Abstract
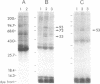
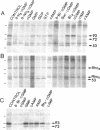
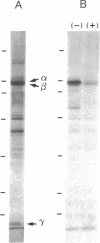
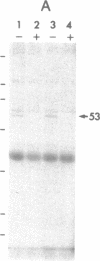
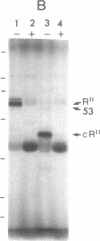
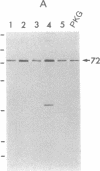
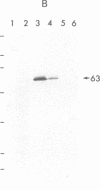
Cyclic GMP-binding proteins present in membrane fractions of bovine retina and, in particular, rod outer segments (ROS) were identified by photoaffinity labeling with 8-azido-[32P]cGMP. Two soluble proteins and two membrane-associated proteins were specifically labeled. The soluble proteins, 93 and 72 kDa, corresponded respectively to the alpha subunit of ROS cGMP phosphodiesterase and cGMP-dependent protein kinase. One of the two membrane-associated proteins, 53 kDa, was present in all particulate retinal fractions. Its function is unknown. It is distinct from cAMP-dependent protein kinase or the 63-kDa cGMP-activated channel from ROS. The second membrane-associated protein, 37 kDa, was present only in fractions that did not contain ROS. The molecular mass of this protein was similar to that of a cGMP-binding protein previously attributed to rod cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehr W., Devlin M. J., Applebury M. L. Isolation and characterization of cGMP phosphodiesterase from bovine rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11669–11677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caretta A., Saibil H. Visualization of cyclic nucleotide binding sites in the vertebrate retina by fluorescence microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1517–1522. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook N. J., Hanke W., Kaupp U. B. Identification, purification, and functional reconstitution of the cyclic GMP-dependent channel from rod photoreceptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):585–589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook N. J., Molday L. L., Reid D., Kaupp U. B., Molday R. S. The cGMP-gated channel of bovine rod photoreceptors is localized exclusively in the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6996–6999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnecki J., Geahlen R., Haley B. Synthesis and use of azido photoaffinity analogs of adenine and guanine nucleotides. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:642–653. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber D. B., Brown B. M., Lllley R. N. Cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and the phosphorylation of endogenous proteins of retinal rod outer segments. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 23;18(2):370–378. doi: 10.1021/bi00569a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie P. G., Beavo J. A. Characterization of a bovine cone photoreceptor phosphodiesterase purified by cyclic GMP-sepharose chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8133–8141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie P. G., Beavo J. A. cGMP is tightly bound to bovine retinal rod phosphodiesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4311–4315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES R. E., ROBINS R. K. PURINE NUCLEOSIDES. IX. THE SYNTHESIS OF 9-BETA-D-RIBOFURANOSYL URIC ACID AND OTHER RELATED 8-SUBSTITUTED PURINE RIBONUCLEOSIDES. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Apr 20;87:1772–1776. doi: 10.1021/ja01086a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Purification and characterization of the gamma regulatory subunit of the cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase from retinal rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11094–11099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch K. W., Stryer L. Highly cooperative feedback control of retinal rod guanylate cyclase by calcium ions. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):64–66. doi: 10.1038/334064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matesic D., Liebman P. A. cGMP-dependent cation channel of retinal rod outer segments. Nature. 1987 Apr 9;326(6113):600–603. doi: 10.1038/326600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Gold G. H. A cyclic nucleotide-gated conductance in olfactory receptor cilia. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):442–444. doi: 10.1038/325442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papermaster D. S. Preparation of retinal rod outer segments. Methods Enzymol. 1982;81:48–52. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)81010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polans A. S., Hermolin J., Bownds M. D. Light-induced dephosphorylation of two proteins in frog rod outer segments: influence of cyclic nucleotides and calcium. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Nov;74(5):595–613. doi: 10.1085/jgp.74.5.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter R. L., Taylor S. S. Correlation of the cAMP binding domain with a site of autophosphorylation on the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase II from porcine skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9000–9005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puckett K. L., Goldin S. M. Guanosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate stimulates release of actively accumulated calcium in purified disks from rod outer segments of bovine retina. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 8;25(7):1739–1746. doi: 10.1021/bi00355a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shichi H., Somers R. L. Light-dependent phosphorylation of rhodopsin. Purification and properties of rhodopsin kinase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):7040–7046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozawa T., Sokabe M., Terada S., Matsusaka H., Yoshizawa T. Detection of cyclic GMP binding protein and ion channel activity in frog rod outer segments. J Biochem. 1987 Aug;102(2):281–290. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster T. A., Nagy A. K., Farber D. B. 8-Azido-ATP (alpha 32P) binding to rod outer segment proteins. Exp Eye Res. 1988 Apr;46(4):475–484. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(88)80005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Cyclic GMP cascade of vision. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:87–119. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter U., Miller P., Wilson F., Menkes D., Greengard P. Immunological distinction between guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3757–3762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilden U., Kühn H. Light-dependent phosphorylation of rhodopsin: number of phosphorylation sites. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 8;21(12):3014–3022. doi: 10.1021/bi00541a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki A., Bartucca F., Ting A., Bitensky M. W. Reciprocal effects of an inhibitory factor on catalytic activity and noncatalytic cGMP binding sites of rod phosphodiesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3702–3706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman A. L., Yamanaka G., Eckstein F., Baylor D. A., Stryer L. Interaction of hydrolysis-resistant analogs of cyclic GMP with the phosphodiesterase and light-sensitive channel of retinal rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8813–8817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]