity (Table 1). To identify compounds that repressed WNT1 expression through the formation of G-quadruplex structure at its promoter, the SEAP activity of wild-type, m1 and m6 mutants were next compared (Table 1). Among the tested compounds, only SJ26 did not repress m1 and m6 mutants, suggesting that the observed repression in wild-type promoter is G-quadruplex structure-dependent. We tested the SEAP repressing activity and cytotoxicity using multiple doses of SJ26. Consistent with the screening results, SJ26 selectively repressed wild-type WNT1 promoter activity and the repression is G-quadruplex dependent as it did not significantly affect the other two mutant promoters (Figure 3). It is interesting to note that SJ26 did not show significant cytotoxic activity at concentration up to 30 μM. In addition to the stable lines that we used in the screen (Figure 3A and 3B), we have also conducted the reporter assays using transient transfection method to introduce reporter constructs into H1299 cells. As shown in Figure 3C, SJ26 selectively repressed the wild-type promoter, further confirming that the observed WNT1-repressing activity by SJ26 was mediated through the formation of G-quadruplex structure formed at the WNT1 promoter. It is also apparent that transient transfect method yielded better inhibitory results.
Figure 3. SJ26 repressed WNT1 expression in a G-quadruplex dependent manner.
A. Suppression of WNT1 expression by SJ26 using reporter-harboring stable cell lines. The H1299 cells harboring wild-type, WNT1-m1, and WNT1-m6 reporters were incubated with the indicated concentrations of SJ26 for 24 h. The phosphatase activities were then analyzed using the activity of DMSO-treated cells as 100%. B. Cytotoxic effects of SJ26. About 2 × 104 H1299 cells were seeded in 96-well plates and incubated with SJ26 at various concentrations for 24 h. Cell growth was then determined using the MTT assay. The values are obtained from three experiments using the values of untreated cells as 100%. C. Suppression of WNT1 expression by SJ26 using transient-transfected reporter assays. Reporter plasmid constructs carrying wild-type, WNT1-m1, and WNT1-m6 promoters were transfected into H1299 cells using lipofecamin 2000. The transfected cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of SJ26 for 24 h. The phosphatase activities were then analyzed using the activity of DMSO-treated cells as 100%. Asterisks indicate p < 0.05.
Effect of SJ26 on the melting temperature of WNT1 G-quadruplex
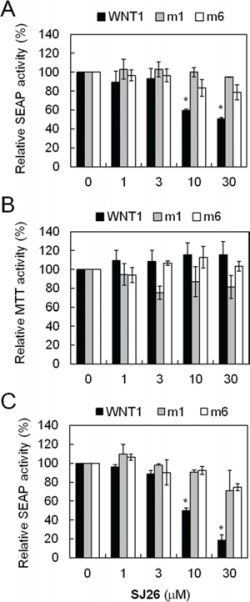
We have previously showed that an oligonucleotide carrying the G-rich sequence of WNT1 promoter was capable of forming a G-quadruplex structure [19, 20]. To evaluate the effect of SJ26 to the G-quadruplex structure of WNT1 promoter, we applied circular dichroism (CD) to monitor the melting temperature (Tm) of WNT1 G-quadruplex. Oligonucleotide containing the G-quadruplex-forming sequences of WNT1 promoter (−193 to −167) were synthesized and analyzed by CD spectormetry. The CD spectrum of WNT1 oligonucleotide displayed a positive band at 264 nm and a negative band at 240 nm together with a relative weak positive band at 292 nm in the presence of 5 mM K+ (Figure 4A). The result is consistent with our previous observation that WNT1 oligonucleotide forms a mixed parallel/antiparallel folding pattern with at least two different G-quadruplex conformations [19, 20]. Addition of SJ26 did not greatly affect the overall CD spectrum of the WNT1 G-quadruplexes. The 265-nm CD band was then measured as a function of temperature to determine the Tm of WNT1 G-quadruplexes in the presence of SJ26. Here we used relatively low molar ratio of SJ26 (3 μM) to WNT1 DNA (5 μM) in our analysis. High molar ratio of SJ26 was not used because we consider that high molar ratio of SJ26 relative to its target DNA is not the pharmacologically equivalent concentration. We found that the Tm of WNT1 G-quadruplexes was elevated from 54.2 to 57.7°C in the presence of 3 μM SJ26, suggesting that it could thermally stabilize the WNT1 G-quadruplexes (Figure 4B).
Figure 4. SJ26 enhances the melting temperature of WNT1 G-quadruplex.
A. CD spectra of the WNT1 G-rich sequence. The CD spectra of 100 μM WNT1 (5′-GGGGGCCACCGGGCAGGGGGCGGGGG-3′) oligonucleotide in the presence of 5 mM KCl were recorded over the spectral range of 210–350 nm. B. Temperature-dependent CD signals at 265 nm of 5 μM WNT1 quadruplex and on interaction with 3 μM SJ26 were measured, respectively.
