Abstract
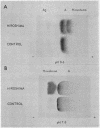
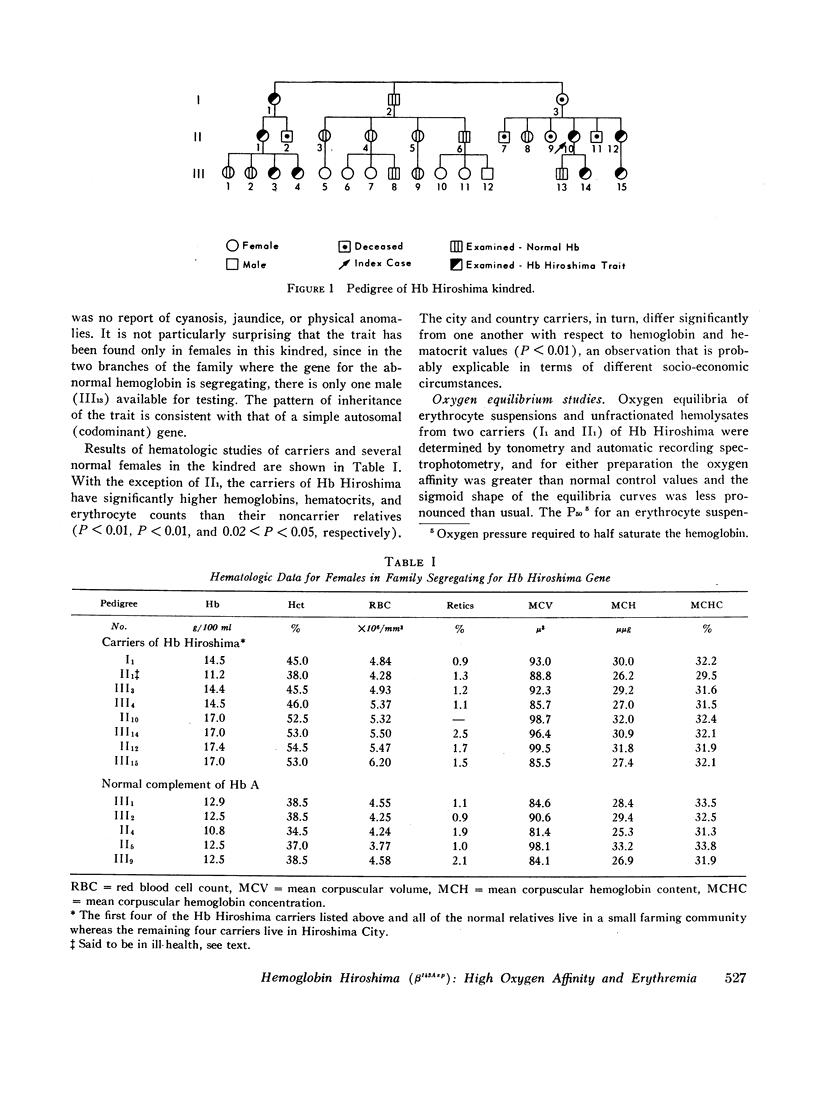
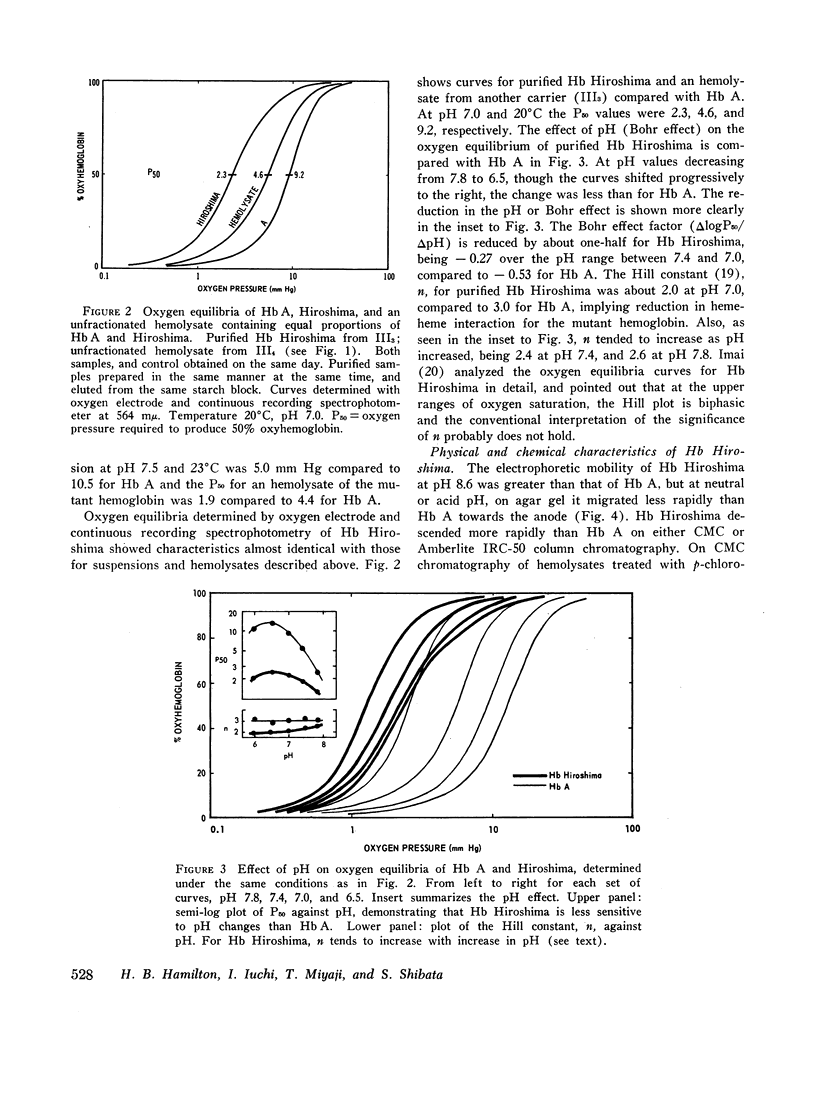
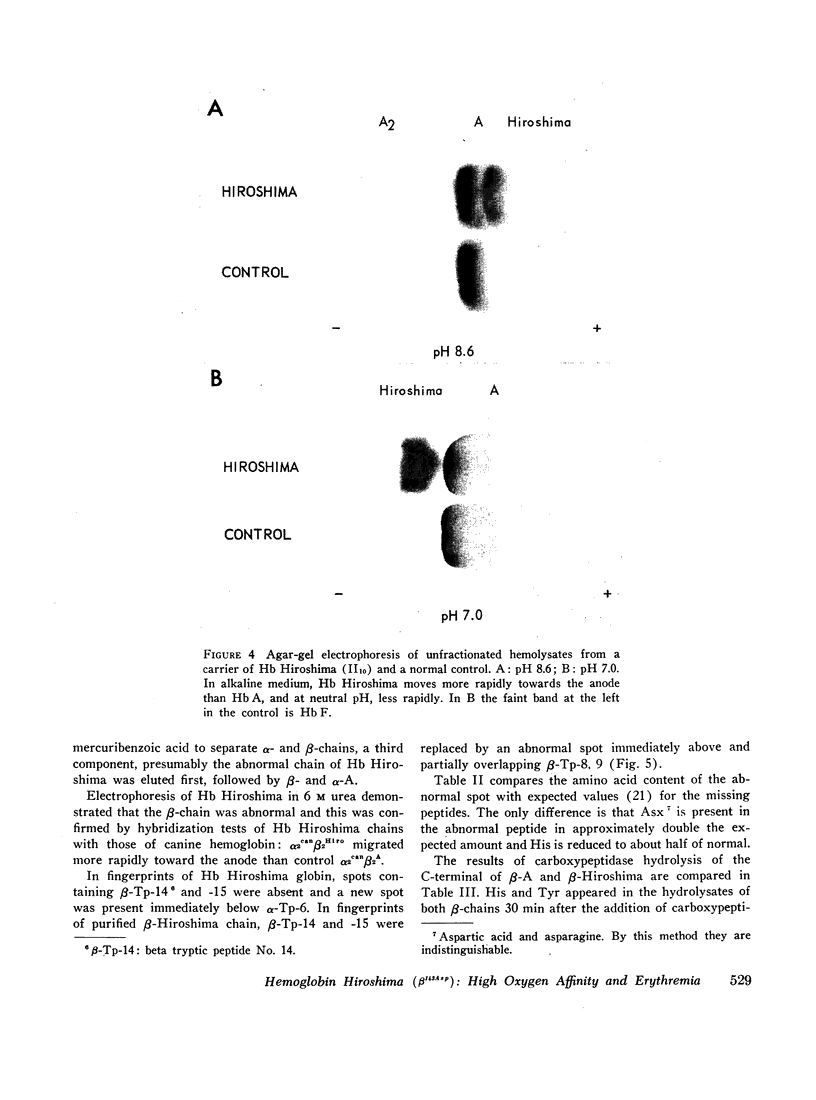
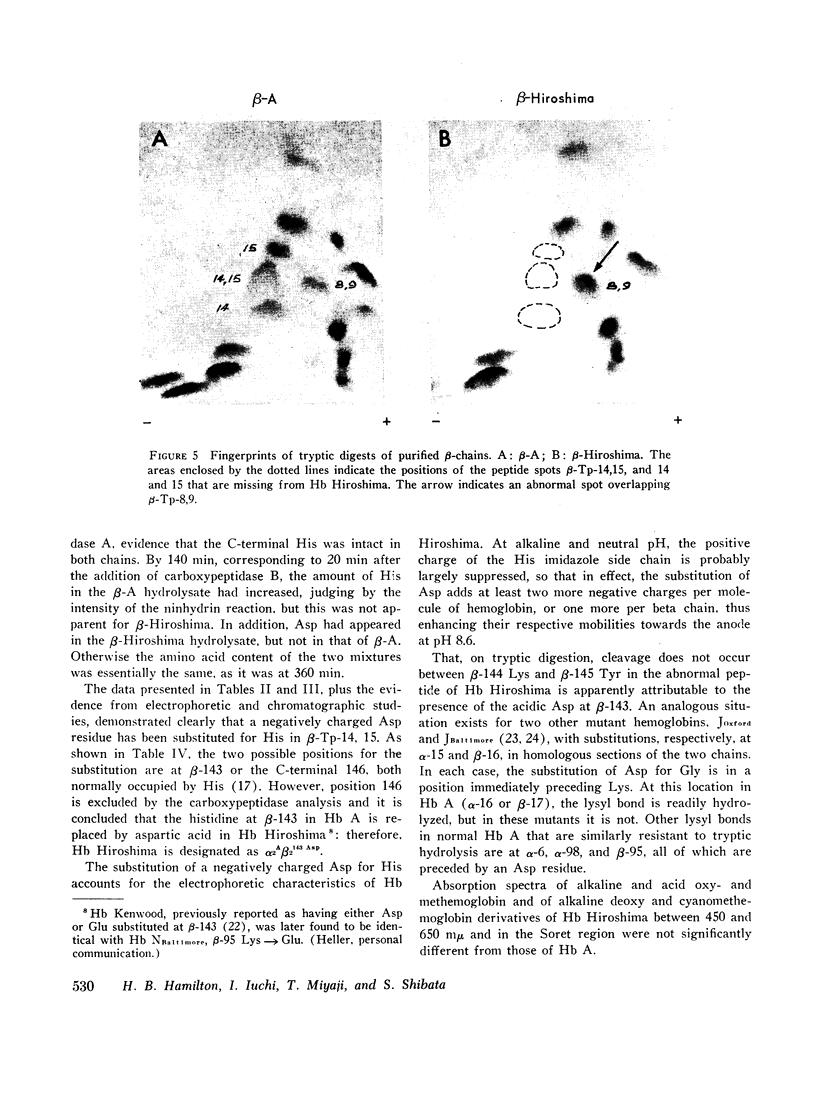
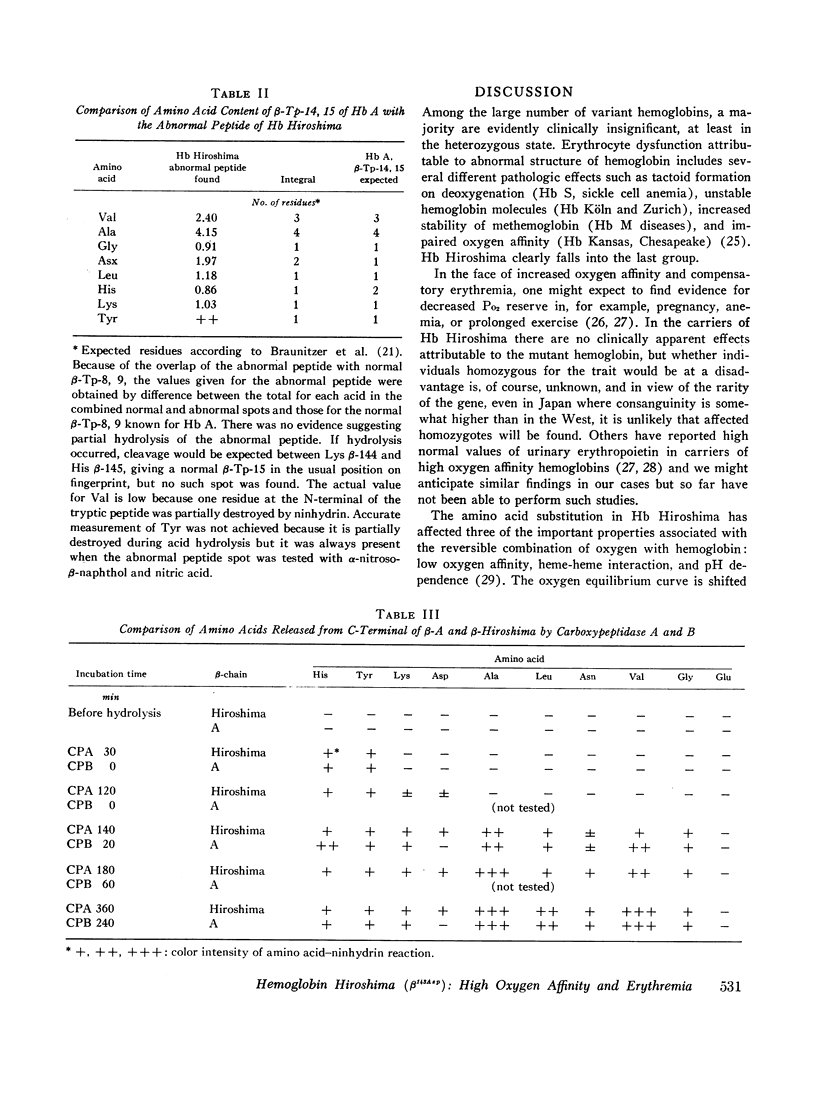
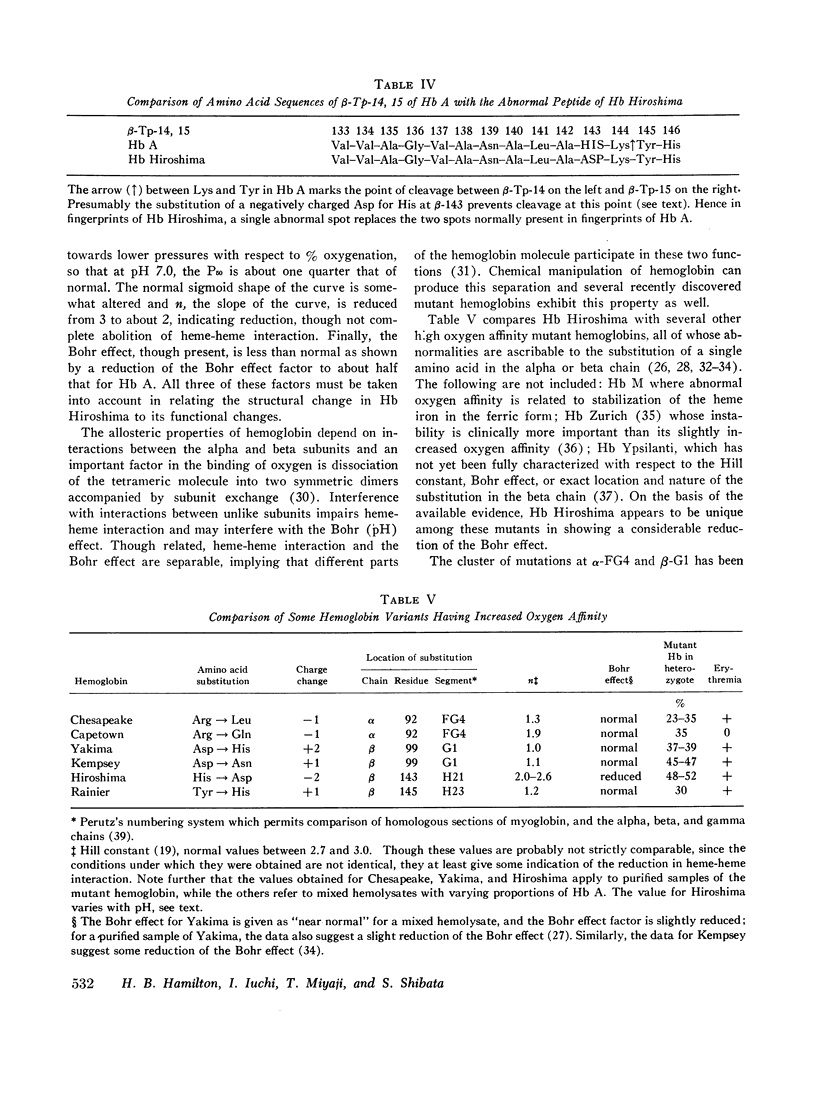
During a survey for hemoglobinopathies in over 9000 residents of Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan, a fast moving hemoglobin was identified in eight members of three generations in a Japanese family. The abnormal hemoglobin, named Hb Hiroshima, constitutes about 50% of the total hemoglobin in hemolysates from the carriers who have a mild erythremia but are otherwise apparently clinically unaffected. All preparations of Hb Hiroshima have increased affinity for oxygen, by either tonometric or oxygen electrode determinations. At pH 7.0, the oxygen pressure, P50 required to half saturate an unfractionated hemolysate from a carrier was one-half that of Hb A, and the P50 of a purified sample containing no Hb A was one-fourth that of Hb A. The pH dependence of the oxygen equilibrium (Bohr effect) is below normal, as shown by the absolute value of the Bohr effect factor which is about half that of Hb A, in the pH range between 7.0 and 7.4. The Hill constant, n, for Hb Hiroshima between pH 7.0 and 7.4 is 2-2.4, compared to 2.8-3 for Hb A under the same conditions, indicating reduction of, but not complete abolition of heme-heme interaction. Urea dissociation and canine hybridization tests located the biochemical lesion in the beta chain. Fingerprints (Ingram), carboxypeptidase digestion, and amino acid analysis demonstrated that the substitution was at residue 143 in the beta chain, where histidine was replaced by aspartic acid.
