Abstract
In order to expedite the rapid and efficient discovery and isolation of novel specialized metabolites, whilst minimizing the waste of resources on rediscovery of known compounds, it is crucial to develop efficient approaches for strain prioritization, rapid dereplication, and the assessment of favored cultivation and extraction conditions. Herein we interrogated bacterial strains by systematically evaluating cultivation and extraction parameters with LC-MS/MS analysis and subsequent dereplication through the Global Natural Product Social Molecular Networking (GNPS) platform. The developed method is fast, requiring minimal time and sample material, and is compatible with high throughput extract analysis, thereby streamlining strain prioritization and evaluation of culturing parameters. With this approach, we analyzed 146 marine Salinispora and Streptomyces strains that were grown and extracted using multiple different protocols. In total, 603 samples were analyzed, generating approximately 1.8 million mass spectra. We constructed a comprehensive molecular network and identified 15 molecular families of diverse natural products and their analogues. The size and breadth of this network shows statistically supported trends in molecular diversity when comparing growth and extraction conditions. The network provides an extensive survey of the biosynthetic capacity of the strain collection and a method to compare strains based on the variety and novelty of their metabolites. This approach allows us to quickly identify patterns in metabolite production that can be linked to taxonomy, culture conditions, and extraction methods, as well as informing the most valuable growth and extraction conditions.
Graphical Abstract
Nearly half of all small molecule drugs approved for use in humans are derived from natural products.1 The ability to sequence bacterial genomes at constantly decreasing costs and time has dramatically changed the field of natural products discovery research over the past decade. With a growing number of genomes sequenced, comparative genomics and novel bioinformatics approaches have been used to analyze and classify biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) on a larger scale.2 It has been commonly observed that many organisms contain far more BGCs than characterized natural products. One approach to overcome this gap and further characterize natural product diversity is to culture and extract the microbes in many different ways. This approach has been named OSMAC (one strain, many compounds) by Zeeck and co-workers.3 It was first employed in the early 2000s and has led to the isolation of large numbers of novel metabolites by systematically altering cultivation parameters.4
Natural products chemists frequently face the challenge of rediscovery of known compounds. Several mass-spectrometry-based metabolomics workflows have been developed to ameliorate this high rediscovery rate, referred to as “dereplication”.5 However, many of these approaches solely use MS1 data, thus identifying compounds only by mass, and chromatographic and spectroscopic properties, and are not able to determine structural relationships between the metabolites.
Molecular networking is a recently introduced concept for the analysis of mass spectrometric fragmentation data and assessment of structural similarities between measured metabolites. The molecular networking concept enables the visualization of large datasets and the grouping of fragmented ions into clusters, using an algorithm to compare the similarity of the fragmentation spectra.6 In a natural product molecular network, these clusters represent molecular families (MFs) putatively synthesized by gene cluster families (GCFs).7 Molecular networking is a powerful approach that has advanced several natural product-related research projects involving dereplication and quantification,8 discovery,9 biosynthesis,10 and chemical ecology.11 It has also been integrated as a central component of the Global Natural Products Social (GNPS) molecular networking platform, where dereplication is performed against a large, community-acquired reference library of spectra.12 Molecular networking further allows for the screening of large numbers of strains for metabolic assessment.7
Creating networks with large numbers of closely related strains provides opportunities to identify new molecular families and investigate differences when growth and extraction conditions are changed. In this study, we screened 146 marine Salinispora and Streptomyces strains using HPLC-MS/MS, molecular networking, and the GNPS platform. We aimed to systematically explore the culturing and extraction of these strains to gain insight into the distribution of known and unknown metabolites and the effects of different growth and extraction protocols on the compounds detected. Analysis of the networks showed that varying conditions such as culture medium, extraction solvent, and time impact the networks. Furthermore, this study highlights species- and genus-specific metabolite production on a larger scale and allows for the prioritization of strains and optimized conditions for future MS-guided natural product discovery projects.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Cultivation, Extraction and Generation of Molecular Networks
The objective of this study was to apply large-scale molecular networking to a related group of sequenced bacteria to comprehensively interrogate the effects of growth media and extraction methods on the production and recovery of specialized metabolites respectively and to prioritize strains that produce novel molecular families for further study. We selected marine actinomycete bacteria, as they are known to be prolific producers of secondary metabolites.13 First, we established an effective small-scale extraction method for the HPLC-MS/MS-based screening and analysis. Extraction was carried out sequentially with three solvents of increasing polarity (EtOAc, n-butanol and MeOH). To evaluate the relationships between bacterial species and chemical diversity, 120 Salinispora strains were cultivated on A1 agar (Table S1). The obligate marine actinomycete genus Salinispora consists of three closely related species, arenicola, pacifica and tropica,14,15 that produce a wide range of bioactive secondary metabolites.16 Recent studies have shown that certain secondary metabolites are consistently produced by individual species,15, 17 which has been supported at the genomic level based on BGC distributions.2c, 18 We additionally selected 26 marine Streptomyces strains and, in order to evaluate the effects of media composition on metabolite production, grew them on three different media, A1, MS and R5 agar (Table S1). Complete genomes are available for all strains to facilitate future research programs. In total, 603 samples were analyzed, generating approximately 1.8 million mass spectra that were processed with the GNPS molecular networking workflow.12
A comprehensive network was generated for spectra with a minimum of four fragment ions and by merging all identical spectra into individual consensus nodes. Only nodes that had at least two identical spectra were displayed. After removal of nodes associated with the solvent controls, the molecular network consisted of 5526 nodes connected with 7396 edges. 54.6% of the nodes were organized into a total of 472 molecular families, comprised of two or more nodes each. The remainder of the MS/MS spectra are sufficiently unique that they did not form any connections to other spectra. Additionally, previously published data from 35 Salinispora strains19 grown in liquid culture were incorporated from the publically available GNPS-MassIVE database,12 allowing for comparisons between liquid and solid cultivation conditions. For comparisons between growth media, only the samples obtained from Streptomyces were networked with each other (Figure S1). It is important to note that the number of nodes in the network does not correspond exactly to the number of metabolites, as different adducts or different charge states of the same chemical species can generate different nodes. Rather, molecular networking provides an overview of the different chemistries detected by mass spectrometry.
