Abstract
Understanding the molecular mechanisms that drive adipogenesis is important in developing new treatments for obesity and diabetes. Epigenetic regulations determine the capacity of adipogenesis. In this study, we examined the role of a histone H3 lysine 27 demethylase, the ubiquitously transcribed tetratricopeptide repeat protein on the X chromosome (Utx), in the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) to adipocytes. Using gene trapping, we examined Utx-deficient male mESCs to determine whether loss of Utx would enhance or inhibit the differentiation of mESCs to adipocytes. Utx-deficient mESCs showed diminished potential to differentiate to adipocytes compared to that of controls. In contrast, Utx-deficient preadipocytes showed enhanced differentiation to adipocytes. Microarray analyses indicated that the β-catenin/c-Myc signaling pathway was differentially regulated in Utx-deficient cells during adipocyte differentiation. Therefore, our data suggest that Utx governs adipogenesis by regulating c-Myc in a differentiation stage-specific manner and that targeting the Utx signaling pathway could be beneficial for the treatment of obesity, diabetes, and congenital utx-deficiency disorders.
Introduction
Obesity is a major health concern worldwide [1–3]. Overconsumption of energy-rich foods facilitates fat deposition in adipose tissue [4]. Adipose tissue has a significant buffering capacity that permits it to adapt to excessive energy intake by changing the number and size of adipocytes [5,6]. The pathological accumulation of fat in the body leads to the risk of developing obesity-associated metabolic disorders [4,7]. Multiple processes of adipocyte differentiation including commitment to mesoderm, preadipocytes, and terminal differentiation into adipocytes are involved during adipocyte differentiation [8]. However, the mechanism of stage-specific regulation of adipogenesis is not still fully understood.
Histone methylation plays a pivotal role in diverse biological processes including adipogenesis [9,10]. The ubiquitously transcribed tetratricopeptide repeat protein on the X chromosome (Utx or Kdm6a) functions as a demethylase for a marker of gene repression, the histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) [11–14]. Utx is ubiquitously expressed and indispensable for normal female development [15–17]. Utx is required for the maintenance of pluripotency in iPS cells [18], as well as for proper differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) to mesenchymal and cardiac lineages [19]. Interestingly, Utx deficiency results in enhanced adipogenesis and decreased osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) [20]. These reports suggest that Utx has distinct roles during the process of adipocyte differentiation.
In this study, we examined the role of Utx in adipogenesis. In the differentiation of mESCs to adipocytes, Utx-deficient cells showed the lower number of terminally differentiated adipocytes than the control cells did. In contrast, the number of adipocytes was increased when Utx-deficient preadipocytes were differentiated. Microarray analysis showed that c-Myc is responsible for the distinct function of Utx in adipogenesis.
Materials and methods
Targeting Utx in mESCs
The Utx-targeting vector was constructed such that the β-geo cassette was flanked by FRT (flippase recognition target) sequences (black rectangles), and exon 24 of Utx was flanked by loxP sequences (black triangles); a portion of the wild-type murine Utx locus including exon 24 (grey rectangle) and a 0.5 kb SpeI-XhoI fragment are depicted alongside the targeting vector in Fig 1A. The conditional targeting vector was used to generate three independent ES cell lines 129/Ola (a kind gift from Dr. Tak W. Mak, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, Campbell Family Institute for Breast Cancer Research, University Health Network). The β-geo cassette was removed in vitro by expressing a flippase recombinase. Homologous recombination in mESCs was confirmed by Southern blot analysis.
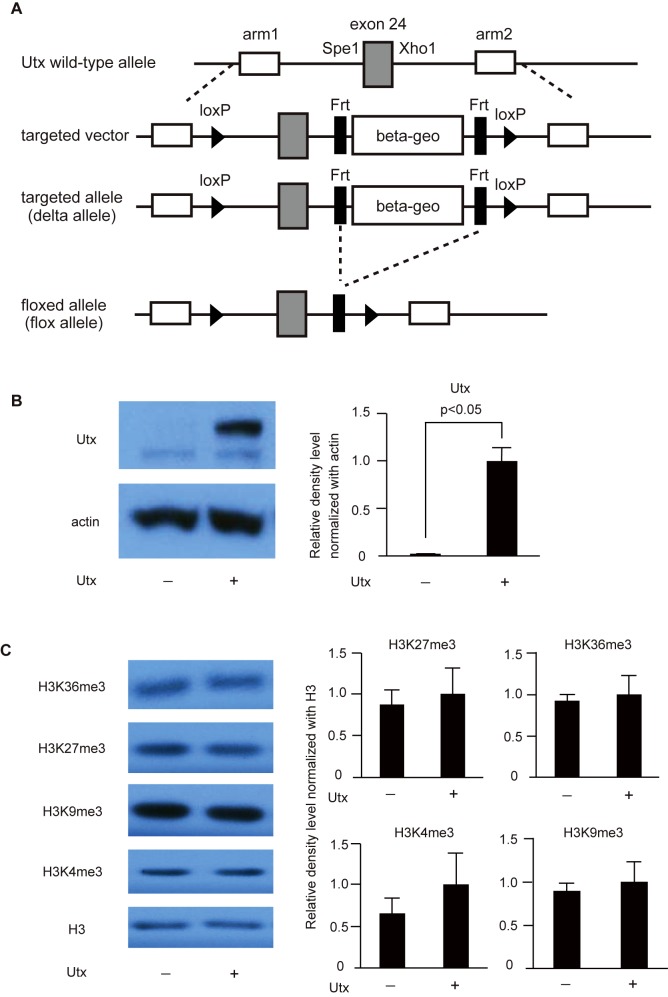
Fig 1. Construction and characterization of Utx-deficient mESCs.
