Abstract
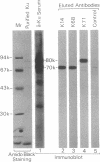
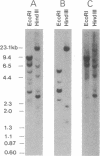
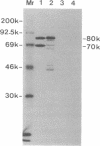
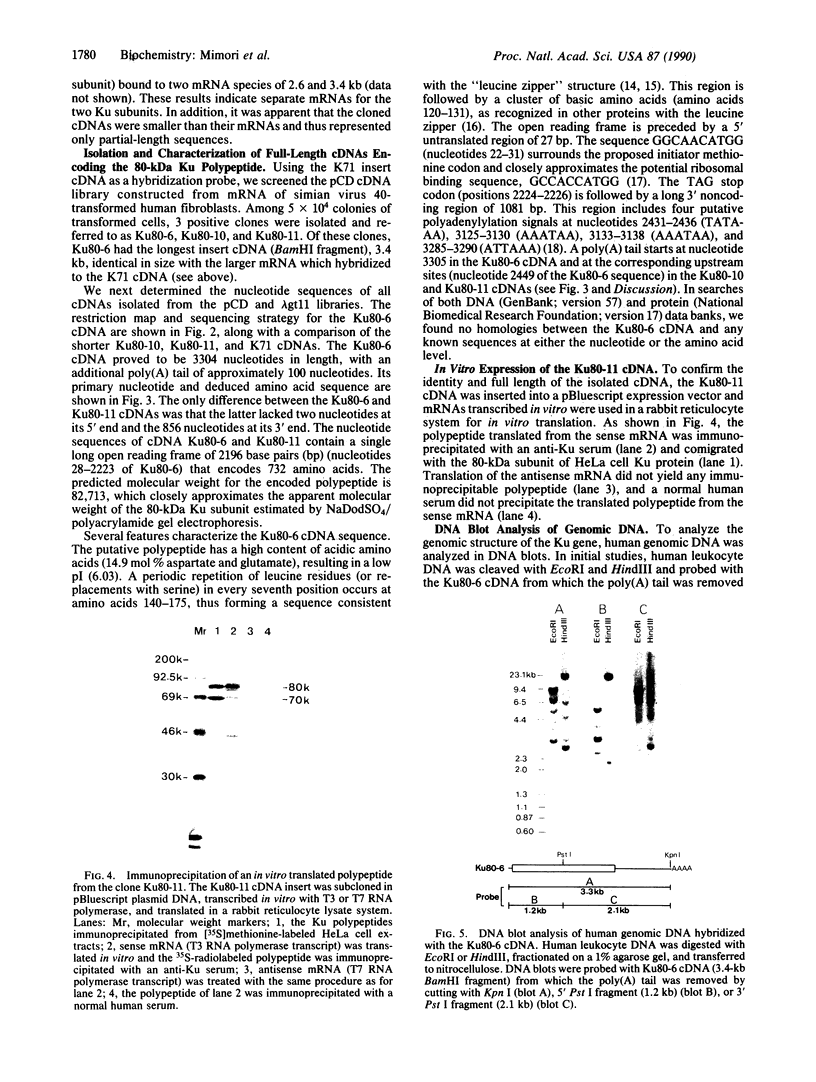
Anti-Ku (p70/p80) autoantibodies in patients with scleroderma-polymyositis overlap syndrome recognize a 70-kDa/80-kDa protein heterodimer which binds to terminal regions of double-stranded DNA. In the present study, we isolated full-length cDNAs that encode the 80-kDa Ku subunit. Initial screening of a human spleen cDNA library with anti-Ku antibodies yielded a cDNA of 1.0 kilobase (kb) (termed K71) encoding a portion of the 80-kDa Ku polypeptide (identification based on immunological criteria). In RNA blots, this cDNA hybridized with two mRNAs of 3.4 and 2.6 kb. In rescreening of a cDNA library constructed from simian virus 40-transformed human fibroblast mRNA with the K71 cDNA as a hybridization probe, three positive clones were isolated, and that bearing the longest insert (termed Ku80-6) was selected for further characterization. In vitro transcription and translation experiments produced an immunoprecipitable polypeptide which comigrated with the 80-kDa Ku subunit. The Ku80-6 cDNA proved to be 3304 nucleotides in length, with an additional poly(A) tail, closely approximating the size of the larger mRNA. It contains a single long open reading frame encoding 732 amino acids (Mr = 82,713). The putative polypeptide has a high content of acidic amino acids and a region with periodic repeat of leucine in every seventh position which may form the "leucine zipper" structure. In genomic DNA blots, probes derived from the opposite ends of cDNA Ku80-6 hybridized with several nonoverlapping restriction fragments from human leukocyte DNA, indicating that the gene encoding the 80-kDa Ku polypeptide is divided into several exons by intervening sequences.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francoeur A. M., Peebles C. L., Gompper P. T., Tan E. M. Identification of Ki (Ku, p70/p80) autoantigens and analysis of anti-Ki autoantibody reactivity. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1648–1653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimori T., Akizuki M., Yamagata H., Inada S., Yoshida S., Homma M. Characterization of a high molecular weight acidic nuclear protein recognized by autoantibodies in sera from patients with polymyositis-scleroderma overlap. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):611–620. doi: 10.1172/JCI110295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimori T., Hardin J. A. Mechanism of interaction between Ku protein and DNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10375–10379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimori T., Hardin J. A., Steitz J. A. Characterization of the DNA-binding protein antigen Ku recognized by autoantibodies from patients with rheumatic disorders. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2274–2278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. H., Sthoeger Z. M. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding the p70 (Ku) lupus autoantigen. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5047–5052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. H. Use of monoclonal antibodies for the characterization of novel DNA-binding proteins recognized by human autoimmune sera. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):18–39. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaneva M., Busch H. A 10S particle released from deoxyribonuclease-sensitive regions of HeLa cell nuclei contains the 86-kilodalton-70-kilodalton protein complex. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5057–5063. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaneva M., Wen J., Ayala A., Cook R. cDNA-derived amino acid sequence of the 86-kDa subunit of the Ku antigen. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13407–13411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]