Analysis of Known Molecular Families in the Molecular Network
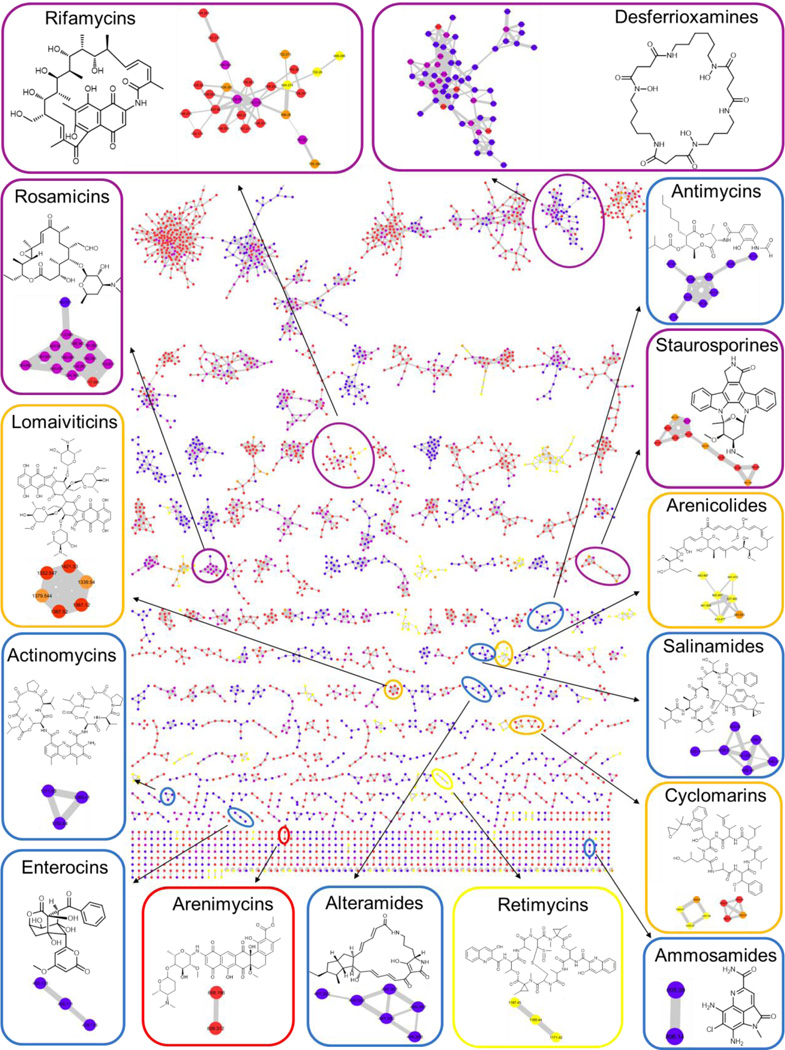
We identified 15 molecular families that contained spectra that matched known compounds in the network based on the curated GNPS natural products library (Figure 1, Table S2). In our analysis, we applied a mass exclusion threshold of 400 Da to limit our detection to large metabolites. In doing so we excluded well-known Salinispora molecules such as the saliniketals and salinisporamides, although we did identify some small molecules that formed oligomers in the gas phase of the mass spectrometer, such as ammosamide B ([3M+Na]+: 896.14 Da). Several of these known compounds, such as the enterocins,20 were identified in strains that were not previously known as producers. A large number of putative new analogues of known compounds were also identified in the network. For example there are three analogues of salinamide which do not correspond to any library variants, one of which, based on the parent mass, likely corresponds to salinamide F.21
Figure 1. Molecular Network of all Generated Extracts.
