Abstract
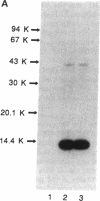
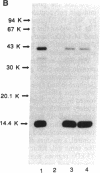
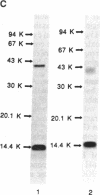
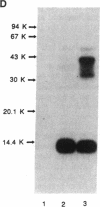
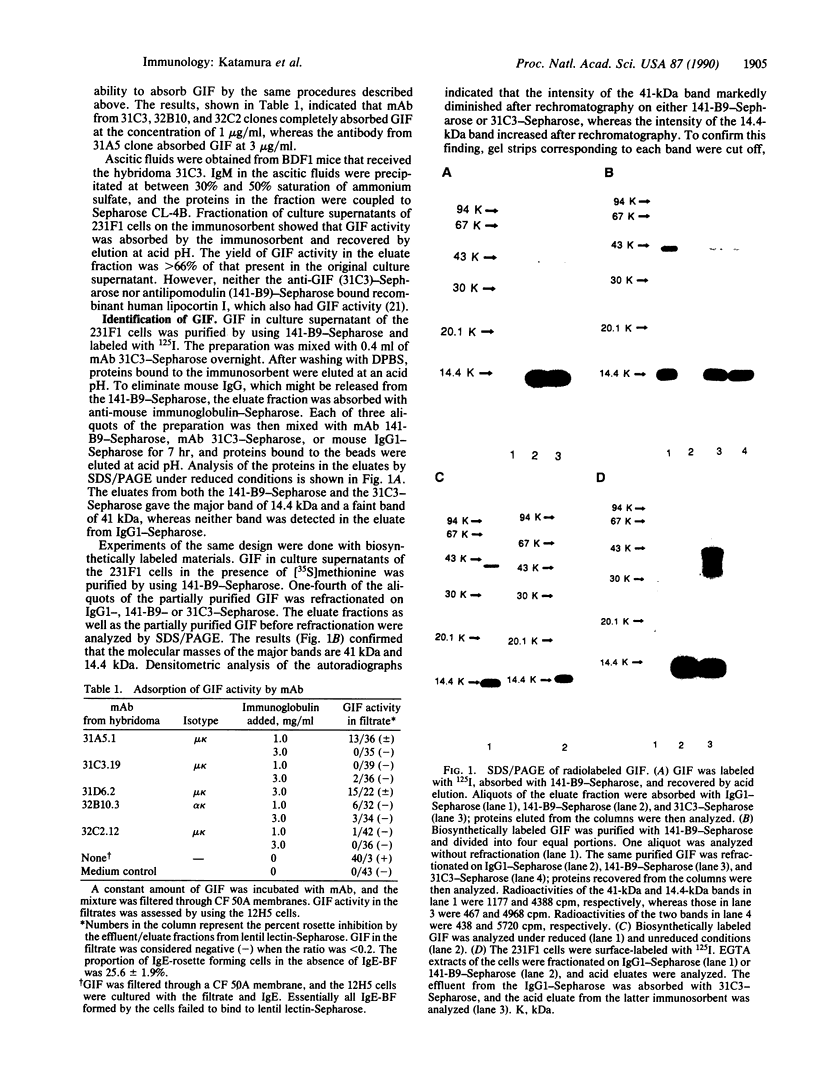
Rat monoclonal antibody against mouse glycosylation inhibiting factors was obtained, and radiolabeled glycosylation inhibiting factors from the mouse T-cell hybridoma, 231F1 cells, were purified by using the monoclonal antibody and antilipomodulin antibody. Analysis of the affinity-purified lymphokine by PAGE demonstrated two proteins of 14.4 kDa and 41 kDa. Both proteins migrated similarly under the reduced and unreduced conditions, indicating that each of the two species consist of a single polypeptide chain. Biologic activity of the lymphokine was recovered by extraction of the proteins from gel slices followed by renaturation. Evidence was obtained that suggested the 14.4-kDa peptide was a degradation product of the 41-kDa molecules. The 14.4-kDa peptide was also recovered by extraction of the surface-labeled 231F1 cells with Ca2+ chelator, indicating that the glycosylation inhibiting factor is associated with the cell surface.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akasaki M., Jardieu P., Ishizaka K. Immunosuppressive effects of glycosylation inhibiting factor on the IgE and IgG antibody response. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3172–3179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman K. D., Cone R. E. Production and purification of monoclonal T lymphocyte antigen binding molecules (TABM). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 14;125(2):475–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90565-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad D. H., Froese A. Characterization of the target cell receptor for IgE. II. Polyacrylamide gel analysis of the surface IgE receptor from normal rat mast cells and from rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):319–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Parker C. W., Kulczycki A., Jr Characterization of the IgE receptor isolated from human basophils. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2283–2291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Tizard R., Burne C., Frey A., Hession C., McGray P., Sinclair L. K., Chow E. P. Two human 35 kd inhibitors of phospholipase A2 are related to substrates of pp60v-src and of the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90736-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K. Regulation of IgE synthesis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:159–182. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata M., Adachi M., Ishizaka K. Antigen-specific T cells that form IgE-potentiating factor, IgG-potentiating factor, and antigen-specific glycosylation-enhancing factor on antigenic stimulation. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2534–2542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata M., Huff T. F., Ishizaka K. Modulation of the biologic activities of IgE-binding factor. V. The role of glycosylation-enhancing factor and glycosylation-inhibiting factor in determining the nature of IgE-binding factors. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1286–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata M., Ishizaka K. Construction of antigen-specific suppressor T cell hybridomas from spleen cells of mice primed for the persistent IgE antibody formation. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3270–3277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardieu P., Akasaki M., Ishizaka K. Carrier-specific suppression of antibody responses by antigen-specific glycosylation-inhibiting factors. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1494–1501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardieu P., Uede T., Ishizaka K. Presence of an antigen-specific T cell subset that forms IgE-suppressive factor and IgG-suppressive factor on antigenic stimulation. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):922–929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno H., Iwata M., Nakamura T., Ishizaka K. Effect of phospholipase A2 inhibitors on mouse T lymphocytes. I. Phospholipase A2 inhibitors exert similar immunological activities as glycosylation inhibiting factor. Int Immunol. 1989;1(4):425–433. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.4.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Sinclair L. K., Browning J. L., Mattaliano R. J., Smart J. E., Chow E. P., Falbel T., Ribolini A., Garwin J. L., Wallner B. P. Purification and partial sequence analysis of a 37-kDa protein that inhibits phospholipase A2 activity from rat peritoneal exudates. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4239–4246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Tizard R., Mattaliano R. J., Sinclair L. K., Miller G. T., Browning J. L., Chow E. P., Burne C., Huang K. S., Pratt D. Five distinct calcium and phospholipid binding proteins share homology with lipocortin I. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10799–10811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito T., Taniguchi M. Chemical features of an antigen-specific suppressor T cell factor composed of two polypeptide chains. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1984;1(3):137–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., Tack B. F., Kristensen T., Glenney J. R., Jr, Hunter T. The cDNA sequence for the protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36 (calpactin I heavy chain) reveals a multidomain protein with internal repeats. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90737-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele J. K., Kuchroo V. K., Kawasaki H., Jayaraman S., Iwata M., Ishizaka K., Dorf M. E. A monoclonal antibody raised to lipomodulin recognizes T suppressor factors in two independent hapten-specific suppressor networks. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2213–2220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turck C. W., Kapp J. A., Webb D. R. Structural analyses of a monoclonal heterodimeric suppressor factor specific for L-glutamic acid60-L-alanine30-L-tyrosine10. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1904–1909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uede T., Hirata F., Hirashima M., Ishizaka K. Modulation of the biologic activities of IgE-binding factors. I. Identification of glycosylation-inhibiting factor as a fragment of lipomodulin. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):878–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Hession C., Cate R. L., Tizard R., Sinclair L. K., Foeller C., Chow E. P., Browing J. L., Ramachandran K. L. Cloning and expression of human lipocortin, a phospholipase A2 inhibitor with potential anti-inflammatory activity. Nature. 1986 Mar 6;320(6057):77–81. doi: 10.1038/320077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yodoi J., Ishizaka K. Lymphocytes bearing Fc receptors for IgE. IV. Formation of IgE-binding factor by rat T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1322–1329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]