(A) Conditional gene targeting of the murine Utx locus. (B) Immunoblotting for Utx and β-actin in Utx-deficient and control mESCs. A representative result from three independent mESC clones is shown. Band densities of Utx and β-actin were quantified by ImageQuant TL ver. 8.1 and normalized to β-actin. The data are presented relative to the signal of control mESCs. (C) Immunoblotting for H3, H3K4me3, H3K9me3, H3K27me3, and H3K36me3 in mESCs. A representative result from three independent mESC clones is shown. Band density of histones was quantified by ImageQuant TL ver. 8.1 (GE healthcare life sciences, Pittsburgh, PA, USA), and data are shown by the relative value of histone methylations normalized to H3.
The mESCs were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM; Invitrogen, Burlington, ON, Canada) containing 20% fetal bovine serum (Hyclone, GE Healthcare, Amersham, Buckinghamshire, U.K.), leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF; Merck Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany), L-glutamate (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), sodium pyruvate (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), penicillin/streptomycin (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), and 2-β-mercaptoethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) on 0.5% gelatin-coated dishes at 37°C with 5% CO2.
Adipogenic differentiation of mESCs
Differentiation of mESCs was induced using the Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Adipogenesis Kit (SCR100; Merck Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany). In this method, 0.1 μM retinoic acid (RA), 20 nM Triiodothyronine (T3), and 850 nM insulin were used to induce the differentiation to adipocytes [21,22]. After removing feeder cells, 3 × 106 mESCs were cultured in 10 mL embryonic body Formation Medium on a non-adhesive 10 cm Petri dish at 37°C with 10% CO2 for 2 days without LIF. RA (Inducer A Solution) was added to the culture for an additional 3 days to induce efficient differentiation into adipocytes (37°C with 10% CO2). Subsequently, for an additional 21 days, 10–20 EBs were cultured in 1 mL of Adipocyte Differentiation Medium supplemented with T3 and insulin on 0.1% gelatin-coated 24-well plates at 37°C with 10% CO2. For the inhibition of c-Myc, 25 μM 10058-4F (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) was added during differentiation from mESCs to adipocytes.
Culture and differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells to adipocytes
3T3-L1 cells were purchased from ATCC and cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% calf serum (Invitrogen, Burlington, ON, Canada) and penicillin/streptomycin at 37°C with 5% CO2. For adipocyte differentiation, two days after cells grew to confluency in 10% calf serum/DMEM, they were cultured in DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum (Invitrogen, Burlington, ON, Canada), 1 μg/mL insulin (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), 0.5 mM isobutylmethylxanthine (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), and 10 μM dexamethasone (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA). Two days after the culture, cells were cultured with 10% fetal bovine serum/DMEM supplemented with 1 μg/mL insulin. Two days after culturing cells in insulin, to differentiate them to adipocytes, the cells were cultured with 10% fetal bovine serum/DMEM by changing the media every alternate day. For the inhibition of c-Myc, 50 μM 10058-4F was added during adipocyte differentiation.
Lentiviral vector-mediated stable knockdown
The pLKO.1 puro lentiviral vector and control scrambled shRNA were purchased from Addgene (Addgene # 8453 and #1864) (Addgene, Cambridge, MA, USA). The mouse Utx target sequence was cloned into pLKO.1 vector. To generate lentivirus, pLKO.1-Utx with pMD2.G and psPAX2 (Addgene #12259 and #12260) were transfected into HEK293 cells. The target sequence was shown in S1 Table.
Total RNA isolation and qRT-PCR analysis
Total RNA was extracted using the Trizol reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA). First-strand cDNA was synthesized using the iScriptTM cDNA Synthesis Kit (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA), followed by PCR with primers specific for target genes. Quantitative real time-PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed using the Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA), and the data were collected using the ABI Prism 7900HT Fast Real-time PCR system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA). Specificity of the signals was confirmed by a dissociation curve analysis (containing a single peak), followed by electrophoresis of the PCR product. The results are shown as mean mRNA levels normalized to the amount of Actb or Gapdh mRNA ± SE from three independent experiments with three different clones or triplicate of qPCR with one clone as indicated. The primers used in the study were shown in S1 Table.
Immunoblotting assay
Whole cell lysates were prepared with CHAPS lysis buffer supplemented with 40 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 120 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 0.3% CHAPS, 50 mM NaF, 1.5 mM Na3VO4, 10 mM glycerophosphate, 10 mM pyrophosphate, 1 mM PMSF, protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland), and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland). Triton extraction buffer was used to harvest the histones. Triton extraction buffer is composed of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; pH 7.4) containing 0.5% Triton X-100, 5 mM sodium butyrate, and protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland). Lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to a PVDF membrane (Merck Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany). The membranes were blocked in blocking buffer (5% w/v BSA or 5% w/v skim milk, 0.05% v/v Tween-20 in TBS), and subsequently incubated with primary and secondary antibodies in the blocking buffer. ECL blotting reagents (GE Healthcare, Buckinghamshire, UK) were used to detect the immunoreactive proteins. Antibodies recognizing the following proteins were used: Utx (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), β-actin (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Texas, USA), H3 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), H3K4me3 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), H3K9me3 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), H3K27me3 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), and H3K36me3 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK).
Oil Red O staining
Cells were fixed on the tissue culture plate for 10 min with 10% formalin. After fixation, cells were washed twice with PBS and once with 60% isopropanol. Cells were stained with Oil Red O (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) for 15 min and then washed twice with PBS.
