Abstract
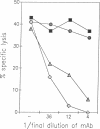
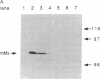
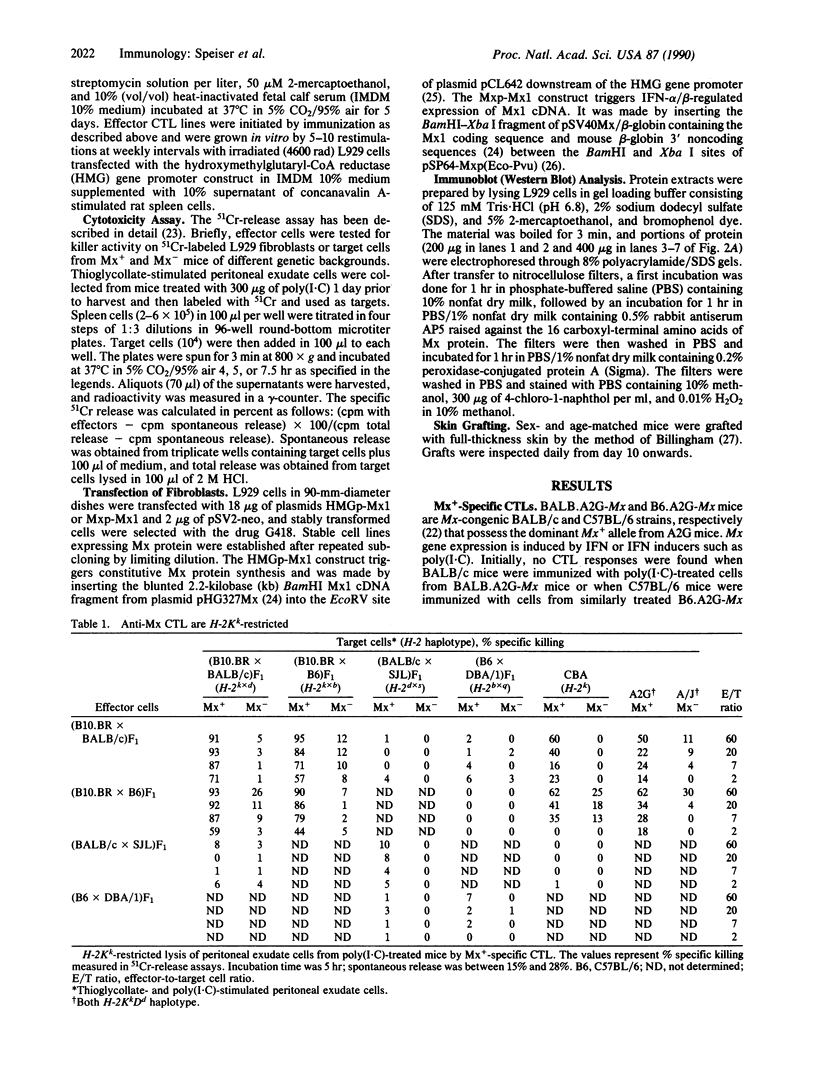
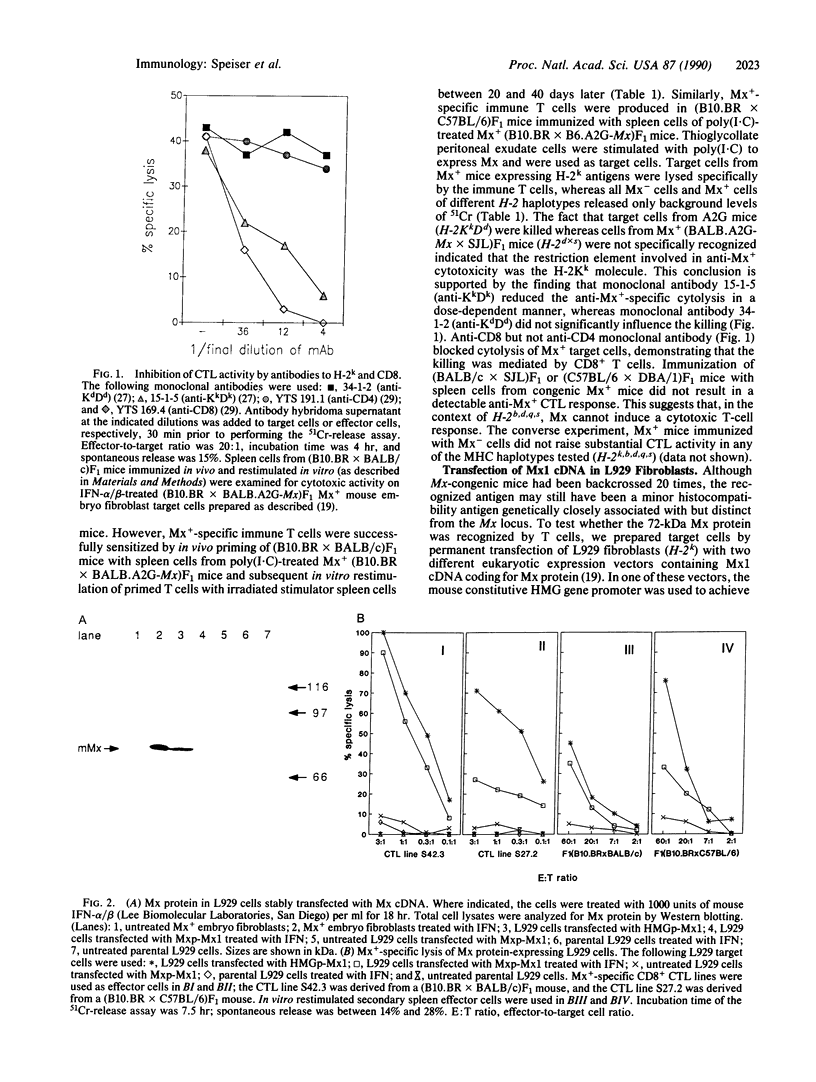
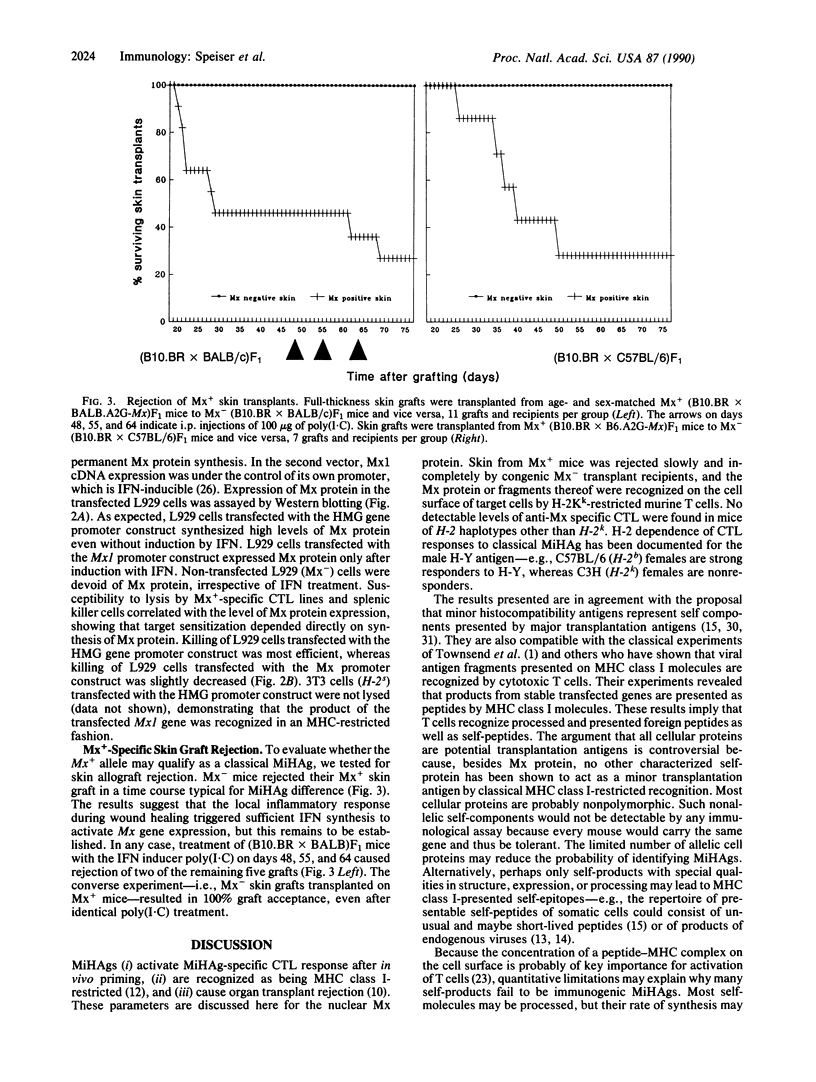
Minor histocompatibility antigens (MiHAgs) cause slow-to-rapid organ transplant rejection by immunocompetent hosts and mild-to-severe graft-versus-host reactions in immunosuppressed hosts. MiHAgs are allelic forms of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-restricted self-antigens recognized by cytotoxic T cells and usually are defined immunogenetically. Although structurally not identified as yet, it is assumed that MiHAgs are internal cell antigens that are processed and then presented by MHC class I proteins similar to viral antigens. To define a MiHAg both molecularly and functionally, we took advantage of the allelic difference of the structurally characterized intracellular myxovirus-resistance protein (Mx) and investigated its antigenicity. Skin grafts from congenic Mx+ mice carrying the functional Mx1 gene were rejected by mice lacking a functional Mx1 gene (Mx- mice). In parallel, cytotoxic MHC class I-restricted effector T cells specific for Mx protein and the H-2Kk antigen (but not for several other allelic H-2 antigens) were strongly induced in Mx- mice immunized with spleen cells from interferon-treated Mx+ mice. These data show that allelic forms of cell internal proteins presented by MHC class I may act as MiHAgs.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adorini L., Muller S., Cardinaux F., Lehmann P. V., Falcioni F., Nagy Z. A. In vivo competition between self peptides and foreign antigens in T-cell activation. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):623–625. doi: 10.1038/334623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M. J. Antigen recognition. Class discrimination in the world of immunology. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):192–194. doi: 10.1038/325192b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M. J. The major histocompatibility complex determines susceptibility to cytotoxic T cells directed against minor histocompatibility antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1349–1364. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogen B., Malissen B., Haas W. Idiotope-specific T cell clones that recognize syngeneic immunoglobulin fragments in the context of class II molecules. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Nov;16(11):1373–1378. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon T., Van Pel A. T cell-recognized antigenic peptides derived from the cellular genome are not protein degradation products but can be generated directly by transcription and translation of short subgenic regions. A hypothesis. