Abstract
The defensive tail-withdrawal reflex of Aplysia californica, mediated by identified sensory neurons in pleural ganglia that form synapses on motor cells in pedal ganglia, can be sensitized by stimulating the animal with electric shock. The neurophysiological basis of this simple form of learning is thought to be the increased release of transmitter by the sensory neurons. Earlier work has focused on cAMP-dependent protein phosphorylation as the cause of the presynaptic facilitation underlying short-term sensitization. Using physiological concentrations of Mg2+ during fractionation, we now find that, independent from cAMP, protein kinase C is translocated in sensory neurons by sensitizing stimuli. Translocation occurred after behavioral training of the animal and after application to isolated ganglia of serotonin or phorbol esters. Taken together with the neurophysiological evidence presented in the accompanying paper that phorbol esters can produce the facilitation, these biochemical results suggest that protein kinase C plays a role in producing the presynaptic facilitation that underlies short-term sensitization and dishabituation of defensive reflexes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akers R. F., Lovinger D. M., Colley P. A., Linden D. J., Routtenberg A. Translocation of protein kinase C activity may mediate hippocampal long-term potentiation. Science. 1986 Feb 7;231(4738):587–589. doi: 10.1126/science.3003904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bank B., DeWeer A., Kuzirian A. M., Rasmussen H., Alkon D. L. Classical conditioning induces long-term translocation of protein kinase C in rabbit hippocampal CA1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1988–1992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter D. A., Byrne J. H. Serotonergic modulation of two potassium currents in the pleural sensory neurons of Aplysia. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Sep;62(3):665–679. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.62.3.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernier L., Castellucci V. F., Kandel E. R., Schwartz J. H. Facilitatory transmitter causes a selective and prolonged increase in adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in sensory neurons mediating the gill and siphon withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. J Neurosci. 1982 Dec;2(12):1682–1691. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-12-01682.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braha O., Dale N., Hochner B., Klein M., Abrams T. W., Kandel E. R. Second messengers involved in the two processes of presynaptic facilitation that contribute to sensitization and dishabituation in Aplysia sensory neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):2040–2044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.2040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellucci V., Kandel E. R. Presynaptic facilitation as a mechanism for behavioral sensitization in Aplysia. Science. 1976 Dec 10;194(4270):1176–1178. doi: 10.1126/science.11560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingrich K. J., Byrne J. H. Simulation of synaptic depression, posttetanic potentiation, and presynaptic facilitation of synaptic potentials from sensory neurons mediating gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Mar;53(3):652–669. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.3.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenring J. R., Lasher R. S., Vallano M. L., Ueda T., Naito S., Sternberger N. H., Sternberger L. A., DeLorenzo R. J. Association of synapsin I with neuronal cytoskeleton. Identification in cytoskeletal preparations in vitro and immunocytochemical localization in brain of synapsin I. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8495–8504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. M., Castellucci V. F., Bayley H., Schwartz J. H. A molecular mechanism for long-term sensitization in Aplysia. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):62–65. doi: 10.1038/329062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho A. K., Thomas T. P., Chik C. L., Anderson W. B., Klein D. C. Protein kinase C: subcellular redistribution by increased Ca2+ influx. Evidence that Ca2+-dependent subcellular redistribution of protein kinase C is involved in potentiation of beta-adrenergic stimulation of pineal cAMP and cGMP by K+ and A23187. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9292–9297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
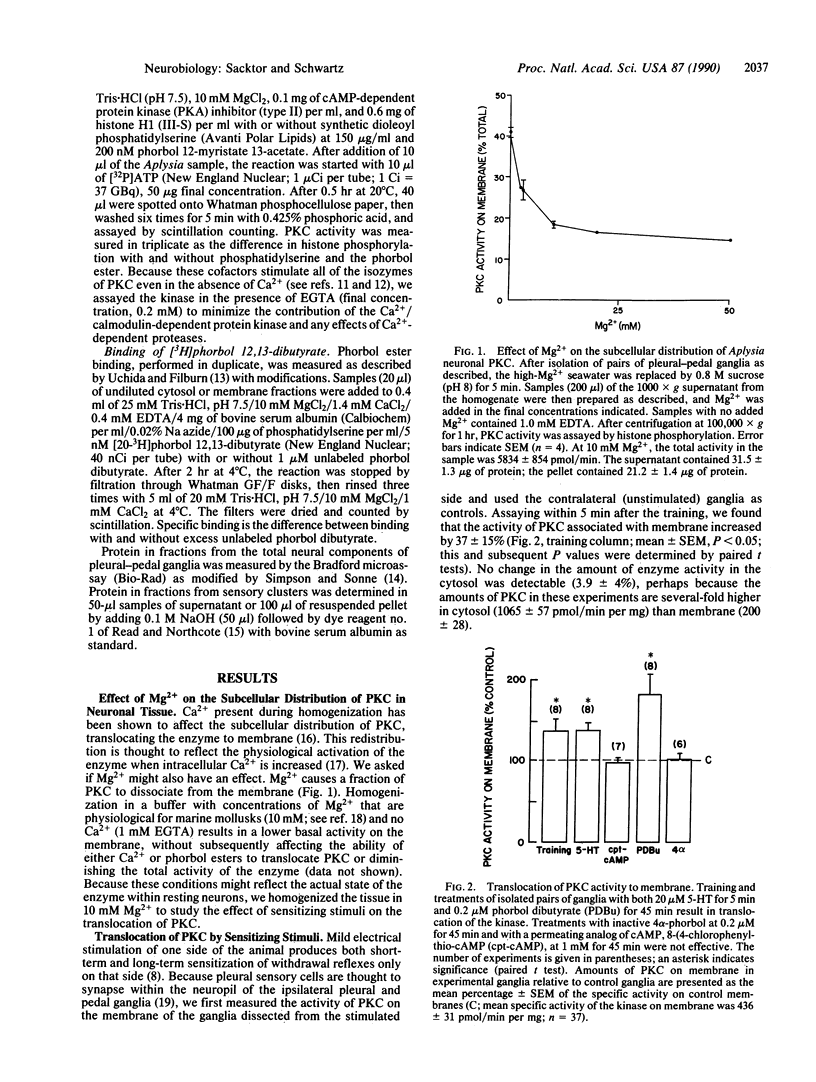
- Hochner B., Klein M., Schacher S., Kandel E. R. Additional component in the cellular mechanism of presynaptic facilitation contributes to behavioral dishabituation in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8794–8798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu G. Y., Hvalby O., Walaas S. I., Albert K. A., Skjeflo P., Andersen P., Greengard P. Protein kinase C injection into hippocampal pyramidal cells elicits features of long term potentiation. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):426–429. doi: 10.1038/328426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel E. R., Schwartz J. H. Molecular biology of learning: modulation of transmitter release. Science. 1982 Oct 29;218(4571):433–443. doi: 10.1126/science.6289442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Kandel E. R. Mechanism of calcium current modulation underlying presynaptic facilitation and behavioral sensitization in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6912–6916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B. Phorbol esters increase the amount of Ca2+, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase associated with plasma membrane. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):621–623. doi: 10.1038/301621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., McGuinness T. L., Leonard C. S., Sugimori M., Greengard P. Intraterminal injection of synapsin I or calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alters neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3035–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C., Ayoub G. S., Nicoll R. A. Phorbol esters enhance transmitter release in rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1987 Feb 10;403(1):198–203. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinow R., Schulman H., Tsien R. W. Inhibition of postsynaptic PKC or CaMKII blocks induction but not expression of LTP. Science. 1989 Aug 25;245(4920):862–866. doi: 10.1126/science.2549638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus E. A., Nolen T. G., Rankin C. H., Carew T. J. Behavioral dissociation of dishabituation, sensitization, and inhibition in Aplysia. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):210–213. doi: 10.1126/science.3388032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R. A., Haycock J. W., Wang J. K., Greengard P. Phorbol ester enhancement of neurotransmitter release from rat brain synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1987 Feb;48(2):615–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb04137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Kuhn L. J., Vandenbark G. R. Phorbol diester receptor copurifies with protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
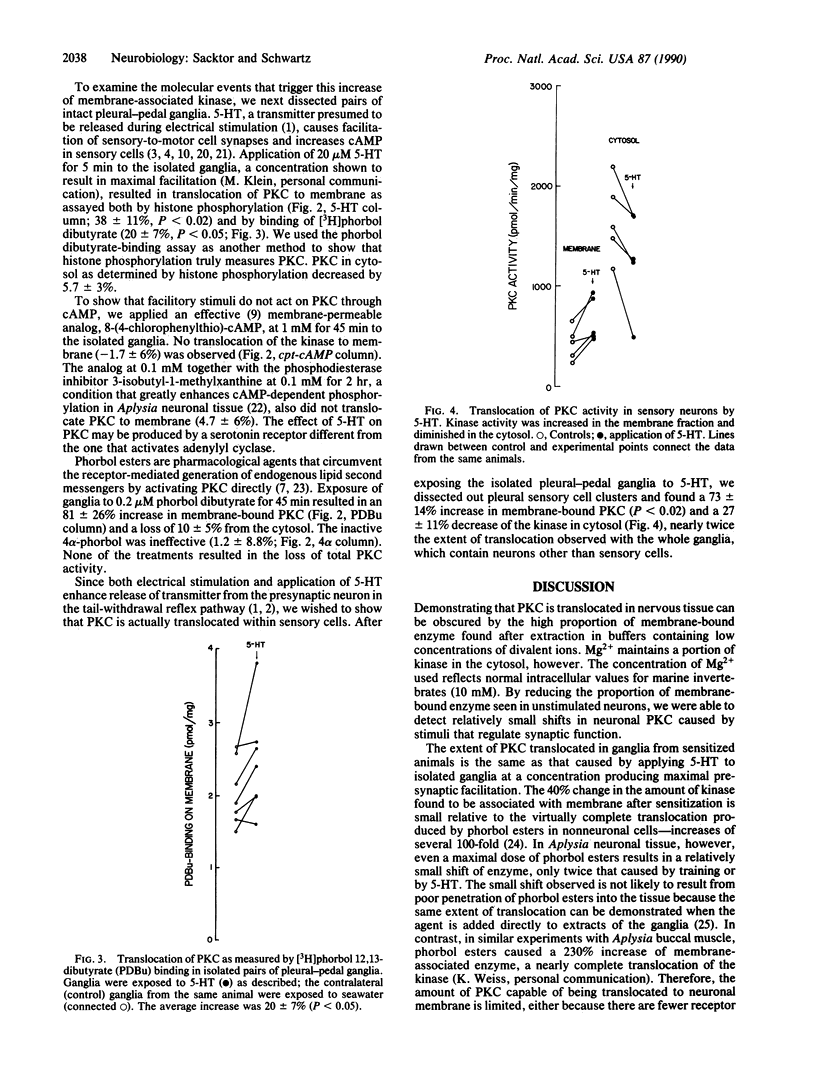