Effect of SJ26 represses WNT1 expression and reduces the migration activity of H1299 cells
The effect of SJ26 on WNT1 expression was further analyzed. As shown in Figure 5, real time RT-PCR analysis showed that the WNT1 mRNA level was significantly decreased in cells that were treated with SJ26 (Figure 5A). Moreover, immunoblotting analysis of the SJ26-treated lung cancer H1299 cells showed that the Wnt1 protein levels were greatly decreased by SJ26 treatment at a dose as low as 1 μM (Figure 5B). These results indicate that SJ26 could stabilize G-quadruplex structure and reduce the expression of WNT1. It is also interesting to note that although it requires ∼10 μM to observed the repressing effect in our cell-based SEAP reporter system, SJ26 at concentration as low as 1 μM was able to suppress the endogenous WNT1 expression. Although the reason is not clear to us, the apparent differences might be due to the difference of sensitivity in these assay systems. The downstream effect of Wnt1-mediated signaling pathway by SJ26 was also analyzed. Immunoblotting analysis showed that the β-catenin levels were decreased by SJ26 (Figure 5B). Since the Wnt1-mediated signaling pathway was shown to have an important role in cancer migration and invasion, the cellular effects of suppressing WNT1 expression by SJ26 were analyzed. The migration activity of SJ26-treated cells was first evaluated using scratch assays. As shown in Figure 5C, the healing activity of H1299 cells was decreased by SJ26 in a dose dependent manner. The anti-proliferation efficacy of SJ26 was also determined. We found SJ26 did not affect the proliferation of H1299 cells, suggesting the observed healing-inhibitory effect was not due to inhibition of proliferation. To show that the anti-healing effect of SJ26 was through suppression of Wnt1-mediated pathway, we overexpressed WNT1 in SJ26-treated cells. We expected that expressing of excess amount of Wnt1 should reverse the anti-healing effect by SJ26. Plasmid construct harboring WNT1 under the control of a CMV promoter was transfected into H1299 cells. Indeed, the scratch analysis also indicated that the inhibitory effect of SJ26 was reversed in WNT1-overexpressing cells (Figure 5D). The results indicate that the migration inhibitory effect of SJ26 was mediated through suppressing the Wnt1-mediated signaling pathway.
Figure 5. SJ26 repressed WNT1 expression and reduced the migration activity of H1299 cells.
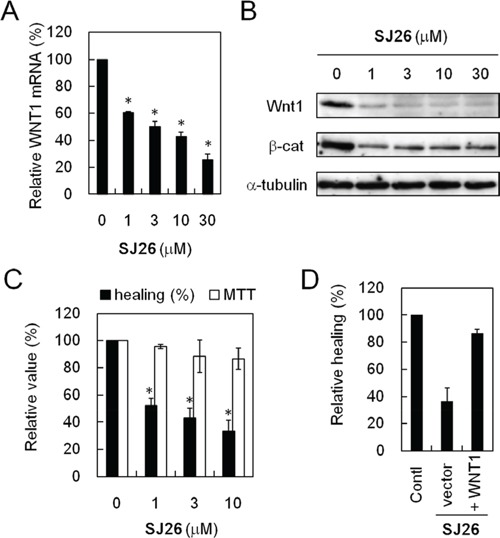
A. SJ26 reduced the WNT1 mRNA level. The H1299 cells was incubated with 1, 3, 10, or 30 μM SJ26 for 24 h and then subjected to quantitative RT-PCR analysis. The GAPDH expression level was used as an internal control. The mRNA level of WNT1 expression in untreated H1299 cells was defined as 100%. Results were obtained from the average of three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate p < 0.05. B. SJ26 reduced the Wnt1 protein and its down strean mediator β-catenin levels. H1299 cells were incubated with 1, 3, 10, or 30 μM SJ26 for 24 h. Total cell extracts were prepared, and immunoblotting analysis was conducted using antibodies against Wnt1, β-catenin, or α-tubulin. C. SJ26 reduced the healing activity of H1299 cells. H1299 cells were incubated with 10 μM DMSO or 1, 3, or 10 μM SJ26 for 48 h, and then the treated cells were subjected for scratch assays. Relative migration rates of H1299 cells were determined by migration distance over the time. Cell growth was also determined using the MTT assay. The value of migration rate or cell growth in DMSO-treated cells was defined as 100%. Asterisks indicate p < 0.05. D. WNT1-overexpression reversed the healing-inhibitory activity of SJ26. The relative healing rates were determined in 10 μM SJ26-treated cells that overexpressing WNT1. The relative healing rate in DMSO-treated H1299 cells was defined as 100%.
Suppression of Wnt1-mediated cell migration by SJ26 was not limited to H1299 cells
To test the effects of WNT1 expression and migration upon SJ26 treatments on other cancer cell lines, the MCF7 (breast cancer) and Hep2B 2.17 (liver cancer) cells were also tested. We found SJ26 effectively repressed the expression of WNT1 and β-catenin in these cells (Figure 6A). The migration activity was next evaluated using trans-well assays. As shown in Figure 6B, SJ26 effectively inhibited the migration activity of H1299 cells. Both the migration activities of MCF7 and Hep3B cells were also inhibited by SJ26, although not as effective as in H1299 cells. It was noted that the level of Wnt1/β-catenin repression by SJ26 correlated with their reduction in migration activity. Thus, the cellular context in different cell types might also have a role in modulating the repressing effects of SJ26. Nevertheless, the correlation between Wnt1/β-catenin repressing and migration inhibition by SJ26 provides strong indication that SJ26 inhibit the migration activity of cancer cells through repressing the expression of WNT1.
