Significance
Fighting wildfires in the United States costs billions of dollars annually. Public dialog and ongoing research have focused on increasing wildfire risk because of climate warming, overlooking the direct role that people play in igniting wildfires and increasing fire activity. Our analysis of two decades of government agency wildfire records highlights the fundamental role of human ignitions. Human-started wildfires accounted for 84% of all wildfires, tripled the length of the fire season, dominated an area seven times greater than that affected by lightning fires, and were responsible for nearly half of all area burned. National and regional policy efforts to mitigate wildfire-related hazards would benefit from focusing on reducing the human expansion of the fire niche.
Keywords: anthropogenic wildfires, fire starts, ignitions, modern fire regimes, wildfire causes
Abstract
The economic and ecological costs of wildfire in the United States have risen substantially in recent decades. Although climate change has likely enabled a portion of the increase in wildfire activity, the direct role of people in increasing wildfire activity has been largely overlooked. We evaluate over 1.5 million government records of wildfires that had to be extinguished or managed by state or federal agencies from 1992 to 2012, and examined geographic and seasonal extents of human-ignited wildfires relative to lightning-ignited wildfires. Humans have vastly expanded the spatial and seasonal “fire niche” in the coterminous United States, accounting for 84% of all wildfires and 44% of total area burned. During the 21-y time period, the human-caused fire season was three times longer than the lightning-caused fire season and added an average of 40,000 wildfires per year across the United States. Human-started wildfires disproportionally occurred where fuel moisture was higher than lightning-started fires, thereby helping expand the geographic and seasonal niche of wildfire. Human-started wildfires were dominant (>80% of ignitions) in over 5.1 million km2, the vast majority of the United States, whereas lightning-started fires were dominant in only 0.7 million km2, primarily in sparsely populated areas of the mountainous western United States. Ignitions caused by human activities are a substantial driver of overall fire risk to ecosystems and economies. Actions to raise awareness and increase management in regions prone to human-started wildfires should be a focus of United States policy to reduce fire risk and associated hazards.
The United States has experienced some of the largest wildfire years this decade, with over 36,000 km2 burned in 2006, 2007, 2012, and 2015 (1). There is national and global concern over how fire regimes have changed in the past few decades and how they will change in the future (2–4). In the western United States, there is strong evidence that regional warming and drying, including that directly attributed to anthropogenic climate change, are linked to increased fire frequency and size and longer fire seasons (5–9). However, the role that humans play in starting these fires and the direct role of human-ignitions on recent increases in wildfire activity have been overlooked in public and scientific discourse because of the difficulty in ascribing a cause, either human- or lightning-started (10). Humans primarily alter fire regimes in three ways: changing the distribution and density of ignitions, shifting the seasonality of burning, or altering available fuels (2, 3). Geographic variability in regional and continental-scale fire activity in the United States is strongly tied to proxies for these human-caused changes, including population and road density, and different land-use and development patterns (10–15). Although changing climate and fuels also influence fire regimes across the United States (10, 16, 17), there can be no fire without an ignition source. Here, we explore the role that human-started wildfires play in modern United States fire regimes.
Ignitions are often presumed to be saturated (18, 19), and therefore have limited ability to predict fire activity. However, several studies suggest that humans play an important role in redistributing ignitions (20–22), particularly where lightning rarely occurs or where lightning is not concurrent with dry conditions (23). The human–fire connection in the modern era appears strongest at intermediate levels of development, as fires become less likely in the landscape beyond a certain population density, level of urbanization, or dependence on fossil fuels (11, 13, 24). Overall, humans expand the spatial and temporal “fire niche” by introducing ignitions into landscapes when fuels are sufficiently dry enough to ignite and carry fire, but when lightning is rare. Human ignitions are therefore a critical force acting to expand how the fire niche is realized across United States ecoregions.
National-scale analysis of human alteration of the fire niche is critical given that the annual expense of fighting wildfires has exceeded $2 billion in recent years, and the accrued direct and indirect impacts of wildfire on infrastructure and communities could be 30 times that amount (25). Policies that govern wildfire management and response are also directed at the national level, demanding analysis at a national scale (10, 22, 26). Although recent human influence on fire regimes has been studied at local (13) to regional scales (14), human influence nationally remains poorly understood (10). National policies can strongly influence fire regimes (27) and, with sufficient information on human ignitions, policy directives could target human behavior in ways that remediate increasing trends in wildfire risk.
Here, we ask how human ignitions have altered the spatial extents, seasonality, and temporal trends in wildfire across the coterminous United States. We analyze over 1.5 million records of both human- and lightning-started fires in the United States from 1992 to 2012 (28). All of these wildfires necessitated an agency response to manage or suppress them, and therefore posed a threat to ecosystems or infrastructure; this record does not include intentionally set prescribed burns or managed agricultural fires. To our knowledge, this is the most comprehensive assessment of the role of human-started wildfires across the United States over the past two decades. We compare: (i) the spatial extents of human- vs. lightning-started wildfires, (ii) the seasonality of human vs. lightning wildfires, (iii) the climate niche for human- vs. lightning-started wildfires, and (iv) 21-y trends in large human vs. lightning wildfires. Our analysis documents the pronounced expansion of wildfire extent, seasonality of wildfires, and increasing numbers of large wildfires through time as a result of human-related ignitions across the United States.
