Abstract
Aims
Admission hyperglycemia is associated with increased mortality and major adverse cardiac events (MACE) in patients with or without diabetes mellitus after acute myocardial infarction (AMI). However, effects of glycemic variability (GV) on outcomes of non-diabetes patients with AMI still remains unclear. The aim of this study is to compare the prognostic value of in-hospital GV with admission blood glucose (ABG) for 3-month MACE in non-diabetes patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Methods
We analyzed 256 non-diabetes patients with STEMI in study. The GV accessed by mean amplitude of glycemic excursions (MAGE) was calculated from blood glucose profiles of continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) during hospitalization. ABG was measured on admission. Main endpoints were 3-month MACE; secondary endpoints were GRACE scores and enzymatic infarct size. Predictive effects of MAGE and ABG on the MACE in patients were analyzed.
Results
In all participants, MAGE level was associated with ABG level (r = 0.242, p < 0.001). Both elevated MAGE levels (p = 0.001) and elevated ABG (p = 0.046) were associated with incidences of short-term MACE. Patients with a higher MAGE level had a significantly higher cardiac mortality (5.8 vs. 0.6%, p = 0.017) and incidence of acute heart failure (12.8 vs. 2.4%, p = 0.001) during 3 months follow-up. In multivariable analysis, high MAGE level (HR 2.165, p = 0.023) was significantly associated with incidence of short-term MACE, but ABG (HR 1.632, p = 0.184) was not. The area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve for MAGE (0.690, p < 0.001) was superior to that for ABG (0.581, p = 0.076).
Conclusions
To compare with ABG, in-hospital GV may be a more important predictor of short-term MACE and mortality in non-diabetes patients with STEMI treated with PCI.
Keywords: Glycemic variability, Admission blood glucose, Acute myocardial infarction, Major adverse cardiac events
Background
Acute hyperglycemia on admission is common in non-diabetes patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI), and is a risk factor for increased mortality and in-hospital adverse outcomes [1, 2]. It has shown that high admission blood glucose (ABG) levels are associated with increased mortality after AMI [3, 4]. However, recent studies have shown that glycemic variability (GV) may be of prognostic value with regard to future cardiovascular events [5, 6]. Some studies showed that glucose fluctuations could play a deleterious role through the activation of oxidative stress, one of the key pathophysiological mechanisms for the development of cardiovascular complications [7, 8]. However, whether GV has the important prognostic significance of short-term major adverse cardiac events (MACE) in non-diabetes patients is unknown. In this study, we investigated the independent prognostic value of the in-hospital GV and ABG levels in patients without known diabetes mellitus who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
Methods
Study population
This was a single-center, prospective follow-up study. 265 non-diabetes patients with STEMI who underwent PCI had baseline clinical and laboratory studies, including the Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) risk scores [9], the mean amplitude of glycemic excursions (MAGE) and ABG levels (All patients’ ABG level is less than 16.7 mmol/L). STEMI was defined as complaints of chest pain with ECG signs compatible with AMI (ST-segment elevation >2 mm in precordial leads and >1 mm in limb leads). Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) flow was scored according to the TIMI flow grading system before and after PCI. Myocardial infarct size was measured by peak creatinine kinase (CK) level in the first 24 h after admission. Diabetes mellitus was diagnosed according to the American Diabetes Association criteria or the use of insulin or glucose-lowering medication. Hypertension was defined as systolic blood pressure ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mmHg or treatment with oral antihypertension drugs. Hyperlipidemia was diagnosed according to the modified National Cholesterol Education Program-Adult Treatment Panel III. The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) value was calculated by modification of diet in renal disease equation [10].
To enable completed follow-up and repeated visits to our outpatient clinic, only patients under the age of 80 and living within the hospital’s catchment area were eligible. The exclusion criteria were severe non-cardiac disease with expected survival of less than 3 months and unwillingness to participate. A patient could only be included once. Thus, 256 patients with complete data were included in the final analysis. Patients were categorized according to MAGE and ABG value, respectively (MAGE group1: the highest tertile, MAGE >3.26 mmol/L; MAGE group2: MAGE ≤3.26 mmol/L; ABG group1: the highest tertile, ABG >7.8 mmol/L; ABG group2: ABG ≤7.8 mmol/L). Blood samples were collected on admission in Emergency department and after overnight fasting and stored at −70 °C prior to analysis. Blood glucose, creatinine, total cholesterol, and triglyceride levels were measured by automatic biochemical analyzer (Hitachi 747; Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan).