Figure 6. SJ26 suppressed cell migration in H1299, MCF7 and Hep3B 2.17 cells.
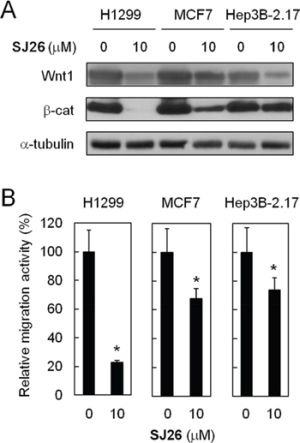
A. SJ26 suppressed Wnt1/β-catenin-signaling pathway in H1299, MCF7 and Hep3B 2.17 cells. Cells were treated with 10 μM SJ26 and the total cell extracts were prepared. Immunoblotting analysis was conducted using antibodies against Wnt1, β-catenin, or α-tubulin. B. H1299, MCF7 or Hep3B 2.17 cells were incubated with 10 μM of SJ26 and were subjected to trans-well assay analysis. The extent of cell migration across the wells was recorded after 6 hours. The value of migration rate in DMSO-treated cells was defined as 1. Asterisks indicate p < 0.05.
DISCUSSION
Aberrant activation of the Wnt pathway is implicated in driving the formation of various human cancers. Many cancers show evidence of inappropriate activation of the Wnt pathway, including raised levels of β-catenin [44, 45]. Moreover, defective Wnt signaling might also play a role in the generation and maintenance of cancer stem cells [46]. Thus, Wnt signaling plays a pivotal role in cancer, and compounds that dampen Wnt pathway activity could provide useful molecular targeted therapeutics for the treatment of cancers [11, 47–49]. An assortment of small molecule inhibitors has been identified that target the mediators of the Wnt signaling pathway. For example, compound ICG-001 was shown to block the interaction between β-catenin and the transcriptional coactivator protein CREB binding protein (CBP) [50]. Recently, several new compounds that target tankyrase activity were also developed such as NVP-TNKS656 [51], G007-LK [52], and LGK974 [53]. Moreover, a small-molecule porcupine (PORCN) acyltransferase inhibitor, IWP-2, was found to inhibit the secretion of functional WNT ligands [13]. Here we identify repressors that inhibit WNT1 expression through stabilizing the G-quadruplex structure formed at its promoter. The 6-substituted 9-chloro-11H-indeno[1,2-c]quinolin-11-one derivatives are capable of inhibiting the WNT-signaling pathway through suppressing the expression of WNT1. Thus, our results support a unique approach to inhibit WNT-mediated signaling pathway through suppression of WNT1 expression. The identified target compounds should have potential to be further developed into drugs to treat Wnt-related diseases.
The cell-based reporter assay we established enables efficient monitoring and analyzing WNT1 expression. In our screen system, we have also added WNT1-m1 and -m6 mutation constructs to enable the determination of whether the repression requires G-quadruplex structure formation. Thus, this cell-based system could be applied to gauge the expression of WNT1 in a G-quadruplex structure dependent manner. Using the reporter system, we have successfully identified SJ26. SJ26 effectively represses the expression of WNT1, its downstream signaling pathway, and the migration activity of cancer cells. Importantly, the WNT1 inhibitory effect mediated by SJ26 appears to be selective and specific as it does not affect the general proliferation property of cells at concentrations as high as 30 μM. It is also interesting to note that SJ26 only moderately elevates the melting temperature of a G-quadruplex structure formed by WNT1 promoter sequences. Although moderate, the melting-temperature elevation is sufficient to repress WNT1 expression and inhibit its downstream signaling pathway. Thus, the results suggest that our reporter assay could identify G-quadruplex stabilizers with high sensitivity.
Azafluorenone compounds show diverse pharmacological activities. For example, they have been reported to have antifungal, antimicrobial, and antimalarial activities [54–56]. They were also shown to have cytotoxic properties to induce cancer cells into apoptosis [57–59]. Moreover, an arylindenopyrimidine was shown to be a potent dual A2A/A1 receptor antagonist that might have the potential for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorder such as Parkinson's disease [60]. Our results in stabilization of the G-quadruplex structure point to a new pharmacological direction that azafluorenone compounds could also target to specific DNA structure. Much work yet needs to be done to fully understand the precise mechanisms of these series compounds. In conclusion, we demonstrated that SJ26 play a novel anti-cancer mechanism, and it has the potential to be further developed into anti-cancer drugs that targets the migration activity of cancer cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemicals and test derivatives
In this study, we systematically synthesized tetracyclic and heterocyclic pharmacophores by introducing a series of side chains linked to the 9-chloro-11H-indeno[1,2-c]quinolin-11-one moiety. The synthesis of 3,6-bis(1-methyl-4-vinylpyridinium)carbazole diiodide (BMVC) has been described previously [61]. General chemicals used in this study were purchased from (Sigma-Aldrich). Cell lines (human lung cancer H1299; human breast cancer MCF7; human liver cancer Hep3B 2.17) were obtained from the Bioresource Collection and Research Center in Taiwan. All reactions were monitored by TLC (silica gel 60 F254). 1H NMR and 13C NMR were measured on Varian GEMINI-300 (300 MHz) or Agilent 400 MR DD2 (400 MHz); δ values are in ppm relative to TMS as an internal standard. Multiplicities are recorded as s (singlet), d (doublet), t (triplet), q (quartet), quin (quintuplet), dd (doublet of doublets), dt (triplet of doublets), td (doublet of triplets), m (multiplet), and br (broadened). Mass spectral analyses were conducted using high resolution electron impact ionization (HREI, Finnigan MAT MAT-95XL) in the Instrumentation Center of National Tsing-Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan. Melting points of synthetic compounds were determined with a Büchi B-545 melting point apparatus. The purity of all compounds was analyzed on a C18 reverse-phase column (XBridge BEH Shield RP18 Column, 130Å, 5 μm, 4.6 mm X 250 mm, Waters) by HPLC (model L-2000, HITACHI) with UV detection (model L-2400, HITACHI). Compound was dissolved in MeOH; the mobile phase was water and MeOH. A preliminary evaluation of the UV spectra was carried out by spectrophotometric analysis to determine the value of λmax for each compound. The purities of the synthetic compounds for biological evaluation were greater than 95%. Reagents and solvents were purchased from Merck and Sigma Aldrich and used without further purification. Typical experiments illustrating the general procedures for the preparation of the compounds are described below.