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(2):75–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00395854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold S. P., Jayasuriya A., Nash A., Prospero T. D., Waldmann H. Therapy with monoclonal antibodies by elimination of T-cell subsets in vivo. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):548–551. doi: 10.1038/312548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier C., Mehtali M., Lathe R. A ubiquitous mammalian expression vector, pHMG, based on a housekeeping gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 25;17(20):8389–8389. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.20.8389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N. Immunology. The ins and outs of antigen processing and presentation. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):687–689. doi: 10.1038/322687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulmy E., Termijtelen A., Bradley B. A., van Rood J. J. Y-antigen killing by T cells of women is restricted by HLA. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):544–545. doi: 10.1038/266544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M. A., Staeheli P., Haller O. Interferon induces a unique protein in mouse cells bearing a gene for resistance to influenza virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1910–1914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug H., Costas M., Staeheli P., Aebi M., Weissmann C. Organization of the murine Mx gene and characterization of its interferon- and virus-inducible promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3065–3079. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz R. G., Allen P. M. Direct evidence for functional self-protein/Ia-molecule complexes in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5220–5223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryanski J. L., Pala P., Corradin G., Jordan B. R., Cerottini J. C. H-2-restricted cytolytic T cells specific for HLA can recognize a synthetic HLA peptide. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):578–579. doi: 10.1038/324578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzinger P., Bevan M. J. Hypothesis: why do so many lymphocytes respond to major histocompatibility antigens? Cell Immunol. 1977 Mar 1;29(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90269-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzinger P., Bevan M. J. Induction of H-2-restricted cytotoxic T cells: in vivo induction has the appearance of being unrestricted. Cell Immunol. 1977 Sep;33(1):92–100. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meruelo D., Rossomando A., Offer M., Buxbaum J., Pellicer A. Association of endogenous viral loci with genes encoding murine histocompatibility and lymphocyte differentiation antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5032–5036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noteborn M., Arnheiter H., Richter-Mann L., Browning H., Weissmann C. Transport of the murine Mx protein into the nucleus is dependent on a basic carboxy-terminal sequence. J Interferon Res. 1987 Oct;7(5):657–669. doi: 10.1089/jir.1987.7.