Continuous glucose monitoring
All patients were equipped with continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS, Medtronic MiniMed, USA), and were monitored for 72 consecutive hours after PCI. A CGMS sensor was inserted into the subcutaneous abdominal fat tissue, calibrated according to the standard Medtronic MiniMed operating guidelines. During CGMS monitoring, patients checked their blood glucose level with a self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) device (Medisafe Mini, Terumo, Japan) at least 4 times per day. Then, they entered the SMBG data and time of each meal into the CGMS. After monitoring for 72 h, the recorded data were downloaded into a personal computer for analysis of the glucose profile and glycemic excursion parameters with MiniMed Solutions software. The MAGE was calculated from the intermediate 24 h of recordings to avoid bias due to insertion and removal of the CGMS or insufficient stability of the monitoring system. Since measurable range of glucose by CGMS was mechanically limited from 2.2 to 22.2 mmol/L, the case showing the data out of this range was excluded from the study. The MAGE was calculated by measuring the arithmetic mean of the differences between consecutive peaks and nadirs, provided that the differences are greater than one standard deviation of the mean glucose value [11]. Patients would avoid glucose infusion during CGMS monitoring period. Otherwise, the patient would be excluded from the study.
Coronary intervention
All patients were performed with subsequent PCI when indicated as part of the routine treatment for all STEMI patients in Beijing An Zhen Hospital. Coronary intervention was performed using standard techniques, including percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty, thrombus aspiration, intracoronary stenting, and/or mechanical rotational atherectomy. The PCI strategy was at the operator’s discretion. All patients were pretreated with aspirin, heparin, and clopidogrel before PCI. After intracoronary stent implantation, all patients received aspirin and clopidogrel for at least 6 months. Other adjunctive pharmacotherapy was administered at the discretion of the operator. Repeat cardiac catheterization was performed for recurrent symptoms or objective evidence of ischemia during provocative testing. Routine angiographic follow-up was not undertaken.
Follow-up
All patients meeting criteria for this analysis were invited to participate in the study. After informed consent was obtained from the patient or a family member, clinical follow-up was performed by telephone interview and review of hospital records. Patients were followed up prospectively for 3 months. During follow-up period, incidences of MACE were registered, including new-onset myocardial infarction, acute heart failure, repeat target vessel revascularization (TVR) after initial revascularization and cardiac death. All MACE data were adjudicated by an experienced cardiovascular physician blinded to clinical details and outcomes.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed by using SPSS for Windows 20.0 (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA). Data are presented as frequencies and percentages for categorical variables, median for abnormal distributed parameters and mean ± SD for continuous distributed variables, unless otherwise indicated. Differences between two groups were assessed by using the Chi square, Mann-Whitney rank analysis and unpaired t-tests. Correlation between continuous variables was determined by Pearson correlation coefficients. The primary end point was 3-month MACE. Secondary end points were GRACE scores and enzymatic infarct size. MAGE levels were included as continuous and as categorized (≤3.26 or >3.26 mmol/L) variables. ABG levels were also included as continuous and categorized (≤7.8 or >7.8 mmol/L) variables. The predictive values of MAGE and ABG for the presence of MACE were calculated by constructing receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves. To ascertain the independent contribution to MACE, multivariate regression analysis was made (Cox regression using backward stepwise variable selection methods). A value of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Baseline characteristics
During the study period, 265 patients were enrolled. 256 patients (96.6%) with complete data were included in the final analysis (9 patients were removed from study, 5 for failure of CGMS monitoring and 4 for incomplete follow-up data). Mean age was 61.7 ± 6.4 years, 60.5% were male. Baseline characteristics of patient groups based on levels of MAGE and ABG are shown in Tables 1 and 2. There was a strong correlation between MAGE and ABG (Pearson r = 0.242, p < 0.001). Higher MAGE or higher ABG was older, and more often had lower values of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and eGFR. High MAGE levels were associated with more frequent presence of multivessel disease and more stents planted.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics in non-diabetic patients with STEMI based on MAGE levels