Cell-based assay for monitoring WNT1 expression
The WNT1 promoter ranging from −600 to 201 relative to the transcription starting site was PCR-amplified from H1299 genomic DNA and cloned upstream to a secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) reporter gene to generate pWNT1-SEAP [19]. This DNA fragment contains the G-quadruplex forming sequences and the cis-regulatory elements of WNT1 transcription. To construct a mutant that fails to form G-quadruplex structure, plasmid pWNT1-SEAP was used as the template for mutagenesis using Pfu DNA polymerase (Stratagene). The resulting mutations were verified by DNA sequencing of the plasmids. These plasmids were introduced into cancer cell line H1299 and the stable cell lines harboring these plasmids were then isolated. Compared to their parental H1299 cell, no apparent change in the morphology or growth rate was observed in these stable lines.
SEAP assay [62]
Secreted alkaline phosphatase was used as the reporter gene to monitor the transcriptional activity of WNT1. About 2 × 104 each of cells were grown in 96-well plates and incubated at 37°C for 24 h and then changed with fresh media. Indicated amounts of drugs were added and then incubated for another 24 h. The culture media were collected and heated at 65°C for 10 min to inactivate heat-labile phosphatases. To assay phosphatase activity. an equal amount of SEAP buffer (2 M diethanolamine, 1 mM MgCl2, and 20 mM L-homoarginine) was added to the media, and p-nitrophenylphosphate was added to a final concentration of 12 mM. Absorptions at 405 nm were taken (BECKMAN BIOMEK 3000), and the rate of absorption increase was determined.
MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay
Cells were first grown in 96-well plates (∼2000 cells per well) in the presence of 5% CO2 at 37°C. To examine the cytotoxic effect of the tested compounds, cells were incubated with different concentrations of compounds for 24 h. The cytotoxicity was then determined by adding MTT solution to cells to a final concentration of 0.45 mg/ml and incubated at 37°C for 1 hour. The resulting formazan crystals was dissolved and analysed spectrophotometrically at the absorbance of 570 nm.
DNA preparation
All oligonucleotides were purchased from Bio Basic (Ontario, Canada) and used without further purification. DNA samples were prepared by dissolving oligonucleotides in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5). DNA concentrations were determined using a UV-visible absorption nanophotometer (Implen). KCl at 5 mM was added to the DNA samples 70 min before experiments. For SJ26 treatments, the DNA samples were incubated with SJ26 for 30 min before experiments.
Circular dichroism (CD) spectra and melting temperature
The CD spectra were recorded using a spectropolarimeter (J-815, Jasco, Japan) with a bandwidth of 2 nm at a scan speed of 50 nm/min and a step resolution of 0.2 nm under N2 over the spectral range of 210–350 nm to monitor the G4 structures. Thermal melting curves were recorded by a Peltier thermal coupler chamber (PFD-425S/15, Jasco) and the molar ellipticity was monitored at 265 nm between 10 and 100°C with a temperature ramping rate of 1°C/min rate. The melting temperature (Tm) was measured from the first differential of the melting curve.
Quantification of WNT1 RNA
The real-time quantitative RT-PCR was also used to determine the mRNA of WNT1. Cells were treated with SJ26 for 1 day and then subjected to RT-PCR analysis. Total RNA was isolated using TRIzol reagent (Sigma) and reverse-transcribed by random hexamers using cDNA reverse transcription kit (Applied Biosystem). The reverse-transcribed products were then analyzed using Cyber Green I system (FastStart Universal SYBR Green Master, Roche Applied Science). Primers used for PCR reactions were: WNT1 (forward primer 5′-CTGTCCTGCCTCCTCATC-3′ and reverse primer 5′-GGACCCAGCACAATAAATAGTT-3′); GAPDH (forward primer 5′-TAACTCTGGTAAAGTGGATA-3′ and reverse primer 5′-AAGATGGTGATGGGATTT-3′). The parameter Ct is defined as the fractional cycle number at which the fluorescence is generated by the Cyber green I system. Quantifications were first determined by normalizing the Ct values of the tested mRNA with the Ct of GAPDH. The relative values were then obtained using no drug treatment as 100%. Quantification results were obtained from three independent experiments.