In contrast to other recently described high oxygen affinity mutants that show intact Bohr effects, all three of the major characteristics of the reversible combination of hemoglobin with oxygen (oxygen equilibrium, heme-heme interaction, and pH dependence) are affected in Hb Hiroshima. A tentative interpretation of these effects, relating structure to function, is offered in terms of recently developed models of normal hemoglobin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN D. W., GUTHE K. F., WYMAN J., Jr Further studies on the oxygen equilibrium of hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1950 Nov;187(1):393–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANTONINI E. INTERRELATIONSHIP BETWEEN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION IN HEMOGLOBIN AND MYOGLOBIN. Physiol Rev. 1965 Jan;45:123–170. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACHMANN F., MARTIHR Hemoglobin Zurich. II. Physicochemical properties of the abnormal hemoglobin. Blood. 1962 Sep;20:272–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAGLIONI C. An improved method for the fingerprinting of human hemoglobin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 1;48:392–396. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90490-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BETKE K., MARTI H. R., SCHLICHT I. Estimation of small percentages of foetal haemoglobin. Nature. 1959 Dec 12;184(Suppl 24):1877–1878. doi: 10.1038/1841877a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUNITZER G., GEHRING-MUELLER R., HILSCHMANN N., HILSE K., HOBOM G., RUDLOFF V., WITTMANN-LIEBOLD B. [The structure of normal adult human hemoglobins]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1961 Sep 20;325:283–286. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1961.325.1.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCCI E., FRONTICELLI C. A NEW METHOD FOR THE PREPARATION OF ALPHA AND BETA SUBUNITS OF HUMAN HEMOGLOBIN. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:PC551–PC552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benesch R., Benesch R. E., Tyuma I. Subunit exchange and ligand binding. II. The mechanism of the allosteric effect in hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1268–1274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benesch R., Benesch R. E., Yu C. I. Reciprocal binding of oxygen and diphosphoglycerate by human hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):526–532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSBY W. H., MUNN J. I., FURTH F. W. Standardizing a method for clinical hemoglobinometry. U S Armed Forces Med J. 1954 May;5(5):693–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charache S., Weatherall D. J., Clegg J. B. Polycythemia associated with a hemoglobinopathy. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jun;45(6):813–822. doi: 10.1172/JCI105397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley C. L., Charache S. Mechanisms by which some abnormal hemoglobins produce clinical manifestations. Semin Hematol. 