Microarray assay
The preparation of total RNA from mESCs and differentiated adipocytes was carried out using the Trizol reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA). Illumina whole mouse genome arrays (Mouse Ref-8 v2 Beadchip) were used for the microarray chip. The microarray analysis, including hybridization and data collection, was performed by Illumina. The transcript assignments were based on the National Center for Biotechnology Information Reference Sequence (NCBI RefSeq) database (Build 36, Release 22). After importing compressed library files, we used the lumi package with default settings from R-Bioconductor for subsequent analyses, including normalization. After calculating the expression ratios before and after adipocyte differentiation, candidate genes with a ratio exceeding four standard deviations (SDs) were selected simultaneously in two different clones. The upregulated or downregulated genes were then analyzed by Ingenuity pathway analysis software (IPA; Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) to predict upstream regulators. Gene set enrichment analyses (GSEA) were performed with a GSEAv2.0 package (http://www.broad.mit.edu/gsea) with the following settings: a signal-to-noise metric for gene ranking, and 1000 permutations of gene sets. We used the established collections of gene sets (c2, c4, c5, and c6) provided by Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB, http://www.broad.mit.edu/gsea/msigdb). The nominal p value for ANOVA analysis was set as p<0.05 and further adjusted by FDR (Step Up, FDR <0.25).
Statistical analysis
All data are presented as mean ± SE. All statistical analyses except the microarray analyses were done using the Student’s t-test or Welch’s correction. A p-value of < 0.05 was considered significant in all tests.
Results
Generation of Utx-deficient mESCs
To examine whether Utx is involved in adipogenesis, we generated Utx-deficient mESCs (Fig 1A). Utx-null female mESCs are unable to differentiate into mesoderm and Utx-null female embryos arrest at E10.5 [16,19]. Male mESCs have one copy of Utx and one copy of a related demethylase, Uty, on the Y-chromosome. Utx-deficient male zygotes survive until birth, demonstrating that Uty can compensate for Utx [15–17]. Therefore, the roles of Utx during adipocyte differentiation can be investigated using Utx-deficient male mESCs. Through expression of the flippase recombinase, we removed the gene-trapping element of the construct, restoring normal expression of the target gene. We generated three independent clones of Utx-deficient mESCs. Endogenous Utx protein expression was mostly undetected in Utx-deficient mESCs, whereas in control mESCs, a band of Utx is detected after expression of flippase (Fig 1B). Consistent with previous reports [16], Utx deficiency did not affect the global levels of H3K4me3, H3K9me3, H3K27me3, or H3K36me3 (Fig 1C, left). To further confirm this, we measured the band density of the histone modifications in three independent clones. The intensity of the bands showed no differences between control and Utx-deficient mESCs (Fig 1C, right). These data confirm that our targeted mESCs showed diminished Utx expression and retained normal levels of lysine modifications in histone H3.
Utx deficiency in mESCs impairs adipocyte differentiation
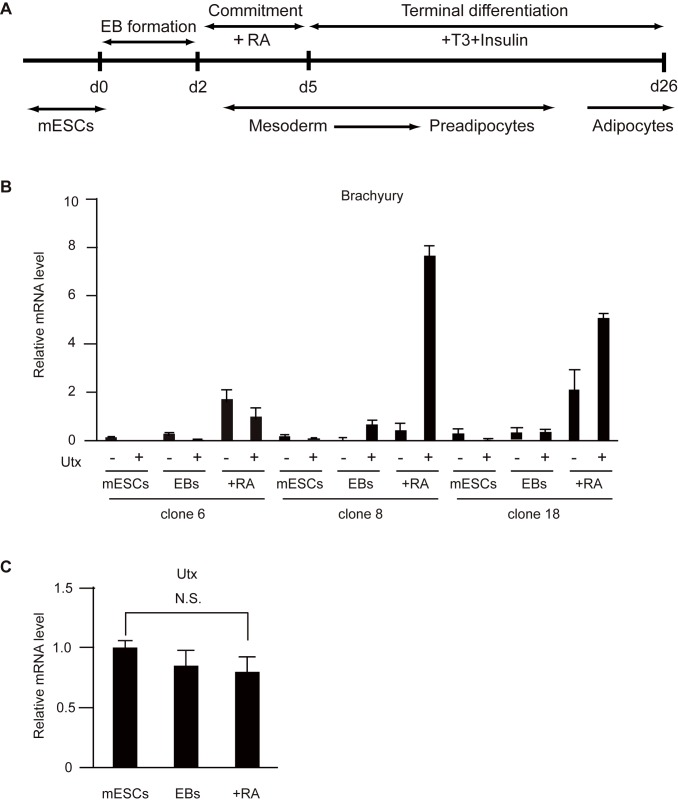
To examine roles of Utx in adipogenesis, we performed adipocyte differentiation assays using control and Utx-deficient mESCs (Fig 2A). As the protocol, we obtained mesoderm with the potential to differentiate into adipocytes, after treatment with RA from day 2 to day 5, to form EBs [21,22]. The levels of Brachyury were evaluated to determine whether our Utx-deficient mESCs could differentiate into mesoderm in EBs (Fig 2B). Depending on the clone, Brachyury was differentially expressed in Utx-deficient EBs compared to that in controls. Our Utx-deficient male mESCs established by gene-trapping show some potential to differentiate into mesoderm because of residual Utx expression in contrast to the previous papers [16,17,23].
Fig 2. Utx-deficient mESCs showed some potential to differentiate into mesoderm.
