Abstract
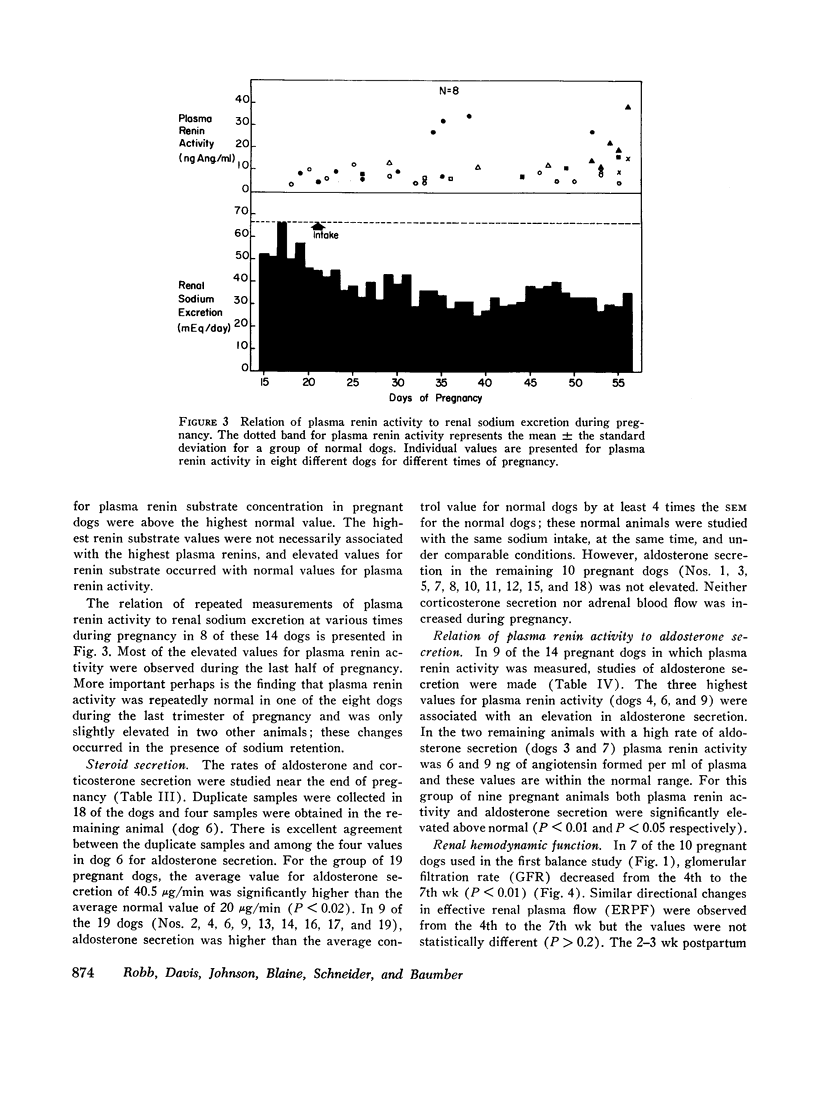
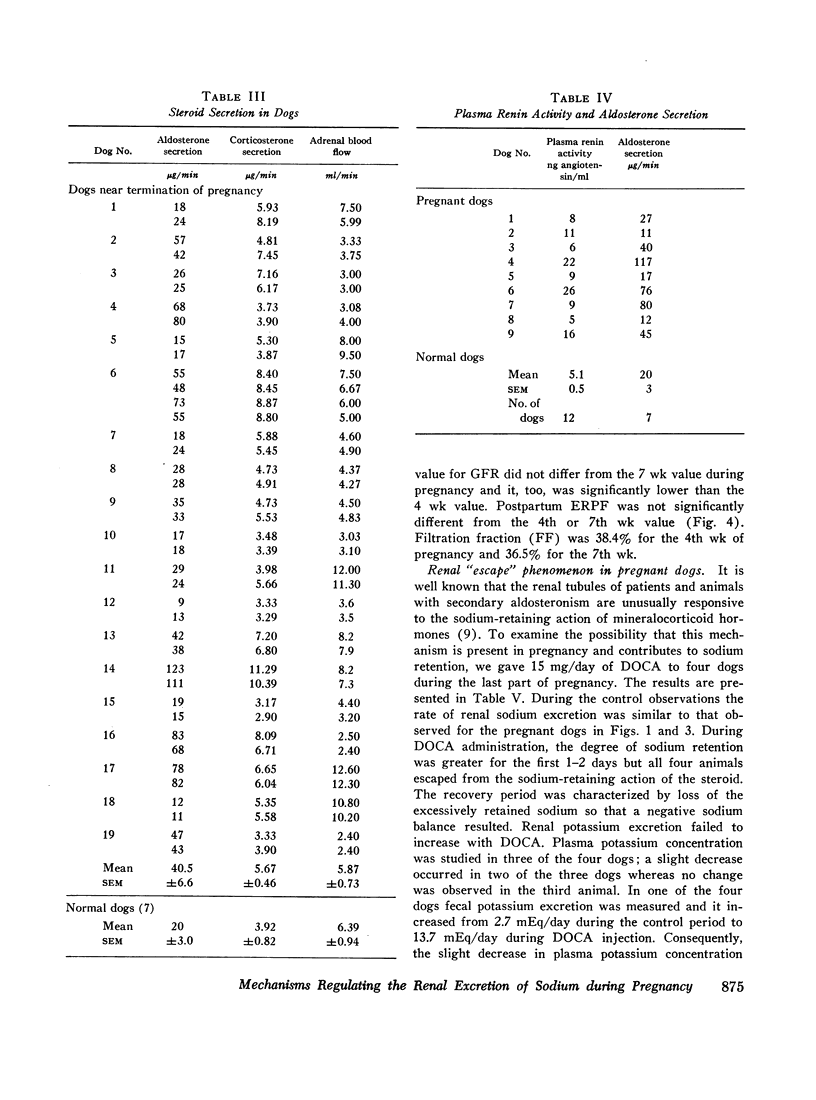
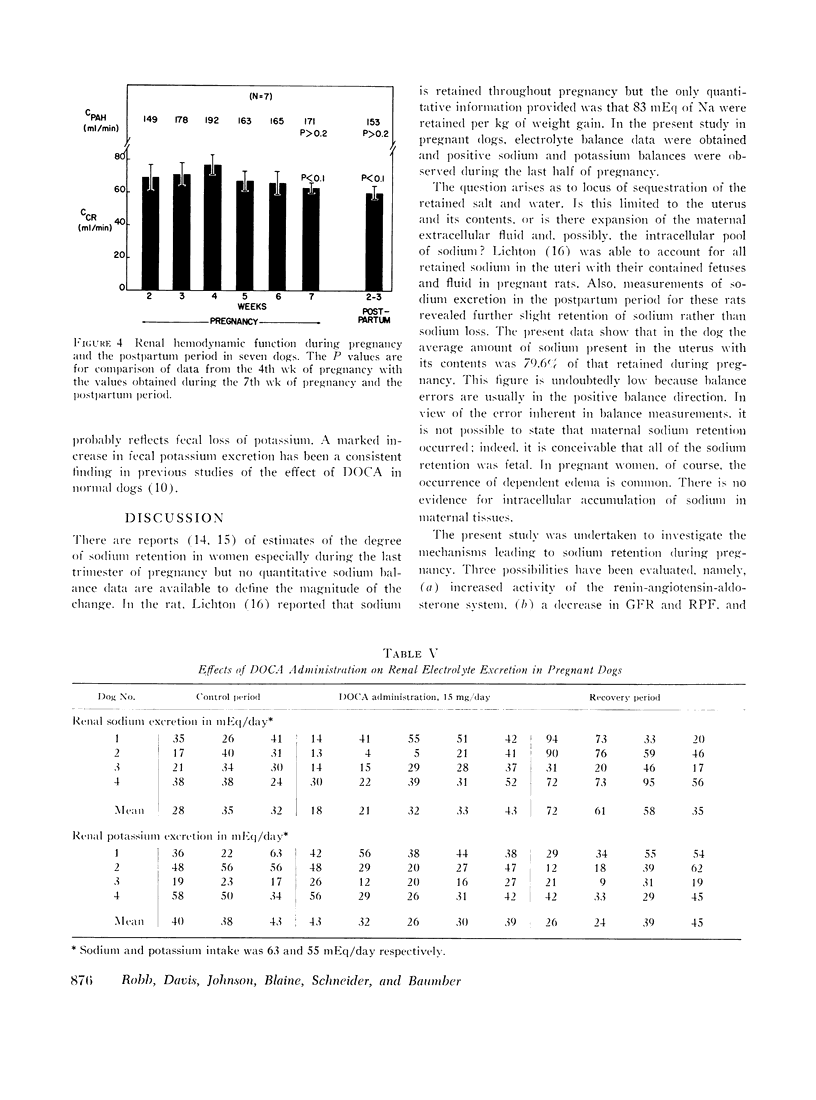
Observations were made on the relation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and renal hemodynamic function to sodium balance in 43 pregnant dogs. Daily balance studies revealed that about 30-40% of ingested sodium was retained during the last half of pregnancy; during the same period, potassium balance was also positive but to a lesser extent. For groups of pregnant dogs, plasma renin activity (n = 14) and aldosterone secretion (n = 19) were significantly higher than normal; however, in some animals one or both functions were normal even though sodium retention was present. In contrast, plasma renin substrate concentration was consistently elevated during pregnancy in seven dogs. In a group of nine dogs in which both aldosterone secretion and plasma renin activity were measured, aldosterone secretion was elevated in the three dogs with the highest values for plasma renin activity; in two of the remaining six animals aldosterone secretion was elevated but plasma renin activity was normal or only slightly increased. The sequestration of sodium and water into the uterine contents was defined quantitatively in this study but evidence was lacking to support the idea that such changes led to renin release. The glomerular filtration rate (GFR) was significantly elevated throughout pregnancy but a significant decrease from the high level of mid-pregnancy occurred during the last half of pregnancy; this decrease in GFR probably contributed to the sodium retention. Administration of a large dose of deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA) to dogs in late pregnancy produced marked sodium retention but “escape” from the sodium-retaining steroid occurred. The data demonstrate that although