Blue nodes represent ions detected only from Streptomyces, red nodes represent ions detected only from Salinispora strains grown on agar. The yellow nodes represent ions detected from Salinispora only in liquid medium,19 while the orange nodes represent ions detected both in liquid and solid media. Purple nodes represent ions detected in both Streptomyces and Salinispora. Molecular families that include standards from the GNPS library are highlighted in the network (displaying the structure of the most abundant analogue) and color-coded according to their source. GNPS IDs of the standards can be found in Table S2. Only clusters containing at least two nodes are shown.
Four molecular families were produced by both Salinispora and Streptomyces. The desferrioxamine family, a group of hydroxamate siderophores,22 includes over 50 congeners, including acylated derivatives have only been detected from Streptomyces strains before.11b, 23 The staurosporine molecular family24 consists of a total of 11 members, mainly produced by Salinispora strains, but hydroxystaurosporine was also found in Streptomyces CNQ-149. This molecular family is produced by a large portion of the Salinispora strains - staurosporine was detected from a total of 61 strains, 56 S. arenicola and 5 S. pacifica, while the gene cluster is present in all 62 S. arenicola and 16 S. pacifica strains.25 The rifamycin molecular family consists of 25 members mostly detected in S. arenicola strains;26 however, rifamycin W was also produced by one Streptomyces strain. The rosamicin family, a group of glycosylated polyketides, is produced by five Salinispora strains and one Streptomyces strain. Having initially detected this family in this dataset, we recently isolated and characterized three novel rosamicins, and their biosynthetic byproducts salinipyrones and pacificanones from S. pacifica CNS-237.27
Analysis of Network by Genus and Species and PCoA Visualization of the Overall Chemical Diversity
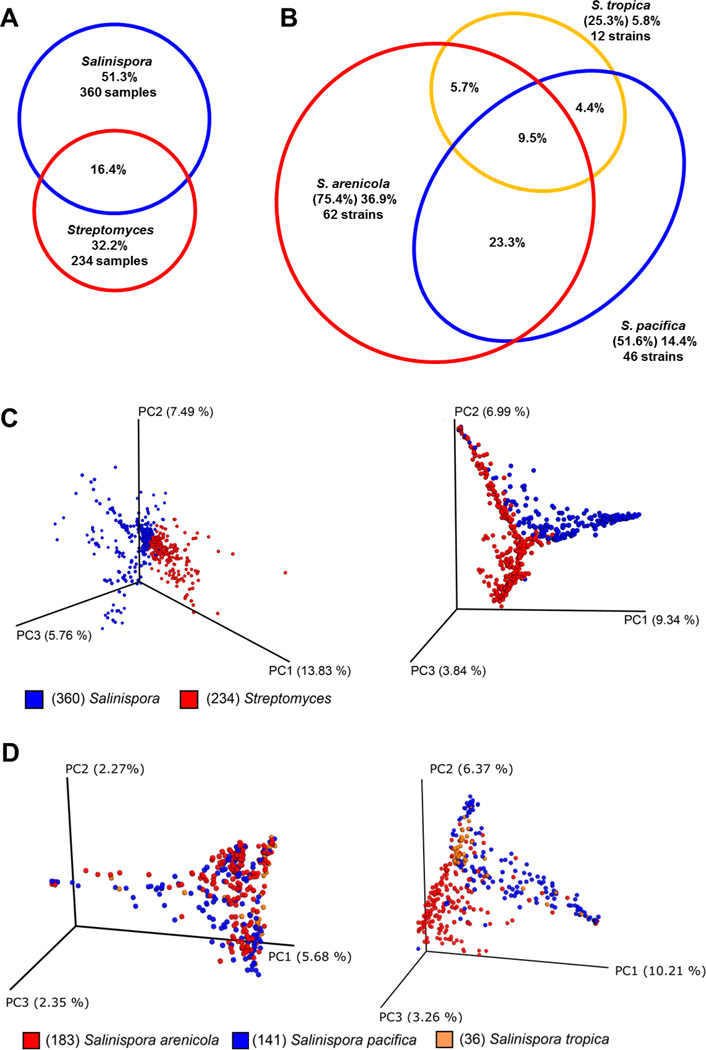
As might be expected for bacteria in different families, there was little overlap in the parent ions detected (16.4%) in the Salinispora and Streptomyces extracts (Figures 2A, S2). Those shared between the two genera include lipids but also natural products, including the desferrioxamines and the rosamicins, as described above. Salinispora and Streptomyces extracts in general have similar molecular diversities, averaging 10.4 and 11.5 different nodes per sample, respectively. However, the larger number of Salinispora extracts examined accounts for the relatively high percentage of the total (51.3%) that is specific to this genus. Within the closely related and well-defined Salinispora strains, it is possible to analyze the distribution of extracted metabolites by species (Figures 2B, S3). As described above, Salinispora is known to produce species-specific metabolites.17 In this work, the production of known molecules follows a similar pattern as in previous studies showing rifamycins as a strong marker for S. arenicola, while lomaiviticins are only produced by S. pacifica and S. tropica. Staurosporines are produced by S. arenicola and S. pacifica, while desferrioxamines are produced by all three species (Table S2). The wide distribution of desferrioxamines and staurosporines is reflected in the corresponding gene cluster patterns, where, of the 120 strains, 92 and 78, respectively, possess these gene clusters.
