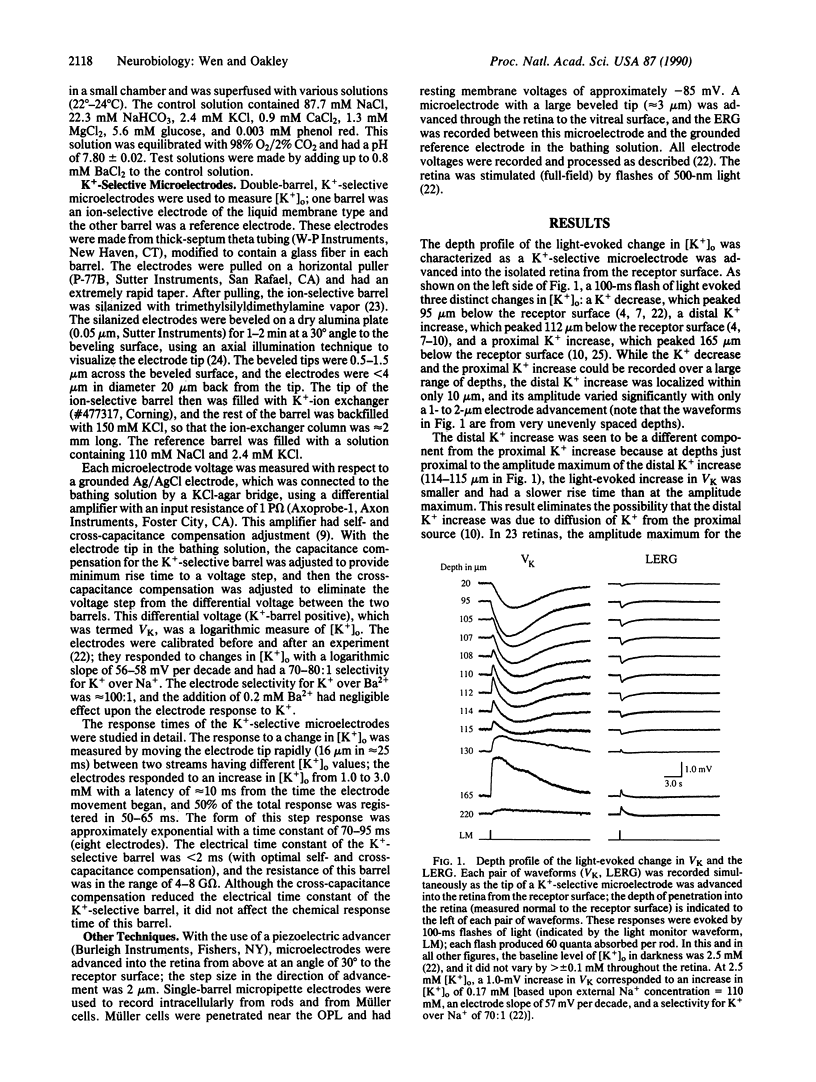
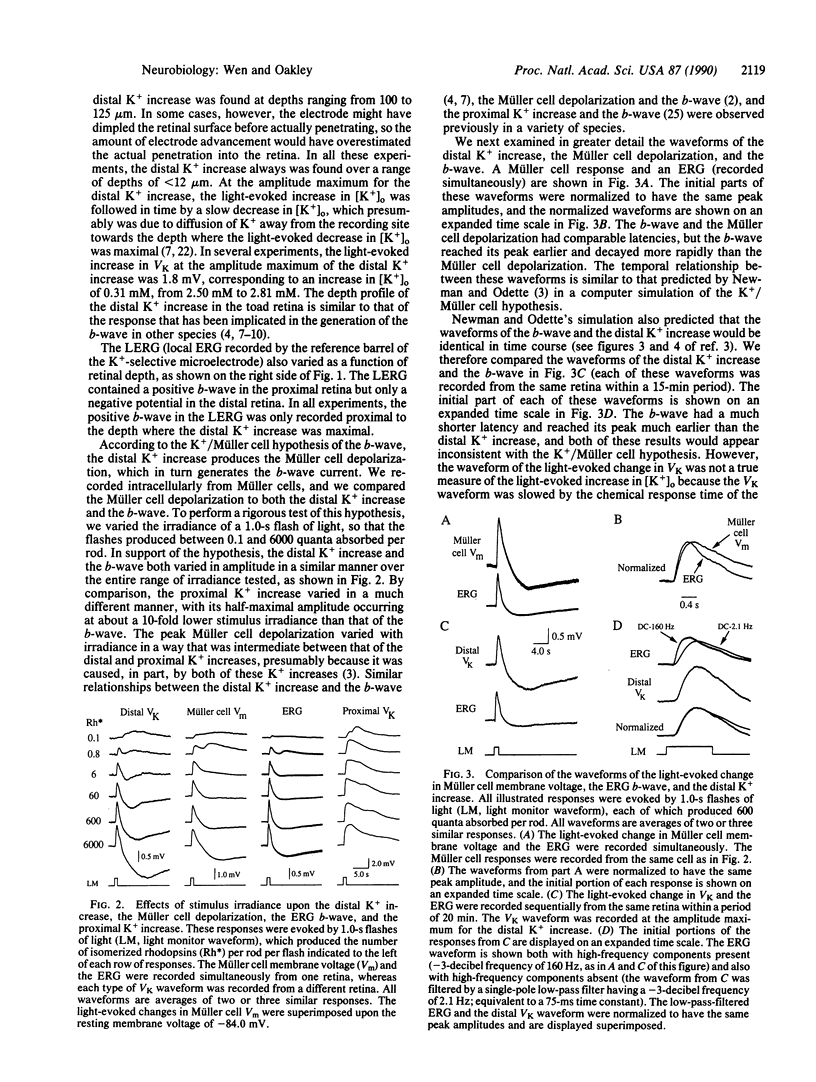
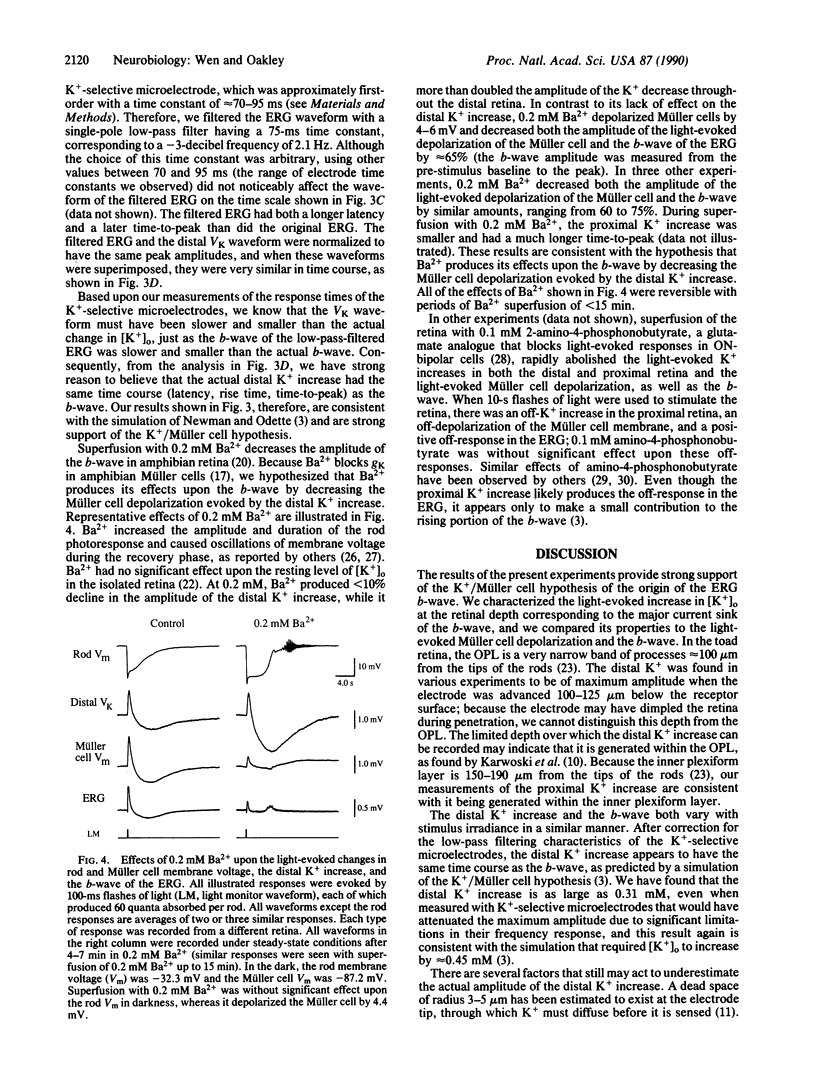
Abstract
We tested the hypothesis that a light-evoked increase in [K+]o produces a depolarization of the Müller cell membrane, which in turn generates the electroretinogram b-wave current. Using Bufo marinus isolated retinas and K(+)-selective microelectrodes, we recorded two distinct light-evoked increases in extracellular K+ concentration: one in the inner plexiform layer and the other near the outer plexiform layer; the "distal" K+ increase was found over only 10-microns depth and had a maximum amplitude of 0.3 mM. We also recorded the electroretinogram and the light-evoked responses of rods and Müller cells. After correction for the response time of the K(+)-selective microelectrode, the waveforms of all three of these responses were almost exactly as predicted by an earlier computer simulation of the K+/Müller cell hypothesis of the b-wave by Newman and Odette [Newman, E.A. & Odette, L.L. (1984) J. Neurophysiol. 51, 164-182]. The distal K+ increase and the b-wave varied in a similar manner as a function of stimulus irradiance. Superfusion with 0.2 mM Ba2+ attenuated both the Müller cell depolarization and the b-wave by approximately 65% but had no significant effect upon the distal K+ increase. Because Ba2+ reduces K+ conductance of Müller cells, these results are very strong support of the K+/Müller cell hypothesis of the origin of the electroretinogram b-wave; the light-evoked increase in extracellular potassium concentration still is present during superfusion with Ba2+, but the K(+)-evoked Müller cell depolarization and the b-wave are decreased in amplitude because Müller cell K+ conductance is reduced.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brew H., Attwell D. Electrogenic glutamate uptake is a major current carrier in the membrane of axolotl retinal glial cells. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):707–709. doi: 10.1038/327707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brew H., Gray P. T., Mobbs P., Attwell D. Endfeet of retinal glial cells have higher densities of ion channels that mediate K+ buffering. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):466–468. doi: 10.1038/324466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. T., Flaming D. G. Opposing effects of calcium and barium in vertebrate rod photoreceptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1587–1590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman P. A., Carras P. L., Miller R. F. Barium reverses the transretinal potassium gradient of the amphibian retina. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Sep 11;80(1):61–65. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90495-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick E., Miller R. F. Extracellular K+ activity changes related to electroretinogram components. I. Amphibian (I-type) retinas. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jun;85(6):885–909. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.6.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick E., Miller R. F. Light-evoked potassium activity in mudpuppy retina: its relationship to the b-wave of the electroretinogram. Brain Res. 1978 Oct 13;154(2):388–394. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90711-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L., Gerschenfeld H. M., Quandt F. N. Calcium spikes in toad rods. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:495–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. A. An improved method for illuminating pipet tips for fire-polishing. J Neurosci Methods. 1985 Nov-Dec;15(3):239–241. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(85)90104-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frishman L. J., Steinberg R. H. Intraretinal analysis of the threshold dark-adapted ERG of cat retina. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Jun;61(6):1221–1232. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.61.6.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griff E. R., Shirao Y., Steinberg R. H. Ba2+ unmasks K+ modulation of the Na+-K+ pump in the frog retinal pigment epithelium. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Dec;86(6):853–876. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.6.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu K. G., Marmor M. F. Selective actions of barium on the c-wave and slow negative potential of the rabbit eye. Vision Res. 1984;24(10):1153–1156. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(84)90169-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karwoski C. J., Lu H. K., Newman E. A. Spatial buffering of light-evoked potassium increases by retinal Müller (glial) cells. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):578–580. doi: 10.1126/science.2785716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karwoski C. J., Newman E. A., Shimazaki H., Proenza L. M. Light-evoked increases in extracellular K+ in the plexiform layers of amphibian retinas. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Aug;86(2):189–213. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline R. P., Ripps H., Dowling J. E. Generation of b-wave currents in the skate retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5727–5731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline R. P., Ripps H., Dowling J. E. Light-induced potassium fluxes in the skate retina. Neuroscience. 