Abstract
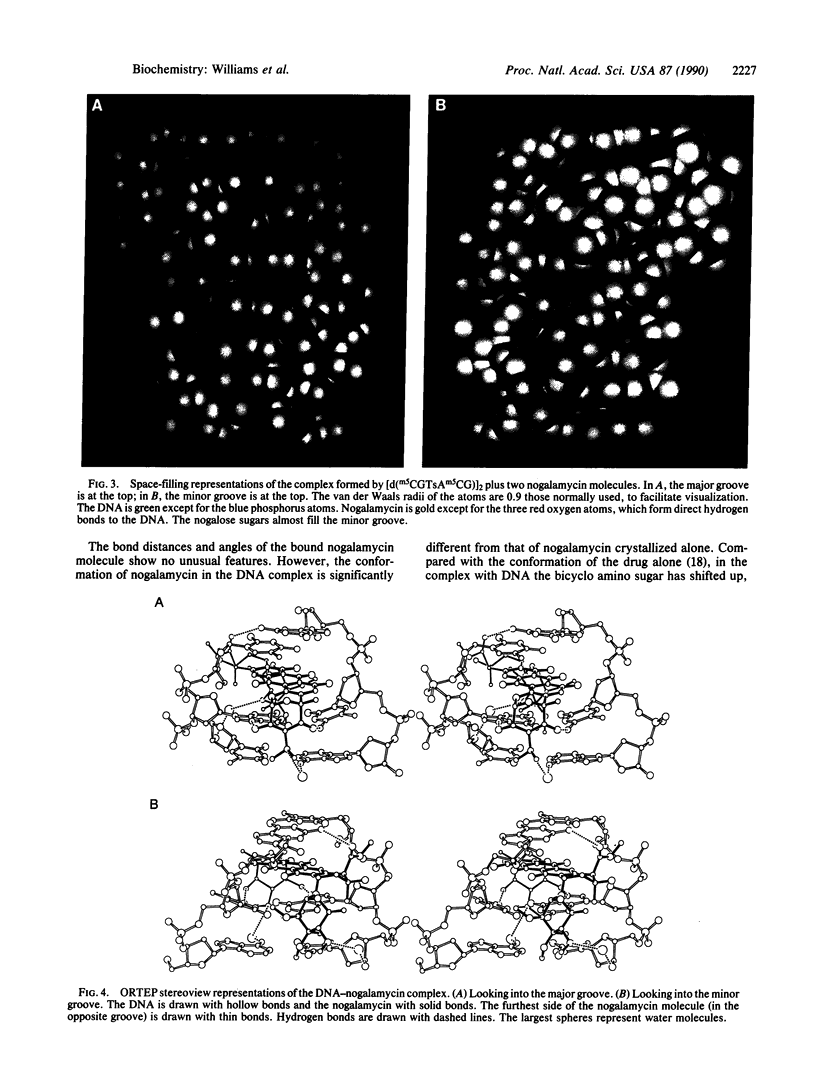
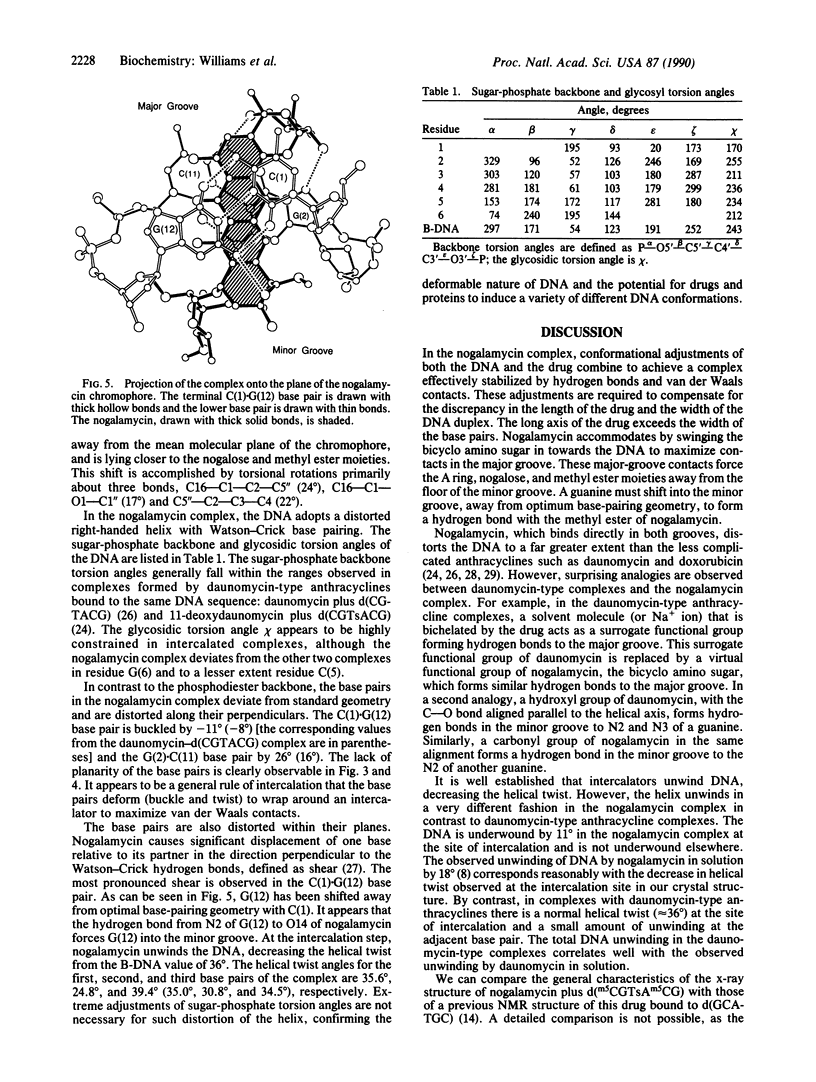
The anthracycline antibiotic nogalamycin, which binds to DNA, is composed of a planar aglycone substituted on each end to form an unusual dumbbell-shaped molecule. At one end nogalamycin contains an uncharged nogalose sugar and a methyl ester. At the other end nogalamycin contains a positively charged bicyclo amino sugar. We report the crystal structure of nogalamycin bound to the self-complementary DNA hexamer d(m5CGTsAm5CG). In this complex, the cytosines are methylated at the 5 position and the DNA contains a phosphorothioate linkage at the TpA step. Two nogalamycin molecules bind to the 6-base-pair fragment of double-helical DNA. The drug has threaded between the phosphodiester backbones with three aromatic rings intercalated within the DNA. In the major groove, the bicyclo amino sugar forms two direct hydrogen bonds to span a CG base pair and interacts indirectly with the next base pair of the duplex via a water-mediated hydrogen bond. In the minor groove, a carbonyl oxygen of nogalamycin forms a hydrogen bond directly to N2 of a guanine. The DNA base pairs are severely buckled by up to 26 degrees and are also distorted in directions perpendicular to the Watson-Crick hydrogen bonds. This complex illustrates the deformable nature of DNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhuyan B. K., Reusser F. Comparative biological activity of nogalamycin and its analogs. Cancer Res. 1970 Apr;30(4):984–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier D. A., Neidle S., Brown J. R. Molecular models for the interaction of the anti-tumour drug nogalamycin with DNA. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 15;33(18):2877–2880. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruse W. B., Salisbury S. A., Brown T., Cosstick R., Eckstein F., Kennard O. Chiral phosphorothioate analogues of B-DNA. The crystal structure of Rp-d[Gp(S)CpGp(S)CpGp(S)C]. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 20;192(4):891–905. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das G. C., Dasgupta S., Das Gupta N. N. Interaction of nogalamycin with DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 11;353(3):274–282. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. Definitions and nomenclature of nucleic acid structure components. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1797–1803. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis H. L. Nogalamycin inhibits ribonucleic acid synthesis in growing and developing cells of the slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):657–665. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fok J., Waring M. Breakdown of pulse-labeled ribonucleic acid in Bacillus megaterium, revealed by exposure to the antibiotics mithramycin, chromomycin, and nogalamycin. Mol Pharmacol. 