Figure 2. Effects of Genus and Species on Molecular Diversity-Network Analysis.
A. Venn diagram for Salinispora and Streptomyces specific nodes in the networks. B. Venn diagram displaying Salinispora species node distribution. Percentages are shown for each sector, with the total percentage for each species in parentheses. C. PCoA plots of Salinispora (blue) and Streptomyces (red) samples separated using Gower (left) and random forest classifier (right). D. Salinispora samples were reanalyzed with unsupervised (left) and supervised (right) random forest based on Salinispora species.
When the whole Salinispora network is analyzed for metabolite production by species, it is apparent that more than half of the total nodes (57.6%) were found in only one of the three species. This observation clearly shows that that there can be great differences in secondary metabolism even among very closely related species. Less than 10% of the nodes are produced by all three species, suggesting secondary metabolism is more a species defining trait than a genus characteristic.
In addition, network consensus nodes in each sample were subjected to multivariate analyses. Intra-sample distances were determined using both the Gower distance metric, as well as the random forest classifier, and visualized using PCoA dimensional reduction. The PCoA analysis showed that Salinispora and Streptomyces samples occupy mutually exclusive areas of this chemical space outside of a shared core (Figure 2C). Since the unsupervised Gower PCoA analysis (Figure 2C, left) did not show a clear grouping pattern between most metadata labels, we turned to the random forest classifier (Figure 2C, right).28 With the PCoA approach, one can use the random forest algorithm’s ability to classify samples into specified (supervised) or unspecified (unsupervised) groups as the basis of a dissimilarity metric retrieved from proximity matrices.29 We applied this technique to the 360 Salinispora-derived samples, classifying on the basis of species (Figure 2D). The random forest classifier was able to differentiate the Salinispora species with an accuracy of 87%, showing that the metabolic information captured by mass spectrometry provides a consistent fingerprint of each species. Interestingly, the top drivers for this species-specific PCoA separation were analogs of the previously discussed bioactive alkaloid staurosporine while the influence of media components for this analysis could be excluded (Figure S4). The PCoA analysis thus supports the observations from the molecular network and helps in building a global and comprehensive metabolic picture for the genus Salinispora.
Impact of Additional Attributes on the Network
Strain
For the prioritization of strains for chemical analysis, a direct comparison of their metabolic profiles is beneficial. Within the network, each strain contributes to a certain number of nodes, thus giving a direct measure of extracted molecular diversity. Because the strains from each genus were grown and extracted under the same conditions, it was possible to compare them in the network. One example of a chemically rich strain is Streptomyces sp. CNQ-329 that contributes to 451 nodes in the network (Table S1). This number can be further broken down into nodes by medium, revealing that medium R5 gives the most diversity with 339 nodes. Looking at extraction solvents, from the R5 samples, MeOH and n-butanol (BuOH) provide the most chemical diversity, with 269 and 252 nodes per sample respectively. From the Salinispora strains, S. arenicola CNT-798 yielded the highest chemical diversity contributing to 288 nodes in total. In this case, each solvent extracts a similar amount of molecular diversity (239, 245 and 261 nodes from BuOH, EtOAc and MeOH, respectively). It is important to note that the individual Salinispora strains were grown on just one medium, giving rise to the smaller total number of nodes compared to Streptomyces strains. Conversely, some strains yielded very little chemical diversity, with the approach used. Salinispora pacifica CNY-703, for example, contributed to only six nodes in the network. These results help to prioritize strains with higher chemical diversity and also to define the culture and extraction conditions that give the highest metabolite yields.
