Abstract
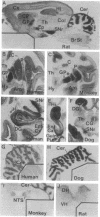
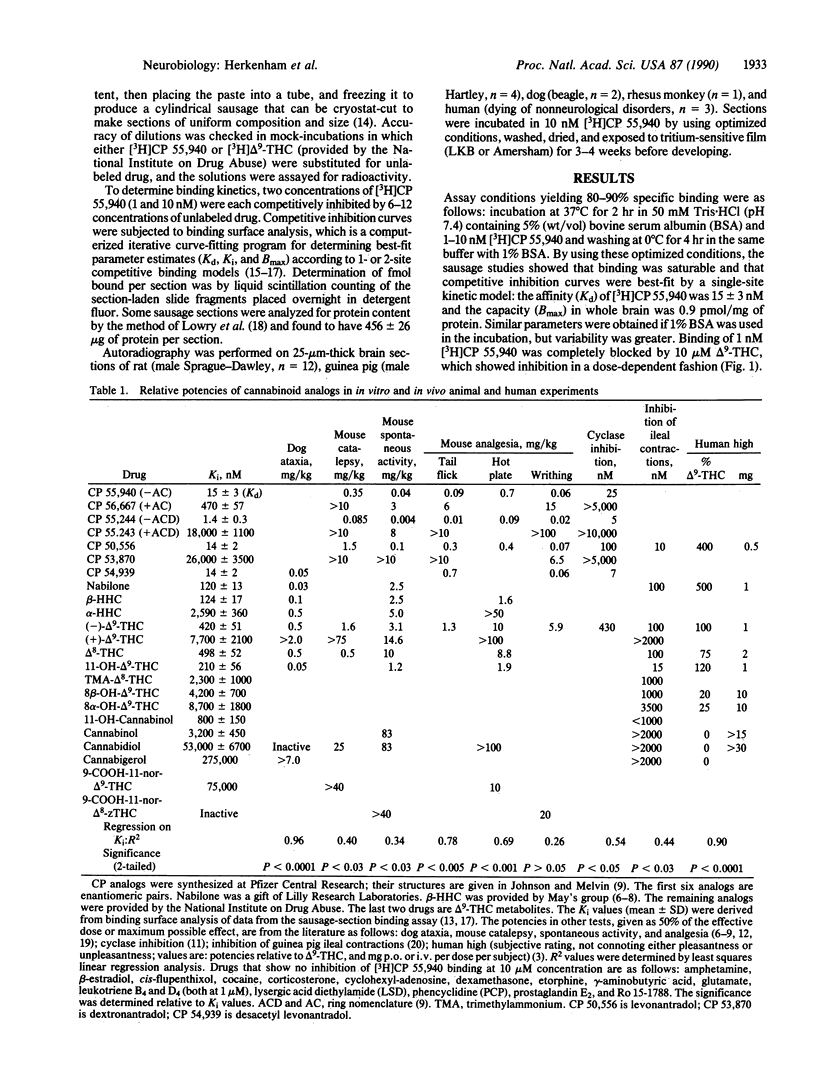
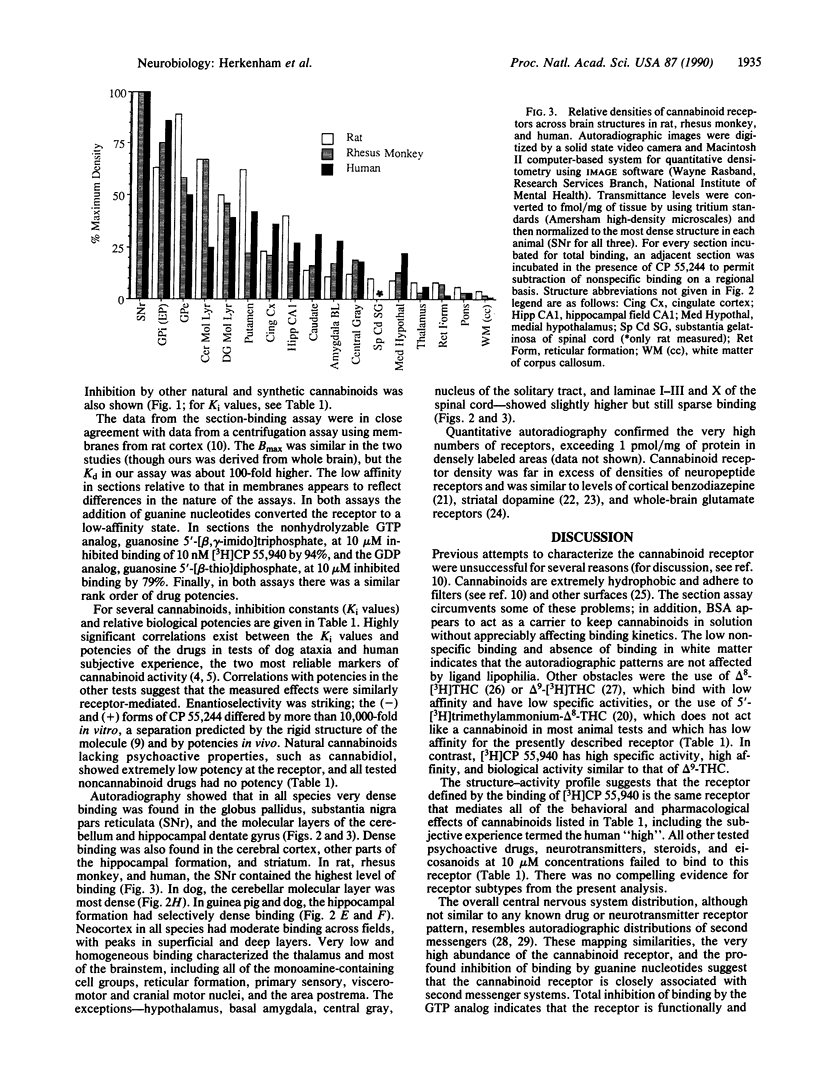
[3H]CP 55,940, a radiolabeled synthetic cannabinoid, which is 10-100 times more potent in vivo than delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol, was used to characterize and localize a specific cannabinoid receptor in brain sections. The potencies of a series of natural and synthetic cannabinoids as competitors of [3H]CP 55,940 binding correlated closely with their relative potencies in several biological assays, suggesting that the receptor characterized in our in vitro assay is the same receptor that mediates behavioral and pharmacological effects of cannabinoids, including human subjective experience. Autoradiography of cannabinoid receptors in brain sections from several mammalian species, including human, reveals a unique and conserved distribution; binding is most dense in outflow nuclei of the basal ganglia--the substantia nigra pars reticulata and globus pallidus--and in the hippocampus and cerebellum. Generally high densities in forebrain and cerebellum implicate roles for cannabinoids in cognition and movement. Sparse densities in lower brainstem areas controlling cardiovascular and respiratory functions may explain why high doses of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol are not lethal.
Full text
PDF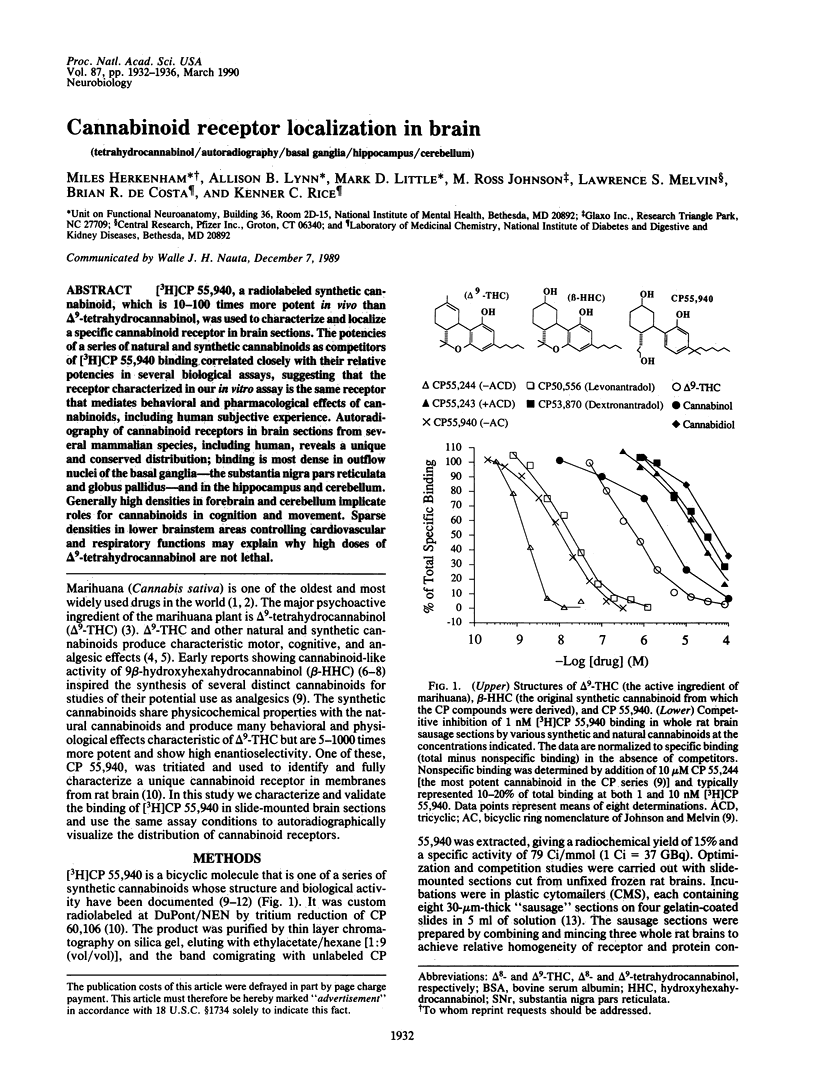


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aigner T. G. Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol impairs visual recognition memory but not discrimination learning in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1988;95(4):507–511. doi: 10.1007/BF00172964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyson S. J., McGonigle P., Molinoff P. B. Quantitative autoradiographic localization of the D1 and D2 subtypes of dopamine receptors in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1986 Nov;6(11):3177–3188. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-11-03177.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein S. H., Hull K., Hunter S. A., Latham V. Cannabinoids and pain responses: a possible role for prostaglandins. FASEB J. 1988 Nov;2(14):3022–3026. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.14.2846397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. A., Foster T. C., Hampson R. E., Deadwyler S. A. Effects of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol on sensory-evoked discharges of granule cells in the dentate gyrus of behaving rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Dec;239(3):941–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifford D. B. Tetrahydrocannabinol for tremor in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1983 Jun;13(6):669–671. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devane W. A., Dysarz F. A., 3rd, Johnson M. R., Melvin L. S., Howlett A. C. Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;34(5):605–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewey W. L. Cannabinoid pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1986 Jun;38(2):151–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Chiara G., Imperato A. Drugs abused by humans preferentially increase synaptic dopamine concentrations in the mesolimbic system of freely moving rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5274–5278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas R. J. The hippocampus and behavior. Psychol Bull. 1967 Jun;67(6):416–422. doi: 10.1037/h0024599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichenbaum H., Cohen N. J. Representation in the hippocampus: what do hippocampal neurons code? Trends Neurosci. 1988 Jun;11(6):244–248. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner E. L., Paredes W., Smith D., Donner A., Milling C., Cohen D., Morrison D. Facilitation of brain stimulation reward by delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1988;96(1):142–144. doi: 10.1007/BF02431546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett E. R., Hunt C. A. Physiochemical properties, solubility, and protein binding of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol. J Pharm Sci. 1974 Jul;63(7):1056–1064. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600630705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenamyre J. T., Young A. B., Penney J. B. Quantitative autoradiographic distribution of L-[3H]glutamate-binding sites in rat central nervous system. J Neurosci. 1984 Aug;4(8):2133–2144. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-08-02133.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris L. S., Carchman R. A., Martin B. R. Evidence for the existence of specific cannabinoid binding sites. Life Sci. 1978 Apr 3;22(13-15):1131–1137. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollister L. E. Health aspects of cannabis. Pharmacol Rev. 1986 Mar;38(1):1–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooker W. D., Jones R. T. Increased susceptibility to memory intrusions and the Stroop interference effect during acute marijuana intoxication. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1987;91(1):20–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00690920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett A. C., Johnson M. R., Melvin L. S., Milne G. M. Nonclassical cannabinoid analgetics inhibit adenylate cyclase: development of a cannabinoid receptor model. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;33(3):297–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornetsky C. Brain-stimulation reward: a model for the neuronal bases for drug-induced euphoria. NIDA Res Monogr. 1985;62:30–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little P. J., Compton D. R., Johnson M. R., Melvin L. S., Martin B. R. Pharmacology and stereoselectivity of structurally novel cannabinoids in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Dec;247(3):1046–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGonigle P., Neve K. A., Molinoff P. B. A quantitative method of analyzing the interaction of slightly selective radioligands with multiple receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Oct;30(4):329–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. L., Branconnier R. J. Cannabis: effects on memory and the cholinergic limbic system. Psychol Bull. 1983 May;93(3):441–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng Cheong Ton J. M., Gerhardt G. A., Friedemann M., Etgen A. M., Rose G. M., Sharpless N. S., Gardner E. L. The effects of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol on potassium-evoked release of dopamine in the rat caudate nucleus: an in vivo electrochemical and in vivo microdialysis study. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 7;451(1-2):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90749-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. S., Seltzman H. H., Pitt C. G., Snyder S. H. High-affinity cannabinoid binding sites in brain membranes labeled with [3H]-5'-trimethylammonium delta 8-tetrahydrocannabinol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Sep;234(3):784–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petro D. J., Ellenberger C., Jr Treatment of human spasticity with delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol. J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Aug-Sep;21(8-9):413S–416S. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1981.tb02621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razdan R. K. Structure-activity relationships in cannabinoids. Pharmacol Rev. 1986 Jun;38(2):75–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richfield E. K., Young A. B., Penney J. B. Properties of D2 dopamine receptor autoradiography: high percentage of high-affinity agonist sites and increased nucleotide sensitivity in tissue sections. Brain Res. 1986 Sep 24;383(1-2):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S. H., Williams P. J. The non-specific membrane binding properties of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and the effects of various solubilizers. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1979 Apr;31(4):224–230. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1979.tb13484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman R. B. Binding surface analysis: an intuitive yet quantitative method for the design and analysis of ligand binding studies. Alcohol Drug Res. 1985;6(5):309–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman R. B., Long J. B., Bykov V., Jacobson A. E., Rice K. C., Holaday J. W. beta-FNA binds irreversibly to the opiate receptor complex: in vivo and in vitro evidence. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Nov;247(2):405–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman R. B., Schumacher U. K., Pert C. B. Binding of radiolabeled opiates to slide-mounted sections of molded minced rat brain: a novel method for conducting radioreceptor assays. Neuropeptides. 1983 Oct;3(6):493–499. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(83)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze G. E., McMillan D. E., Bailey J. R., Scallet A., Ali S. F., Slikker W., Jr, Paule M. G. Acute effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol in rhesus monkeys as measured by performance in a battery of complex operant tests. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Apr;245(1):178–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark P., Dews P. B. Cannabinoids. I. Behavioral effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Jul;214(1):124–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. S., May E. L. 9-Nor-9-hydroxyhexahydrocannabinols. Synthesis, Some behavioral and analgesic properties, and comparison with the tetrahydrocannabinols. J Med Chem. 1976 Sep;19(9):1165–1167. doi: 10.1021/jm00231a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. S., May E. L. Analgesic properties of the tetrahydrocannabinols, their metabolites, and analogs. J Med Chem. 1975 Jul;18(7):700–703. doi: 10.1021/jm00241a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. S., May E. L., Dewey W. L. Some 9-hydroxycannabinoid-like compounds. Synthesis and evaluation of analgesic and behavioral properties. J Med Chem. 1979 Jul;22(7):886–888. doi: 10.1021/jm00193a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., De Souza E. B., Snyder S. H. Mapping second messenger systems in the brain: differential localizations of adenylate cyclase and protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4053–4057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H. Heterogeneous localization of protein kinase C in rat brain: autoradiographic analysis of phorbol ester receptor binding. J Neurosci. 1986 Jan;6(1):199–207. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-01-00199.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zezula J., Cortés R., Probst A., Palacios J. M. Benzodiazepine receptor sites in the human brain: autoradiographic mapping. Neuroscience. 1988 Jun;25(3):771–795. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]