(A) Scheme of the differentiation assay of mESCs to adipocytes. (B, C) mRNA levels of Brachyury (B), Utx (C) normalized to β-actin in mESCs and adipocytes. The experiments were performed independently with three clones, and the results are expressed as mean ± SE (n = 3); *p<0.05.
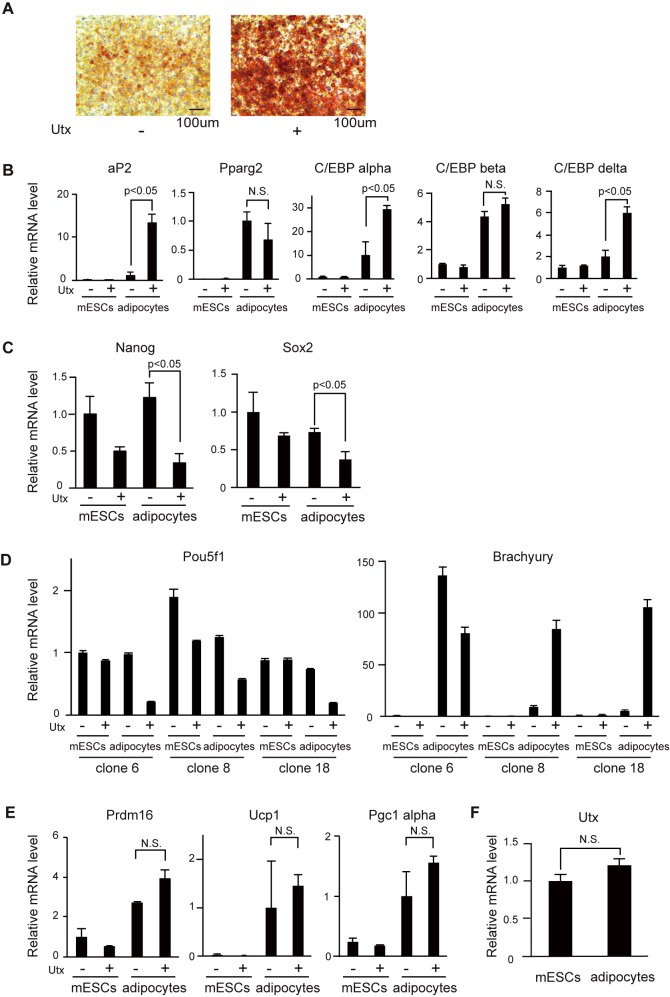
It has not been investigated whether Utx deficiency affects terminal adipocyte differentiation. Because our Utx-deficient mESCs with gene trapping have some potential to induce the genes responsible for mesoderm, induction of adipocytes with insulin and T3 after the RA-induced differentiation was performed. All of the clones of Utx-deficient cells after induction (described as adipocytes) showed a lower number of Oil-red O positive cells (Fig 3A) and decreased expression of the adipocyte marker, aP2 (Fig 3B). The expression levels of C/EBP alpha and C/EBP delta were also significantly lower in Utx-deficient adipocytes (Fig 3B). Pparg2 and C/EBP beta were induced at similar levels in control and Utx-deficient adipocytes (Fig 3B). The expression of Nanog, Sox2, and Pou5f1 was consistently higher in Utx-deficient adipocytes, suggesting that some cells remained undifferentiated in the Utx-deficient cells (Fig 3C and 3D). The expression of Brachyury was differentially induced in Utx-deficient adipocytes depending on the clones (Fig 3D). Recently, Utx has been reported to promote the expressions of genes responsible for thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue [24,25]. In our experiment, Utx deficiency did not affect the expression of Prdm16, Pgc1 alpha, or Ucp1, which are critical for thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue (Fig 3E). During differentiation, Utx expression in adipocytes was comparable to that in mESCs (Fig 3F). Our results indicate that RA-induced differentiation in Utx-deficient cells has lower potential to differentiate to adipocytes, and that Utx is required for adipogenesis during differentiation of mESCs to adipocytes.
Fig 3. Utx-deficient mESCs showed diminished differentiation to adipocytes.
(A) Oil-red O staining of adipocytes. Representative results from three independent mESC clones are shown. (B-F), mRNA levels of aP2, Pparg2, C/EBP alpha, C/EBP beta, C/EBP delta (B); Nanog, Sox2 (C); Pou5f1, Brachyury (D); Prdm16, Ucp1, Pgc1 alpha (E); Utx (F) normalized to β-actin in mESCs and adipocytes. The experiments were performed with three independent clones, and the results are expressed as mean ± SE (n = 3); *p<0.05.