Solvent and Medium
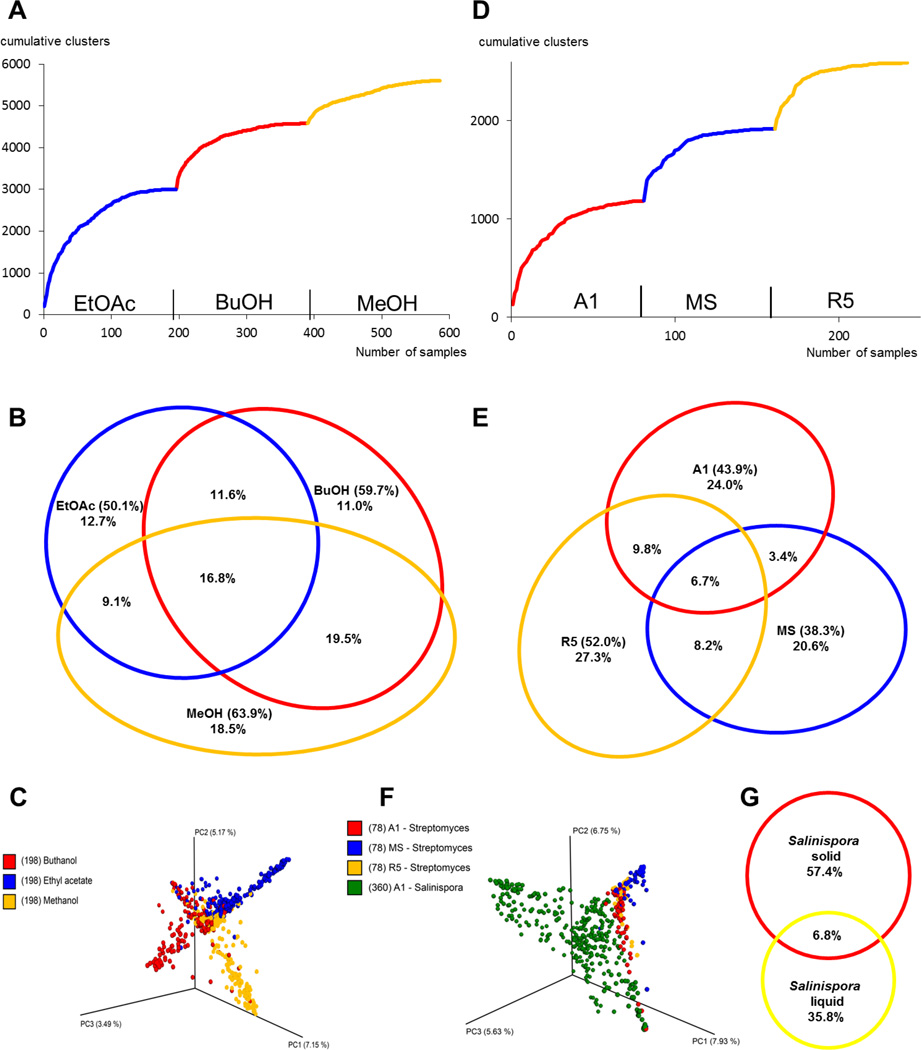
When the network was sorted by solvent, a comparable number of nodes were shown to be extracted by each of the three solvents (Figures 3A, B, S5). This can be visualized with an accumulation curve describing the number of unique clusters added by each additional sample, incorporating all of those extracted with EtOAc, before adding those from BuOH and then MeOH, reflecting the order they were used in the extraction (Figure 3A). The inflection upon addition of spectra from samples extracted with a new solvent indicates an influx of new clusters. A Venn diagram of the nodes originating from each solvent shows that almost half (42%) of the nodes were extracted by just one solvent and, of the three solvents, MeOH yielded the highest number of unique nodes (Figure 3B). A total of 57 molecular families were extracted by a single solvent (EtOAc = 12, BuOH = 20, and MeOH = 25), which may have been missed in the network by the exclusion of any of these solvents. Several of the known compounds were only extracted by one solvent, including salinamide E (BuOH), antimycin A1 (MeOH), and arenimycin A (EtOAc). Three analogues of the lomaiviticin family, including lomaiviticin A, were extracted by only EtOAc, and two compounds of the cyclomarin family by MeOH only. When random forest dissimilarities are visualized in PCoA space, the distinctions caused by solvent differences spread samples in distinct directions (Figure 3C). The three solvents are likely able to capture a common core metabolome, but also allow for capturing solvent-specific metabolites. These results clearly demonstrate that using three extraction solvents, instead of one, greatly enhances the molecular diversity that can be detected by mass spectrometry.
Figure 3. Effects of Additional Attributes on Molecular Diversity-Network Analysis.
Cumulative consensus curves for added unique spectra by each additional solvent (A) and Venn diagram for node distributions in the network for each solvent (B). C. Supervised random forest analysis of all samples classified by solvent. Cumulative consensus curves (D) and Venn diagram (E) for each medium (only from the Streptomyces extracts). Percentages are shown for each sector, with the total percentage for each treatment in parentheses. F. Supervised random forest analysis of all samples classified by growth medium. G. Comparison of liquid and solid extraction for 30 Salinispora strains (solvent: EtOAc).
