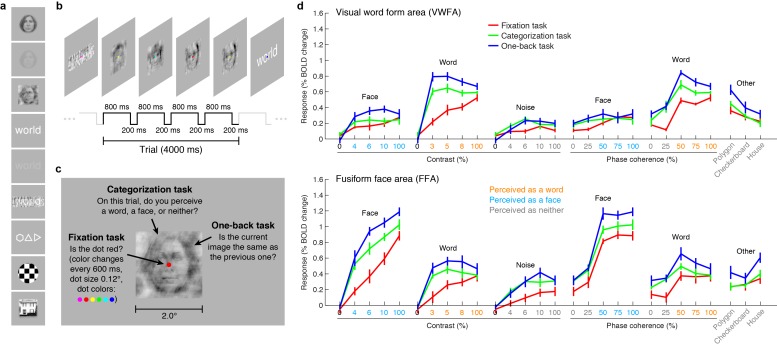
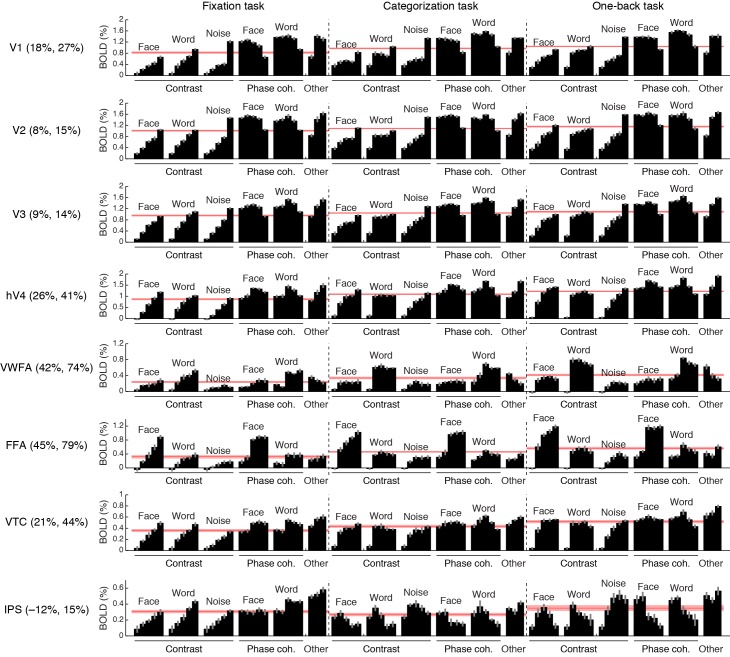
Figure 1. VTC responses depend on both stimulus properties and cognitive task.
(a) Stimuli. Stimuli included faces, words, and noise patterns presented at different contrasts and phase-coherence levels, as well as full-contrast polygons, checkerboards, and houses. (b) Trial design. Each trial consisted of four images drawn from the same stimulus type. (c) Tasks. On a given trial, subjects performed one of three tasks. (d) Evoked responses in VWFA (top) and FFA (bottom) for different stimuli and tasks. Color of x-axis label indicates the perceived stimulus category as reported by the subjects. Error bars indicate bootstrapped 68% CIs.