1972 Jan;8(1):65–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Brassett C., Waring M. J. Kinetics of dissociation of nogalamycin from DNA: comparison with other anthracycline antibiotics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 5;840(3):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R. Footprinting studies on the interactions of nogalamycin, arugomycin, decilorubicin and viriplanin with DNA. Anticancer Drug Des. 1988 Dec;3(3):157–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. Evidence of different binding sites for nogalamycin in DNA revealed by association kinetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Nov 28;802(2):162–168. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersten W., Kersten H., Szybalski W. Physicochemical properties of complexes between deoxyribonucleic acid and antibiotics which affect ribonucleic acid synthesis (actinomycin, daunomycin, cinerubin, nogalamycin, chormomycin, mithramycin, and olivomycin). Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):236–244. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L. H., Kuentzel S. L., Murch L. L., Pschigoda L. M., Krueger W. C. Comparative biological and biochemical effects of nogalamycin and its analogs on L1210 leukemia. Cancer Res. 1979 Dec;39(12):4816–4822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. H., Hunter W. N., d'Estaintot B. L., Kennard O. DNA-drug interactions. The crystal structure of d(CGATCG) complexed with daunomycin. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):693–705. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90577-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumbridge T. W., Brown J. R. The effect of modification at the carbocyclic ring of nogalamycin on the interaction DNA. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Nov 1;28(21):3231–3234. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley G. J., Wang A. H., Ughetto G., van der Marel G., van Boom J. H., Rich A. Molecular structure of an anticancer drug-DNA complex: daunomycin plus d(CpGpTpApCpG). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7204–7208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle M. S., Hall J. G., Denny W. A., Wakelin L. P. NMR studies of the interaction of the antibiotic nogalamycin with the hexadeoxyribonucleotide duplex d(5'-GCATGC)2. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 14;27(12):4340–4349. doi: 10.1021/bi00412a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha R. K., Talapatra P., Mitra A., Mazumder S. Studies on the interactions of nogalamycin with duplex DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 20;474(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Ughetto G., Quigley G. J., Rich A. Interactions between an anthracycline antibiotic and DNA: molecular structure of daunomycin complexed to d(CpGpTpApCpG) at 1.2-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1987 Feb 24;26(4):1152–1163. doi: 10.1021/bi00378a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. Variation of the supercoils in closed circular DNA by binding of antibiotics and drugs: evidence for molecular models involving intercalation. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):247–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]