Human-Related Ignitions Vastly Expanded the Extent of Wildfire
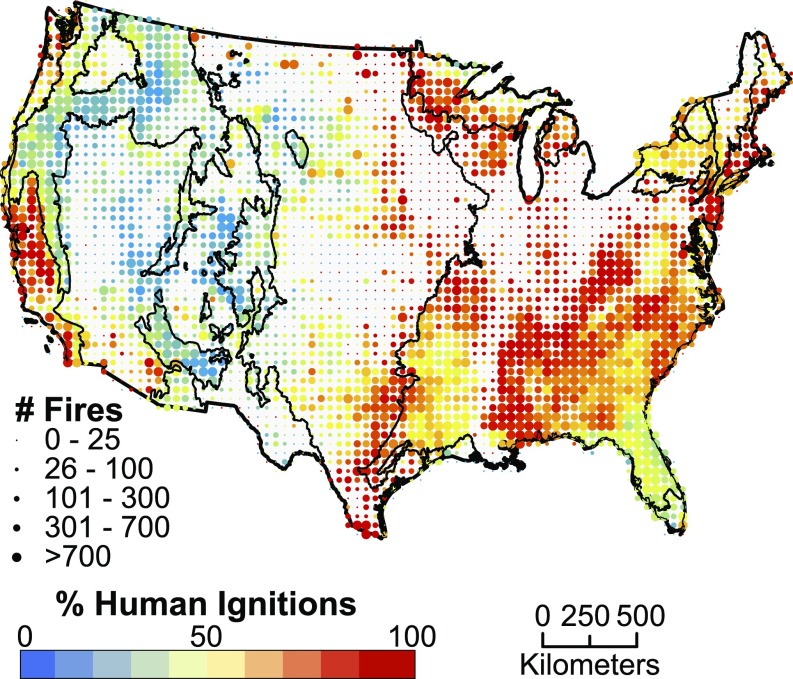
Human-started wildfires represented 84% of the 1.5 million wildfires included in this analysis (n = 245,446 lightning-started fires; n = 1,272,076 human-started wildfires). The eastern United States and western coastal areas were dominated by human-started wildfires, whereas lightning-started fires dominated the mountainous regions of the western United States (Fig. 1, Table 1 and Table S1). Here we define a fire regime as dominated by either human or lighting ignitions when one cause accounts for more than 80% of the number of fires in a given 50 × 50-km grid cell. Based on this definition, 5.1 million km2, or 60% of the total land area of the coterminous United States, was dominated by human-started wildfires, whereas only 0.7 million km2, or 8% of the area, was dominated by lightning-started fires. In addition to expanding the numbers of fires, humans also expanded the total area burned. Human-started wildfires burned a total of 160,274 km2, or ∼44% of the total area burned from 1992 to 2012 (Table 1).
Fig. 1.
The total number of wildfires (dot size) and the proportion started by humans (dot color: red indicating greater number of human started fires) within each 50 km × 50-km grid cell across the coterminous United States from 1992 to 2012. Black lines are ecoregion boundaries, as defined in the text.
Table 1.
The number of wildfires, total burned area (ha), and fire season length (IQR, in days), by ecoregion (ordered by percent human-caused fires) and within the coterminous United States from 1992 to 2012
| Ecoregion | No. of fires | Human caused (%) | Area burned (ha) | Human caused (%) | Length (IQR, days) | Human expansion (%) | |||
| Human | Light | Human | Light | Human | Light | ||||
| MC | 87,274 | 2,855 | 97 | 2,143,282 | 253,210 | 89 | 85 | 45 | 189 |
| NF | 61,673 | 2,574 | 96 | 302,561 | 82,721 | 79 | 51 | 79 | N/A |
| ETF | 815,499 | 44,859 | 95 | 3,827,045 | 829,293 | 82 | 167 | 66 | 253 |
| MWCF | 14,586 | 925 | 94 | 19,251 | 27,291 | 41 | 67 | 52 | 129 |
| GP | 134,944 | 17,586 | 88 | 3,992,557 | 2,564,955 | 61 | 148 | 47 | 315 |
| SSH | 7,504 | 2,167 | 78 | 340,873 | 254,418 | 57 | 55 | 41 | 134 |
| TWF | 4,832 | 1,917 | 72 | 357,150 | 350,477 | 50 | 98 | 52 | 188 |
| NAD | 55,422 | 52,044 | 52 | 2,394,677 | 8,880,691 | 21 | 92 | 40 | 230 |
| NFM | 76,735 | 94,017 | 45 | 1,895,622 | 5,731,733 | 25 | 75 | 36 | 208 |
| TS | 13,607 | 26,502 | 34 | 754,393 | 1,152,064 | 40 | 85 | 39 | 218 |
| CONUS | 1,272,076 | 245,446 | 84 | 16,027,412 | 20,126,852 | 44 | 154 | 46 | 335 |
CONUS, Coterminous United States; ETF, Eastern Temperate Forests; GP, Great Plains; MC, Mediterranean California; MWCF, Marine West Coast Forests; NAD, North American Desert; NF, Northern Forests; NFM, Northwest Forested Mountains; SSH, Southern Semiarid Highlands; TWF, Tropical Wet Forests; TS, Temperate Sierras.
Table S1.
The number of wildfires, total burned area (ha), and fire season length (IQR, in days), by state
| State | No. of fires | Human caused (%) | Area burned (ha) | Human caused (%) | Fire season length (days) | Human expansion (%) | |||
| Human | Lightning | Human | Lightning | Human | Lightning | ||||
| AL | 59216 | 1256 | 98 | 313576 | 17191 | 95 | 185 | 59 | 314 |
| AR | 26031 | 2029 | 93 | 156562 | 24302 | 87 | 179 | 39 | 459 |
| AZ | 33982 | 26909 | 56 | 1030802 | 967306 | 52 | 69 | 39 | 177 |
| CA | 136259 | 23513 | 85 | 2802056 | 1389429 | 67 | 86 | 49 | 176 |
| CO | 7844 | 18212 | 30 | 208888 | 372366 | 36 | 93 | 43 | 216 |
| CT | 4532 | 17 | 100 | 3763 | 31 | 99 | 53 | 51 | 104 |
| DC | 53 | 1 | 98 | 11 | 0 | 100 | 116 | NA | NA |
| DE | 143 | 10 | 93 | 2626 | 4 | 100 | 111 | 20 | 569 |
| FL | 59815 | 19576 | 75 | 837140 | 738861 | 53 | 114 | 49 | 233 |
| GA | 151769 | 7280 | 95 | 374219 | 247724 | 60 | 173 | 52 | 333 |
| IA | 789 | 8 | 99 | 6884 | 65 | 99 | 177 | 87 | 204 |
| ID | 8367 | 18586 | 31 | 796896 | 4003685 | 17 | 63 | 27 | 233 |
| IL | 1879 | 30 | 98 | 8651 | 302 | 97 | 193 | 88 | 220 |
| IN | 1944 | 28 | 99 | 4902 | 4 | 100 | 162 | 67 | 243 |
| KS | 1348 | 118 | 92 | 41809 | 5569 | 88 | 127 | 60 | 214 |
| KY | 18172 | 118 | 99 | 314416 | 1356 | 100 | 221 | 122 | 182 |
| LA | 22555 | 2832 | 89 | 153839 | 70038 | 69 | 195 | 189 | 103 |
