Abstract
After mixed infection, up to half of related retroviruses are recombinants. During infection, retroviral RNA genomes are first converted to complementary DNA (cDNA) and then to double-stranded DNA. Thus recombination could occur during reverse transcription, by RNA template switching, or after reverse transcription, by breakage and reunion of DNA. It has not been possible to distinguish between these two potential mechanisms of recombination because both single-stranded cDNA and double-stranded proviral DNA exist in infected cells during the eclipse period. Therefore we have analyzed for recombinant molecules among cDNA products transcribed in vitro from RNA of disrupted virions. Since recombinants from allelic parents can only be distinguished from parental genomes by point mutations, we have examined the cDNAs from virions with distinct genetic structures for recombinant-specific size and sequence markers. The parents share a common internal allele that allows homology-directed recombination, but each contains specific flanking sequences. One parent is a synthetically altered Harvey murine sarcoma virus RNA that lacks a retroviral 3' terminus but carries a Moloney murine retrovirus-derived envelope gene (env) fragment 3' of its transforming ras gene. The other parent is intact Moloney virus. Using a Harvey-specific 5' primer and a Moloney-specific 3' primer, we have found recombinant cDNAs with the polymerase chain reaction, proving directly that retroviruses can recombine during reverse transcription unassisted by cellular enzymes, probably by template switching during cDNA synthesis. The recombinants that were obtained in vitro were identical with those obtained in parallel experiments in vivo.
Full text
PDF


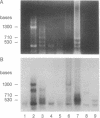
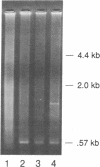
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beemon K., Duesberg P., Vogt P. Evidence for crossing-over between avian tumor viruses based on analysis of viral RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4254–4258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G. Genetic recombination between avian leukosis and sarcoma viruses. Experimental variables and the frequencies of recombination. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):534–544. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90479-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani E., Helm K. V., Duesberg P. Evidence for 30-40S RNA as precursor of the 60-70S RNA of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):401–405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M. Structure, replication, and recombination of retrovirus genomes: some unifying hypotheses. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jan;42(1):1–26. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-42-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Bister K., Vogt P. K. The RNA of avian acute leukemia virus MC29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4320–4324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H. Physical properties of Rous Sarcoma Virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1511–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H. Physical properties of Rous Sarcoma Virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1511–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. P., Tabin C. J., Wang J. Y., Weinberg R., Baltimore D. Transfection of fibroblasts by cloned Abelson murine leukemia virus DNA and recovery of transmissible virus by recombination with helper virus. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):271–285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.271-285.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb M. P., Weinberg R. A. Generation of novel, biologically active Harvey sarcoma viruses via apparent illegitimate recombination. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):136–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.136-150.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich D. W., Duesberg P. H. Retroviral transduction of oncogenic sequences involves viral DNA instead of RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3733–3737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman S. A., Coffin J. M. Efficient packaging of readthrough RNA in ALV: implications for oncogene transduction. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):845–848. doi: 10.1126/science.3033828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. C., Hay N., Bishop J. M. The role of RNA molecules in transduction of the proto-oncogene c-fps. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):935–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E. The mechanism for genetic recombination in the avian retroviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;79:295–309. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66853-1_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junghans R. P., Boone L. R., Skalka A. M. Retroviral DNA H structures: displacement-assimilation model of recombination. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junghans R. P., Duesberg P. H., Knight C. A. In vitro synthesis of full-length DNA transcripts of Rous sarcoma virus RNA by viral DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4895–4899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisel J., Bender W., Hu S., Duesberg P. H., Davidson N. Structure of 50 to 70S RNA from Moloney sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):384–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.384-394.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg E., Donoghue D. J., Baltimore D. Analysis of a 5' leader sequence on murine leukemia virus 21S RNA: heteroduplex mapping with long reverse transcriptase products. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):435–451. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90318-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg E., Smotkin D., Baltimore D., Weinberg R. A. In vitro synthesis of infectious DNA of murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 8;269(5624):122–126. doi: 10.1038/269122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., Parker R. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Transduction of a cellular oncogene: the genesis of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2519–2523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Evolution of cancer genes as a mutation-driven process. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1697–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E. The molecular genetics of cellular oncogenes. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:553–612. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.003005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]