Abstract
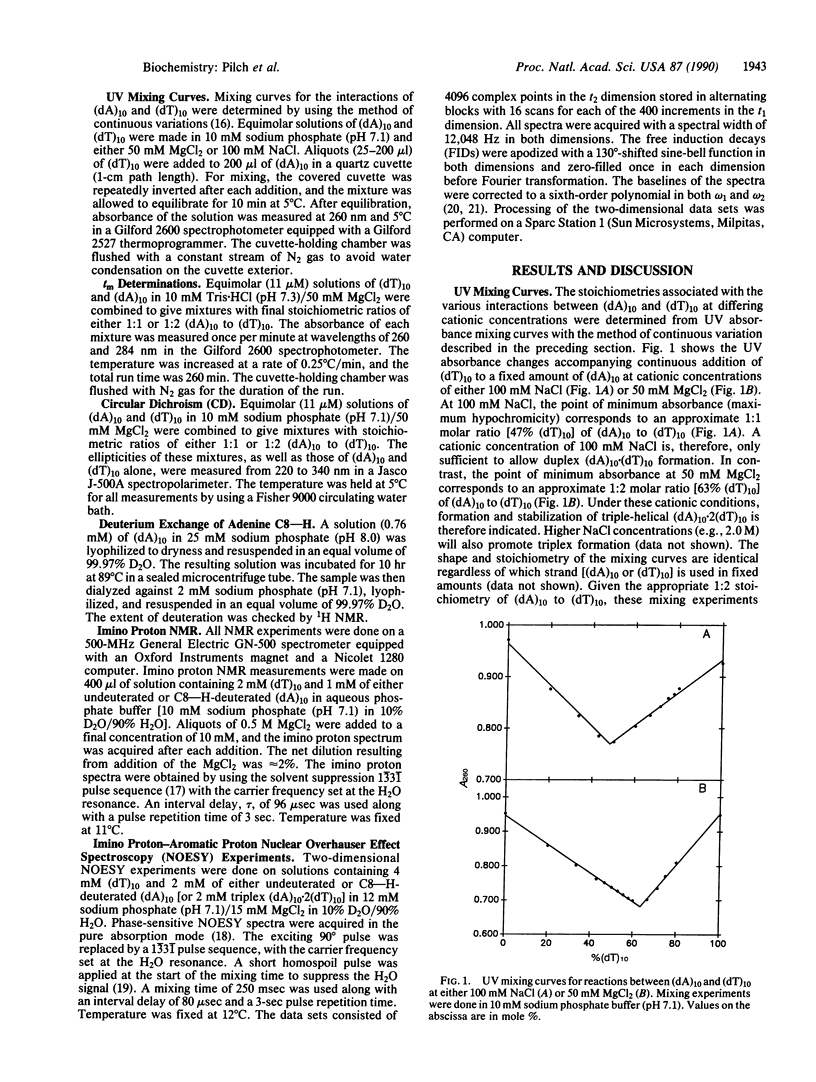
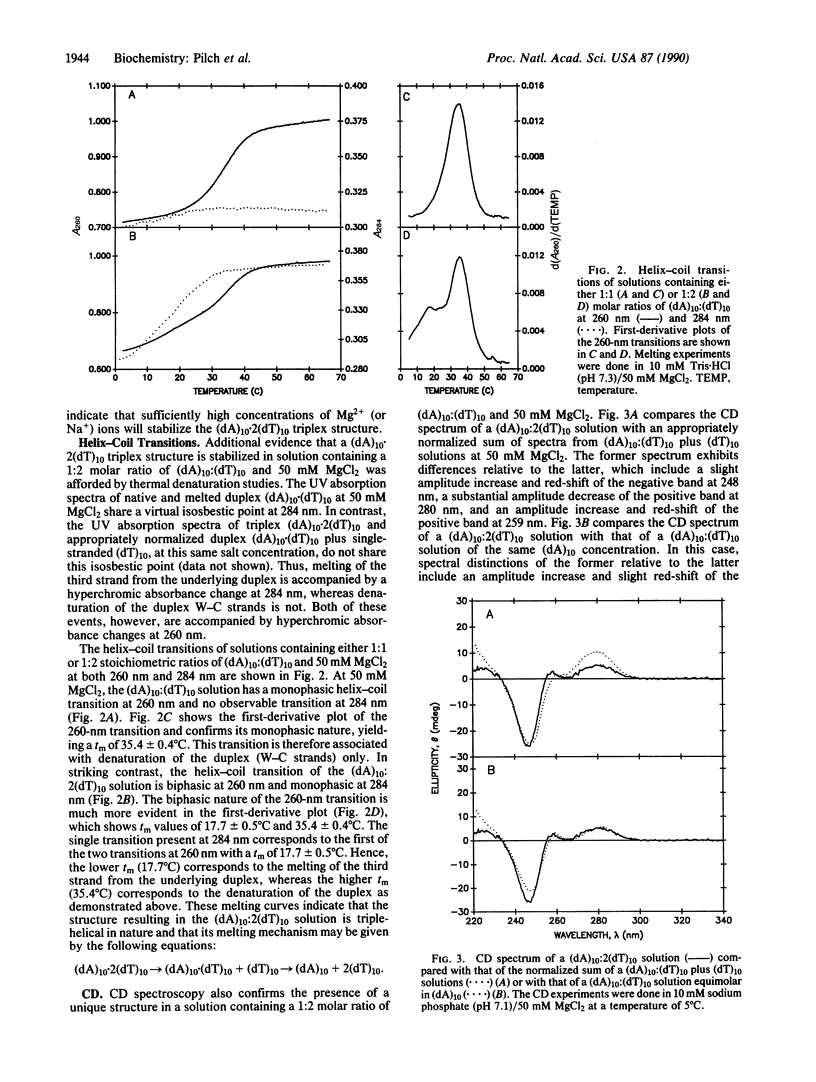
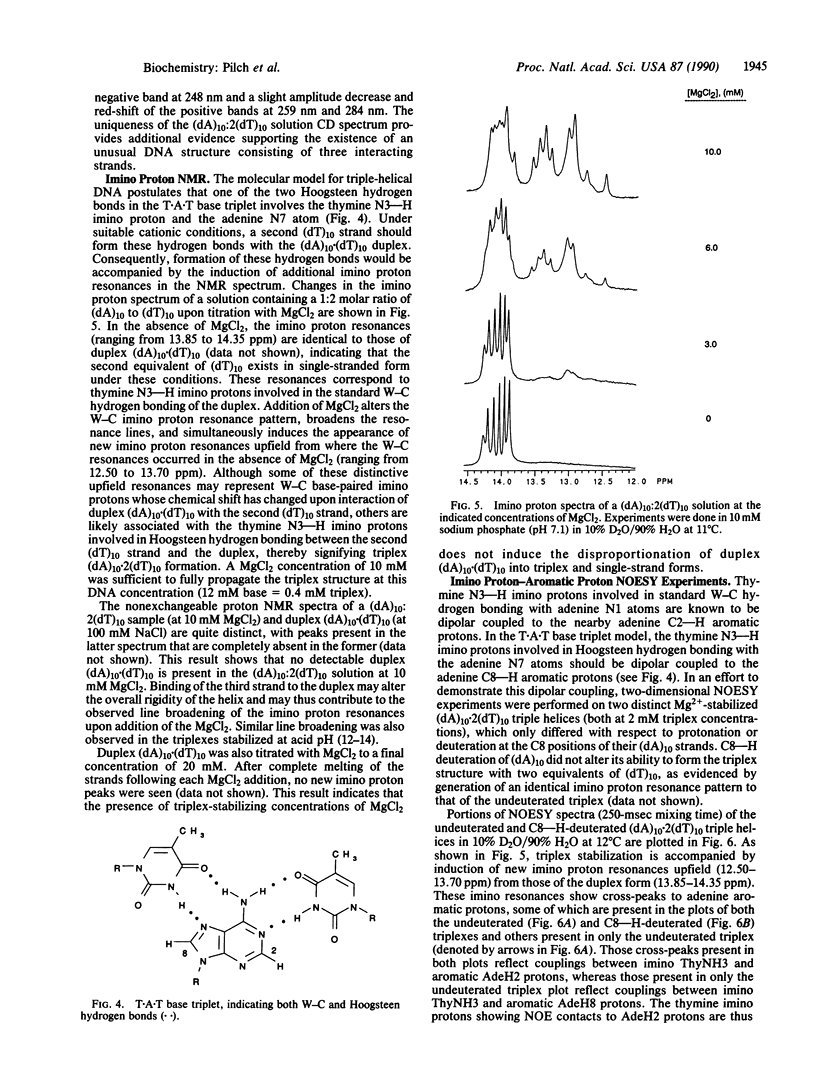
The existence of DNA triple helices in vitro has been known for some time. Recent evidence suggesting that DNA triplexes exist in vivo and showing their potential for chemotherapeutic applications has renewed interest in these triple-strand conformations. However, little structural information is currently known about these unusual nucleic acid forms. We have induced and stabilized triple-helical (dA)10.2(dT)10 with MgCl2 at neutral pH. UV mixing curves demonstrate a 1:2 (dA)10 to (dT)10 stoichiometry at suitable MgCl2 concentrations. Thermal denaturation profiles establish a melting mechanism characterized by the initial loss of the third strand, followed by dissociation of the remaining duplex. The circular dichroic spectrum of the triplex form is distinct from that of a duplex equimolar in (dA)10. NMR studies show that magnesium-induced triplex formation is accompanied by an upfield shift of several imino proton resonances present before stabilization of the triplex form with MgCl2 and the induction of new upfield imino proton resonances. Nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy measurements on both undeuterated and C8--H-deuterated (dA)10.2(dT)10 triplexes demonstrate dipolar contacts between resolvable imino proteins and both adenine C8--H and C2--H aromatic protons. Hence, MgCl2 stabilizes a triplex structure in which thymine N3--H imino protons are involved in both Watson-Crick and Hoogsteen base pairing.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Bond P. J., Selsing E., Smith P. J. Models of triple-stranded polynucleotides with optimised stereochemistry. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2459–2470. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Hukins D. W., Smith P. J., Watts L. Structural details of double-helix observed for DNAs containing alternating purine and pyrimidine sequences. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90499-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Selsing E. Structures for the polynucleotide complexes poly(dA) with poly (dT) and poly(dT) with poly(dA) with poly (dT). J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):509–521. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90498-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J. Comparative properties of DNA, RNA, and hybrid homopolymer pairs. Fed Proc. 1965 Nov-Dec;24(6):1446–1457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney M., Czernuszewicz G., Postel E. H., Flint S. J., Hogan M. E. Site-specific oligonucleotide binding represses transcription of the human c-myc gene in vitro. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):456–459. doi: 10.1126/science.3293213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Burkholder G. D., Latimer L. J., Haug B. L., Braun R. P. A monoclonal antibody to triplex DNA binds to eucaryotic chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1047–1061. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letai A. G., Palladino M. A., Fromm E., Rizzo V., Fresco J. R. Specificity in formation of triple-stranded nucleic acid helical complexes: studies with agarose-linked polyribonucleotide affinity columns. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9108–9112. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkin S. M., Lyamichev V. I., Drushlyak K. N., Dobrynin V. N., Filippov S. A., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. DNA H form requires a homopurine-homopyrimidine mirror repeat. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):495–497. doi: 10.1038/330495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. R., Wells R. D. Specificity of the three-stranded complex formation between double-stranded DNA and single-stranded RNA containing repeating nucleotide sequences. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. E., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific cleavage of double helical DNA by triple helix formation. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):645–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3118463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praseuth D., Perrouault L., Le Doan T., Chassignol M., Thuong N., Hélène C. Sequence-specific binding and photocrosslinking of alpha and beta oligodeoxynucleotides to the major groove of DNA via triple-helix formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1349–1353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopal P., Feigon J. NMR studies of triple-strand formation from the homopurine-homopyrimidine deoxyribonucleotides d(GA)4 and d(TC)4. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7859–7870. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopal P., Feigon J. Triple-strand formation in the homopurine:homopyrimidine DNA oligonucleotides d(G-A)4 and d(T-C)4. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):637–640. doi: 10.1038/339637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley M., Maling B. Physical and chemical characterization of two- and three-stranded adenine-thymine and adenine-uracil homopolymer complexes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(2):359–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Collier D. A., Hanvey J. C., Shimizu M., Wohlrab F. The chemistry and biology of unusual DNA structures adopted by oligopurine.oligopyrimidine sequences. FASEB J. 1988 Nov;2(14):2939–2949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de los Santos C., Rosen M., Patel D. NMR studies of DNA (R+)n.(Y-)n.(Y+)n triple helices in solution: imino and amino proton markers of T.A.T and C.G.C+ base-triple formation. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7282–7289. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]