| MA | 397 | 20 | 95 | 236 | 53 | 82 | 97 | 22 | 446 |
| MD | 2558 | 100 | 96 | 20368 | 278 | 99 | 138 | 46 | 298 |
| ME | 5234 | 292 | 95 | 4066 | 104 | 98 | 55 | 43 | 128 |
| MI | 8287 | 471 | 95 | 30300 | 19375 | 61 | 63 | 57 | 112 |
| MN | 39781 | 911 | 98 | 386848 | 62640 | 86 | 37 | 71 | 52 |
| MO | 15134 | 157 | 99 | 140172 | 1789 | 99 | 126 | 129 | 98 |
| MS | 64913 | 497 | 99 | 375452 | 3234 | 99 | 189 | 66 | 286 |
| MT | 17797 | 15791 | 53 | 403806 | 1846692 | 18 | 84 | 30 | 280 |
| NC | 82029 | 1775 | 98 | 170912 | 63587 | 73 | 123 | 61 | 203 |
| ND | 12685 | 378 | 97 | 120154 | 19358 | 86 | 99 | 52 | 191 |
| NE | 5287 | 926 | 85 | 100326 | 203391 | 33 | 149 | 55 | 272 |
| NH | 1967 | 78 | 96 | 1217 | 41 | 97 | 48 | 76 | 63 |
| NJ | 22862 | 195 | 99 | 43754 | 938 | 98 | 121 | 57 | 214 |
| NM | 13042 | 16694 | 44 | 820379 | 1185463 | 41 | 96 | 42 | 229 |
| NV | 4604 | 10176 | 31 | 326896 | 3361102 | 9 | 78 | 36 | 217 |
| NY | 61703 | 4102 | 94 | 30540 | 1706 | 95 | 117 | 108 | 108 |
| OH | 1855 | 14 | 99 | 4431 | 30 | 99 | 197 | 60 | 330 |
| OK | 24243 | 1373 | 95 | 688333 | 24665 | 97 | 177 | 150 | 118 |
| OR | 25385 | 27146 | 48 | 371106 | 2112155 | 15 | 71 | 32 | 222 |
| PA | 6258 | 136 | 98 | 15534 | 516 | 97 | 38 | 105 | 36 |
| RI | 312 | 0 | 100 | 149 | 0 | 100 | 45 | NA | NA |
| SC | 52270 | 1865 | 97 | 142324 | 9904 | 93 | 158 | 53 | 298 |
| SD | 21868 | 5086 | 81 | 348596 | 241294 | 59 | 134 | 38 | 353 |
| TN | 27459 | 415 | 99 | 164883 | 7135 | 96 | 213 | 95 | 224 |
| TX | 108182 | 6037 | 95 | 2520956 | 694090 | 78 | 184 | 71 | 259 |
| UT | 5356 | 15083 | 26 | 429690 | 1062150 | 29 | 67 | 39 | 172 |
| VA | 18606 | 1008 | 95 | 107536 | 16621 | 87 | 130 | 80 | 162 |
| VT | 186 | 8 | 96 | 310 | 4 | 99 | 73 | 72 | 101 |
| WA | 19583 | 8212 | 70 | 519324 | 607610 | 46 | 63 | 34 | 185 |
| WI | 28855 | 636 | 98 | 27930 | 848 | 97 | 81 | 78 | 104 |
| WV | 19401 | 260 | 99 | 213293 | 2495 | 99 | 219 | 111 | 197 |
| WY | 4783 | 5801 | 45 | 189045 | 693882 | 21 | 99 | 39 | 254 |
NA, not applicable.
Human-Related Ignitions More Than Tripled the Length of the Wildfire Season
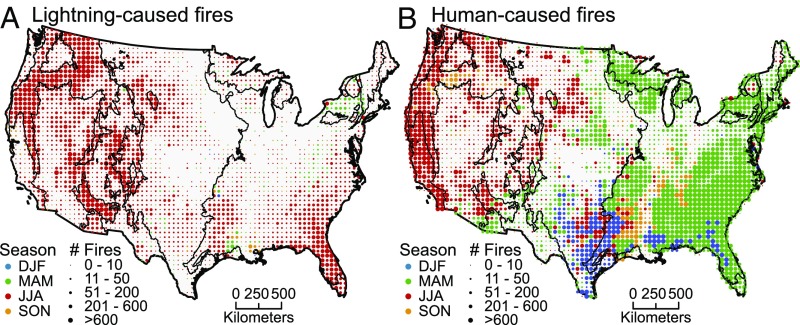
Human ignitions dramatically expanded the wildfire season in the United States, particularly during spring. The length of the human-started wildfire season [defined as the interquartile range (IQR) of human-ignited fires] was 154 d, more than triple that of the lightning wildfire season (IQR = 46 d) (Fig. 2 and Table 1). This national-scale expansion is driven by earlier (spring) human-started fires in eastern ecoregions coupled with later (late summer or fall) human-started fires in western ecoregions (Table S2). The median discovery date for human-started fires was over 2-mo (May 20th) earlier than lightning-started fires (July 25th). Summed across the 21-y record, the most common day for human-started fires by far was July 4th, US Independence Day, with 7,762 fires starting that day over the course of the record (Fig. 2), whereas, the most common day for lightning-started fires was July 22nd. Of all lightning-ignited fires, 78% occurred in the summer (June–August), 9% in the spring (March–May), and 12% in the fall (September–November). In contrast, human-ignited wildfires were more evenly distributed throughout the year, with 24% in summer, 38% in spring, 19% in fall, and 19% in winter. This pronounced expansion of the wildfire season was also evident spatially (Fig. 3), with human-ignited wildfires occurring predominantly in spring in the eastern United States and in the fall and winter in Texas and the Gulf states. Table S1 for state-level analysis.When lightning-started fires were rare (<5% and >95% quantile; i.e., before May 13th or after September 16th), humans ignited 842,289 wildfires, effectively increasing the number of wildfires 35-fold compared with the 24,081 lightning-ignited wildfires during these spring, fall, and winter seasons.
Fig. 2.
Frequency distributions of human and lightning-caused wildfires by Julian day of year. (A) Frequency distribution of wildfires across the coterminous United States from 1992 to 2012 (n = 1.5 million); (B) map of United States ecoregions; (C) frequency distributions of wildfires by ecoregions, ordered by decreasing human dominance.
Table S2.
