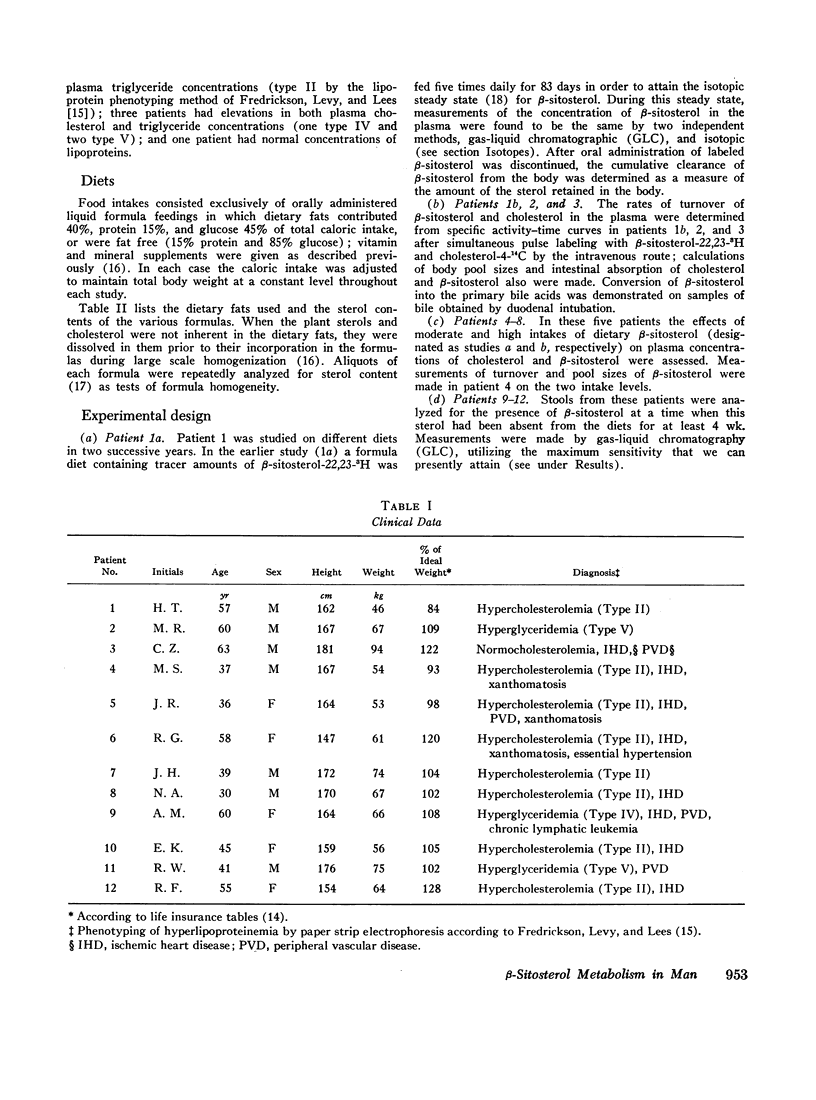
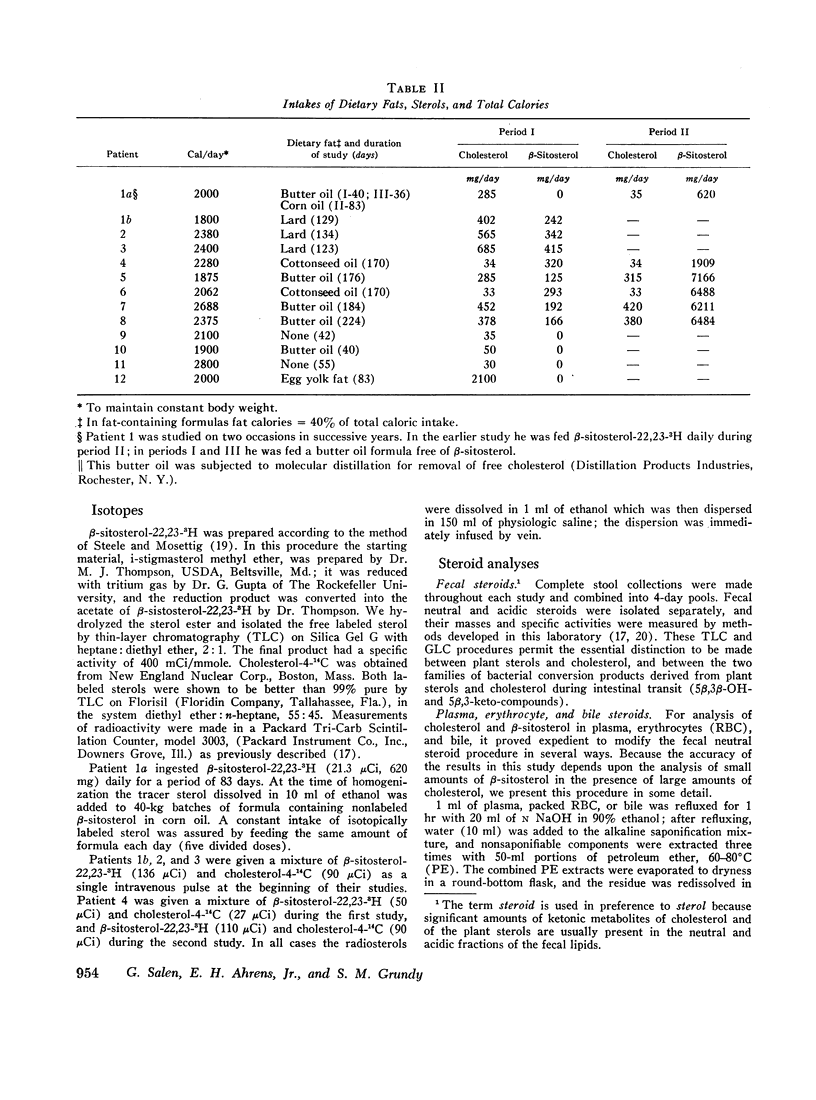
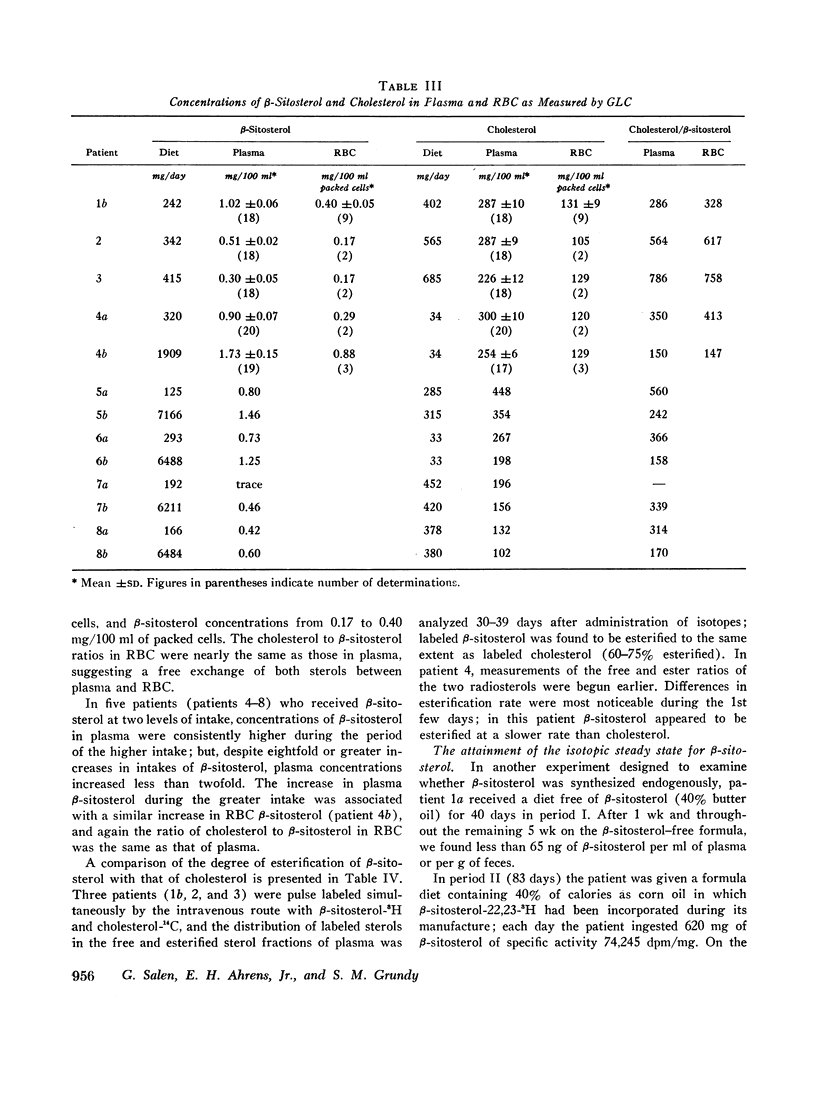
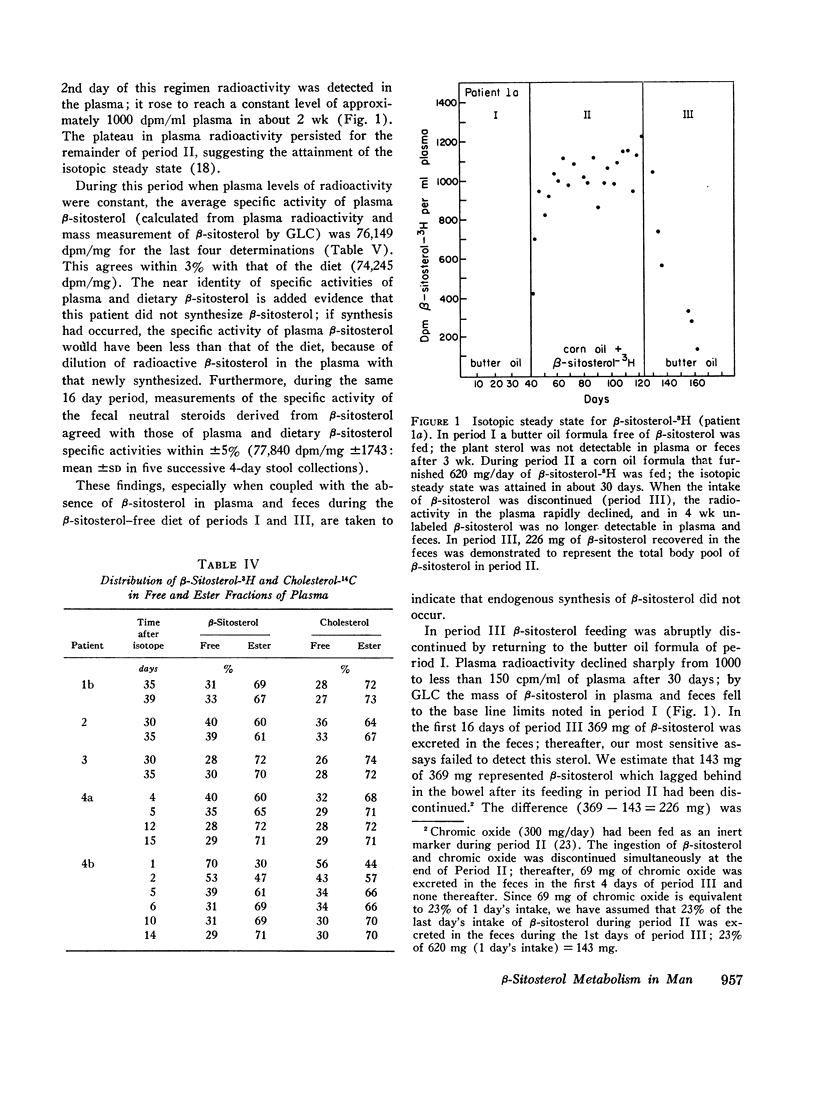
Abstract
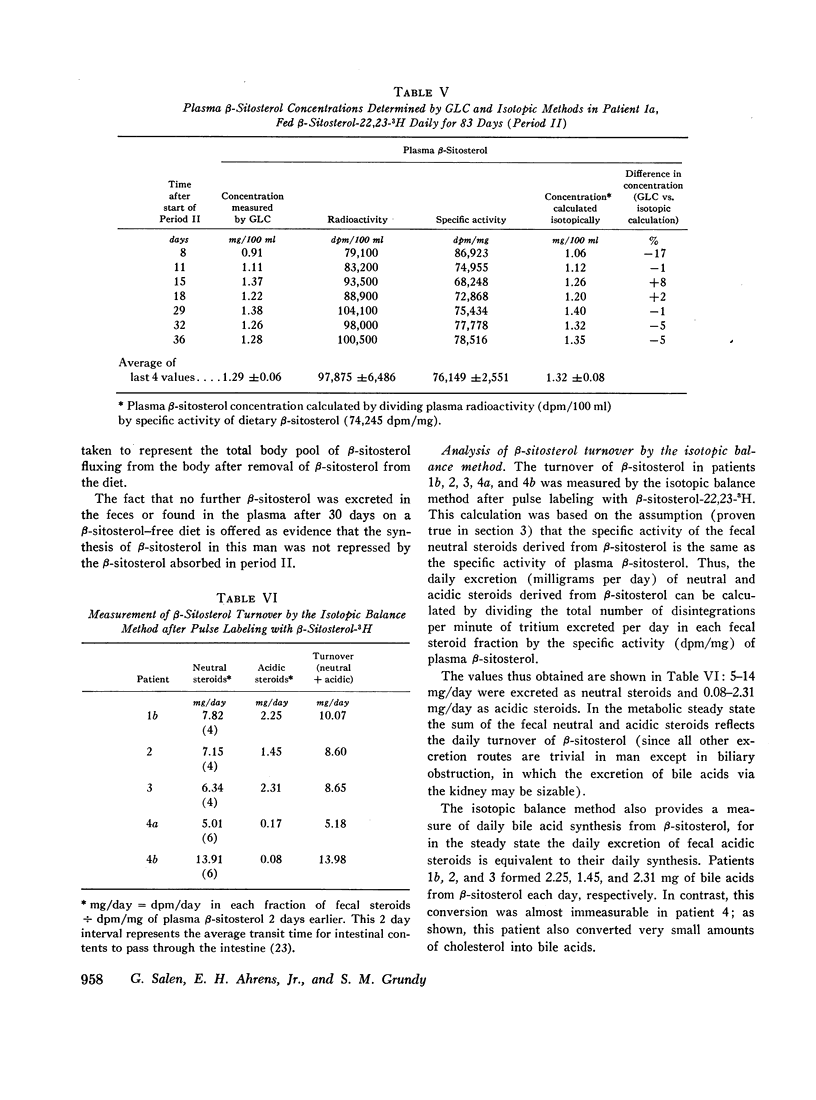
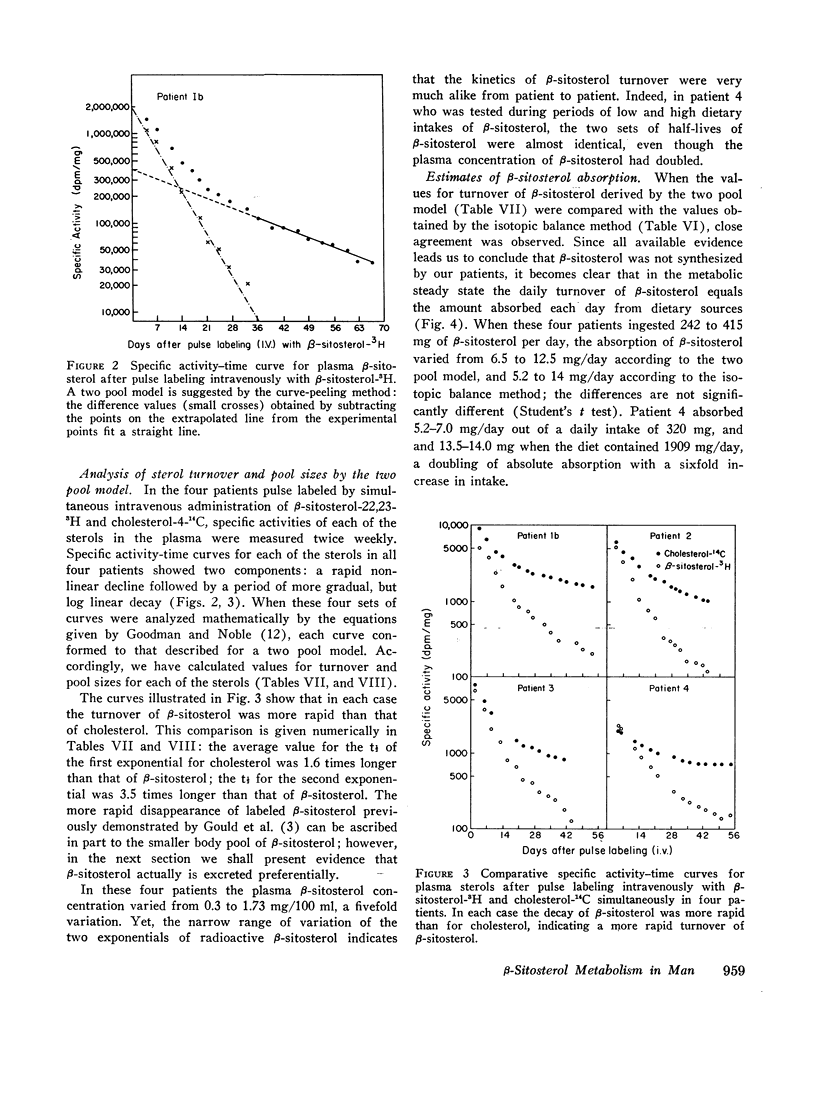
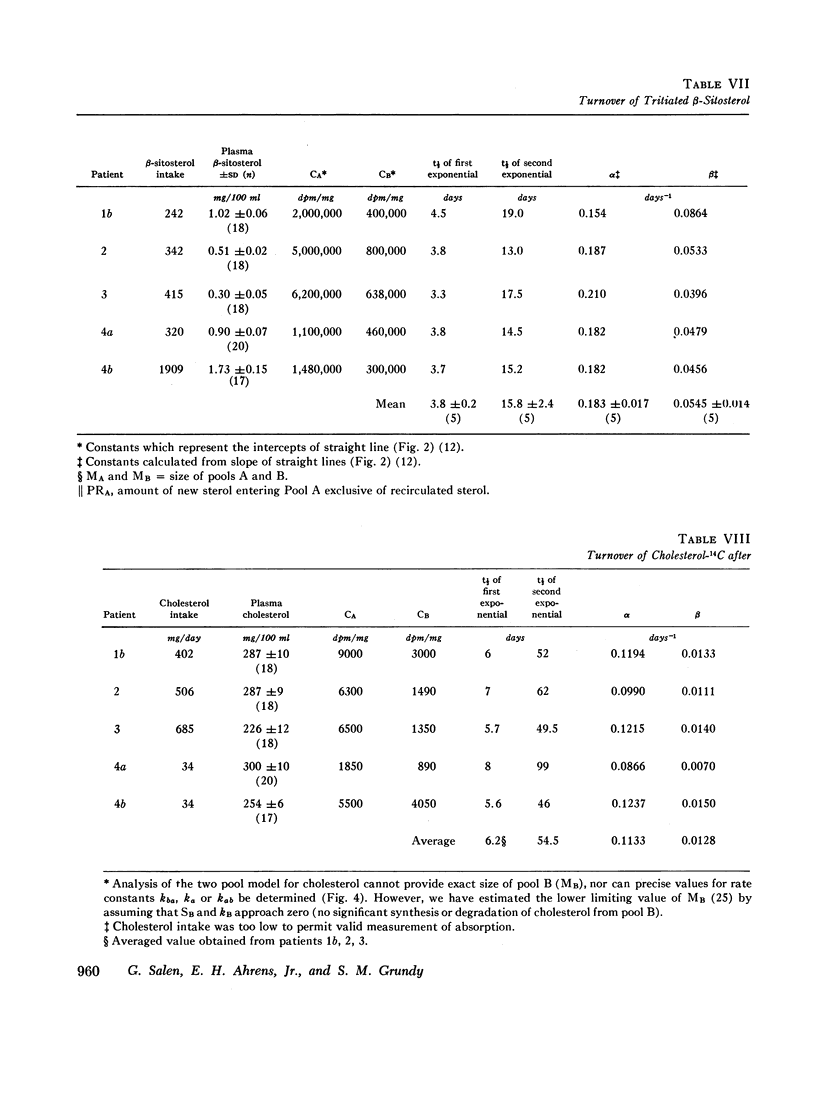
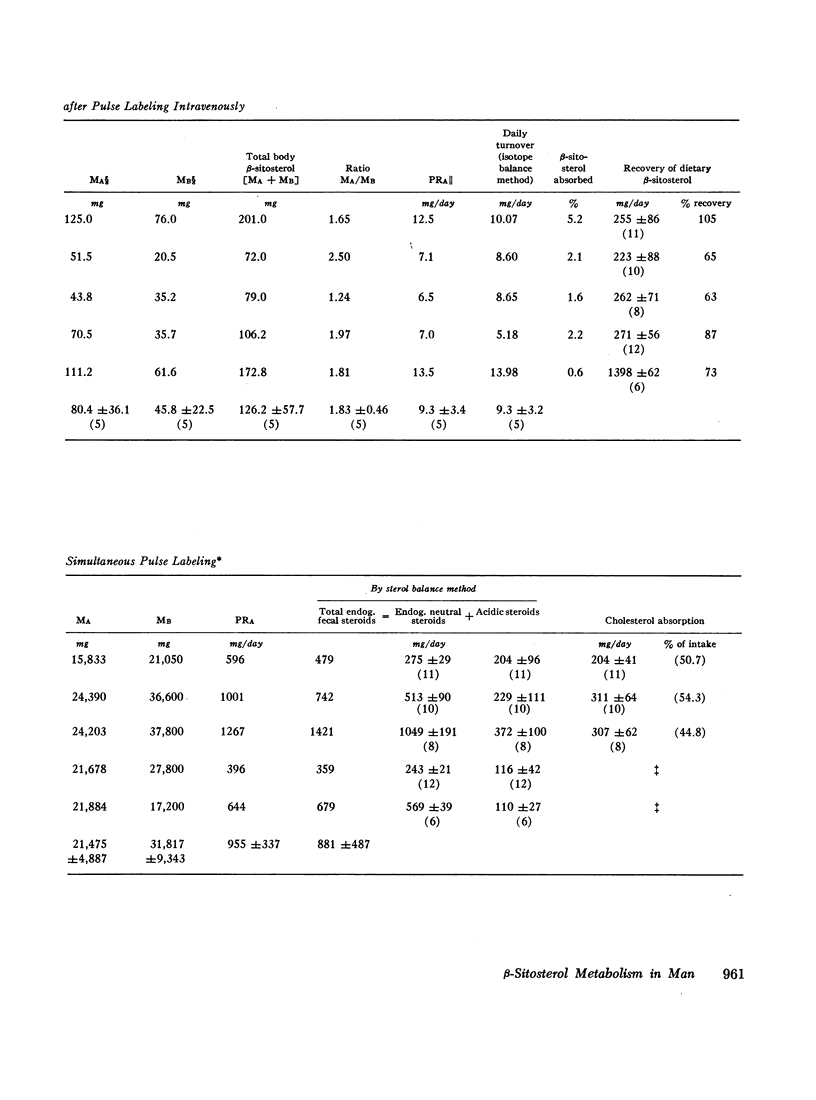
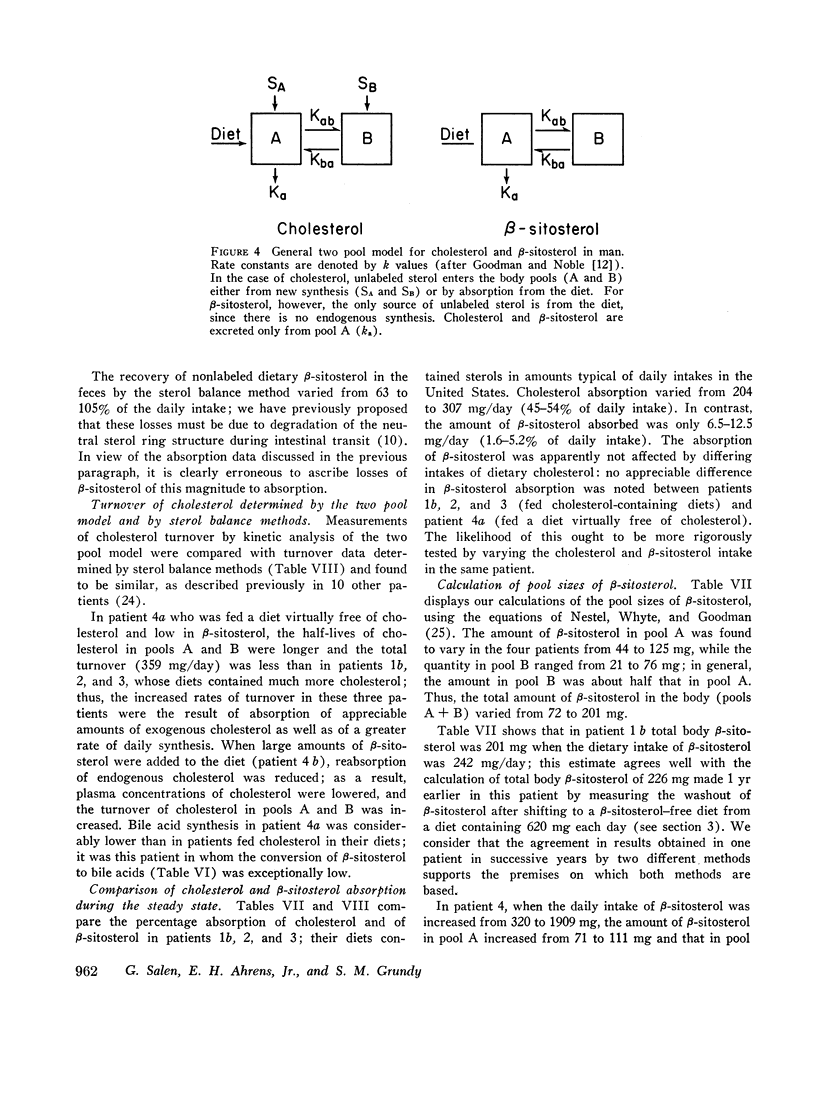
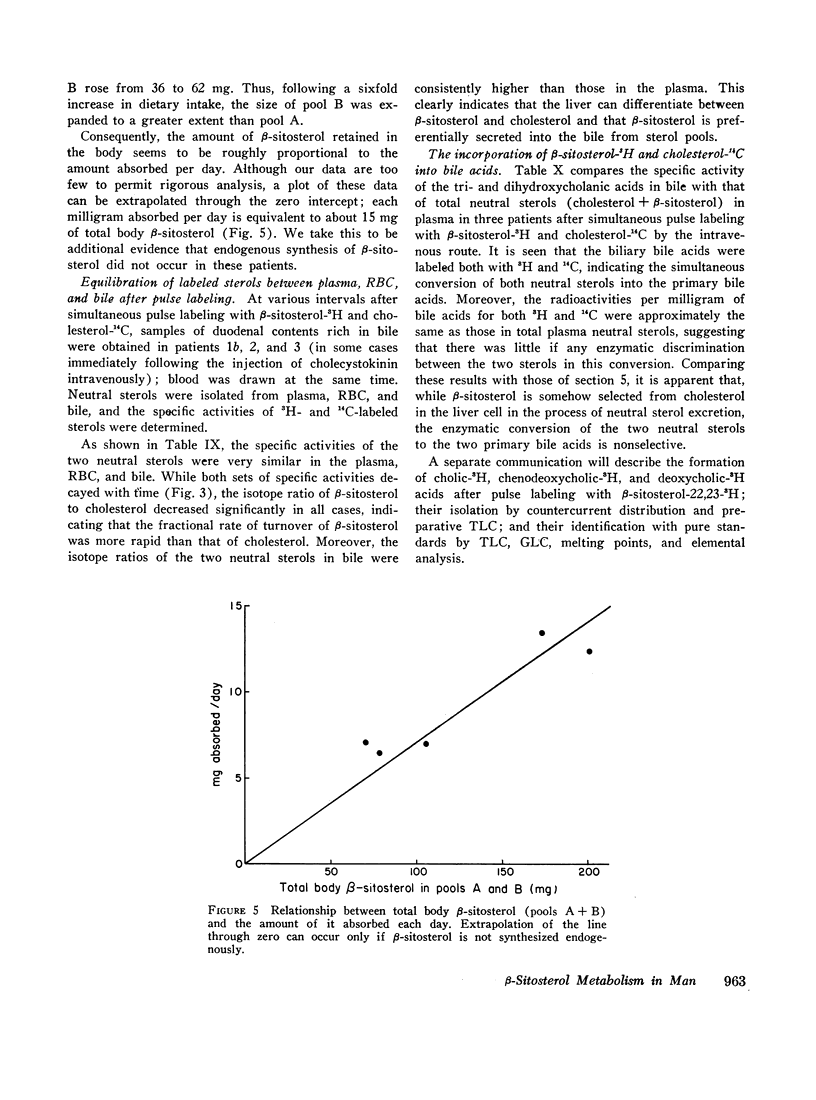
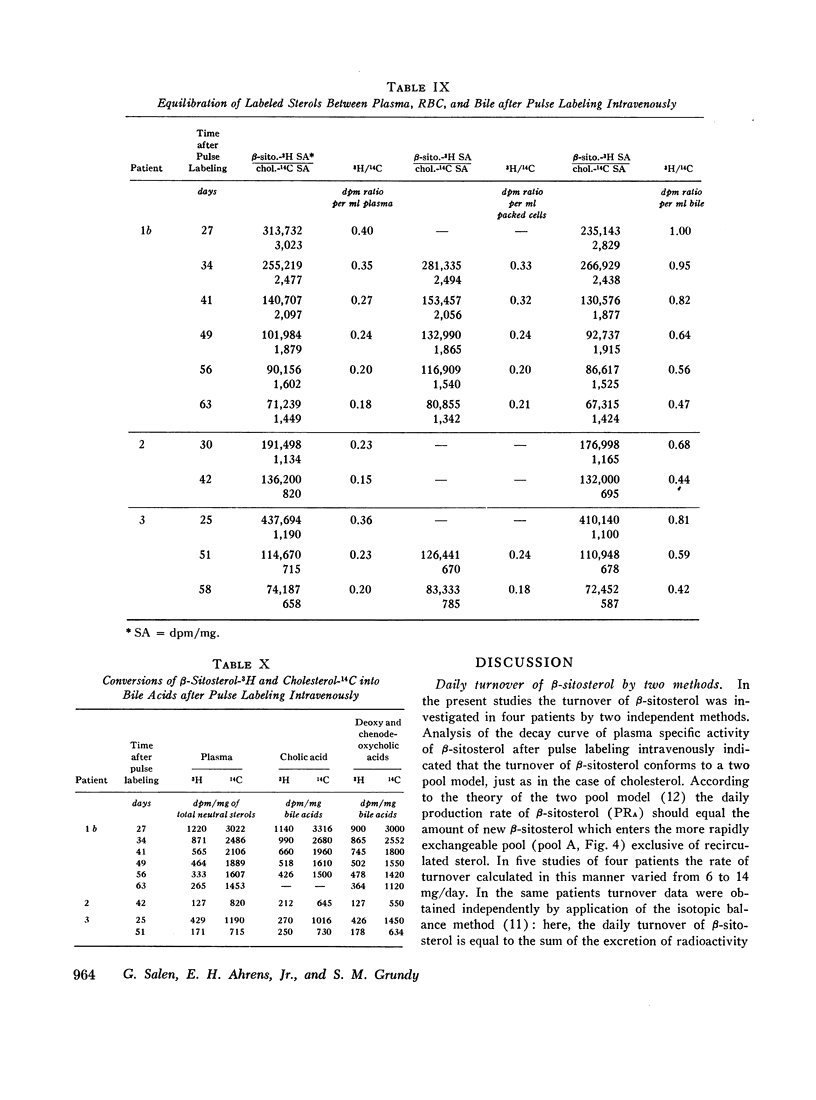
The metabolism of β-sitosterol was compared to that of cholesterol in 12 patients. Sterol balance methods were supplemented by radiosterol studies, with the following results. (a) Plasma concentrations of β-sitosterol ranged from 0.30 to 1.02 mg/100 ml plasma in patients on intakes of β-sitosterol typical of the American diet. Plasma levels were raised little when intakes were increased greatly, and on fixed intakes they were