To gain insight into medium-dependent metabolomics, all Streptomyces strains were grown on three different media (A1, MS and R5). Extracts from these cultures were networked together and then analyzed for extracted nodes by culture medium (Figures 3D,E, S1). In this case, the generated accumulation curve shows a similar trend as with the solvent extraction analysis for all samples, showing a rapid increase in molecular diversity with each change of medium (Figure 3D). Analysis of nodes in the network by medium reveals that over 70% of the nodes were extracted from just one of the three media (Figure 3E).
This observation corroborates observations from the OSMAC method,3 that culture medium is a key factor in secondary metabolite biosynthesis. We identified a total of 89 clusters in the Streptomyces network that were produced on just one medium (35 on A1, 29 on MS, and 25 on R5), including some of the detected standards. As we only evaluated metabolites with a molecular weight over 400 Da, we do not anticipate inclusion of by-products of core metabolism. To provide some examples, most of the rosamicin molecular family was only produced on A1, which was also necessary for production of five of the seven known salinamides, including salinamides A and E. Additionally, many of the detected desferrioxamine family analogues were only produced on medium R5, as were the entire alteramide and antimycin molecular families. All samples were classified with supervised random forest by the media information (Figure 3F) and differences are clearly seen to spread samples in distinct directions in the PCoA space. Thus, this analysis rapidly visualizes how much the metabolic repertoire is dependent on medium composition.
Solid Versus Liquid Media
Previously, 35 Salinispora strains were grown in liquid A1 medium, extracted and analyzed in a similar way to this project.19 When the comparable data from this previous work is networked with the same 30 sequenced strains from solid A1 media, we observed less than 7% overlap of extracted metabolites (Figures 3G, S6). Interestingly, most of the metabolic overlap belongs to known molecular families that could be dereplicated by comparison to standards in the GNPS database. The cyclomarins are represented in two adducts in the network, the sodiated form and the dehydrated and protonated form (Figure 1). These adducts display significantly different fragmentation patterns, and thus they form two distinct molecular families. Analysis of both molecular families shows that only cyclomarin A was extracted from both solid and liquid cultures. We observed that some cyclomarin analogues were extracted from only the liquid or the solid cultures, thereby clearly demonstrating the culture-dependent variability in production of compounds of the same class. In the case of the arenicolide molecules, we detected only an unprecedented hydrated analogue of arenicolide A on the solid growth medium (Figure S7), while six arenicolide analogues were produced in liquid medium.
Taken together, the comparison between growth on solid and liquid media for 30 Salinispora strains shows production of almost entirely different chemistry. The observed metabolic differences of liquid versus solid media suggest that a network with liquid culturing data of all 146 strains would look significantly different and may help to capture a broader map of the metabolic potential of these bacteria.
Location
The network was also queried for molecular families produced by several strains from one collection location or locations relatively close to each other (Figure S8). One example is a molecular cluster found to be extracted from two strains collected from Guam, Salinispora pacifica CNQ-768 and Streptomyces sp. CNQ-865 with a parent mass of m/z 878.152. This observation implies that the corresponding gene cluster, which we have yet to identify, is shared between these two geographically related strains. Although other strains may also have the cluster, it was apparently not expressed under these experimental conditions. A second cluster, consisting of 16 nodes, is derived from ten strains of S. pacifica and S. arenicola isolated from expeditions to Hawaii and Fiji in the central Pacific. A third cluster, consisting of four nodes, is produced by four Fijian S. pacifica strains. One of the largest molecular families consisted of 152 nodes in which 137 were extracted from strains collected from Hawaii. The remaining 15 nodes were derived from Salinispora and Streptomyces strains isolated from the Pacific (Fiji, Guam, Palmyra, San Diego, Channel Islands and the Sea of Cortez). Thus, it appears that the biosynthetic genes responsible for these metabolites are locally restricted to strains in our collection isolated from the Pacific Ocean.