Fire season start (first quartile, Julian day), median discovery day (Julian day) and fire season length (IQR, in days) by ecoregion and averaged across the entire coterminous United States
| Ecoregion | Fire season start (Julian day) | Human advancement (d) | Median discovery day (Julian day) | Human advancement (d) | Fire season length (IQR, days) | Human expansion (d) | |||
| Human | Lightning | Human | Lightning | Human | Lightning | ||||
| Coterminous United States | 81 | 182 | 101 | 140 | 206 | 66 | 154 | 46 | 108 |
| Eastern Temperate Forests | 69 | 149 | 80 | 111 | 181 | 70 | 167 | 66 | 101 |
| Great Plains | 84 | 181 | 97 | 163 | 207 | 44 | 148 | 47 | 101 |
| North American Deserts | 129 | 187 | 58 | 178 | 207 | 29 | 92 | 40 | 52 |
| Temperate Sierras | 126 | 180 | 54 | 166 | 201 | 35 | 85 | 39 | 46 |
| Tropical Wet Forests | 64 | 153 | 89 | 107 | 175 | 68 | 98 | 52 | 46 |
| Mediterranean California | 161 | 201 | 40 | 198 | 226 | 28 | 85 | 45 | 40 |
| Northwestern Forested Mountains | 175 | 196 | 21 | 212 | 215 | 3 | 75 | 36 | 39 |
| Marine West Coast Forest | 184 | 194 | 10 | 218 | 217 | NA | 67 | 52 | 15 |
| Southern Semiarid Highlands | 124 | 173 | 49 | 151 | 192 | 41 | 55 | 41 | 14 |
| Northern Forests | 105 | 148 | 43 | 120 | 196 | 76 | 51 | 79 | NA |
Note that the national-scale tripling of fire season length by human ignitions is driven by earlier (spring) fires in eastern ecoregions coupled with later (fall) fires in western ecoregions.
Fig. 3.
Comparison of seasonality for (A) lightning- vs. (B) human-ignited wildfires. Human ignitions expand the seasonal fire niche considerably into spring and fall months. Colors show the season with the maximum ignitions caused by lightning and human within each 50 km × 50-km grid cell. Size of dot indicates the number of unique lightning and human fires between 1992 and 2012. Ecoregion boundaries are overlaid for visualization.
Human-Driven Expansion of the Fire Niche
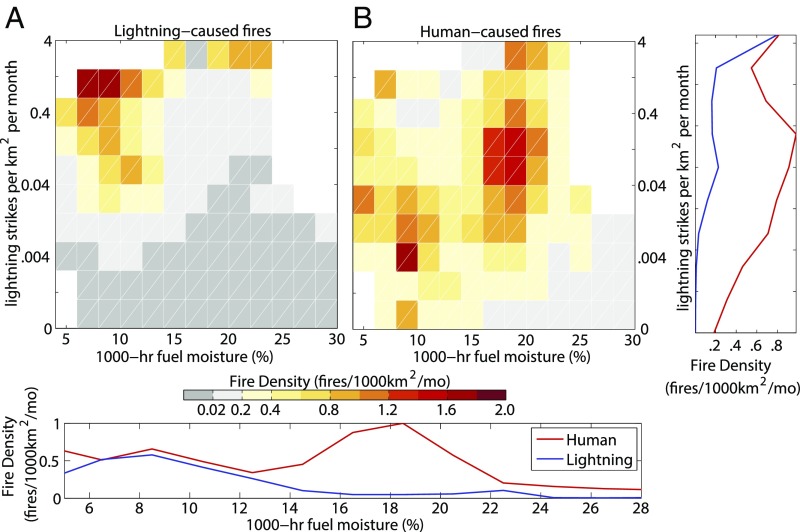
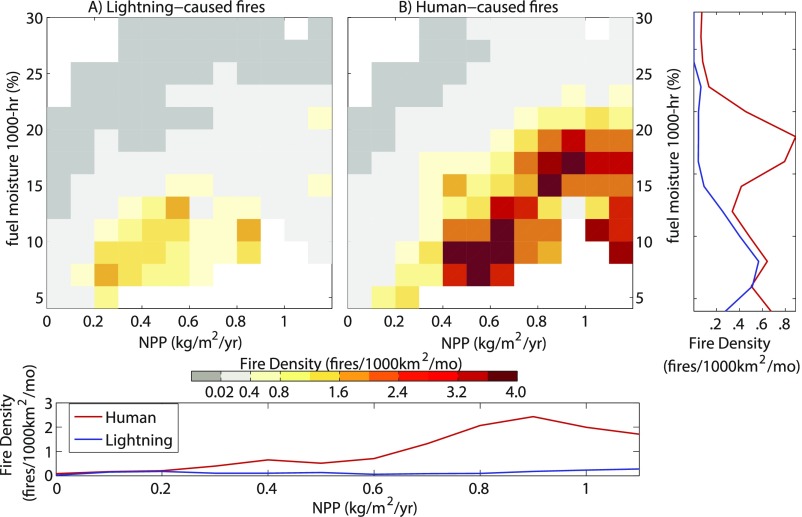
Humans greatly expanded the natural fire niche (Fig. 4), which we calculated as the co-occurrence of the average monthly lightning density and 1,000-h dead fuel moisture. Regions and seasons of moderate to high lightning-started fire density (>0.4 fires per 1,000 km2 per month) had a median lightning-strike density of 0.19 (IQR: 0.065–0.57) strikes per square kilometer per month and a median 1,000-h fuel moisture of 11.9% (IQR: 9.25–15.6%) (Fig. 4A). In contrast, regions and seasons of moderate to high human-started fire density (>0.4 fires per 1,000 km2 per month) had a median lightning-strike density of only 0.11 (IQR: 0.025–0.39) strikes per square kilometer per month and a median 1,000-h fuel moisture of 17.8% (IQR: 15.95–19.25%) (Fig. 4B). The median fuel moisture and lightning conditions when human-started wildfires occurred were significantly different from those values for lightning-started fires (P < 0.0001). Areas and months of moderate to high human-caused fire density had approximately 40% fewer lightning strikes, and nearly 50% higher fuel moisture levels (based on median values) than for moderate to high lightning-caused fire density. Additional exploration of the fire niche for human-started and lightning-started fires relative to lightning density, fuel moisture, and net primary production (NPP), a proxy for fuels, is provided in Figs. S1 and S2.
Fig. 4.