Immunoblotting analysis
The SJ26-treated H1299 cells were washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and lysed using radioimmune precipitation assay buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 1% Triton X-100, 100 μM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 1 mg/ml leupeptin, 1 mg/ml aprotinin, and 25 mM dithiothreitol). Equal amount of total proteins were separated on SDS-PAGE gels and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. Antibodies against Wnt1 (1:1000 dilution, Spring, REF E3960), β-catenin (1:1000 dilution, GeneTex, GTX61089), and α-tubulin (1:5000 dilution, Millipore, MAB374) were used as the primary antibodies. Horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse IgG or anti-rabbit IgG (Amersham Biosciences) were used as the secondary antibodies. Blots were visualized using enhanced chemiluminescence system (PerkinElmer Life Sciences).
Scratch assay
Cells were treated with compound SJ26 for 1 day and subjected to scratch assay. The drug treated cells were plated and scratched with a pipette tip to generate a cell-free zone. Cells were then incubated at 1% serum culture medium to avoid further cell proliferation. Migration of cells toward the cell-free zone was monitored after 24 h using a Leica DFC 420c camera (Leica Microsystems), and the migration rates were determined. The relative healing activities were obtained using the value of solvent control as 100%.
Trans-well assay
About 2 x105 of the drug-treated cells were grown in the inner chamber of Millicell Hanging Cell Culture Insert (pore size 8.0 μm, Merck Millipore) in a serum-free medium and with 10% serum medium in the outer chamber. The cells were incubated at 37°C for 6 h to allow the migration toward the outer side of the inner chamber. Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 2 min, and then permeabilized with methanol for 20 min. The cells on the inner layer were softly removed with a cotton swab, and the adherent cells on outer surface were stained with 0.3% crystal violet dye for 15 min and then counted. The relative migration activities were obtained using the value of solvent control as 100%.
Statistical analysis
Student's t-test was applied to assess whether the means of two groups are statistically different from each other. Here, we consider P < 0.05 as significant.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Fong-Chun Huang for his kind support on establishing the assay system. We also thank the Biophysical Instrumentation Laboratory at the Institute of Biological Chemistry, Academia Sinica, Taiwan for assistance in CD analysis. The present study was also supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology and Taipei Medical University grants (NSC 101-2113-M-016-001, TMU102-AE1-B32 and TMUTOP-103003 to H.S. Huang and NSC 101-2311-B-002-020-MY3 to J.J. Lin.)
Abbreviations
- WNT1
wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 1
- CD
circular dichroism
- Tm
melting temperature
- SEAP
secreted alkaline phosphatase
- SARs
structure-activity relationships
- CPT
Camptothecin
- Topo
topoisomerase
- BMVC
3,6-bis(1-methyl-4-vinylpyridinium)carbazole diiodide
- CD
circular dichroism
- H1299
human non-small cell lung carcinoma cell
- HRMS
high resolution mass
- PBS
phosphate-buffered saline
- DMSO
dimethyl sulfoxide
- THF
tetrahydrofuran
- TEA
triethylamine.
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Author contributions
Lien-Cheng Chang established the biological assay system and conducted the analyses; Tsung-Chih Chen, Chun-Liang Chen, Shiag-Jiun Chen, Chia-Chung Lee, synthesized and characterized the compounds used in this study; Shih-Hsiung Wu, Yun Yen, Jing-Jer Lin, and Hsu-Shan Huang designed the research, analyzed results and writing the manuscript. These authors contributed equally to this work.
REFERENCES
- 1.Wan L, Pantel K, Kang Y. Tumor metastasis: moving new biological insights into the clinic. Nature Med. 2013;19:1450–1464. doi: 10.1038/nm.3391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Clevers H, Nusse R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell. 2012;149:1192–1205. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wong SCC, Lo SFE, Lee KC, Yam JWP, Chan JKC, Hsiao WLW. Expression of frizzled-related protein and Wnt-signalling molecules in invasive human breast tumours. J Pathol. 2002;196:145–153. doi: 10.1002/path.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kim YC, Clark RJ, Ranheim EA, Alexander CM. Wnt1 expression induces short-range and long-range cell recruitments that modify mammary tumor development and are not induced by a cell-autonomous beta-catenin effector. Cancer Res. 2008;68:10145–10153. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tao W, Pennica D, Xu L, Kalejta RF, Levine AJ. Wrch-1, a novel member of the Rho gene family that is regulated by Wnt-1. Genes Dev. 2001;15:1796–1807. doi: 10.1101/gad.894301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.He W, Tan RJ, Li Y, Wang D, Nie J, Hou FF, Liu Y. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 as a surrogate marker predicts renal Wnt/β-catenin activity in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23:294–304. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011050490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Xu X, Sun PL, Li JZ, Jheon S, Lee CT, Chung JH. Aberrant Wnt1/β-catenin expression is an independent poor prognostic marker of non-small cell lung cancer after surgery. J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6:716–724. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31820c5189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chen G, Shukeir N, Potti A, Sircar K, Aprikian A, Goltzman D, Rabbani SA. Up-regulation of Wnt1 and β-catenin production in patients with advanced metastatic prostate carcinoma: potential pathogenetic and prognostic implications. Cancer. 2004;101:1345–1356. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nakashima T, Liu D, Nakano J, Ishikawa S, Yokomise H, Ueno M, Kadota K, Huang CL. Wnt1 overexpression associated with tumor proliferation and a poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Oncol Rep. 2008;19:203–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Polakis P. Drugging Wnt signalling in cancer. EMBO J. 2012;31:2737–2746. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Anastas JN, Moon RT. WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:11–26. doi: 10.1038/nrc3419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lepourcelet M, Chen Y-NP, France DS, Wang H, Crews P, Petersen F, Bruseo C, Wood AW, Shivdasani RA. Small-molecule antagonists of the oncogenic Tcf/β-catenin protein complex. Cancer Cell. 2004;5:91–102. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen B, Dodge ME, Tang W, Lu J, Ma Z, Fan C-W, Wei S, Hao W, Kilgore J, Williams NS, Roth MG, Amatruda JF, Chen C, Lum L. Small molecule-mediated disruption of Wnt-dependent signaling in tissue regeneration and cancer. Nat Chem Biol. 2009;5:100–107. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ewan K, Pajak B, Stubbs M, Todd H, Barbeau O, Quevedo C, Botfield H, Young R, Ruddle R, Samuel L, Battersby A, Raynaud F, Allen N, Wilson S, Latinkic B, Workman P, et al. A useful approach to identify novel small-molecule inhibitors of Wnt-dependent transcription. Cancer Res. 2010;70:5963–5973. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sack U, Walther W, Scudiero D, Selby M, Aumann J, Lemos C, Fichtner I, Schlag PM, Shoemaker RH, Stein U. S100A4-induced cell motility and metastasis is restricted by the Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibitor calcimycin in colon cancer cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2011;22:3344–3354. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-09-0739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Huang SM, Mishina YM, Liu S, Cheung A, Stegmeier F, Michaud GA, Charlat O, Wiellette E, Zhang Y, Wiessner S, Hild M, Shi X, Wilson CJ, Mickanin C, Myer V, Fazal A, et al. Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt signalling. Nature. 2009;461:614–620. doi: 10.1038/nature08356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wei W, Chua MS, Grepper S, So SK. Blockade of Wnt-1 signaling leads to anti-tumor effects in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer. 2009;8:76. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-8-76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.He B, Reguart N, You L, Mazieres J, Xu Z, Lee AY, Mikami I, McCormick F, Jablons DM. Blockade of Wnt-1 signaling induces apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells containing downstream mutations. Oncogene. 2005;24:3054–3058. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wang J-M, Huang F-C, Kuo MH-J, Wang Z-F, Tseng T-Y, Chang L-C, Yen S-J, Chang T-C, Lin J-J. Inhibition of cancer cell migration and invasion through suppressing the Wnt1-mediating signal pathway by G-quadruplex structure stabilizers. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:14612–14623. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.548230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kuo MH-J, Wang Z-F, Tseng T-Y, Li M-H, Hsu S-TD, Lin J-J, Chang T-C. The conformational transition of a hairpin structure to G-quadruplex within the WNT1 gene promoter. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137:210–218. doi: 10.1021/ja5089327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sun D, Thompson B, Cathers BE, Salazar M, Kerwin SM, Trent JO, Jenkins TC, Neidle S, Hurley LH. Inhibition of human telomerase by a G-quadruple-interactive compound. J Med Chem. 1997;40:2113–2128. doi: 10.1021/jm970199z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Huang H-S, Chou C-L, Guo C-L, Yuan C-L, Lu Y-C, Shieh F-Y, Lin J-J. Human telomerase inhibition and cytotoxicity of regioisomeric disubstituted amidoanthraquinones and aminoanthraquinones. Bioorg Med Chem. 2005;13:1435–1444. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2004.12.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Huang H-S, Chen I-B, Chen T-C, Huang K-F, Lu W-C, Shieh F-Y, Huang Y-Y, Huang F-C, Lin J-J. Synthesis and human telomerase inhibition of a series of regioisomeric disubstituted amidoanthraquinones. Chem Pharm Bull. 2007;55:284–292. doi: 10.1248/cpb.55.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Huang H-S, Huang K-F, Li C-L, Huang Y-Y, Chiang Y-H, Huang F-C, Lin J-J. Synthesis, human telomerase inhibition and anti-proliferative studies of a series of 2,7-bis-substituted amido-anthraquinone derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008;16:6976–6986. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.05.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Huang H-S, Chen T-C, Chen R-H, Huang K-F, Huang F-C, Jhan J-R, Chen C-L, Lee C-C, Lo Y, Lin J-J. Synthesis, cytotoxicity and human telomerase inhibition activities of a series of 1,2-heteroannelated anthraquinones and anthra[1,2-d]imidazole-6,11-dione homologues. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009;17:7418–7428. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.09.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lee C-C, Huang K-F, Lin P-Y, Huang F-C, Chen C-L, Chen T-C, Guh J-H, Lin J-J, Huang H-S. Synthesis, antiproliferative activities and telomerase inhibition evaluation of novel asymmetrical 1,2-disubstituted amidoanthraquinone derivatives. Eur J Med Chem. 2012;47:323–336. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.10.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lee C-C, Hsu J-J, Huang F-C, Shih K-N, Huang K-F, Chen C-L, Chen T-C, Chen R-H, Lin J-J, Huang H-S. Design, synthesis and evaluation of telomerase inhibitory, hTERT repressing, and anti-proliferation activities of symmetrical 1,8-disubstituted amidoanthraquinones. Eur J Med Chem. 2012;50:102–112. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.01.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Perry PJ, Read MA, Davies RT, Gowan SM, Reszka AP, Wood AA, Kelland LR, Neidle S. 2,7-disubstituted amidofluorenone derivatives as inhibitors of human telomerase. J Med Chem. 1999;42:2679–2684. doi: 10.1021/jm990084q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Perry PJ, Gowan SM, Reszka AP, Polucci P, Jenkins TC, Kelland LR, Neidle S. 1,4- and 2,6-disubstituted amidoanthracene-9,10-dione derivatives as inhibitors of human telomerase. J Med Chem. 1998;41:3253–3260. doi: 10.1021/jm9801105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Perry PJ, Reszka AP, Wood AA, Read MA, Gowan SM, Dosanjh HS, Trent JO, Jenkins TC, Kelland LR, Neidle S. Human telomerase inhibition by regioisomeric disubstituted amidoanthracene-9,10-diones. J Med Chem. 1998;41:4873–4884. doi: 10.1021/jm981067o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zagotto G, Sissi C, Lucatello L, Pivetta C, Cadamuro SA, Fox KR, Neidle S, Palumbo M. Aminoacyl-anthraquinone conjugates as telomerase inhibitors: synthesis, biophysical and biological evaluation. J Med Chem. 2008;51:5566–5574. doi: 10.1021/jm800160v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cairns D, Michalitsi E, Jenkins TC, Mackay SP. Molecular modeling and cytotoxicity of substituted anthraquinones as inhibitors of human telomerase. Bioorg Med Chem. 2002;10:803–807. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(01)00337-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Read MA, Wood AA, Harrison JR, Gowan SM, Kelland LR, Dosanjh HS, Neidle S. Molecular modeling studies on G-quadruplex complexes of telomerase inhibitors: structure-activity relationships. J Med Chem. 1999;42:4538–4546. doi: 10.1021/jm990287e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Aoyagi Y, Kobunai T, Utsugi T, Wierzba K, Yamada Y. Establishment and characterization of 6-[[2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl]amino]-3-hydroxy-7H-indeno[2,1-c]quinolin-7-one dihydrochloride (TAS-103)-resistant cell lines. Japanese journal of cancer research: Gann. 2000;91:543–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2000.tb00979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yoshida M, Kabe Y, Wada T, Asai A, Handa H. A new mechanism of 6-((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)amino)-3-hydroxy-7H-indeno(2,1-c)quinolin-7-one dihydrochloride (TAS-103) action discovered by target screening with drug-immobilized affinity beads. Molecular pharmacology. 2008;73:987–994. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.043307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Fujimoto S. Promising antitumor activity of a novel quinoline derivative, TAS-103, against fresh clinical specimens of eight types of tumors measured by flow cytometric DNA analysis. Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin. 2007;30:1923–1929. doi: 10.1248/bpb.30.1923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Shah A, Diculescu VC, Qureshi R, Oliveira-Brett AM. Electrochemical reduction mechanism of camptothecin at glassy carbon electrode. Bioelectrochemistry. 2010;79:173–178. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2010.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kehrer DF, Soepenberg O, Loos WJ, Verweij J, Sparreboom A. Modulation of camptothecin analogs in the treatment of cancer: a review. Anti-cancer drugs. 2001;12:89–105. doi: 10.1097/00001813-200102000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Alagoz M, Gilbert DC, El-Khamisy S, Chalmers AJ. DNA repair and resistance to topoisomerase I inhibitors: mechanisms, biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Current medicinal chemistry. 2012;19:3874–3885. doi: 10.2174/092986712802002590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Aoyagi Y, Kobunai T, Utsugi T, Wierzba K, Yamada Y. Establishment and characterization of 6-[[2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl]amino]-3-hydroxy-7H-indeno[2,1-c] quinolin-7-one dihydrochloride (TAS-103)-resistant cell lines. Jpn J Cancer Res. 2000;91:543–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2000.tb00979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Yoshida M, Kabe Y, Wada T, Asai A, Handa H. A new mechanism of 6-((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)amino)-3-hydroxy-7H-indeno(2,1-c)quinolin-7-one dihydrochloride (TAS-103) action discovered by target screening with drug-immobilized affinity beads. Mol Pharmacol. 2008;73:987–994. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.043307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nusse R, Theunissen H, Wagenaar E, Rijsewijk F, Gennissen A, Otte A, Schuuring E, van Ooyen A. The Wnt1 (int-1) oncogene promoter and its mechanism of activation by insertion of proviral DNA of the mouse mammary tumor virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10:4170–4179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.St-Arnaud R, Moir JM. Wnt1-inducing factor-1: a novel G/C box-binding transcription factor regulating the expression of Wnt1 during neuroectodermal differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993;13:1590–1598. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kim S-J, Crooks H, Foxworth A, Waldman T. Proof-of-principle: Oncogenic β-catenin is a valid molecular target for the development of pharmacological inhibitors. Mol Cancer Ther. 2002;1:1355–1359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Akiri G, Cherian MM, Vijayakumar S, Liu G, Bafico A, Aaronson SA. Wnt pathway abberations including autocrine Wnt activation occur at high frequency in human non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Oncogene. 2009;28:2163–2172. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Takahashi-Yanaga F, Kahn M. Targeting Wnt signalling: Can we safely eradicate cancer stem cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:3153–3162. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Luu HH, Zhang R, Haydon RC, Rayburn E, Kang Q, Si W, Park JK, Wang H, Peng Y, Jiang W, He T-C. Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway as novel cancer drug targets. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2004;4:653–671. doi: 10.2174/1568009043332709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Barker N, Clevers H. Mining the Wnt pathway for cancer therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:997–1014. doi: 10.1038/nrd2154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kahn M. Can we safely target the WNT pathway? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13:513–532. doi: 10.1038/nrd4233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Emami KH, Nguyen C, Ma H, Kim DH, Jeong KW, Eguchi M, Moon RT, Teo JL, Kim HY, Moon SH, Ha JR, Kahn M. A small molecule inhibitor of beta-catenin/CREB-binding protein transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:12682–12687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0404875101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Shultz MD, Cheung AK, Kirby CA, Firestone B, Fan J, Chen CH, Chen Z, Chin DN, Dipietro L, Fazal A, Feng Y, Fortin PD, Gould T, Lagu B, Lei H, Lenoir F, et al. Identification of NVP-TNKS656: The use of structure-efficiency relationships to generate a highly potent, selective, and orally active tankyrase inhibitor. J Med Chem. 2013;56:6495–6511. doi: 10.1021/jm400807n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lau T, Chan E, Callow M, Waaler J, Boggs J, Blake RA, Magnuson S, Sambrone A, Schutten M, Firestein R, Machon O, Korinek V, Choo E, Diaz D, Merchant M, Polakis P, et al. A novel tankyrase small-molecule inhibitor suppresses APC mutation-driven colorectal tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2013;73:3132–3144. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hua Z, Bregman H, Buchanan JL, Chakka N, Guzman-Perez A, Gunaydin H, Huang X, Gu Y, Berry V, Liu J, Teffera Y, Huang L, Egge B, Emkey R, Mullady EL, Schneider S, et al. Development of novel dual binders as potent, selective, and orally bioavailable tankyrase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2013;56:10003–10015. doi: 10.1021/jm401317z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hufford CD, Liu S, Clark AM, Oguntimein BO. Anticandidal activity of eupolauridine and onychine, alkaloids from Cleistopholis patens. J Nat Prod. 1987;50:961–964. doi: 10.1021/np50053a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Prachayasittikul S, Manam P, Chinworrungsee M, Isarankura-Na-Ayudhya C, Ruchirawat S, Prachayasittikul V. Bioactive azafluorenone alkaloids from Polyalthia debilis (Pierre) Finet & Gagnep. Molecules. 2009;14:4414–4424. doi: 10.3390/molecules14114414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Mueller D, Davis RA, Duffy S, Avery VM, Camp D, Quinn RJ. Antimalarial activity of azafluorenone alkaloids from the Australian tree Mitrephora diversifolia. J Nat Prod. 2009;72:1538–1540. doi: 10.1021/np900247f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Manpadi M, Uglinskii PY, Rastogi SK, Cotter KM, Wong YS, Anderson LA, Ortega AJ, Van Slambrouck S, Steelant WF, Rogelj S, Tongwa P, Antipin MY, Magedov IV, Kornienko A. Three-component synthesis and anticancer evaluation of polycyclic indenopyridines lead to the discovery of a novel indenoheterocycle with potent apoptosis inducing properties. Org Biomol Chem. 2007;5:3865–3872. doi: 10.1039/b713820b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Pumsalid K, Thaisuchat H, Loetchutinat C, Nuntasaen N, Meepowpan P, Pompimon W. A new azafluorenone from the roots of Polyalthia cerasoides and its biological activity. Nat Prod Commun. 2010;5:1931–1934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Banjerdpongchai R, Khaw-On P, Ristee C, Pompimon W. 6,8-dihydroxy-7-methoxy-1-methyl-azafluorenone induces caspase-8- and -9-mediated apoptosis in human cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14:2637–2641. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.4.2637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Shook BC, Rassnick S, Osborne MC, Davis S, Westover L, Boulet J, Hall D, Rupert KC, Heintzelman GR, Hansen K, Chakravarty D, Bullington JL, Russell R, Branum S, Wells KM, Damon S, et al. In vivo characterization of a dual adenosine A2A/A1 receptor antagonist in animal models of Parkinson's disease. J Med Chem. 2010;53:8104–8115. doi: 10.1021/jm100971t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Chang C-C, Wu J-Y, Chang T-C. A carbazole derivative synthesis for stabilizing the quadruplex structure. J Chin Chem Soc. 2003;50:185–188. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Cullen BR, Malim MH. Secreted placental alkaline phosphatase as a eukaryotic reporter gene. Methods Enzymol. 1992;216:362–368. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)16033-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