Culture Time
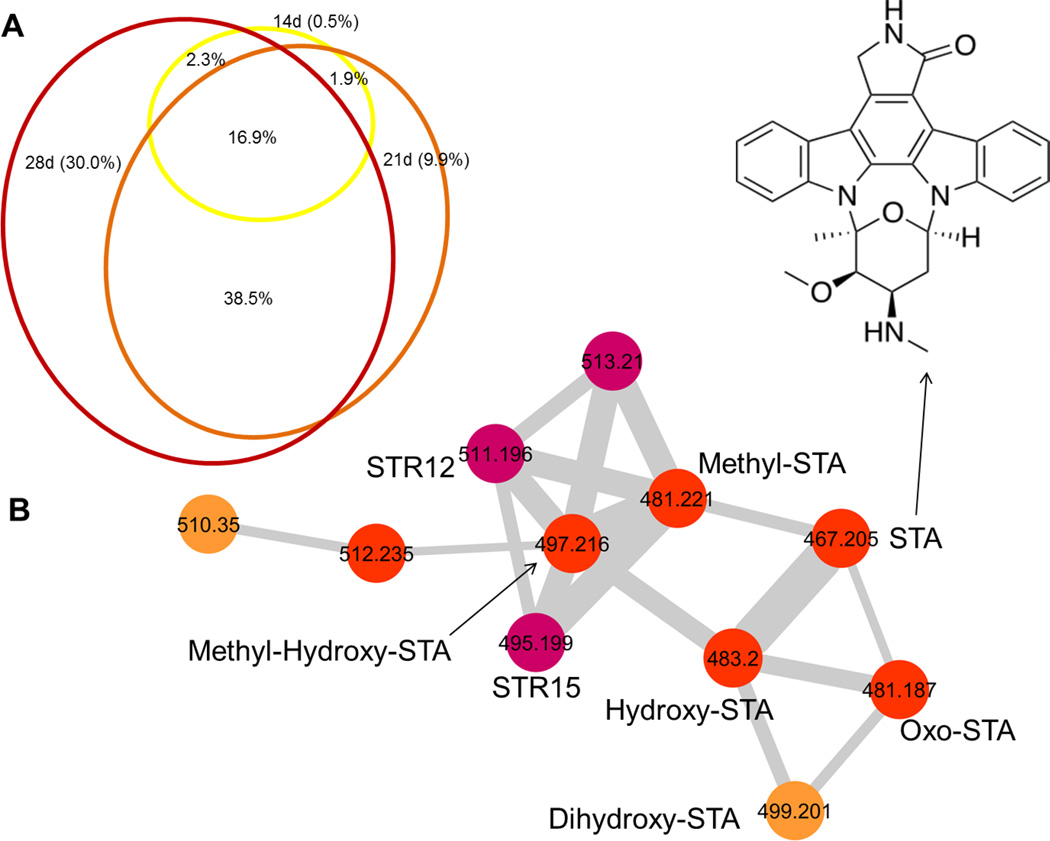
Another dimension that can be added to the analyses is the length of culturing before extraction. This is particularly valuable for experiments seeking to determine the best time point for preparative isolation of molecules, or to observe formation and changes of compound patterns over time.6b To gain insight into temporal changes in natural product production, we grew S. arenicola CNH-877 in four different liquid media and extracted at three different time points: 14, 21 and 28 days post inoculation (Figure S9). We observed that the number of extracted ions steadily increased over time (Figure 4A), and that after 28 days, there is far higher molecular diversity than at 14 or 21 days. The temporal changes in metabolite production and distribution can be exemplified with the staurosporine molecular family group (Figure 4B, Table S3).24 The staurosporine (STA) molecular family in the ISP2 network consists of 11 nodes, eight of which can be connected to known STA analogues by exact mass. Analysis of the nodes reveals a steady number of spectral counts for STA and oxo-STA across the different samples, while there is an increase in spectra corresponding to hydroxy-STA, methyl-STA and methyl-hydroxy-STA. Dihydroxy-STA was detected after 21 days and with an increase in spectral counts in the last time point. The production of minor analogues, whose masses were previously reported from a Saccharothrix strain, was only detected after 28 days.30 These results illustrate the biosynthetic changes and intramolecular conversions within a family of related molecules over time.6b, 31
Figure 4. Time-dependent Changes in Natural Product Distribution in Salinispora arenicola CNH-877, Grown in ISP2.
A. Venn diagram representing node distributions in the molecular network at three time points (14, 21 and 28 days). B. The staurosporine (STA) molecular family in the network. Nodes represent masses (m/z) and edge thickness corresponds to cosine score between the nodes. Highlighted in red are masses that are present in samples taken at 14, 21 and 28 days. Orange nodes represent masses only present after 21 and 28 days, violet nodes are only present after 28 days.
CONCLUSIONS
Natural products discovery and structure elucidation is a time consuming and sometimes inefficient process fraught with the rediscovery of known compounds. To advance natural product research, it is thus crucial to develop rational and effective strategies for the discovery of novel natural products entities and scaffolds. Emerging concepts like genome mining and MS-guided metabolomics have accelerated this process in recent years. We believe that one efficient strategy in a rational, state-of-the-art drug discovery program is the quick assessment of the metabolic capacities of natural product producers under various lab conditions, coupled with correlation of genomic and metabolic data for accelerated discovery and dereplication processes. In this study, we generated a comprehensive picture of the molecular diversity from 146 actinomycete strains from the marine environment. The selection of strains with sequenced genomes will help in the utilization of this data in future studies. To maximize molecular diversity in an efficient manner, we developed a simple culturing and extraction protocol and evaluated the variables that influence metabolite identification.