increased activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system was frequently present during pregnancy, a normal rate of aldosterone secretion occurred. This finding and the observed “escape” from DOCA suggest the existence of sodium-retaining mechanisms other than the mechanism provided by a high plasma level of aldosterone.
Full text
PDF
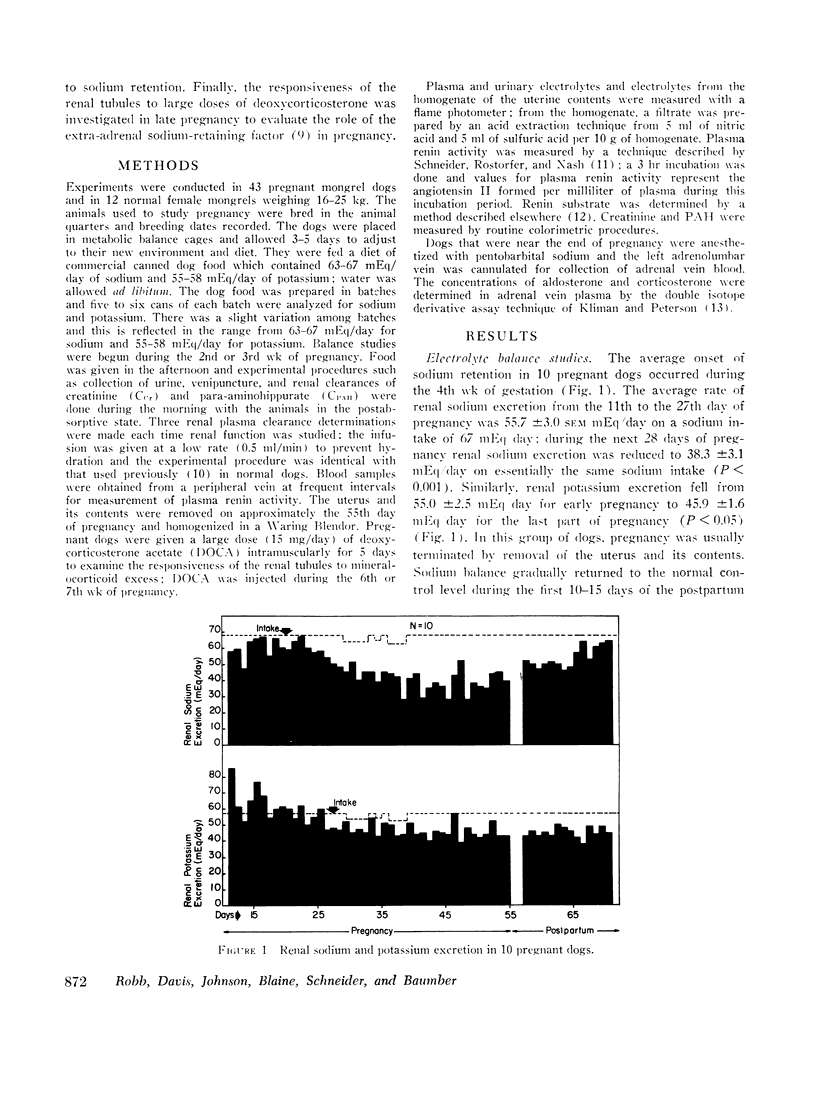
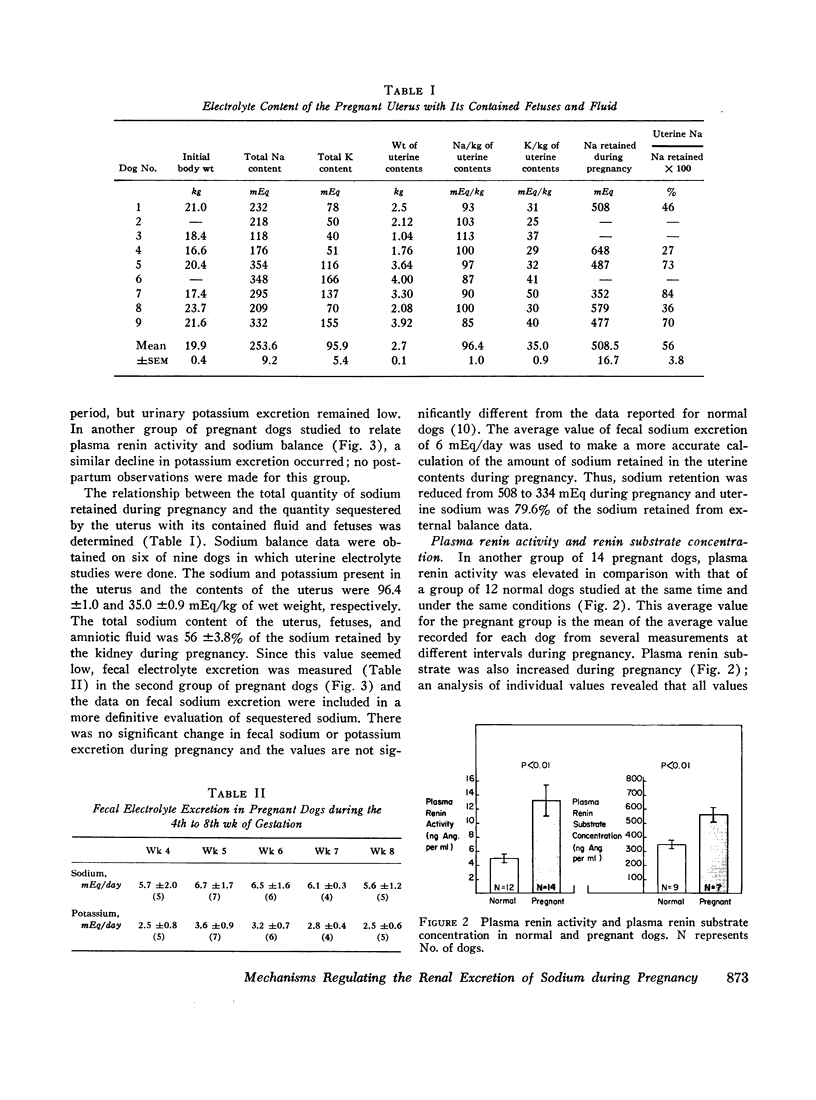




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN J. J., DAVIES D. L., DOAK P. B., LEVER A. F., ROBERTSON J. I. PLASMA-RENIN IN NORMALPREGNANCY. Lancet. 1963 Nov 2;2(7314):900–901. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90614-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCHT H. Studies on renal function in man; with special reference to glomerular filtration and renal plasma flow in pregnancy. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1951;3 (Suppl 3):1–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS J. O., HOLMAN J. E., CARPENTER C. C., URQUHART J., HIGGINS J. T., Jr AN EXTRA-ADRENAL FACTOR ESSENTIAL FOR CHRONIC RENAL SODIUM RETENTION IN PRESENCE OF INCREASED SODIUM-RETAINING HORMONE. Circ Res. 1964 Jan;14:17–31. doi: 10.1161/01.res.14.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS J. O., HOWELL D. S. Comparative effect of ACTH, cortisone and DCA on renal function, electrolyte excretion and water exchange in normal dogs. Endocrinology. 1953 Mar;52(3):245–255. doi: 10.1210/endo-52-3-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS J. O., LINDSAY A. E., SOUTHWORTH J. L. Mechanisms of fluid and electrolyte retention in experimental preparations in dogs. I. Acute and chronic pericarditis. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1952 Jan;90(1):64–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY M. J., MUNRO A. B., SIMS E. A., MEEKER C. I., SOLOMON S., WATANABE M. REGULATION OF SODIUM AND TOTAL BODY WATER METABOLISM IN PREGNANCY. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1964 Jul 15;89:760–765. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(64)90179-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geelhoed G. W., Vander A. J. Plasma renin activities during pregnancy and parturition. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Mar;28(3):412–415. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-3-412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. D., Fishman L. M., Liddle G. W. Plasma renin activity and aldosterone secretion in a pregnant woman with primary aldosteronism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Mar;27(3):385–388. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-3-385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGGINS J. T., Jr, DAVIS J. O., URQUHART J., OLICHNEY M. J. INCREASED PLASMA LEVEL OF RENIN IN EXPERIMENTAL SECONDARY HYPERALDOSTERONISM. Am J Physiol. 1964 Oct;207:814–820. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.4.814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmer O. M., Judson W. E. Influence of high renin substrate levels on renin-angiotensin system in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1967 Sep 1;99(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)34484-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodari A. A., Bumpus F. M., Smeby R. Renin in experimental "toxemia of pregnancy". Obstet Gynecol. 1967 Jul;30(1):8–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodari A. A., Hodgkinson C. P. Fetal kidney as a source of renin in the pregnant dog. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1968 Nov 1;102(5):691–701. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(68)90383-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES K. M., LLOYD-JONES R., RIONDEL A., TAIT J. F., TAIT S. A., BULBROOK R. D., GREENWOOD F. C. Aldosterone secretion and metabolism in normal men and women and in pregnancy. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1959 Mar;30(3):321–342. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0300321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLIMAN B., PETERSON R. E. Double isotope derivative assay of aldosterone in biological extracts. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1639–1648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz F. H., Kappas A. The effects of estradiol and estriol on plasma levels of cortisol and thyroid hormone-binding globulins and on aldosterone and cortisol secretion rates in man. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1768–1777. doi: 10.1172/JCI105667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAIDLAW J. C., RUSE J. L., GORNALL A. G. The influence of estrogen and progesterone on aldosterone excretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962 Feb;22:161–171. doi: 10.1210/jcem-22-2-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDAU R. L., LUGIBIHL K. Inhibition of the sodium-retaining influence of aldosterone by progesterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1958 Nov;18(11):1237–1245. doi: 10.1210/jcem-18-11-1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDAU R. L., PLOTZ E. J., LUGIBIHL K. Effect of pregnancy on the metabolic influence of administered progesterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1960 Dec;20:1561–1567. doi: 10.1210/jcem-20-12-1561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LICHTON I. J. Salt saving in the pregnant rat. Am J Physiol. 1961 Nov;201:765–768. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.5.