Human vs. lightning fire niche relative to fuel moisture and lightning density, with greatest resulting wildfire density represented by dark red. (A) Lightning-started fires occur in areas with high lightning-strike density and dry fuels. (B) Human-started wildfires expand the fire niche to include areas with low lightning-strike density as well as areas with higher fuel moisture. Graphs on the bottom and far right show histograms of 1,000-h dead fuel moisture and lightning strikes, respectively, for human- and lightning-started fires.
Fig. S1.
Human vs. lightning fire niche relative to NPP and fuel moisture, with greatest resulting fire density represented by dark red. (A) Lightning fires occur in areas with moderate NPP and dry fuels. (B) Human fires expand the fire niche to include areas with high NPP as well as areas with higher fuel moisture. Graphs on the bottom and far right show histograms of NPP and 1,000-h dead fuel moisture, respectively, for human- and lightning-started fires.
Fig. S2.
Human vs. lightning fire niche relative to NPP and lightning density, with greatest resulting fire density represented by dark red. (A) Lightning fires occur in areas with high lightning-strike density. (B) Human fires expand the fire niche to include areas with low lightning-strike density as well as areas with high NPP. Graphs on the bottom and far right show histograms of NPP and lightning strikes, respectively, for human- and lightning-started fires.
Increasing Trends in Large Human-Started Wildfires
During the 21-y time period, there were significant increasing trends in large wildfires ignited by both lightning (n = 4,312; Theil-Sen estimated slope = 12.2; P = 0.001) and humans (n = 4,143; Theil-Sen estimated slope = 3.6; P = 0.004) (Fig. S3). There was a strong dichotomy in human vs. lightning trends seasonally (Fig. 5). Overall trends in lightning-caused fires were primarily driven by increasing numbers of large summer fires (Fig. 5B), whereas overall trends in human-caused fires were primarily driven by increasing numbers of large spring fires (Fig. 5D). Spatially, lightning-caused fires increased the most in the Northwest Forested Mountains ecoregion (Fig. S4A), whereas human-caused wildfires increased the most in the Great Plains ecoregion (Fig. S4B).
Fig. S3.
Both human- (red) and lightning- (blue) caused large wildfires show significant increasing trends over the 21-y time series. Data are based on 8,455 fires in the MTBS record.
Fig. 5.
Trends in the number of large wildfires verified by MTBS records from 1992 to 2012 for lightning-started fires (A–C) vs. human-started fires (D–F) in the spring (green: A and D), summer (red: B and E), and fall (orange: C and F). Where trend lines are shown, Theil-Sen estimated slopes are significantly different from zero (P < 0.05).
Fig. S4.
Temporal trends in large, MTBS fires for lightning- (A) and human- (B) caused wildfires by ecoregion. Red ecoregions have significant increasing trends, blue ecoregions have significant decreasing trends, and gray ecoregions have no significant trend or insufficient data for analysis. Scatter plots show number of fires per year and plots with trend lines denote a significant slope based on Theil-Sen analysis.
Discussion
Humans, the keystone fire species (29), play a primary role in spatially and temporally redistributing ignitions and resulting wildfires. We document that over 84% of the government-recorded wildfires were started by people from 1992 to 2012. Sixty percent of the total land area of the coterminous United States was dominated by human-started wildfires, whereas only 8% of the area was dominated by lightning fires. Humans tripled the length of the wildfire season, extending burning into the spring, fall, and winter months. During the spring, fall, and winter, people added more than 840,000 wildfires, a 35-fold increase over the number of lightning-started fires in those seasons. This expansion of the fire-niche was caused by human-related ignitions under higher fuel moisture conditions, compared with lightning-started fires. Moreover, during this 21-y record, large human-started wildfires increased significantly.
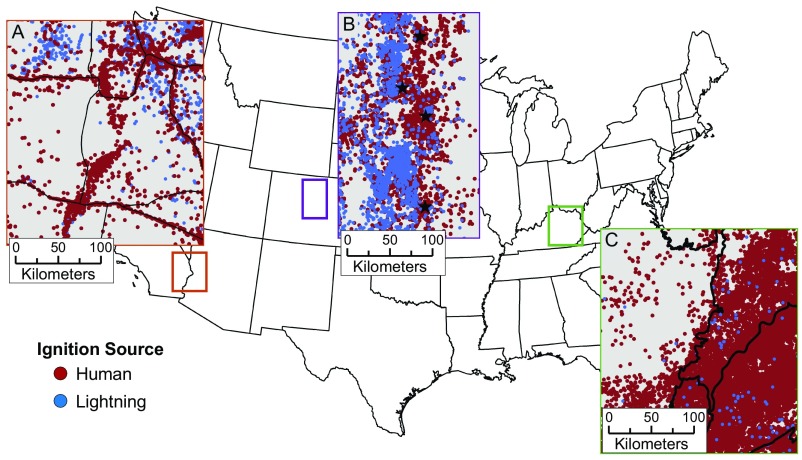
There was a strong national east–west dichotomy in the spatial distribution of human-started wildfires. Although human-started wildfires were pervasive across the United States (Fig. 1), the expansion of human-started wildfires relative to lightning-started fires was most dramatic in the eastern United States and central and southern California (Figs. 1 and 2C). Recent work for California confirms the important role of humans, with anthropogenic variables explaining half of the variability in fire probability over the past four decades (30). In contrast, lightning-started fires were found primarily in the intermountain west and Florida and occurred predominantly in the summer, reflecting national lightning strike patterns (31) (Fig. 2C). This finding supports other studies of human vs. lightning ignition sources that have found an important distinction between eastern and western United States fire patterns (10, 21) and drivers (32). Some explanations for this distinction include higher population and housing densities, lower proportions of public land, and more extensive land use and development in the eastern United States (33, 34), all of which could lead to more sources of anthropogenic ignitions. Synchrony between lightning activity and the seasonal nadir of fuel moisture in the western United States also likely contributes to these geographic differences. However, even with a projected increase in the number of lightning strikes as a result of anthropogenic climate change (50% by 2100) (35), humans would still remain the dominant ignition source across the majority of the United States land area. The majority of the wildfires requiring agency suppression in the east can be attributed to escaped fires from debris burning occurring in the spring months (or winter in Texas and the Gulf Coast) (Fig. 3). Between 1992 and 2012, wildfires caused by debris burning tended to be small (median fire size 0.4 ha, IQR: 0.14–1.62 ha), but still an important source of risk to surrounding ecosystems. At finer scales, there are also notable patterns in human- vs. lightning-started wildfires (Fig. S5). Increased wildfires can follow road networks (36), the wildland–urban interface (13), and boundaries between agricultural and forested areas (37), highlighting just a few examples of how human activities and cultural drivers provide ignitions that substantially change the distribution of fire across the United States (38).