Gene expression profile of control and Utx-deficient cells
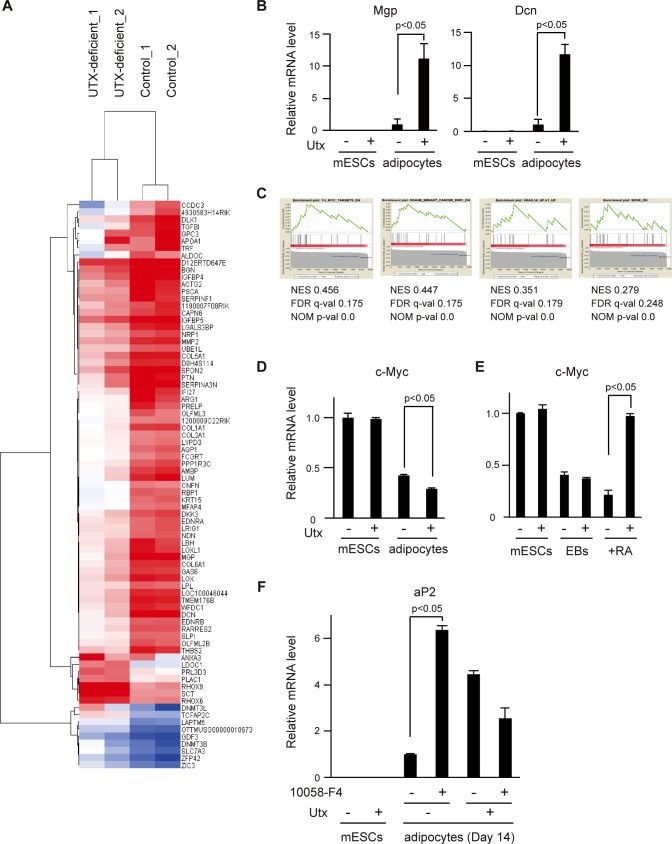
To investigate the genes affected by the loss of Utx, we analyzed gene expression profiles of control and Utx-deficient mESCs and adipocytes. We performed microarray analyses of two different sets of the mESC clones, clone 8 and clone 18. After calculating the expression ratio before and after adipocyte differentiation, candidate genes with a ratio exceeding 4 SD were selected. Both data sets of mESCs and adipocytes were clustered in a heat map and a tree diagram (Fig 4A). The major clusters, including genes upregulated in control cells (63 genes) and those upregulated in Utx-deficient cells (16 genes), are shown in Fig 4A. Validation of the microarray data was performed with qRT-PCR for Mgp and Dcn, the genes with the largest changes in expression between the sets (Fig 4B).
Fig 4. Effects of Utx deficiency on gene expression in mESCs and adipocytes.
(A) Heat map visualizations of the 79 genes that are differentially expressed in Utx-deficient and control mESCs and adipocytes. Two clones were used for each group. Data for the heat maps are normalized using average linkage clustering on entities and represent median-centered log-transformed values. Red and blue correspond to high and low expression, respectively, compared with the experiment-wide median. (B) mRNA levels of Mgp and Dcn normalized to β-actin. The experiments were performed independently with three clones, and the results are expressed as mean ± SE (n = 3); *p<0.05. (C) GSEA enrichment score curves described with two sets of adipocytes from the Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB). The graph at the bottom of each panel represents the ranked, ordered, non-redundant list of genes. Vertical black lines indicate the position of genes from the studied gene set in the ordered, non-redundant data set. The green curve corresponds to the enrichment score (ES) curve, which is the running sum of the weighted enrichment score obtained with the GSEA software. NES, normalized enrichment score: FDR, false discovery rate; NOM, nominal. (D, E) mRNA levels of c-Myc normalized to β-actin in (D) mESC and adipocytes, (E) mESCs, EBs, and RA-induced differentiation. The experiments were performed independently with three clones, and the results are expressed as mean ± SE. (n = 3) *p<0.05. (F) mRNA levels of aP2 normalized to Gapdh in Utx-deficient or control mESCs and adipocytes in the presence of 10058-F4. The representative result is shown as mean ± SE. (n = 3) *p<0.05.
To study the genetic networks regulated by Utx, we performed a pathway analysis on the gene sets exceeding 4 SD with IPA. The gene sets upregulated in Utx-deficient cells suggest that critical genes for pluripotency, such as Nanog, Pou5f1, and Lamtor3, are involved in Utx signaling (S2 Table). The gene sets upregulated in control cells suggest that Htt, α-catenin, and Fas are the most significant upstream regulators of Utx (S3 Table).
We also performed GSEA with the gene sets of adipocytes to find the sets regulated by Utx. This revealed similar gene expression patterns involving c-Myc, ER1, k-Ras, and E1F4E signaling pathways in the data set from Utx-deficient adipocytes (Fig 4C). Both GSEA and IPA analyses suggested increased expression of genes in the Wnt/β-catenin/c-Myc axis, which includes α-catenin and c-Myc [26–29]. First, we examined the expression of c-Myc during the differentiation from mESCs to adipocytes in Utx-deficient and control cells. The expression of c-Myc was significantly upregulated in Utx-deficient adipocytes while the expression of c-Myc was downregulated in Utx-deficient cells after RA-induced differentiation (Fig 4D and 4E). Secondly, to determine whether Utx affects adipogenesis by regulating c-Myc function, we examined adipocyte differentiation of Utx-deficient mESCs with a Myc inhibitor, 10058-F4. The expression level of aP2 was significantly higher in the adipocytes differentiated from Utx-deficient mESCs in the presence of 10058-F4 compared to those in the untreated Utx-deficient adipocytes (Fig 4F). Taken together, our findings indicate that c-Myc plays a significant role in Utx-mediated adipogenesis.