| MAGE (mmol/L) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ≤3.26 | >3.26 | ||
| n | 170 | 86 | |
| Patient demographics | |||
| Age (years) | 61 (39–77) | 64 (36–79) | <0.001 |
| Males | 99 (58.2) | 56 (65.1) | 0.344 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.6 (20.3–33.1) | 26.7 (22.5–41.9) | 0.727 |
| Medical history | |||
| Prior MI | 16 (9.4) | 14 (16.3) | 0.148 |
| Prior PCI | 26 (15.3) | 14 (16.3) | 0.857 |
| Prior CABG | 10 (5.9) | 7 (8.1) | 0.596 |
| Risk factors | |||
| Hypertension | 112 (65.9) | 61 (70.9) | 0.480 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 87 (51.2) | 54 (62.8) | 0.085 |
| Current smoking | 82 (48.2) | 47 (54.7) | 0.356 |
| LVEF (%) | 55.47 ± 9.94 | 50.27 ± 9.89 | <0.001 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 71.67 ± 29.05 | 62.55 ± 17.76 | 0.008 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.60 ± 0.95 | 4.67 ± 1.02 | 0.588 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.82 ± 1.39 | 1.90 ± 0.73 | 0.591 |
| ABG (mmol/L) | 7.01 ± 1.68 | 7.91 ± 2.20 | <0.001 |
| MAGE (mmol/L) | 2.17 ± 0.73 | 4.28 ± 1.06 | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 4.71 ± 0.90 | 5.70 ± 1.50 | <0.001 |
| Angiographic data | |||
| Culprit vessel, LAD | 68 (40.0) | 38 (44.2) | 0.591 |
| Multi-vessel CAD | 78 (45.9) | 53 (61.6) | 0.024 |
| TIMI grade 3 before PCI | 46 (27.1) | 15 (17.4) | 0.120 |
| TIMI grade 3 after PCI | 163 (95.9) | 78 (90.7) | 0.156 |
| Stents | 1.51 ± 0.87 | 1.79 ± 1.09 | 0.027 |
Data are mean ± SD and number (%)
STEMI ST elevated myocardial infarction, MAGE the mean amplitude of glycemic excursions, BMI body mass index, MI myocardial infarction, PCI percutaneous coronary intervention, CABG coronary artery bypass graft, LVEF left ventricular ejection fraction, eGFR estimated glomerular filtration rate, TC total cholesterol, TG triglyceride, ABG admission blood glucose, HbA 1c glycated hemoglobin, LAD left anterior descending artery, CAD coronary artery disease
Table 2.
Baseline characteristics in non-diabetic patients with STEMI based on ABG levels
| ABG (mmol/L) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ≤7.80 | >7.80 | ||
| n | 170 | 86 | |
| Patient demographics | |||
| Age (years) | 60 (36–79) | 64 (44–72) | 0.011 |
| Males | 105 (61.8) | 50 (58.1) | 0.590 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.6 (23.5–41.9) | 26.6 (20.3–32.7) | 0.233 |
| Medical history | |||
| Prior MI | 18 (10.6) | 12 (14.0) | 0.420 |
| Prior PCI | 27 (15.9) | 13 (15.1) | 1.000 |
| Prior CABG | 11 (6.5) | 6 (7.0) | 1.000 |
| Risk factors | |||
| Hypertension | 114 (67.1) | 59 (68.6) | 0.888 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 92 (54.1) | 49 (57.0) | 0.692 |
| Current smoking | 88 (51.8) | 41 (47.7) | 0.597 |
| LVEF (%) | 55.81 ± 10.34 | 51.57 ± 9.80 | 0.017 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 73.54 ± 28.54 | 58.85 ± 16.86 | <0.001 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.58 ± 0.96 | 4.71 ± 0.95 | 0.287 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.81 ± 1.39 | 1.93 ± 0.75 | 0.376 |
| ABG (mmol/L) | 6.17 ± 1.07 | 9.56 ± 1.27 | <0.001 |
| MAGE (mmol/L) | 2.62 ± 1.15 | 3.40 ± 1.45 | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 4.76 ± 1.28 | 5.81 ± 1.42 | <0.001 |
| Angiographic data | |||
| Culprit vessel, LAD | 65 (38.2) | 41 (47.7) | 0.179 |
| Multi-vessel CAD | 82 (48.2) | 49 (57.0) | 0.233 |
| TIMI grade 3 before PCI | 43 (25.3) | 18 (20.9) | 0.535 |
| TIMI grade 3 after PCI | 162 (95.3) | 79 (91.9) | 0.273 |
| Stents | 1.54 ± 0.911 | 1.72 ± 1.04 | 0.170 |
Data are mean ± SD and number (%)
STEMI ST elevated myocardial infarction, ABG admission blood glucose, BMI body mass index, MI myocardial infarction, PCI percutaneous coronary intervention, CABG coronary artery bypass graft, LVEF left ventricular ejection fraction, eGFR estimated glomerular filtration rate, TC total cholesterol, TG triglyceride, MAGE the mean amplitude of glycemic excursions, HbA 1c glycated hemoglobin, LAD left anterior descending artery, CAD coronary artery disease
Outcomes of patients
At the end of 3-month follow-up, 6 patients had died (2.3%) for cardiac causes, 8 patients had new-onset myocardial infarction (3.1%), 15 patients had acute heart failure (5.9%) and 21 patients had TVR (8.2%). Incidence of total short-term MACE was significantly higher with increasing MAGE levels and ABG levels. GRACE scores and infarct size measured by peak CK were also strongly associated with higher MAGE and ABG levels. To compare with patients of lower MAGE, higher MAGE patients had significantly higher cardiac mortality (5.8 vs. 0.6%, p = 0.017) and incidence of acute heart failure (12.8 vs. 2.4%, p = 0.001). Differences of rates of cardiac death, repeat infarction, acute heart failure and TVR were not statistically significant between two ABG groups (Table 3 and Fig. 1).