Fig. S5.
Visualization of how spatial patterns of human ignitions (red dots) vary across the United States. (A) In the southwest, human ignitions extend linearly along major highways (black lines) and into agricultural areas. (B) Urban development along the Colorado Front Range is a source of many fires in the wildland–urban interface. Stars indicate (from north) the cities of Fort Collins, Boulder, Denver, and Colorado Springs. (C) Human-caused fires increase substantially as ecosystems transition from the agriculture-dominated Interior Plateau in western Kentucky to Appalachian forest in eastern Kentucky (black lines are ecological region level III boundaries).
Our findings reinforce the strong imprint of people on fire regimes through changes in wildfire seasonality, which has been documented globally (39). In the past few decades, early onset of warmer and drier conditions has promoted greater fire activity across the western United States (6, 7, 40). However, our study highlights the equally important role of human ignitions in changing modern fire regimes by increasing the fire season length to encompass the entire year. The vast majority (78%) of lightning-started fires occurred during the summer months, whereas 76% of human-started fires occurred during the spring, fall, and winter months. Moreover, this trend varies substantially by ecoregion, reflecting again the principle dichotomy between the eastern and western United States (Fig. 3). Human-started fires extend the fire season earlier in the east, and later in the west (Fig. 3 and Table S2). Observations suggest that climate change has extended the duration of the fire weather season across most of the globe, including parts of the United States by a couple of weeks over the past three decades (5, 9), whereas we show that human ignitions in the United States increased the length of the fire season by more than three mo. There was also a notable mark of American culture on the distribution of wildfires, with the peak day of wildfires occurring on July 4th, concurrent with Independence Day fireworks displays (Fig. 2). Indeed, Americans start over twice as many wildfires on July 4th as any other summer day. A similar cultural mark has also been demonstrated globally with a marked decline in wildfires on Sunday compared with other weekdays (41).
Thus, at the national scale, human ignitions dramatically expand the spatial and seasonal niche of fire. The key components that define the fire niche are ignition sources, fuel mass, and desiccation. By exploring the fire niche along these axes, our results show that lightning fires are primarily constrained to areas with a lightning-strike density of greater than 100 strikes per grid cell per month (0.04 strikes/km2 per month) and are concurrent with drier fuels (< 15% fuel moisture) (Fig. 4). Human ignitions expand fires into regions with higher fuel moisture (Fig. 4) and higher NPP (Figs. S1 and S2), suggesting that humans create sufficient ignition pressure for wetter fuels to burn. As a consequence, human ignitions have expanded the fire niche into areas with historically low lightning-strike density, such as Mediterranean California, or low concurrence of lightning and dry conditions, such as Eastern Temperate Forests (Fig. 1).
Over the past two decades, there was a significant increase across the United States for both human- and lightning-caused large fires (Fig. S3). The significant increase in large lightning fires is driven primarily by fires in summer months (Fig. 5) in the Northwest Forested Mountains ecoregion of the western United States (Fig. S4). This finding is consistent with other studies that have demonstrated an increase in large fires across the western United States (6, 7, 40), likely as a consequence of changes in climate and fuels rather than ignitions. In contrast, the significant trend in human-caused fires is primarily driven by an increase in large fires during spring months (Fig. 5) in the Great Plains ecoregion of the United States (Fig. S4). This increasing trend suggests that earlier springs as a result of climate change (42, 43) may be interacting with human ignition sources to increase the risk of large fires in the central United States.
The strong year-to-year variability in human ignitions (Fig. S3 and S4) may reflect the degree to which human choices can affect fire regimes. However, interannual climate variability also influences fuel moisture, NPP, and short-term weather conditions that enable the spread of human-ignited wildfires (44). There was a significant temporal correlation between large human- and lightning-started fires (R = 0.75). This pattern has been observed previously in the western United States (23) and suggests that large-scale climate drivers affect the frequency of both human- and lightning-caused fires. It is unknown how human actions will be affected by hotter and drier conditions, potentially increasing or decreasing ignitions from land use, recreation, and other sources. Increased public awareness and focused policy and management, particularly in years with elevated fire risk associated with climatic anomalies, are needed to reduce the number of human-caused ignitions.
In conclusion, we demonstrate the remarkable influence that humans have on modern United States wildfire regimes through changes in the spatial and seasonal distribution of ignitions. Although considerable fire research in the United States has rightly focused on increased fire activity (e.g., larger fires and more area burned) because of climate change, we demonstrate that the expanded fire niche as a result of human-related ignitions is equally profound. Moreover, the convergence of warming trends and expanded ignition pressure from people is increasing the number of large human-caused wildfires (Fig. 5). Currently, humans are extending the fire niche into conditions that are less conducive to fire activity, including regions and seasons with wetter fuels and higher biomass (Figs. 3 and 4). Land-use practices, such as clearing and logging, may also be creating an abundance of drier fuels, potentially leading to larger fires even under historically wetter conditions. Additionally, projected climate warming is expected to lower fuel moisture and create more frequent weather conditions conducive to fire ignition and spread (45), and earlier springs attributed to climate change are leading to accelerated phenology (42). Although plant physiological responses to rising CO2 may reduce some drought stress (46), climate change will likely lead to faster desiccation of fuels and increased risk in areas where human ignitions are prevalent.
Uncertainty remains regarding how anthropogenic climate change will alter wildfire activity geographically and seasonally (47, 48), particularly in areas where human-caused fires dominate. Moreover, the current wildland–urban interface, where houses intermingle with natural areas, constitutes 9% of the United States total land area (33) but is projected to double by 2030, predominantly in the intermountain West (49). This expected development expansion will increase not only ignition pressure, but also the vulnerability of new infrastructure. Human-driven expansion of the spatial and temporal distribution of ignitions makes national- and regional-scale policy interventions and increased public awareness critical for reducing national wildfire risk.
