Abstract
Tumor cells attach, degrade, and migrate through basement membranes as they metastasize. Laminin, a major glycoprotein of basement membranes, promotes the metastatic activity of tumor cells by stimulating the attachment and migration of the cells and their secretion of collagenase IV. We have identified a synthetic peptide of 19 amino acids (Cys-Ser-Arg-Ala-Arg-Lys-Gln-Ala-Ala-Ser-Ile-Lys-Val-Ala-Val-Ser-Ala-Asp -Arg) from the sequence of the A chain of laminin that increases experimental metastases of the lungs by murine melanoma cells. The peptide is active when injected either intravenously or intraperitoneally. The peptide increased collagenase IV activity, a key enzyme in the breakdown of basement membranes, to the same extent as laminin. This peptide represents an active site on laminin for promotion of the metastatic phenotype and generates a probe for studying the regulation of malignant activities.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albini A., Iwamoto Y., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R., Aaronson S. A., Kozlowski J. M., McEwan R. N. A rapid in vitro assay for quantitating the invasive potential of tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 15;47(12):3239–3245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aumailley M., Nurcombe V., Edgar D., Paulsson M., Timpl R. The cellular interactions of laminin fragments. Cell adhesion correlates with two fragment-specific high affinity binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11532–11538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow D. P., Green N. M., Kurkinen M., Hogan B. L. Sequencing of laminin B chain cDNAs reveals C-terminal regions of coiled-coil alpha-helix. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2355–2362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsky S. H., Rao C. N., Williams J. E., Liotta L. A. Laminin molecular domains which alter metastasis in a murine model. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):843–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI111501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilozur M. E., Hay E. D. Neural crest migration in 3D extracellular matrix utilizes laminin, fibronectin, or collagen. Dev Biol. 1988 Jan;125(1):19–33. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charonis A. S., Skubitz A. P., Koliakos G. G., Reger L. A., Dege J., Vogel A. M., Wohlhueter R., Furcht L. T. A novel synthetic peptide from the B1 chain of laminin with heparin-binding and cell adhesion-promoting activities. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1253–1260. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung A. E., Jaffe R., Freeman I. L., Vergnes J. P., Braginski J. E., Carlin B. Properties of a basement membrane-related glycoprotein synthesized in culture by a mouse embryonal carcinoma-derived cell line. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clément B., Segui-Real B., Savagner P., Kleinman H. K., Yamada Y. Hepatocyte attachment to laminin is mediated through multiple receptors. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):185–192. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar D., Timpl R., Thoenen H. The heparin-binding domain of laminin is responsible for its effects on neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1463–1468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Metastasis: quantitative analysis of distribution and fate of tumor emboli labeled with 125 I-5-iodo-2'-deoxyuridine. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Oct;45(4):773–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. L., Deutzmann R., von der Mark K. Two distinct cell-binding domains in laminin can independently promote nonneuronal cell adhesion and spreading. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):589–598. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf J., Iwamoto Y., Sasaki M., Martin G. R., Kleinman H. K., Robey F. A., Yamada Y. Identification of an amino acid sequence in laminin mediating cell attachment, chemotaxis, and receptor binding. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):989–996. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90707-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf J., Ogle R. C., Robey F. A., Sasaki M., Martin G. R., Yamada Y., Kleinman H. K. A pentapeptide from the laminin B1 chain mediates cell adhesion and binds the 67,000 laminin receptor. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 3;26(22):6896–6900. doi: 10.1021/bi00396a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Yamada K. M., Olden K. Investigation of the biological effects of anti-cell adhesive synthetic peptides that inhibit experimental metastasis of B16-F10 murine melanoma cells. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):782–790. doi: 10.1172/JCI113384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto Y., Robey F. A., Graf J., Sasaki M., Kleinman H. K., Yamada Y., Martin G. R. YIGSR, a synthetic laminin pentapeptide, inhibits experimental metastasis formation. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1132–1134. doi: 10.1126/science.2961059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Cannon F. B., Laurie G. W., Hassell J. R., Aumailley M., Terranova V. P., Martin G. R., DuBois-Dalcq M. Biological activities of laminin. J Cell Biochem. 1985;27(4):317–325. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240270402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Graf J., Iwamoto Y., Sasaki M., Schasteen C. S., Yamada Y., Martin G. R., Robey F. A. Identification of a second active site in laminin for promotion of cell adhesion and migration and inhibition of in vivo melanoma lung colonization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Jul;272(1):39–45. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., McGarvey M. L., Liotta L. A., Robey P. G., Tryggvason K., Martin G. R. Isolation and characterization of type IV procollagen, laminin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycan from the EHS sarcoma. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6188–6193. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner W., Robey F. A. Automated synthesis and use of N-chloroacetyl-modified peptides for the preparation of synthetic peptide polymers and peptide-protein immunogens. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1987 Dec;30(6):794–800. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1987.tb03388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Lee C. W., Morakis D. J. New method for preparing large surfaces of intact human basement membrane for tumor invasion studies. Cancer Lett. 1980 Dec;11(2):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(80)90105-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A. Tumor invasion and metastases: role of the basement membrane. Warner-Lambert Parke-Davis Award lecture. Am J Pathol. 1984 Dec;117(3):339–348. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Timpl R. Laminin and other basement membrane components. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:57–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio A. M., Shaw L. M. Macrophage interactions with laminin: PMA selectively induces the adherence and spreading of mouse macrophages on a laminin substratum. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1873–1880. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich R., Thompson E. W., Iwamoto Y., Martin G. R., Deason J. R., Fuller G. C., Miskin R. Effects of inhibitors of plasminogen activator, serine proteinases, and collagenase IV on the invasion of basement membranes by metastatic cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 15;48(12):3307–3312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Kato S., Kohno K., Martin G. R., Yamada Y. Sequence of the cDNA encoding the laminin B1 chain reveals a multidomain protein containing cysteine-rich repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):935–939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Kleinman H. K., Huber H., Deutzmann R., Yamada Y. Laminin, a multidomain protein. The A chain has a unique globular domain and homology with the basement membrane proteoglycan and the laminin B chains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16536–16544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Yamada Y. The laminin B2 chain has a multidomain structure homologous to the B1 chain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17111–17117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sephel G. C., Tashiro K. I., Sasaki M., Greatorex D., Martin G. R., Yamada Y., Kleinman H. K. Laminin A chain synthetic peptide which supports neurite outgrowth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jul 31;162(2):821–829. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92384-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro K., Sephel G. C., Weeks B., Sasaki M., Martin G. R., Kleinman H. K., Yamada Y. A synthetic peptide containing the IKVAV sequence from the A chain of laminin mediates cell attachment, migration, and neurite outgrowth. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16174–16182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., Liotta L. A., Russo R. G., Martin G. R. Role of laminin in the attachment and metastasis of murine tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1982 Jun;42(6):2265–2269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., Rao C. N., Kalebic T., Margulies I. M., Liotta L. A. Laminin receptor on human breast carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):444–448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., Williams J. E., Liotta L. A., Martin G. R. Modulation of the metastatic activity of melanoma cells by laminin and fibronectin. Science. 1984 Nov 23;226(4677):982–985. doi: 10.1126/science.6505678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Johansson S., van Delden V., Oberbäumer I., Hök M. Characterization of protease-resistant fragments of laminin mediating attachment and spreading of rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8922–8927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
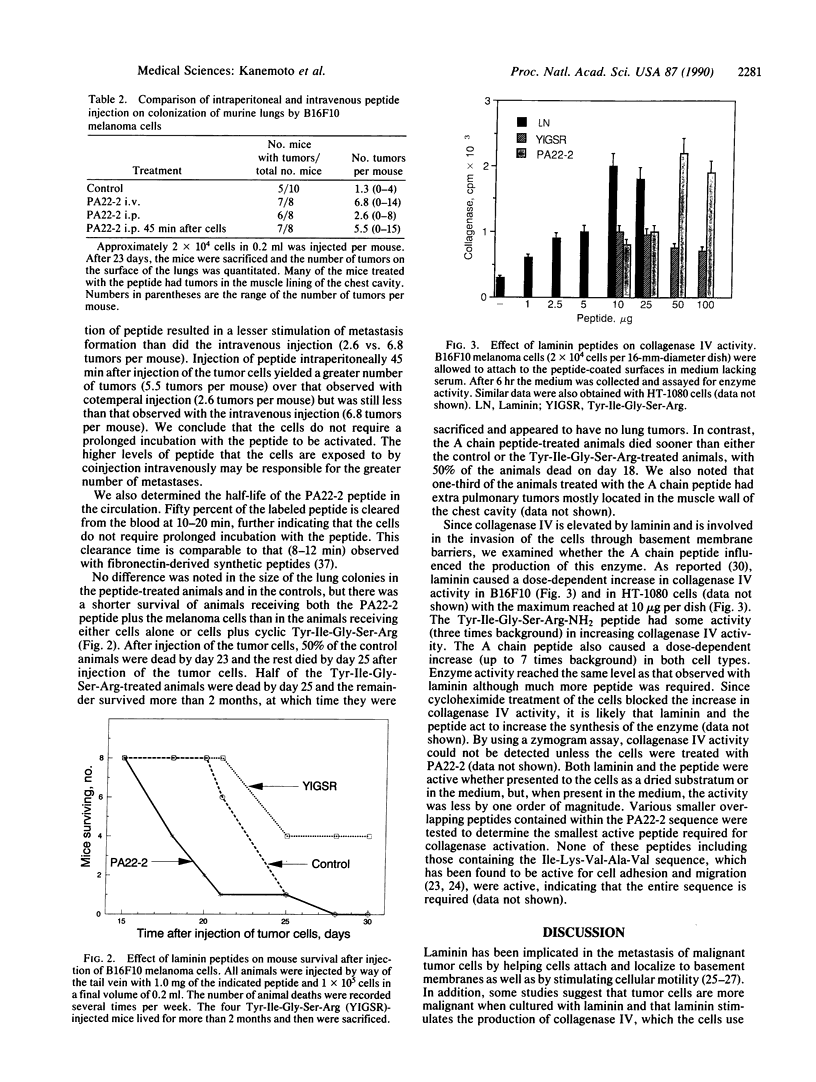
- Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T., Thorgeirsson U. P., Rao C. N., Liotta L. A. Laminin increases the release of type IV collagenase from malignant cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1883–1889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Gospodarowicz D. Respective roles of laminin and fibronectin in adhesion of human carcinoma and sarcoma cells. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):304–306. doi: 10.1038/289304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewer U. M., Liotta L. A., Jaye M., Ricca G. A., Drohan W. N., Claysmith A. P., Rao C. N., Wirth P., Coligan J. E., Albrechtsen R. Altered levels of laminin receptor mRNA in various human carcinoma cells that have different abilities to bind laminin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7137–7141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]