constant from week to week. On diets devoid of plant sterols, the plasma and feces rapidly became free of β-sitosterol. (b) The percentage of esterified β-sitosterol in the plasma was the same as for cholesterol. However, the rate of esterification of β-sitosterol was slower than that for cholesterol. (c) Specific activity-time curves after simultaneous pulse labeling with β-sitosterol-3H and cholesterol-14C conformed to two-pool models. The two exponential half-lives of β-sitosterol were much shorter than for cholesterol, and pool sizes were much smaller. Values of turnover for β-sitosterol obtained by the sterol balance method agreed closely with those derived by use of the two-pool model. There was no endogenous synthesis of β-sitosterol in the patients studied; hence, daily turnover of β-sitosterol equaled its daily absorption. Absorption of β-sitosterol was 5% (or less) of daily intake, while cholesterol absorption ranged from 45 to 54% of intake. (d) About 20% of the absorbed β-sitosterol was converted to cholic and chenodeoxycholic acids. The remainder was excreted in bile as free sterol; this excretion was more rapid than that of cholesterol. (e) The employment of β-sitosterol as an internal standard to correct for losses of cholesterol in sterol balance studies is further validated by the results presented here.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLAYTON R. B. THE UTILIZATION OF STEROLS BY INSECTS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:3–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davignon J., Simmonds W. J., Ahrens E. H. Usefulness of chromic oxide as an internal standard for balance studies in formula-fed patients and for assessment of colonic function. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jan;47(1):127–138. doi: 10.1172/JCI105703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson D. S., Levy R. I., Lees R. S. Fat transport in lipoproteins--an integrated approach to mechanisms and disorders. N Engl J Med. 1967 Jan 19;276(3):148–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196701192760305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDRICK B., HIRSCH J. A TECHNIQUE FOR QUANTITATIVE RECOVERY OF LIPIDS FROM CHROMATOPLATES. J Lipid Res. 1963 Oct;4:482–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD R. G. Symposium on sitosterol. IV. Absorbability of beta-sitosterol. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1955 Dec;18(2):129–134. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1955.tb00428.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDY S. M., AHRENS E. H., Jr, MIETTINEN T. A. QUANTITATIVE ISOLATION AND GAS--LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF TOTAL FECAL BILE ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:397–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S., Noble R. P. Turnover of plasma cholesterol in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Feb;47(2):231–241. doi: 10.1172/JCI105719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordan G. S., Fitzpatrick M. E., Lubich W. P. Identification of osteolytic sterols in human breast cancer. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1967;80:183–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. G., Jones R. J., LeRoy G. V., Wissler R. W., Taylor C. B. Absorbability of beta-sitosterol in humans. Metabolism. 1969 Aug;18(8):652–662. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(69)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr, Davignon J. The interaction of cholesterol absorption