Materials and Methods
For this analysis, we used the publically available US Forest Service Fire Program Analysis-Fire Occurrence Database (FPA-FOD) (28). This comprehensive dataset includes United States federal, state, and local records of wildfires (both on public and private lands) that were suppressed from 1992 to 2012, a total of ∼1.6 million records. Previous studies have focused on the western United States (20), federal lands (22), or records from just one agency (21). Each entry includes at minimum the location, discovery date, and cause of the wildfire. We excluded 114,191 wildfires with an unknown cause and analyzed the spatial, seasonal, and temporal patterns of human- vs. lightning-started wildfires. In total, 1,517,522 wildfires were included in the analysis. Human-started wildfires were caused by a variety of sources, including the US Forest Service-designated categories of equipment use, smoking, campfire, railroad, arson, debris burning, children, fireworks, power line, structure, and miscellaneous fires (28). Spatially, we calculated the proportion of human- vs. lightning-caused wildfires within equal-area 50 × 50-km grid cells across the coterminous United States. This grid size corresponds roughly to the size of an average United States county. For each grid cell, we calculated the season (winter, spring, summer, or fall) when the majority of human-caused and lightning-caused wildfires were started. All spatial analyses were conducted in the Albers-Conical equal-area projection. To determine the seasonal distribution of wildfires, we plotted the distribution of human- and lightning-started fires by the day of year for the coterminous United States and for individual ecoregions. We used the level 1 ecological regions of North America, developed by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (50). We calculated the length of the human- and lightning-caused fire seasons as the IQR of the Julian day of recorded fire ignition: that is, the difference between the first and third quartiles.
We determined how humans expanded the fire niche by comparing the lightning-strike density (i.e., natural ignition pressure) and fuel-moisture conditions under which actual human- and lightning-started fire events occurred. We obtained daily 1,000-h dead fuel moisture data from the surface meteorological data (51) on a 4-km grid from 1992 to 2012, and computed monthly averages across the 21-y study period. We obtained 4-km gridded monthly lightning-strike data from the Vaisala National Lightning Detection Network (https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/data-access/severe-weather/lightning-products-and-services) and averaged the data over the 21-y study period. To account for fuel limitations, we also explored the fire niche as a function of fuel amount (approximated by NPP). We used MODIS mean annual NPP data (1-km resolution, from 2002 to 2015) (52) for this purpose. These three datasets were aggregated to the common 50 × 50-km grid cell. We calculated the number of human- and lightning-started fires by grid cell using the FPA-FOD dataset (28). We excluded any grid cells from subsequent analyses that did not report at least one lightning-caused or human-caused wildfire over the period of record. We tested whether fire niche expansion (as determined by fuel moisture and lightning-strike density) caused by human ignitions was significant based on Mann–Whitney tests between human- vs. lightning-started fires.
To assess trends in human- vs. lightning-caused wildfires through time, we used only large fires that were independently verified by the Monitoring Trends in Burn Severity (MTBS) project (53). We specifically focused on these large fires (>400 ha in the west, >200 ha in the east; n = 8,455) for comparability with previous research, which has examined temporal trends in the western United States and the link to climate warming (6, 7, 40), but has not investigated the relative contribution of human-started fires at a national scale. In addition to overall temporal trends, we tested for significant trends by ignition source versus season (spring, summer, fall) and versus ecoregion based on the level I ecological regions of North America (50). We explored a similar analysis using all available FPA-FOD data, but changes in reporting frequency through time for some states precluded a robust temporal analysis. We tested for trends in wildfire numbers through time using the nonparametric Theil-Sen estimator (54) and tested for trend significance using nonparametric Mann–Kendall tests (55).
Acknowledgments
We thank two anonymous reviewers for their comments. We also thank Karen Short for her efforts to compile the FPA-FOD wildfire database. This work was funded by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration Terrestrial Ecology Program under Award NNX14AJ14G, Joint Fire Sciences Program 15-2-03-6, and Earth Lab through the University of Colorado, Boulder’s Grand Challenge Initiative.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1617394114/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.NIFC 2015 Total Wildland Fires and Acres (1960–2015) and Current Year-to-Date by State. National Interagency Fire Center Statistics. Available at https://www.nifc.gov/. Accessed October 7, 2016.
- 2.Bowman DM, et al. The human dimension of fire regimes on Earth. J Biogeogr. 2011;38(12):2223–2236. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2699.2011.02595.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bowman DMJS, et al. Fire in the Earth system. Science. 2009;324(5926):481–484. doi: 10.1126/science.1163886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stephens SL, et al. Land use. Managing forests and fire in changing climates. Science. 2013;342(6154):41–42. doi: 10.1126/science.1240294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Abatzoglou JT, Williams AP. Impact of anthropogenic climate change on wildfire across western US forests. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113(42):11770–11775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1607171113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Westerling AL, Hidalgo HG, Cayan DR, Swetnam TW. Warming and earlier spring increase western U.S. forest wildfire activity. Science. 2006;313(5789):940–943. doi: 10.1126/science.1128834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Westerling AL. 2016. Increasing western US forest wildfire activity: Sensitivity to changes in the timing of spring. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 371(1696): 20150178, erratum in Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 371(1707):20160373.