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brian C. A., Lawrence D. S., Kaiser E. T., Weinstein I. B. Protein kinase C phosphorylates the synthetic peptide Arg-Arg-Lys-Ala-Ser-Gly-Pro-Pro-Val in the presence of phospholipid plus either Ca2+ or a phorbol ester tumor promoter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 15;124(1):296–302. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90951-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ocorr K. A., Byrne J. H. Membrane responses and changes in cAMP levels in Aplysia sensory neurons produced by serotonin, tryptamine, FMRFamide and small cardioactive peptideB (SCPB). Neurosci Lett. 1985 Apr 9;55(2):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read S. M., Northcote D. H. Minimization of variation in the response to different proteins of the Coomassie blue G dye-binding assay for protein. Anal Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;116(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90321-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz K. P., Byrne J. H. Long-term sensitization in Aplysia: biophysical correlates in tail sensory neurons. Science. 1987 Feb 6;235(4789):685–687. doi: 10.1126/science.2433766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelbaum S. A., Camardo J. S., Kandel E. R. Serotonin and cyclic AMP close single K+ channels in Aplysia sensory neurones. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):413–417. doi: 10.1038/299413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Sonne O. A simple, rapid, and sensitive method for measuring protein concentration in subcellular membrane fractions prepared by sucrose density ultracentrifugation. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 15;119(2):424–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90608-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweatt J. D., Kandel E. R. Persistent and transcriptionally-dependent increase in protein phosphorylation in long-term facilitation of Aplysia sensory neurons. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):51–54. doi: 10.1038/339051a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka C., Taniyama K., Kusunoki M. A phorbol ester and A23187 act synergistically to release acetylcholine from the guinea pig ileum. FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 17;175(1):165–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80591-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Filburn C. R. Affinity chromatography of protein kinase C-phorbol ester receptor on polyacrylamide-immobilized phosphatidylserine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12311–12314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakade A. R., Malhotra R. K., Wakade T. D. Phorbol ester, an activator of protein kinase C, enhances calcium-dependent release of sympathetic neurotransmitter. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;331(1):122–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00498863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. P., Byrne J. H. Modulation of a steady-state Ca2+-activated, K+ current in tail sensory neurons of Aplysia: role of serotonin and cAMP. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Jan;61(1):32–44. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.61.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters E. T., Byrne J. H., Carew T. J., Kandel E. R. Mechanoafferent neurons innervating tail of Aplysia. I. Response properties and synaptic connections. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Dec;50(6):1522–1542. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.6.1522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters E. T., Byrne J. H., Carew T. J., Kandel E. R. Mechanoafferent neurons innervating tail of Aplysia. II. Modulation by sensitizing stimulation. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Dec;50(6):1543–1559. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.6.1543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurgil N., Zisapel N. Phorbol ester and calcium act synergistically to enhance neurotransmitter release by brain neurons in culture. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 17;185(2):257–261. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80918-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