Table 3.
Clinical outcomes of non-diabetic patients with STEMI based on MAGE and ABG
| MAGE (mmol/L) | ABG (mmol/L) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤3.26 | >3.26 | p | ≤7.80 | >7.80 | p | |
| n | 170 | 86 | 170 | 86 | ||
| Peak CK (U/L) | 905 (300–4077) | 1290 (471–4658) | 0.020 | 897 (300–4428) | 1372 (398–4658) | 0.039 |
| GRACE score | 140 ± 33 | 152 ± 34 | 0.005 | 141 ± 34 | 150 ± 33 | 0.036 |
| MACE | 20 (13.5) | 30 (31.4) | 0.001 | 26 (15.9) | 24 (26.7) | 0.046 |
| Cardiac death | 1 (0.6) | 5 (5.8) | 0.017 | 2 (1.2) | 4 (4.7) | 0.100 |
| New-onset MI | 3 (1.8) | 5 (5.8) | 0.123 | 4 (2.4) | 4 (4.7) | 0.448 |
| Acute HF | 4 (2.4) | 11 (12.8) | 0.001 | 7 (4.1) | 8 (9.3) | 0.156 |
| TVR | 12 (7.1) | 9 (10.5) | 0.346 | 13 (7.6) | 8 (9.3) | 0.637 |
Data are mean ± SD and number (%)
STEMI ST elevated myocardial infarction, MAGE the mean amplitude of glycemic excursions, ABG admission blood glucose, CK creatine kinase, MACE major adverse cardiac events, MI myocardial infarction, HF heart failure, TVR repeat target vessel revascularization
Fig. 1.
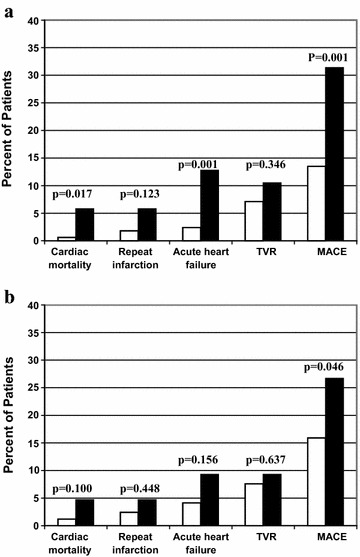
a Incidence of MACE after 3-month follow-up in relation to MAGE levels (white bars MAGE level ≤3.26 mmol/L; black bars MAGE level >3.26 mmol/L). b Incidence of MACE after 3-month follow-up in relation to ABG levels (white bars ABG level ≤7.80 mmol/L; black bars ABG level >7.80 mmol/L)
Multivariate analysis
Cox regression analysis was used to investigate the associations of MAGE and ABG with incidences of MACE with adjusting for age, sex, and all possible predictors of MACE (prior MI, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, current smoking, eGFR, LVEF, body mass index, multivessel coronary artery disease, anterior infarction, TIMI flow before PCI and TIMI flow after PCI). Results of analysis showed that MAGE (HR 2.165, 95% CI 1.114–4.219, p = 0.023), but not ABG, was significantly associated with short-term MACE. Significant predictors are presented in Table 4.
Table 4.