- 8.Williams AP, Abatzoglou JT. Recent advances and remaining uncertainties in resolving past and future climate effects on global fire activity. Curr Clim Change Rep. 2016;2(1):1–14. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jolly WM, et al. Climate-induced variations in global wildfire danger from 1979 to 2013. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7537. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hawbaker TJ, et al. Human and biophysical influences on fire occurrence in the United States. Ecol Appl. 2013;23(3):565–582. doi: 10.1890/12-1816.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bistinas I, et al. Relationships between human population density and burned area at continental and global scales. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e81188. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Parisien M-A, et al. The spatially varying influence of humans on fire probability in North America. Environ Res Lett. 2016;11(7):075005. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Syphard AD, et al. Human influence on California fire regimes. Ecol Appl. 2007;17(5):1388–1402. doi: 10.1890/06-1128.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fusco EJ, Abatzoglou JT, Balch JK, Finn JT, Bradley BA. Quantifying the human influence on fire ignition across the western USA. Ecol Appl. 2016;26:2390–2401. doi: 10.1002/eap.1395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Calef MP, McGuire AD, Chapin FS. Human influences on wildfire in Alaska from 1988 through 2005: An analysis of the spatial patterns of human impacts. Earth Interact. 2008;12(1):1–17. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Morton DC, et al. Satellite-based assessment of climate controls on US burned area. Biogeosci Disc. 2013;10:247–260. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Littell JS, McKenzie D, Peterson DL, Westerling AL. Climate and wildfire area burned in western U.S. ecoprovinces, 1916-2003. Ecol Appl. 2009;19(4):1003–1021. doi: 10.1890/07-1183.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Krawchuk MA, Moritz MA, Parisien M-A, Van Dorn J, Hayhoe K. Global pyrogeography: The current and future distribution of wildfire. PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e5102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Thonicke K, Venevsky S, Sitch S, Cramer W. The role of fire disturbance for global vegetation dynamics: Coupling fire into a dynamic global vegetation model. Glob Ecol Biogeogr. 2001;10(6):661–677. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bartlein PJ, Hostetler SW, Shafer SL, Holman JO, Solomon AM. Temporal and spatial structure in a daily wildfire-start data set from the western United States (198696) Int J Wildland Fire. 2008;17(1):8–17. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Malamud BD, Millington JDA, Perry GLW. Characterizing wildfire regimes in the United States. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102(13):4694–4699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500880102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Stephens SL. Forest fire causes and extent on United States Forest Service lands. Int J Wildland Fire. 2005;14:213–222. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Abatzoglou JT, Kolden CA, Balch JK, Bradley BA. Controls on interannual variability in lightning-caused fire activity in the western US. Environ Res Lett. 2016;11(4):045005. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Balch JK, et al. Global combustion: The connection between fossil fuel and biomass burning emissions (1997-2010) Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016;371(1696):371. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schoennagel T, et al. 2016 Insights from wildfire science: A resource for fire policy discussions. Headwaters Economics, pp 1–9. Available at https://headwaterseconomics.org/wildfire/insights. Accessed January 20, 2017.
- 26.Stephens SL, Ruth LW. Federal forest-fire policy in the United States. Ecol Appl. 2005;15(2):532–542. [Google Scholar]
- 27.North MP, et al. Environmental science. Reform forest fire management. Science. 2015;349(6254):1280–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.aab2356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Short KC. A spatial database of wildfires in the United States, 1992–2011. Earth Syst Sci Data. 2014;6(1):1–27. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pyne SJ. Fire creature. In: Scott AC, Bowman DMJS, Bond WJ, Alexander ME, editors. Fire on Earth: An Introduction. John Wiley and Sons; West Sussex, UK: 2014. pp. 195–230. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mann ML, et al. Incorporating anthropogenic influences into fire probability models: Effects of human activity and climate change on fire activity in California. PLoS One. 2016;11(4):e0153589. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Orville RE, Huffines GR. Cloud-to-ground lightning in the United States: NLDN results in the first decade, 1989–98. Mon Weather Rev. 2001;129(5):1179–1193. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pyne SJ. Between Two Fires: A Fire History of Contemporary America. Univ of Arizona Press; Tucson, AZ: 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Radeloff VC, et al. The wildland-urban interface in the United States. Ecol Appl. 2005;15(3):799–805. doi: 10.1002/eap.2597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Riitters KH, et al. Fragmentation of continental United States forests. Ecosystems. 2002;5(8):815–822. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Romps DM, Seeley JT, Vollaro D, Molinari J. Climate change. Projected increase in lightning strikes in the United States due to global warming. Science. 2014;346(6211):851–854. doi: 10.1126/science.1259100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cardille JA, Ventura SJ, Turner MG. Environmental and social factors influencing wildfires in the Upper Midwest, United States. Ecol Appl. 2001;11(1):111–127. [Google Scholar]
- 37.McCarty JL, Korontzi S, Justice CO, Loboda T. The spatial and temporal distribution of crop residue burning in the contiguous United States. Sci Total Environ. 2009;407(21):5701–5712. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Pyne SJ. Fire in America. Univ of Washington Press; Seattle, WA: 1982. p. 654. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Le Page Y, Oom D, Silva JMN, Jönsson P, Pereira JMC. Seasonality of vegetation fires as modified by human action: Observing the deviation from eco-climatic fire regimes. Glob Ecol Biogeogr. 2010;19(4):575–588. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dennison PE, Brewer SC, Arnold JD, Moritz MA. Large wildfire trends in the western United States, 1984–2011. Geophys Res Lett. 2014;41(8):2928–2933. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Earl N, Simmonds I, Tapper N. Weekly cycles of global fires—Associations with religion, wealth and culture, and insights into anthropogenic influences on global climate. Geophys Res Lett. 2015;42(21):9579–9589. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schwartz MD, Ahas R, Aasa A. Onset of spring starting earlier across the Northern Hemisphere. Glob Change Biol. 2006;12(2):343–351. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Melillo JM, Richmond T, Yohe GW. Climate Change Impacts in the United States: The Third National Climate Assessment. US Global Change Research Program; Washington, DC: 2014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Jin Y, et al. Contrasting controls on wildland fires in Southern California during periods with and without Santa Ana winds. J Geophys Res Biogeosci. 2014;119(3):432–450. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Flannigan M, et al. Global wildland fire season severity in the 21st century. For Ecol Manage. 2013;294:54–61. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Swann ALS, Hoffman FM, Koven CD, Randerson JT. Plant responses to increasing CO2 reduce estimates of climate impacts on drought severity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113(36):10019–10024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1604581113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Barbero R, Abatzoglou JT, Larkin NK, Kolden CA, Stocks B. Climate change presents increased potential for very large fires in the contiguous United States. Int J Wildland Fire. 2015;24(7):892–899. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Luce CH, et al. Contributing factors for drought in United States forest ecosystems under projected future climates and their uncertainty. For Ecol Manage. 2016;380:299–308. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Theobald DM, Romme WH. Expansion of the US wildland–urban interface. Landsc Urban Plan. 2007;83(4):340–354. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Wiken E, Nava FJ, Griffith G. North American Terrestrial Ecoregions—Level III. Commission for Environmental Cooperation; Montreal: 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Abatzoglou JT. Development of gridded surface meteorological data for ecological applications and modelling. Int J Climatol. 2013;33(1):121–131. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zhao M, Heinsch FA, Nemani RR, Running SW. Improvements of the MODIS terrestrial gross and net primary production global data set. Remote Sens Environ. 2005;95(2):164–176. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Eidenshink J, et al. A project for monitoring trends in burn severity. Fire Ecol. 2007;3(1):3–21. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Wilcox RR. Introduction to Robust Estimation and Hypothesis Testing. Academic; San Diego: 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Mann HB. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica. 1945;13(3):245–259. [Google Scholar]