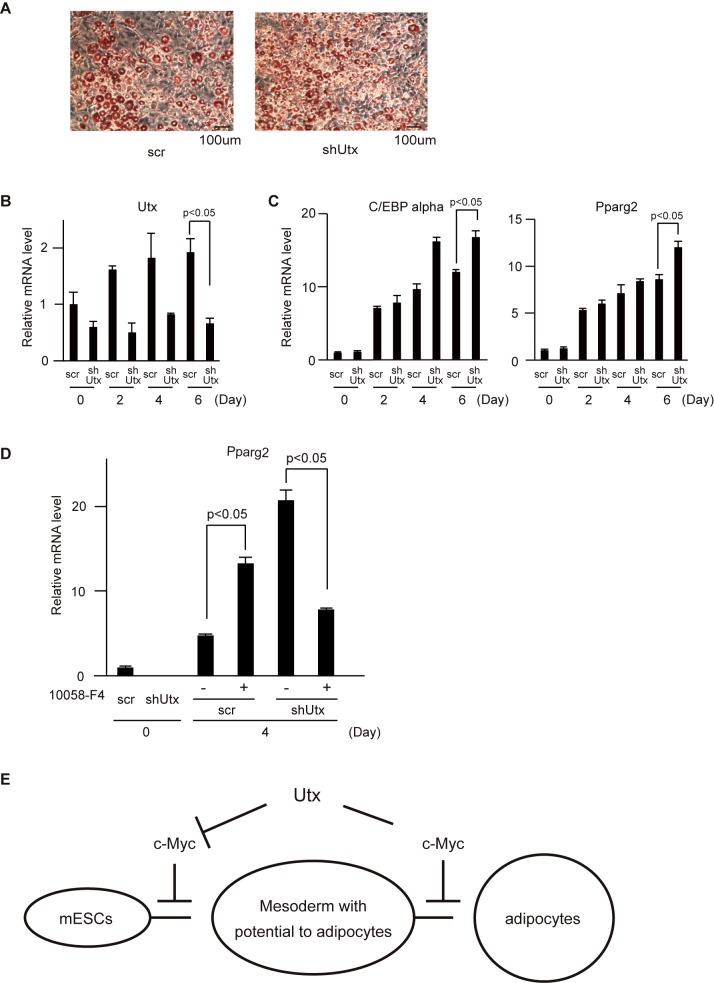
Utx deficiency enhances differentiation of preadipocytes to adipocytes
Differentiation of mESCs to adipocytes involves multiple differentiation steps: formation of mesoderm, mesenchymal lineage, and preadipocytes. In our experiment, each differentiation stage was classified as shown in Fig 2A. Although Utx deficiency resulted in impairment to differentiate to adipocytes, several critical genes for the adipocyte lineage were induced in Utx-deficient adipocytes to levels comparable to those in control cells. In a recent study, Utx deficiency in MSCs resulted in enhanced adipocyte differentiation [20]. Therefore, we hypothesized that Utx functions as a positive or negative regulator, depending on a differentiation stage. To examine whether Utx deficiency enhances or inhibits adipocyte differentiation in preadipocytes, knockdown of Utx was performed in 3T3-L1 cells (preadipocytes) to differentiate them to the white adipocyte lineage. In contrast to mESCs differentiation, Utx depletion in 3T3-L1 cells enhanced adipocyte differentiation (Fig 5A). The efficiency of Utx knockdown was confirmed by qRT-PCR (Fig 5B). The expression of C/EBP alpha and Pparg2 confirmed an enhancement of terminal adipocytes differentiation (Fig 5C). To examine the contribution of c-Myc during differentiation from preadipocytes to adipocytes, we differentiated 3T3-L1 depleted for Utx in the presence of 10058-F4 (Fig 5D). Inhibition of c-Myc in Utx-depleted 3T3-L1 cells resulted in the inhibition of adipocyte differentiation (Fig 5D). In contrast, control 3T3-L1 cells with the Myc inhibitor enhanced adipocyte differentiation (Fig 5D), which is consistent with the previous report [30]. These results indicate that Utx negatively regulates the differentiation of preadipocytes to adipocytes by enhancing activation of c-Myc.
Fig 5. Knockdown of Utx in 3T3-L1 cells resulted in an enhancement of adipocyte differentiation.
(A) Oil-red O staining of adipocytes. Representative results from three independent experiments are shown. mRNA levels of (B) Utx, (C) C/EBP alpha, Pparg2, (D) Pparg2 normalized to β-actin. The experiments were performed independently three times in triplicates and the representative results are shown and expressed as mean ± SE. (n = 3) *p<0.05. (E) Schematic model of Utx during differentiation of mESCs to adipocytes.
Discussion
In this study, we established Utx-deficient mESCs with gene trapping and evaluated their potential to differentiate to adipocytes. Utx-deficient mESCs showed some potential to differentiate to mesoderm. Moreover, Utx-deficient cells after RA-induced differentiation did not differentiate to adipocytes, showing that Utx is required for proper commitment to mesoderm with potential to differentiate to adipocytes. Conversely, Utx knockdown in preadipocytes showed enhanced differentiation to adipocytes. Therefore, Utx differentially regulates adipogenesis depending on the stages of differentiation. Gene expression analysis revealed that c-Myc may be regulated by Utx.
Distinct roles of Utx during adipocyte differentiation
Our results are the first to demonstrate an impairment of adipocyte differentiation in Utx-deficient male mESCs. Utx-deficient male mice can survive over one year, indicating that Utx is dispensable for male mESC development in vivo, despite partial lethality [17]. Although a previous study showed that Utx-deficient male mESCs have mesoderm defects [16,17,23], our results suggest that Utx-deficient mESCs can differentiate to mesoderm (Fig 2B). Recently, Utx deficiency has been reported to induce a subset of critical genes associated with mesoderm differentiation including Brachyury [15,16]. In our Utx-deficient male mESCs, Brachyury was induced though its expression level was dependent on a clone. One possibility is that the time and concentration needed to react with RA to form EBs are critical conditions for mesoderm differentiation because RA inhibits mesoderm differentiation by repressing Brachyury expression [31]. Another possibility is that our Utx-deficient mESCs with gene trapping still express Utx, which could function to induce some of the genes needed for mesoderm differentiation. However, our Utx-deficient mESCs showed impairment to differentiate to adipocyte, consistent with recent studies that Utx is required for proper induction of mesoderm [16,17,23].