Multivariate analysis of determinants of short-term MACE
| Independent variables | HR | 95% CI | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||
| Age (per decade) | 2.158 | 1.435 | 3.245 | <0.001 |
| LVEF <40% | 3.137 | 1.543 | 6.380 | 0.002 |
| TIMI flow after PCI < grade 3 | 2.984 | 1.276 | 6.980 | 0.012 |
| MAGE >3.26 mmol/L | 2.271 | 1.154 | 4.471 | 0.018 |
MACE major adverse cardiac events, HR hazard ratio, CI confidence interval, LVEF left ventricular ejection fraction, TIMI thrombolysis in myocardial infarction, PCI percutaneous coronary intervention, MAGE the mean amplitude of glycemic excursions
ROC curve for MAGE and ABG in predicting short-term MACE
The area under the ROC curve for MAGE (0.690, 95% CI 0.605–0.775, p < 0.001) was superior to that for ABG (0.581, 95% CI 0.492–0.670, p = 0.076) (Fig. 2). MAGE, but not ABG, displayed significant value in predicting short-term MACE in patients.
Fig. 2.
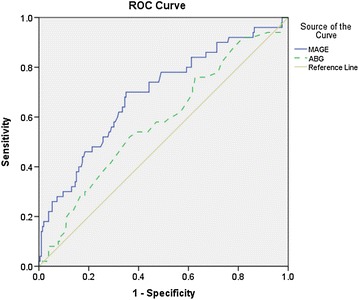
Area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve: MAGE (0.690, 95% CI 0.605–0.775, p < 0.001); ABG (0.581, 95% CI 0.492–0.670, p = 0.076)
Discussion
Our study shows that an elevated MAGE level during hospital is associated with a significantly higher risk of short-term MACE and cardiovascular mortality after PCI in non-diabetes patients with STEMI. Measurement of in-hospital GV by CGMS in non-diabetes patients may improve risk assessment in patients presenting with acute STEMI.
Although acute hyperglycemia on admission has clearly been associated with poor outcomes in AMI patients with or without diabetes, the prognostic value of in-hospital GV in this population has been less well established. Fluctuations of glucose seem to have more deleterious effects than sustained hyperglycemia in the development of cardiovascular complications as acute glucose excursions activate the oxidative stress [12]. More and more evidences show that glycemic variability may be an important role in resolving potential cardiovascular problems in abnormal glucose metabolism. Some researchers suggested that glucose excursions is independently related to carotid intima-media thickness and may contribute to the development of atherosclerosis in individuals with diabetes independent of other risk factors [13, 14]. In our previous study, we found that GV is an important contributing factor in the severity of coronary artery disease, which is independent of the average level of blood glucose [15]. The Verona Diabetes study reported that fasting GV is an independent predictor of mortality in type 2 diabetes patients [16]. We also found that acute glucose excursions would seem to be of greater importance than admission glucose and long-term derangements of glucose metabolism in predicting 1-year outcomes following AMI [17]. Some studies concluded that GV was a significant predictor of mortality in critically ill patients independently from mean glucose level and severity of illness [18–20]. In the present study, patients with a higher MAGE level have higher GRACE risk scores. After 3-month follow-up, a significantly higher incidence of MACE and cardiac mortality were found in those patients. Multivariate analysis disclosed that in participants, in-hospital GV (i.e. MAGE >3.26 mmol/L) was an independent predictor of MACE, but ABG was not. The results indicate that high glucose fluctuations may be associated with the risk of short-term adverse cardiovascular events in non-diabetes patients with STEMI after PCI.
Patients with admission hyperglycemia tend to experience the worst outcomes as demonstrated in several well-conducted prior studies, our study shows that increased glucose excursions should be more important. In this study, multivariate analysis shows that in-hospital GV, age, LVEF and TIMI flow after PCI were independent predictors of short-term MACE, but ABG was not. The area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve for MAGE and ABG in predicting short-term MACE shows that MAGE, but not ABG, displayed significant value in predicting short-term MACE in patients. ABG represents only a marker of point-in-time glucose status and cannot reflect the overall exposure of acute glucose swings. Glycemic disorders are not solely limited to sustained hyperglycemia but can be extended to the glycemic variability which includes both upward and downward acute glucose changes. Patients with similar mean glucose levels can have markedly different glycemic variability [21].