and cholesterol synthesis in man. J Lipid Res. 1969 May;10(3):304–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr Measurements of cholesterol turnover, synthesis, and absorption in man, carried out by isotope kinetic and sterol balance methods. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):91–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr, Salen G. Dietary beta-sitosterol as an internal standard to correct for cholesterol losses in sterol balance studies. J Lipid Res. 1968 May;9(3):374–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IVY A. C., LIN T. M., KARVINEN E. Absorption of dihydrocholesterol and soya sterols by the rat's intestine. Am J Physiol. 1955 Oct;183(1):79–85. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.183.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIETTINEN T. A., AHRENS E. H., Jr, GRUNDY S. M. QUANTITATIVE ISOLATION AND GAS--LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF TOTAL DIETARY AND FECAL NEUTRAL STEROIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:411–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRIS M. D., CHAIKOFF I. L., FELTS J. M., ABRAHAM S., FANSAH N. O. The origin of serum cholesterol in the rat; diet versus synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1957 Feb;224(2):1039–1045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestel P. J., Whyte H. M., Goodman D. S. Distribution and turnover of cholesterol in humans. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jun;48(6):982–991. doi: 10.1172/JCI106079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH M., FAVARGER P. La digestibilité des graisses en présence de certains stérols. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1955;13(3):249–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWELL L., BOITER T. A., FIELD H., Jr, TREADWELL C. R. The absorption of plant sterols and their effect on serum and liver sterol levels. J Nutr. 1956 Mar 10;58(3):385–398. doi: 10.1093/jn/58.3.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWELL L., TROUT E. C., Jr, FIELD H., Jr, TREADWELL C. R. Absorption of H3-beta-sitosterol in the lymph fistula rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jan;100(1):140–142. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenheimer R. NEW CONTRIBUTIONS IN STEROL METABOLISM. Science. 1931 Dec 11;74(1928):579–584. doi: 10.1126/science.74.1928.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvén C., Borgström B. Absorption and lymphatic transport of cholesterol and sitosterol in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1969 Mar;10(2):179–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