In preadipocytes, knockdown of Utx resulted in an enhancement of adipocyte differentiation. The same effect was observed after Utx knockdown in MSCs [20]. Our results uncovered that Utx inhibits adipocyte differentiation after commitment to preadipocytes. In our method, it may be difficult to obtain enough brown adipose cells, as shown previously [32]. We cannot discuss differentiation and function between white adipose cells and brown adipose cells with Utx deficiency, although the genes responsible for thermogenesis were equally induced in Utx-deficient cells as well as control cells (Fig 3D). Collectively, we propose distinct functions of Utx in a differentiation stage-dependent manner (Fig 5E).
Networks of genes and signaling pathways dependent on Utx
Our microarray data analyses have identified potential target genes and signaling pathways regulated by Utx. We focused on the Wnt/β-catenin/c-Myc pathway which involves α-catenin and c-Myc because it is known to be one of the critical pathways of adipocyte differentiation [26–29]. α-catenin counteracts β-catenin, a key component of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway [26,28]. Recently, Utx has been reported to induce Wnt and DKK gene families by removing repressive H3K27me3 marks in endoderm differentiation [33]. The expression profile of c-Myc in differentiation stages of Utx-deficient cells implies that Utx regulates the Wnt signaling pathway during differentiation from mESCs to adipocytes. Furthermore, our experiments with the Myc inhibitor suggest that Utx enhances adipogenesis in mESCs by inhibiting c-Myc and represses adipogenesis in preadipocytes by activating c-Myc (Fig 5E). Since Utx is known to interact with c-Myc [34], we speculate that Utx may modulate transcriptional activation of c-Myc during adipocyte differentiation in a differentiation stage-dependent manner.
Clinical significance
Commitment reflects hyperplasia (cell number) of adipose tissue and is mainly dependent on genetic background, whereas terminal differentiation to adipocytes affects hypertrophy (cell size) of adipose tissue and is mainly dependent on diet [6]. It is reported that adult-onset obesity is mainly caused by hypertrophy, whereas young-onset obesity is due to both hyperplasia and hypertrophy [5]. Because our data showed that Utx promotes commitment from mESCs to mesoderm with potential to adipocytes, Utx may have implications in glucose and fat metabolism in childhood. Additionally, because Utx inhibits the differentiation of preadipocytes to adipocytes, Utx in adipose tissues may reflect potential for adipose tissue development/expansion in adults on diets featuring excess energy intake. With the knowledge of handling and storing of nutrition, the tendency towards obesity and diabetes may be predicted and managed. Further studies using mouse and human samples will verify our hypothesis.
In conclusion, our data indicate that Utx is required for proper differentiation of mESCs to adipocytes. By identifying Utx target genes at different developmental stages during adipocyte differentiation, it may be possible to treat metabolic syndromes and improve the outcomes of their associated diseases.
Supporting information
(DOC)
(XLS)
(XLS)
Acknowledgments
We thank Masato Sasaki (Tohoku Medical and Pharmaceutical University) for helpful advice and reagents. We are grateful to Kazuhiko Igarashi and Ari Itoh-Nakadai (Tohoku University) for providing the IPA software. We would also like to thank the present and former laboratory members, Takeshi Ueda, Juntaro Ikura, Kayoko Saso, Dong-Ok Son, Changkeun Kang, and Mamiko Shimizu, for discussion and technical support.
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by a CIHR grant (MOP84353), the MEXT-Support Program for the Strategic Research Foundation at Private Universities, and by the KAO Research Council for the Study of Healthcare Science. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Hossain P, Kawar B, El Nahas M. Obesity and diabetes in the developing world—a growing challenge. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356: 213–15. 10.1056/NEJMp068177 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Popkin BM, Gordon-Larsen P. The nutrition transition: worldwide obesity dynamics and their determinants. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004; 28 Suppl 3: S2–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kopelman PG. Obesity as a medical problem. Nature. 2000; 404: 635–43. 10.1038/35007508 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Despres JP, Lemieux I. Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature. 2006; 444: 881–7. 10.1038/nature05488 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kissebah AH, Krakower GR. Regional adiposity and morbidity. Physiol Rev. 1994; 74: 761–811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jo J, Gavrilova O, Pack S, Jou W, Mullen S, Sumner AE, et al. Hypertrophy and/or Hyperplasia: Dynamics of Adipose Tissue Growth. PLoS Comput Biol. 2009; 5: e1000324 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000324 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rosen ED, Spiegelman BM. Adipocytes as regulators of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Nature. 2006; 444: 847–53. 10.1038/nature05483 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Phillips BW, Vernochet C, Dani C. Differentiation of embryonic stem cells for pharmacological studies on adipose cells. Pharmacol Res. 2003; 47: 263–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gut P, Verdin E. The nexus of chromatin regulation and intermediary metabolism. Nature. 2013; 502: 489–98. 10.1038/nature12752 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Okamura M, Inagaki T, Tanaka T, Sakai J. Role of histone methylation and demethylation in adipogenesis and obesity. Organogenesis. 2010; 6: 24–32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hong S, Cho YW, Yu LR, Yu H, Veenstra TD, Ge K. Identification of JmjC domain-containing UTX and JMJD3 as histone H3 lysine 27 demethylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104: 18439–44. 