Although we did not address the underlying relationship between GV and cardiovascular outcomes following PCI in non-diabetes patients with STEMI, both oxidative stress and inflammation may be involved in the process. GV acutely increases oxidative stress and exaggerates inflammation [12, 22]. Some studies reported that the apoptosis of endothelial cells exposed to intermittent high glucose may be related to a reactive oxygen species (ROS) overproduction, through protein kinase C (PKC)-dependent activation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-oxidase [23, 24]. In vitro studies indicate that glucose fluctuations can activate nuclear factor-κB and PKC pathway, leading to a greater expression of the adhesion molecules and excess formation of advanced glycation end-products than stable high glucose [25, 26]. These findings suggest that glucose fluctuations may augment inflammation via oxidative mechanisms closely linked to adverse outcomes. Furthermore, severe glycemic excursions may adversely affect sympathetic dysfunction which is associated with mortality and morbidity of cardiovascular disease [27]; and the thrombotic properties of platelets are increased in a hyperglycemic environment, and this can result in additional cardiovascular complications [28]. Hypoglycemia is another possible link between GV and poorer cardiovascular outcomes. Some reported that greater GV predicted more hypoglycemic episodes. Severe hypoglycemia can predict all-cause mortality in patients with diabetes [29, 30]. Hypoglycemia could induce the onset of MACE through induction of inflammation, blood coagulation abnormality, sympathoadrenal response and endothelial dysfunction [31].
Moreover, the relationship between GV and cardiovascular outcomes is still controversial. There is still an extensive debate about GV as a risk factor for MACE [32]. The trial, known as HEART2D study, failed to demonstrate that decreasing GV led to reduced MACE risk [33]. However, the study was discontinued prematurely due to too few MACE and less than expected differences in postprandial glucose values. Only one of three markers of GV was reduced with the prandial-targeted therapy and this was the newest, least established GV marker. Different aim of initial study design and measurements of GV may be important causes for explaining controversial results in these studies. Overall, more well-designed studies are warranted to investigate whether GV will play an important role in cardiovascular complications.
Study limitations
Several study limitations should be considered in the interpretation of the results. First, diabetes was defined as known diabetes status on admission. It is well known that a number of STEMI patients have undetected diabetes mellitus, and they were not excluded in our study. Second, the sample size was relatively small, so that some subgroup comparisons may have lacked power to detect significant differences for selected variables. Third, hypoglycemia is considered as a risk factor of cardiovascular events. However, due to very low incidence of hypoglycemic episodes in our study, we didn’t include this risk factor in analysis. In addition, we examined in-hospital GV which couldn’t reflect daily GV at home. Some factors, such as different diets, operations, physical and emotional factors, which maybe affect patients’ glucose fluctuations couldn’t be analyzed. On the other hand, some limitations of CGMS should be noted including requirement for frequent calibrations, invasive techniques, complex procedure, and so on. Hence, we think that the results of the present study should be interpreted with caution. This study is hypothesis-generating and should stimulate a larger multicenter evaluation.
Conclusions
In-hospital GV would seem to be of greater importance than ABG in predicting short-term cardiovascular outcomes in non-diabetes patients with STEMI after PCI.
Authors’ contributions
SHM and GS participated in the design of the study, participated in the exercise protocols, performed the statistical analysis and drafted the manuscript. HXY, YZ, LT and TZ performed data collection and reduction, as well as continuous glucose monitoring. HT participated in the exercise protocols. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
We convey thanks to the professional technical assistance from the laboratory technicians at the Clinical Laboratory Center. The authors thank the volunteer patients for their participation, and the study nurses Jin Wu and Suyun Liu for their skills and devotion to the patient care.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
The study protocol was approved beforehand by the Medical Ethics Committee of Beijing An Zhen Hospital of Capital Medical University, and written informed consent was obtained from all participants. The study was carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki of the World Medical Association.
Funding
This work was supported by a key grant from Beijing Health Special Foundation (JING 15-10).
Abbreviations
- MACE
major adverse cardiac events
- GV
glycemic variability
- AMI
acute myocardial infarction
- STEMI
ST elevated myocardial infarction
- ABG
admission blood glucose
- MAGE
the mean amplitude of glycemic excursions
- CGMS
continuous glucose monitoring system
- SMBG
self-monitoring of blood glucose
- GRACE
global registry of acute coronary events
- CK
creatine kinase
- TIMI
thrombolysis in myocardial infarction
- HF
heart failure
- TVR
repeat target vessel revascularization
- PCI
percutaneous coronary intervention
- LVEF
left ventricular ejection fraction
- eGFR
estimated glomerular filtration rate
Contributor Information
Shu-hua Mi, Email: mishuhua@hotmail.com.