1985 Jan;14(1):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow R. P., Qian H. H., Ripps H. gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA)-induced currents of skate Muller (glial) cells are mediated by neuronal-like GABAA receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4326–4330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. F., Dowling J. E. Intracellular responses of the Müller (glial) cells of mudpuppy retina: their relation to b-wave of the electroretinogram. J Neurophysiol. 1970 May;33(3):323–341. doi: 10.1152/jn.1970.33.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. A. Current source-density analysis of the b-wave of frog retina. J Neurophysiol. 1980 May;43(5):1355–1366. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.43.5.1355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. A. Membrane physiology of retinal glial (Müller) cells. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2225–2239. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02225.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. A., Odette L. L. Model of electroretinogram b-wave generation: a test of the K+ hypothesis. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Jan;51(1):164–182. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.51.1.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B., 2nd Effects of maintained illumination upon [K+]0 in the subretinal space of the isolated retina of the toad. Vision Res. 1983;23(11):1325–1337. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(83)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B., 2nd, Wen R. Extracellular pH in the isolated retina of the toad in darkness and during illumination. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:353–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odette L. L., Newman E. A. Model of potassium dynamics in the central nervous system. Glia. 1988;1(3):198–210. doi: 10.1002/glia.440010305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter M. M., Miller R. F. 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid: a new pharmacological tool for retina research. Science. 1981 Jan 9;211(4478):182–185. doi: 10.1126/science.6255566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockton R. A., Slaughter M. M. B-wave of the electroretinogram. A reflection of ON bipolar cell activity. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Jan;93(1):101–122. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkovsky P., Stone S., Ripps H. Pharmacological modification of the light-induced responses of Müller (glial) cells in the amphibian retina. Brain Res. 1985 Feb 25;328(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91329-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