10.1073/pnas.0707292104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lan F, Bayliss PE, Rinn JL, Whetstine JR, Wang JK, Chen S, et al. A histone H3 lysine 27 demethylase regulates animal posterior development. Nature. 2007; 449: 689–94. 10.1038/nature06192 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lee MG, Villa R, Trojer P, Norman J, Yan KP, Reinberg D, et al. Demethylation of H3K27 regulates polycomb recruitment and H2A ubiquitination. Science. 2007; 318: 447–50. 10.1126/science.1149042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Agger K, Cloos PA, Christensen J, Pasini D, Rose S, Rappsilber J, et al. UTX and JMJD3 are histone H3K27 demethylases involved in HOX gene regulation and development. Nature. 2007; 449: 731–4. 10.1038/nature06145 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shpargel KB, Sengoku T, Yokoyama S, Magnuson T. UTX and UTY demonstrate histone demethylase-independent function in mouse embryonic development. PLoS Genet. 2012; 8: e1002964 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002964 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wang C, Lee JE, Cho YW, Xiao Y, Jin Q, Liu C, et al. UTX regulates mesoderm differentiation of embryonic stem cells independent of H3K27 demethylase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012; 109: 15324–9. 10.1073/pnas.1204166109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Welstead GG, Creyghton MP, Bilodeau S, Cheng AW, Markoulaki S, Young RA, et al. X-linked H3K27me3 demethylase Utx is required for embryonic development in a sex-specific manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012; 109: 13004–9. 10.1073/pnas.1210787109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mansour AA, Gafni O, Weinberger L, Zviran A, Ayyash M, Rais Y, et al. The H3K27 demethylase Utx regulates somatic and germ cell epigenetic reprogramming. Nature. 2012; 488: 409–13. 10.1038/nature11272 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lee S, Lee JW, Lee SK. UTX, a histone H3-lysine 27 demethylase, acts as a critical switch to activate the cardiac developmental program. Dev Cell. 2012; 22: 25–37. 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.11.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hemming S, Cakouros D, Isenmann S, Cooper L, Menicanin D, Zannettino A, et al. EZH2 and KDM6A act as an epigenetic switch to regulate mesenchymal stem cell lineage specification. Stem Cells. 2014; 32: 802–815. 10.1002/stem.1573 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bost F, Caron L, Marchetti I, Dani C, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Binétruy B. Retinoic acid activation of the ERK pathway is required for embryonic stem cell commitment into the adipocyte lineage. Biochem J. 2002; 361: 621–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dani C, Smith AG, Dessolin S, Leroy P, Staccini L, Villageois P, et al. Differentiation of embryonic stem cells into adipocytes in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1997; 110 (Pt 11): 1279–85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Morales Torres C, Laugesen A, Helin K. Utx is required for proper induction of ectoderm and mesoderm during differentiation of embryonic stem cells. PLoS One. 2013; 8: e60020 10.1371/journal.pone.0060020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zha L, Li F, Wu R, Artinian L, Rehder V, Yu L, et al. The Histone Demethylase UTX Promotes Brown Adipocyte Thermogenic Program Via Coordinated Regulation of H3K27 Demethylation and Acetylation. J Biol Chem. 2015; 290: 25151–63. 10.1074/jbc.M115.662650 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li F, Wu R, Cui X, Zha L, Yu L, Shi H, et al. Histone Deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) Negatively Regulates Thermogenic Program in Brown Adipocytes via Coordinated Regulation of Histone H3 Lysine 27 (H3K27) Deacetylation and Methylation. J Biol Chem. 2016; 291: 4523–36. 10.1074/jbc.M115.677930 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hwang SG, Yu SS, Ryu JH, Jeon HB, Yoo YJ, Eom SH, et al. Regulation of beta-catenin signaling and maintenance of chondrocyte differentiation by ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation of alpha-catenin. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280: 12758–65. 10.1074/jbc.M413367200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Nelson WJ, Nusse R. Convergence of Wnt, beta-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science. 2004; 303: 1483–7. 10.1126/science.1094291 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Piedra J, Miravet S, Castano J, Palmer HG, Heisterkamp N, García de Herreros A, et al. p120 Catenin-associated Fer and Fyn tyrosine kinases regulate beta-catenin Tyr-142 phosphorylation and beta-catenin-alpha-catenin Interaction. Mol Cell Biol. 2003; 23: 2287–97. 10.1128/MCB.23.7.2287-2297.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H, Zawel L, da Costa LT, et al. Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science. 1998; 281: 1509–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Heath VJ, Gillespie DA, Crouch DH. Inhibition of the terminal stages of adipocyte differentiation by cMyc. Exp Cell Res. 2000; 254: 91–8. 10.1006/excr.1999.4736 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Martin BL, Kimelman D. Brachyury establishes the embryonic mesodermal progenitor niche. Genes Dev. 2010; 24: 2778–83. 10.1101/gad.1962910 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dani C. Embryonic stem cell-derived adipogenesis. Cells Tissues Organs. 1999; 165: 173–80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Jiang W, Wang J, Zhang Y. Histone H3K27me3 demethylases KDM6A and KDM6B modulate definitive endoderm differentiation from human ESCs by regulating WNT signaling pathway. Cell Res. 2013; 23: 122–30. 10.1038/cr.2012.119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Choi HJ, Park JH, Park M, Won HY, Joo HS, Lee CH, et al. UTX inhibits EMT-induced breast CSC properties by epigenetic repression of EMT genes in cooperation with LSD1 and HDAC1. EMBO Rep. 2015; 16: 1288–98. 10.15252/embr.201540244 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(DOC)
(XLS)
(XLS)
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.