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Mayer N., Sachs D. H. Hybridoma cell lines secreting monoclonal antibodies to mouse H-2 and Ia antigens. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):533–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rammensee H. G., Robinson P. J., Crisanti A., Bevan M. J. Restricted recognition of beta 2-microglobulin by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):502–504. doi: 10.1038/319502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossomando A., Meruelo D. Viral sequences are associated with many histocompatibility genes. Immunogenetics. 1986;23(4):233–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00373018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz M., Aichele P., Vollenweider M., Bobe F. W., Cardinaux F., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M. Major histocompatibility complex--dependent T cell epitopes of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus nucleoprotein and their protective capacity against viral disease. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Sep;19(9):1657–1667. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E., Gordon R. D. Responsiveness to HY antigen Ir gene complementation and target cell specificity. Immunol Rev. 1977;35:59–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Haller O., Boll W., Lindenmann J., Weissmann C. Mx protein: constitutive expression in 3T3 cells transformed with cloned Mx cDNA confers selective resistance to influenza virus. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90493-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Haller O. Interferon-induced Mx protein: a mediator of cellular resistance to influenza virus. Interferon. 1987;8:1–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A. R., Rothbard J., Gotch F. M., Bahadur G., Wraith D., McMichael A. J. The epitopes of influenza nucleoprotein recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes can be defined with short synthetic peptides. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wekerle H., Schwab M., Linington C., Meyermann R. Antigen presentation in the peripheral nervous system: Schwann cells present endogenous myelin autoantigens to lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Dec;16(12):1551–1557. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester G., Sunshine G. H., Nardi N., Mitchison N. A. Antigen-presenting cells do not discriminate between self and nonself. Immunogenetics. 1984;19(6):487–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00403439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]