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAEBASHI M., AIDA M., YOSHINAGA K., ABE K., MIWA I., WATANABE N. ESTIMATION OF CIRCULATING RENIN IN NORMAL AND TOXEMIC PREGNANCY. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 25;84:55–61. doi: 10.1620/tjem.84.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN J. D., MILLS I. H. Aldosterone excretion in normal and toxaemic pregnancies. Br Med J. 1956 Sep 8;2(4992):571–573. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4992.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton M. A., Sealey J. E., Ledingham J. G., Laragh J. H. High blood pressure and oral contraceptives. Changes in plasma renin and renin substrate and in aldosterone excretion. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1968 Aug 15;101(8):1037–1045. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(68)90345-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMS E. A., KRANTZ K. E. Serial studies of renal function during pregnancy and the puerperium in normal women. J Clin Invest. 1958 Dec;37(12):1764–1774. doi: 10.1172/JCI103769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E. G., Davis J. O., Robb C. A., Baumber J. S. Hepatic clearance of renin in canine experimental models for low- and high-output heart failure. Circ Res. 1969 Feb;24(2):213–219. doi: 10.1161/01.res.24.2.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E. G., Rostorfer H. H., Nash F. D. Distribution volume and metabolic clearance rate of renin in anesthetized nephrectomized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1968 Nov;215(5):1115–1122. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.5.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE M., MEEKER C. I., GRAY M. J., SIMS E. A., SOLOMON S. SECRETION RATE OF ALDOSTERONE IN NORMAL PREGNANCY. J Clin Invest. 1963 Oct;42:1619–1631. doi: 10.1172/JCI104847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]