Abstract
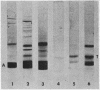
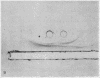
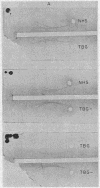
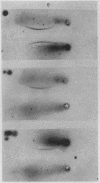
A method for obtaining highly purified thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) from whole human serum is presented. The method employs relatively simple procedures of step-wise ammonium sulfate precipitation followed by column chromatography on DEAE cellulose and DEAE Sephadex. The final product produces a single protein band on disc electrophoresis. The sedimentation constant of the TBG thus purified is 3.91 and its calculated mol wt is 54,000. An antiserum to the highly purified TBG produced a single arc on immunoelectrophoresis. When the antiserum was reacted against normal human serum or against serum from subjects deficient in TBG, each produced two arcs—one identical with that produced by the antigen alone. The second arc is probably the result of a contaminating protein in the antigen, present in too low a concentration to be detectable by disc gel electrophoresis. It is concluded that some persons with TBG “deficiency” have a circulating protein, immunologically indistinguishable from TBG, which is defective in its ability to bind thyroxine.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOMAN H. G., WESTLUNG L. E. Protein chromatography on an anion-exchange resin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Sep;64(1):217–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90255-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgio N. A., Jr, Tabachnick M. Thyroxine-protein interactions. V. Isolation and characterization of a thyroxine-binding globulin from human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2247–2259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCHFELD J. Individual precipitation patterns of normal rabbit sera. A preliminary report. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1959;46:229–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1959.tb00334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H., FREINKEL N. Regulation of the peripheral metabolism of the thyroid hormones. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1960;16:353–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingbar S. H., Braverman L. E., Dawber N. A., Lee G. Y. A new method for measuring the free thyroid hormone in human serum and an analysis of the factors that influence its concentration. J Clin Invest. 1965 Oct;44(10):1679–1689. doi: 10.1172/JCI105275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. S., Levy R. P., Steinberg A. G. Human thyroxine-binding globulin deficiency. A genetic study. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jun 30;274(26):1469–1473. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196606302742604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. S., Tompkins L. S. Effect of o,p'-DDD and similar compounds on thyroxine binding globulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Mar;28(3):386–392. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-3-386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolai T. F., Seal U. S. X-chromosome linked inheritance of thyroxine-binding globulin deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Nov;27(11):1515–1520. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-11-1515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPENHEIMER J. H., SQUEF R., SURKS M. I., HAUER H. BINDING OF THYROXINE BY SERUM PROTEINS EVALUATED BY EQUILIBRUM DIALYSIS AND ELECTROPHORETIC TECHNIQUES. ALTERATIONS IN NONTHYROIDAL ILLNESS. J Clin Invest. 1963 Nov;42:1769–1782. doi: 10.1172/JCI104862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENSKY J., LEVY L. R., LEPOW I. H. Partial purification of a serum inhibitor of C'1-esterase. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jun;236:1674–1679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J., RALL J. E. The interaction of thyroid hormones and protein in biological fluids. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1957;13:161–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN F. S., PENSKY J., DONALDSON V., CHARACHE P. HEREDITARY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA: TWO GENETIC VARIANTS. Science. 1965 May 14;148(3672):957–958. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3672.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Brenner M. A. Free thyroxine in human serum: simplified measurement with the aid of magnesium precipitation. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):153–163. doi: 10.1172/JCI105320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TATA J. R. The purification of thyroxine-binding globulin and thyroxine-binding prealbumin. Clin Chim Acta. 1961 Nov;6:819–832. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(61)90171-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woeber K. A., Ingbar S. H. The contribution of thyroxine-binding prealbumin to the binding of thyroxine in human serum, as assessed by immunoadsorption. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jul;47(7):1710–1721. doi: 10.1172/JCI105861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]