Abstract
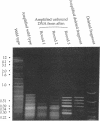
We have developed a technique, called genomic subtraction, for isolating the DNA that is absent in deletion mutants. The method removes from wild-type DNA the sequences that are present in both the wild-type and the deletion mutant genomes. The DNA that corresponds to the deleted region remains. Enrichment for the deleted sequences is achieved by allowing a mixture of denatured wild-type and biotinylated mutant DNA to reassociate. After reassociation, the biotinylated sequences are removed by binding to avidin-coated beads. This subtraction process is then repeated several times. In each cycle we hybridize the unbound wild-type DNA from the previous round with fresh biotinylated deletion mutant DNA. The unbound DNA from the final cycle is ligated to adaptors and amplified by using one strand of the adaptor as a primer in the polymerase chain reaction. The amplified sequences can then be used to probe a genomic library. We applied genomic subtraction to a yeast strain that has a 5-kilobase deletion, corresponding to 1/4000th of the genome. In the experiment reported here, three rounds of subtraction were sufficient to accurately identify genomic clones containing sequences that are missing in the deletion mutant. We discuss the limitations and some potential applications of the method.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bautz E. K., Reilly E. Gene-specific messenger RNA: isolation by the deletion method. Science. 1966 Jan 21;151(3708):328–330. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3708.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjourson A. J., Cooper J. E. Isolation of Rhizobium loti Strain-Specific DNA Sequences by Subtraction Hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2852–2855. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2852-2855.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coté B., Bender W., Curtis D., Chovnick A. Molecular mapping of the rosy locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1986 Apr;112(4):769–783. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.4.769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasher M. S., Pintel D., Ward D. C. Rapid enrichment of HeLa transcription factors IIIB and IIIC by using affinity chromatography based on avidin-biotin interactions. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3117–3127. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley M. R., Mims I. P., Farnet C. M., Dicharry S. A., Lee W. R. Molecular analysis of X-ray-induced alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) null mutations in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1985 Feb;109(2):365–377. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.2.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Whole genome PCR: application to the identification of sequences bound by gene regulatory proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3645–3653. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Middlesworth W., Ochs H. D., Latt S. A. Specific cloning of DNA fragments absent from the DNA of a male patient with an X chromosome deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4778–4782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamar E. E., Palmer E. Y-encoded, species-specific DNA in mice: evidence that the Y chromosome exists in two polymorphic forms in inbred strains. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90312-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Lesko J. G., Lewis R. A., Ledbetter S. A., Ledbetter D. H. Isolation of anonymous DNA sequences from within a submicroscopic X chromosomal deletion in a patient with choroideremia, deafness, and mental retardation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6521–6525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon J. T., Liljestrand-Golden C. A., Dusenbery R. L., Smith P. D. Molecular Analysis of Diepoxybutane-Induced Mutations at the rosy Locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1987 Feb;115(2):323–331. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell L. B., Hunsicker P. R., Cacheiro N. L., Bangham J. W., Russell W. L., Shelby M. D. Chlorambucil effectively induces deletion mutations in mouse germ cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3704–3708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvänen A. C., Bengtström M., Tenhunen J., Söderlund H. Quantification of polymerase chain reaction products by affinity-based hybrid collection. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11327–11338. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welcher A. A., Torres A. R., Ward D. C. Selective enrichment of specific DNA, cDNA and RNA sequences using biotinylated probes, avidin and copper-chelate agarose. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):10027–10044. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.10027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]