Gong Su, Phone: 86-10-64456054, Email: su_gong@yahoo.com.
Hong-xia Yang, Email: hongxiay2001@yahoo.com.cn.
Yun Zhou, Email: whi@tom.com.
Lei Tian, Email: tianlei@sohu.com.
Tao Zhang, Email: jackynh@sina.com.
Hong Tao, Email: vivientao@tom.com.
References
- 1.Timmer JR, Hoekstra M, Nijsten MW, van der Horst IC, Ottervanger JP, Slingerland RJ, Dambrink JH, Bilo HJ, Zijlstra F, van ‘t Hof AW. Prognostic value of admission glycosylated hemoglobin and glucose in non-diabetic patients with ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction treated with percutaneous coronary intervention. Circulation. 2011;124(6):704–711. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.985911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Giraldez RR, Clare RM, Lopes RD, Dalby AJ, Prabhakaran D, Brogan GX, Jr, Giugliano RP, James SK, Tanguay JF, Pollack CV, Jr, et al. Prevalence and clinical outcomes of undiagnosed diabetes mellitus and prediabetes among patients with high-risk non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. Am Heart J. 2013;165(6):918–925. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2013.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gholap NN, Mehta RL, Ng L, Davies MJ, Khunti K, Squire IB. Is admission blood glucose concentration a more powerful predictor of mortality after myocardial infarction than diabetes diagnosis? A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2012;2(5):e001596. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2012-001596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cakmak M, Cakmak N, Cetemen S, Tanriverdi H, Enc Y, Teskin O. The value of admission glycosylated hemoglobin level in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Can J Cardiol. 2008;24(5):375–378. doi: 10.1016/S0828-282X(08)70600-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Picconi F, Di Flaviani A, Malandrucco I, Giordani I, Frontoni S. Impact of glycemic variability on cardiovascular outcomes beyond glycated hemoglobin. Evidence and clinical perspectives. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2012;22(9):691–696. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2012.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Monteiro S, Gonçalves F, Monteiro P, Freitas M, Providência LA. The magnitude of the variation in glycemia: a new parameter for risk assessment in acute coronary syndrome? Rev Esp Cardiol. 2009;62(10):1099–1108. doi: 10.1016/S0300-8932(09)72378-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ceriello A, Esposito K, Piconi L, Ihnat MA, Thorpe JE, Testa R, Boemi M, Giugliano D. Oscillating glucose is more deleterious to endothelial function and oxidative stress than mean glucose in normal and type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes. 2008;57(5):1349–1354. doi: 10.2337/db08-0063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Monnier L, Mas E, Ginet C, Michel F, Villon L, Cristol JP, Colette C. Activation of oxidative stress by acute glucose fluctuations compared with sustained chronic hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. JAMA. 2006;295(14):1681–1687. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.14.1681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Granger CB, Goldberg RJ, Dabbous O, Pieper KS, Eagle KA, Cannon CP, Van De Werf F, Avezum A, Goodman SG, Flather MD, et al. Predictors of hospital mortality in the global registry of acute coronary events. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163(19):2345–2353. doi: 10.1001/archinte.163.19.2345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D, Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130(6):461–470. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-130-6-199903160-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Monnier L, Colette C, Owens DR. Glycemic variability: the third component of the dysglycemia in diabetes. Is it important? How to measure it? J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2008;2(6):1094–1100. doi: 10.1177/193229680800200618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Saisho Y. Glycemic variability and oxidative stress: a link between diabetes and cardiovascular disease? Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(10):18381–18406. doi: 10.3390/ijms151018381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hu Y, Liu W, Huang R, Zhang X. Postchallenge plasma glucose excursions, carotid intima-media thickness, and risk factors for atherosclerosis in Chinese population with type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis. 2010;210(1):302–306. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2009.11.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mo Y, Zhou J, Li M, Wang Y, Bao Y, Ma X, Li D, Lu W, Hu C, Li M, et al. Glycemic variability is associated with subclinical atherosclerosis in Chinese type 2 diabetes patients. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013;12:15. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Su G, Mi S, Tao H, Li Z, Yang H, Zheng H, Zhou Y, Ma C. Association of glycemic variability and the presence and severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2011;10:19. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-10-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Muggeo M, Zoppini G, Bonora E, Brun E, Bonadonna RC, Moghetti P, Verlato G. Fasting plasma glucose variability predicts 10-year survival of type 2 diabetes patient. Diabetes Care. 2000;23(1):45–50. doi: 10.2337/diacare.23.