1967 Jan;4(1):53–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUIDOTTI G. The action of carboxypeptidases A and B on the separated alpha and beta chains of normal adult human hemoglobin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jul 29;42:177–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90774-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai K. Oxygen-equilibrium characteristics of abnormal hemoglobin Hiroshima (alpha-2 beta-2 143 Asp). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Sep 20;127(1):543–547. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. T., Osgood E. E., Brimhall B., Koler R. D. Hemoglobin Yakina. I. Clinical and biochemical studies. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1840–1847. doi: 10.1172/JCI105674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIKUCHI G., HAYASHI N., TAMURA A. OXYGEN EQUILIBRIUM OF HEMOGLOBIN M-IWATE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 15;90:199–201. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90142-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyaji T., Oba Y., Yamamoto K., Shibata S., Iuchi I., Hamilton H. B. Hemoglobin Hijiyama: a new fast-moving hemoglobin in a Japanese family. Science. 1968 Jan 12;159(3811):204–206. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3811.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. M., Battaglia F. C., Hellegers A. E. Whole blood oxygen affinities of women with various hemoglobinopathies. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1967 Jan 1;97(1):63–66. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(67)90593-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muirhead H., Cox J. M., Mazzarella L., Perutz M. F. Structure and function of haemoglobin. 3. A three-dimensional fourier synthesis of human deoxyhaemoglobin at 5.5 Angstrom resolution. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 28;28(1):117–156. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel R. L., Gibson Q. H., Charache S. Relation between structure and function in Hemoglobin Chesapeake. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2395–2402. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nirenberg M., Leder P., Bernfield M., Brimacombe R., Trupin J., Rottman F., O'Neal C. RNA codewords and protein synthesis, VII. On the general nature of the RNA code. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):1161–1168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novy M. J., Edwards M. J., Metcalfe J. Hemoglobin Yakina. II. High blood oxygen affinity associated with compensatory erythrocytosis and normal hemodynamics. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1848–1854. doi: 10.1172/JCI105675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F., Lehmann H. Molecular pathology of human haemoglobin. Nature. 1968 Aug 31;219(5157):902–909. doi: 10.1038/219902a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F., Muirhead H., Cox J. M., Goaman L. C. Three-dimensional Fourier synthesis of horse oxyhaemoglobin at 2.8 A resolution: the atomic model. Nature. 1968 Jul 13;219(5150):131–139. doi: 10.1038/219131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANNEY H. M., BRIEHL R. W., JACOBS A. S. OXYGEN EQUILIBRIA OF HEMOGLOBIN ALPHA-A AND OF HEMOGLOBIN RECONSTITUTED FROM HEMOGLOBINS ALPHA-A AND H. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2442–2447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed C. S., Hampson R., Gordon S., Jones R. T., Novy M. J., Brimhall B., Edwards M. J., Koler R. D. Erythrocytosis secondary to increased oxygen affinity of a mutant hemoglobin, hemoglobin Kempsey. Blood. 1968 May;31(5):623–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi-Bernardi L., Roughton F. J. The effect of temperature on the oxygen-linked ionizations of hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):784–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER K., CHERNOFF A. I., SINGER L. Studies on abnormal hemoglobins. I. Their demonstration in sickle cell anemia and other hematologic disorders by means of alkali denaturation. Blood. 1951 May;6(5):413–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamatoyannopoulos G., Yoshida A., Adamson J., Heinenberg S. Hemoglobin Rainier (beta145 Tyrosine rarr Histidine): Alkali-Resistant Hemoglobin with Increased Oxygen Affinity. Science. 1968 Feb 16;159(3816):741–743. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3816.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel F., Röhrborn G. Amino-acid substitutions in haemoglobins and the mutation process. Nature. 1966 Apr 2;210(5031):116–117. doi: 10.1038/210116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. W., Keehn R. J., Kawamoto S., Johnson K. G. The growth and development of children exposed in utero to the atomic bombs in Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1967 Aug;57(8):1374–1380. doi: 10.2105/ajph.57.8.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]