Abstract
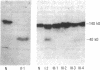
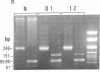
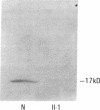
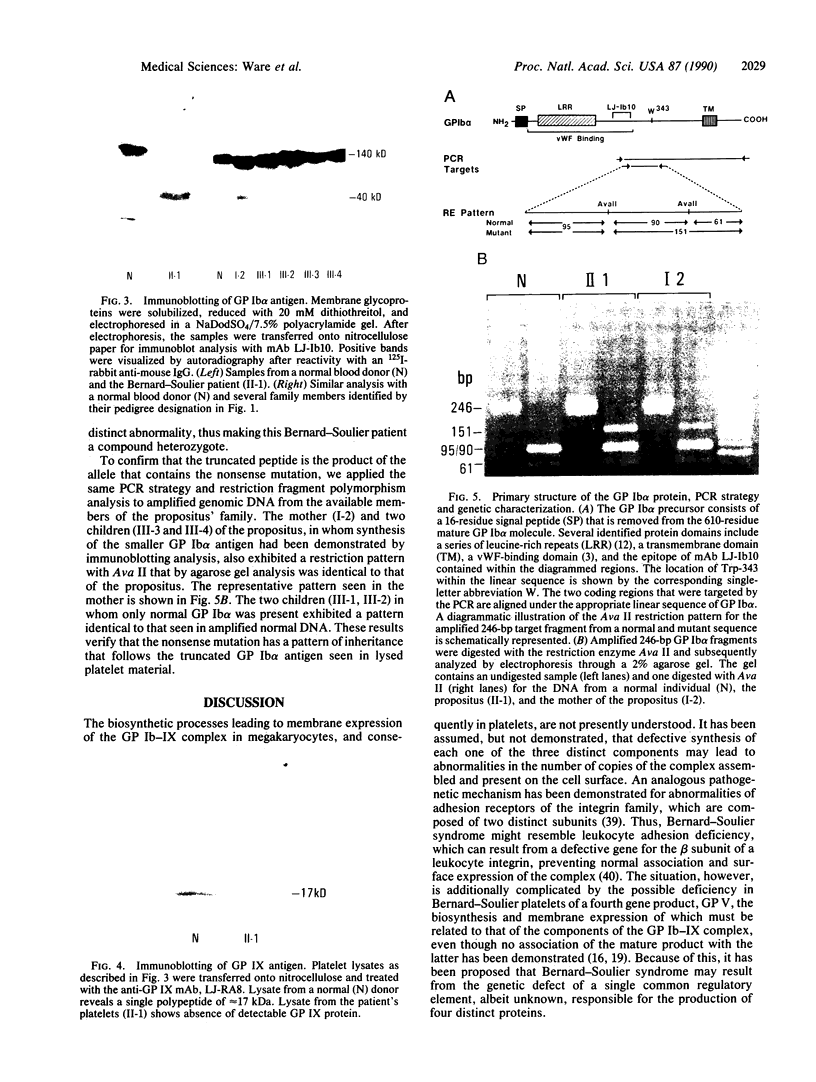
Three distinct gene products, the alpha and beta chains of glycoprotein (GP) Ib and GP IX, constitute the platelet membrane GP Ib-IX complex, a receptor for von Willebrand factor and thrombin involved in platelet adhesion and aggregation. Defective function of the GP Ib-IX complex is the hallmark of a rare congenital bleeding disorder of still undefined pathogenesis, the Bernard-Soulier syndrome. We have analyzed the molecular basis of this disease in one patient in whom immunoblotting of solubilized platelets demonstrated absence of normal GP Ib alpha but presence of a smaller immunoreactive species. The truncated polypeptide was also present, along with normal protein, in platelets from the patient's mother and two of his four children. Genetic characterization identified a nucleotide transition changing the Trp-343 codon (TGG) to a nonsense codon (TGA). Such a mutation explains the origin of the smaller GP Ib alpha, which by lacking half of the sequence on the carboxyl-terminal side, including the trans-membrane domain, cannot be properly inserted in the platelet membrane. Both normal and mutant codons were found in the patient, suggesting that he is a compound heterozygote with a still unidentified defect in the other GP Ib alpha allele. Nonsense mutation and truncated GP Ib alpha polypeptide were found to cosegregate in four individuals through three generations and were associated with either Bernard-Soulier syndrome or carrier state phenotype. The molecular abnormality demonstrated in this family provides evidence that defective synthesis of GP Ib alpha alters the membrane expression of the GP Ib-IX complex and may be responsible for Bernard-Soulier syndrome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berndt M. C., Gregory C., Chong B. H., Zola H., Castaldi P. A. Additional glycoprotein defects in Bernard-Soulier's syndrome: confirmation of genetic basis by parental analysis. Blood. 1983 Oct;62(4):800–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemetson K. J., Lüscher E. F. Membrane glycoprotein abnormalities in pathological platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 24;947(1):53–73. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemetson K. J., McGregor J. L., James E., Dechavanne M., Lüscher E. F. Characterization of the platelet membrane glycoprotein abnormalities in Bernard-Soulier syndrome and comparison with normal by surface-labeling techniques and high-resolution two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):304–311. doi: 10.1172/JCI110618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Fabris F., Casonato A., Fabris P., Dal Ben M. G., Barbato A., Girolami A. Bernard-Soulier syndrome: diagnosis by an ELISA method using monoclonal antibodies in 2 new unrelated patients. Acta Haematol. 1986;75(4):203–208. doi: 10.1159/000206125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Girolami A., Russell S., Ruggeri Z. M. Interaction of asialo von Willebrand factor with glycoprotein Ib induces fibrinogen binding to the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex and mediates platelet aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1198–1203. doi: 10.1172/JCI111816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Shapiro S. S. Properties of human asialo-factor VIII. A ristocetin-independent platelet-aggregating agent. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):321–328. doi: 10.1172/JCI110259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouin J., McGregor J. L., Parmentier S., Izaguirre C. A., Clemetson K. J. Residual amounts of glycoprotein Ib concomitant with near-absence of glycoprotein IX in platelets of Bernard-Soulier patients. Blood. 1988 Sep;72(3):1086–1088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du X., Beutler L., Ruan C., Castaldi P. A., Berndt M. C. Glycoprotein Ib and glycoprotein IX are fully complexed in the intact platelet membrane. Blood. 1987 May;69(5):1524–1527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M., Pickering C., Martin J., Cartwright I., Preston F. E. A new familial 'giant platelet syndrome' with structural, metabolic and functional abnormalities of platelets due to a primary megakaryocyte defect. Br J Haematol. 1987 Apr;65(4):429–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb04145.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruel Y., Boizard B., Daffos F., Forestier F., Caen J., Wautier J. L. Determination of platelet antigens and glycoproteins in the human fetus. Blood. 1986 Aug;68(2):488–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa M., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Roberts J. R., Ruggeri Z. M. The von Willebrand factor-binding domain of platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib. Characterization by monoclonal antibodies and partial amino acid sequence analysis of proteolytic fragments. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12579–12585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon J. T., Jamieson G. A. The glycocalicin portion of platelet glycoprotein Ib expresses both high and moderate affinity receptor sites for thrombin. A soluble radioreceptor assay for the interaction of thrombin with platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13224–13229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey M. J., Williams S. A., Roth G. J. Human platelet glycoprotein IX: an adhesive prototype of leucine-rich glycoproteins with flank-center-flank structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6773–6777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingerslev J., Stenbjerg S., Taaning E. A case of Bernard-Soulier syndrome: study of platelet glycoprotein Ib in a kindred. Eur J Haematol. 1987 Aug;39(2):182–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1987.tb00751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson G. A., Okumura T. Reduced thrombin binding and aggregation in Bernard-Soulier platelets. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):861–864. doi: 10.1172/JCI109000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., Hollander N., Roberts T. M., Anderson D. C., Springer T. A. Heterogeneous mutations in the beta subunit common to the LFA-1, Mac-1, and p150,95 glycoproteins cause leukocyte adhesion deficiency. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):193–202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo V. T., Hodson E., Roberts J. R., Kunicki T. J., Zimmerman T. S., Ruggeri Z. M. Independent modulation of von Willebrand factor and fibrinogen binding to the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex as demonstrated by monoclonal antibody. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1950–1958. doi: 10.1172/JCI112193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. A., Chung D. W., Fujikawa K., Hagen F. S., Davie E. W., Roth G. J. The alpha and beta chains of human platelet glycoprotein Ib are both transmembrane proteins containing a leucine-rich amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2135–2139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. A., Chung D. W., Fujikawa K., Hagen F. S., Papayannopoulou T., Roth G. J. Cloning of the alpha chain of human platelet glycoprotein Ib: a transmembrane protein with homology to leucine-rich alpha 2-glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5615–5619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery R. R., Kunicki T. J., Taves C., Pidard D., Corcoran M. Diagnosis of Bernard-Soulier syndrome and Glanzmann's thrombasthenia with a monoclonal assay on whole blood. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):385–389. doi: 10.1172/JCI110780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. L., Kaese S. E., Gastineau D. A., Otteman L. A., Bowie E. J. Bernard-Soulier syndrome: whole blood diagnostic assays of platelets. Mayo Clin Proc. 1989 May;64(5):522–530. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)65556-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurden A. T., Didry D., Rosa J. P. Molecular defects of platelets in Bernard-Soulier syndrome. Blood Cells. 1983;9(2):333–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole T. E., Loftus J. C., Plow E. F., Glass A. A., Harper J. R., Ginsberg M. H. Efficient surface expression of platelet GPIIb-IIIa requires both subunits. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):14–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Platelet plasma membrane glycoproteins. Evidence for the presence of nonequivalent disulfide bonds using nonreduced-reduced two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2121–2126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., De Marco L., Gatti L., Bader R., Montgomery R. R. Platelets have more than one binding site for von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):1–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI110946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Cunningham M., Hoxie J. A. Detection of activated platelets in whole blood using activation-dependent monoclonal antibodies and flow cytometry. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):307–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricker R. B., Wong D., Saks S. R., Corash L., Shuman M. A. Acquired Bernard-Soulier syndrome. Evidence for the role of a 210,000-molecular weight protein in the interaction of platelets with von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1172/JCI112084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Takio K., Handa M., Ruggeri Z. M. Amino acid sequence of the von Willebrand factor-binding domain of platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5610–5614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicente V., Kostel P. J., Ruggeri Z. M. Isolation and functional characterization of the von Willebrand factor-binding domain located between residues His1-Arg293 of the alpha-chain of glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18473–18479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Turitto V. T., Baumgartner H. R. Effect of shear rate on platelet interaction with subendothelium in citrated and native blood. I. Shear rate--dependent decrease of adhesion in von Willebrand's disease and the Bernard-Soulier syndrome. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Nov;92(5):750–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenger R. H., Kieffer N., Wicki A. N., Clemetson K. J. Structure of the human blood platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib alpha gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):389–395. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80853-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]