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Su G, Mi S, Tao H, Li Z, Yang H, Zheng H, Zhou Y, Tian L. Impact of admission glycemic variability, glucose, and glycosylated hemoglobin on major adverse cardiac events after acute myocardial infarction. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(4):1026–1032. doi: 10.2337/dc12-0925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dossett LA, Cao H, Mowery NT, Dortch MJ, Morris JM, Jr, May AK. Blood glucose variability is associated with mortality in the surgical intensive care unit. Am Surg. 2008;74(8):679–685. doi: 10.1177/000313480807400802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Krinsley JS. Glycemic variability: a strong independent predictor of mortality in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 2008;36(11):3008–3013. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31818b38d2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hirshberg E, Larsen G, Van Duker H. Alterations in glucose homeostasis in the pediatric intensive care unit: hyperglycemia and glucose variability are associated with increased mortality and morbidity. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2008;9(4):361–366. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e318172d401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Monnier L, Colette C, Owens DR. The glycemic triumvirate and diabetes complications: is the whole greater than the sum of its component parts? Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012;95(3):303–311. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2011.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yamazaki M, Hasegawa G, Majima S, Mitsuhashi K, Fukuda T, Iwase H, Kadono M, Asano M, Senmaru T, Tanaka M, et al. Effect of repaglinide versus glimepiride on daily blood glucose variability and changes in blood inflammatory and oxidative stress markers. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2014;6:54. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-6-54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Johnson EL. Glycemic variability in type 2 diabetes mellitus: oxidative stress and macrovascular complications. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;771(6):139–154. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5441-0_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Quagliaro L, Piconi L, Assaloni R, Martinelli L, Motz E, Ceriello A. Intermittent high glucose enhances apoptosis related to oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: the role of protein kinase C and NAD(P)H-oxidase activation. Diabetes. 2003;52(11):2795–2804. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.52.11.2795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Otsuka A, Azuma K, Iesaki T, Sato F, Hirose T, Shimizu T, Tanaka Y, Daida H, Kawamori R, Watada H. Temporary hyperglycaemia provokes monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells in rat thoracic aorta. Diabetologia. 2005;48(12):2667–2674. doi: 10.1007/s00125-005-0005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Azuma K, Kawamori R, Toyofuku Y, Kitahara Y, Sato F, Shimizu T, Miura K, Mine T, Tanaka Y, Mitsumata M, et al. Repetitive fluctuations in blood glucose enhance monocyte adhesion to the endothelium of rat thoracic aorta. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26(10):2275–2280. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000239488.05069.03. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Takei Y, Tomiyama H, Tanaka N, Yamashina A. Close relationship between sympathetic activation and coronary microvascular dysfunction during acute hyperglycemia in subjects with atherosclerotic risk factors. Circ J. 2007;71(2):202–206. doi: 10.1253/circj.71.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gresele P, Guglielmini G, De Angelis M, Ciferri S, Ciofetta M, Falcinelli E, Lalli C, Ciabattoni G, Davì G, Bolli GB. Acute, short-term hyperglycemia enhances shear stress-induced platelet activation in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41(6):1013–1020. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(02)02972-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zoungas S, Patel A, Chalmers J, de Galan BE, Li Q, Billot L, Woodward M, Ninomiya T, Neal B, MacMahon S, et al. Severe hypoglycemia and risks of vascular events and death. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(15):1410–1418. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1003795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.ORIGIN Trial Investigators. Mellbin LG, Rydén L, Riddle MC, Probstfield J, Rosenstock J, Díaz R, Yusuf S, Gerstein HC. Does hypoglycaemia increase the risk of cardiovascular events? A report from the ORIGIN trial. Eur Heart J. 2013;34(40):3137–3144. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Desouza CV, Bolli GV. Hypoglycemia, diabetes, and cardiovascular events. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(6):1389–1394. doi: 10.2337/dc09-2082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kilpatrick ES, Rigby AS, Atkin SL. For debate. Glucose variability and diabetes complication risk: we need to know the answer. Diabet Med. 2010;27(8):868–871. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2010.02929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Siegelaar SE, Kerr L, Jacober SJ, Devries JH. A decrease in glucose variability does not reduce cardiovascular event rates in type 2 diabetic patients after acute myocardial infarction: a reanalysis of the HEART2D study. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(4):855–857. doi: 10.2337/dc10-1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


