Fig. 1.
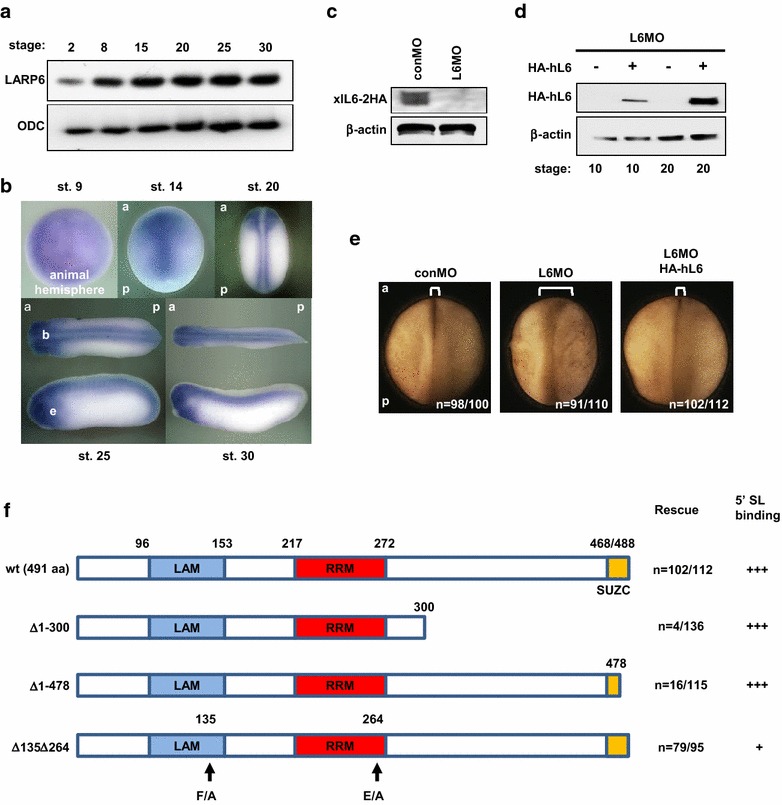
LARP6 morphants have neural tube closure defects. a Temporal expression profiles of LARP6 gene. b Spatial expression profiles of LARP6 gene. c LARP6 MO (L6MO) but not control MO (conMO) depleted X. laevis LARP6 protein (xlL6-2HA) in late neurula stage embryos. conMO or L6MO was injected with xlL6-2HA mRNA, and LARP6 was detected by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibody. d Human LARP6 (HA-hL6) was not knocked down by L6MO in stage 10 or 20 embryos. e Depletion of LARP6 resulted in neural tube closure defects. conMO, L6MO (15 ng/blastomere) and/or HA-hL6 mRNA (250 pg/blastomere) were injected into two dorsal blastomeres of 4-cell stage embryos (between animal pole and marginal zone). Images are dorsal views of late neurula stage embryos. f The summary of rescue experiments: the C-terminus of LARP6 is important for neural tube closure. LAM La motif, RRM RNA recognition motif, SUZC SUZ-C motif. n indicates number of embryos examined. 5′SL binding shows the interaction between LARP6 and the 5′ stem-loop region of collagen RNA. F phenylalanine, A alanine, E glutamic acid, a anterior, p posterior, b brain, e eye. ODC and β-actin were used as a loading control