In previous studies on the molecular diversity of Salinispora, much smaller numbers of strains were grown on just one medium and extracted under just one condition.19, 32 Thus, the data in this study, generated from 120 Salinispora strains with three extraction solvents, and the visualization in a molecular network give a more comprehensive and detailed picture of the Salinispora metabolome. The species-specific production of many known and unknown metabolites is well reflected in the network and clearly visualized by supervised random forest analysis. To produce an even larger picture with two “talented” genera, 26 Streptomyces strains were grown and extracted in the same way as the Salinispora strains, but on three media instead of one. In total, 15 structurally diverse molecular families could be annotated as known compound classes in the network, including numerous as yet undescribed congeners. The size of the network and diversity of the samples allowed us to observe how attributes, such as growth and extraction conditions, affect chemical diversity. It also allowed us to quickly compare strains and prioritize chemically rich isolates for more detailed profiling, as well as informing the most valuable growth and extraction conditions.
In light of the OSMAC approach, the changes of the metabolomes can be rationalized, as the different media represent different environments that the bacteria are exposed to, requiring them to alter their behavior. The culturing in liquid versus solid media, comparable to environments on surfaces versus in suspension, greatly influences the production of specialized metabolites. To our knowledge, there has not been a systematic investigation of the effect of culturing and extraction parameters on a larger number of strains with mass spectrometric tools.33 Here, the expanded molecular diversity that is added to the network by each additional treatment (medium, agar, solvent) shows clearly, how much molecular diversity can be missed when just one medium, solvent, or time point is used to assess the metabolic capacity. Parameters like time of extraction and solvent are of great importance for the extracted metabolite spectrum and should always be kept in mind when creating a natural products isolation workflow. With molecular networking, optimization of culturing and extraction parameters can now be assessed quickly and implemented early into the discovery workflow. The results of this study encourage further applications of the OSMAC approach by natural product chemists and this workflow can be applied to microbes across all three domains of life (Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes, and Archaea). To conclude, this network provides an extensive survey of the biosynthetic capacity of this strain collection and, with the GNPS database continuing to expand, this will provide a living dataset to inform future rational and automated natural product discovery efforts in the genera Salinispora and Streptomyces.
EXPERIMENTAL SECTION
Culturing and Extraction
Salinispora strains were cultured from frozen stock cultures on 10 mL A1 agar (6-well plates, 9 cm2). 10 mg/ml phenol red was added to the medium to indicate the beginning of stationary phase when the color of the medium shifted from yellow to red34 at which point they were extracted. Streptomyces strains were cultured in 24-well plates on A1, MS and R5 agar for 7 days before extraction. For the extraction, a plug of agar and cell lawn was removed and crushed with a glass pipette. First, agar and cells were washed with 500 µL H2O in an ultrasonic bath (30 min) to remove salts. Then, agar and cells were extracted subsequently with 500 µL EtOAc, n-BuOH and MeOH each (ultrasonic bath, 5 min). All Streptomyces samples were extracted by vortexing for 30 s with each solvent. After each extraction the solvent was evaporated, the residue redissolved in 1 mL MeOH and filtered through a 0.2 µm membrane into HPLC vials. Solvent blanks were generated by extracting media using the same protocols. For this study, all strains were grown and analyzed once. For the time course experiment, S. arenicola CNH-877, CNY-011, CNS-690 and CNS-694 were grown in either liquid A1, ISP2, MB, and production medium (1% soytone, 1% soluble starch, 1 % maltose) supplemented with Instant Ocean sea salt. 1 mL of the cultures were extracted after 7, 14, 21 and 28 days with 1 mL EtOAc and BuOH and the solvent treated as above.
HPLC-MS
Samples were analyzed using an Agilent 6530 Accurate-Mass Q-TOF spectrometer coupled to an Agilent 1260 LC system. A Phenomenex Luna C18 HPLC column (2.6 mm, 150×4.6 mm) was used under the following LC conditions with 0.1 % TFA: 1–5 min (10 % MeCN in H2O), 5–26 min (10–100 % MeCN), 26–28 min (100 % MeCN). The divert valve was set to waste for the first 4 min. Q-TOF MS settings during the LC gradient were as follows: positive ion mode mass range 300–1700 m/z, static exclusion 300–400 m/z, MS scan rate 1/s, MS/MS scan rate 3/s, fixed collision energy 20 keV; source gas temperature 300 °C, gas flow 11 L/min, nebulizer 45 psig, scan source parameters: VCap 3000, fragmentor 100, skimmer1 65, octopoleRFPeak 750. The MS was auto-tuned using Agilent tuning solution in positive mode before each measurement. MS data were analyzed with MassHunter software (Agilent).
Molecular networking and data analysis
All MS/MS data were converted from Agilent MassHunter data files (.d) to mzXML file format using the software Trans-Proteomic pipeline (Institute for Systems Biology).35 The data were transferred onto the GNPS server (gnps.ucsd.edu) and molecular networking was performed using the GNPS data analysis workflow using the spectral clustering algorithm.6a Sample attributes were linked to the data (146 strains, 2 genera, 3 species, 3 media, 16 locations, 3 solvents). Different parameters (cosine, minimum matched peaks) were evaluated to determine the best networking conditions. Finally, a cosine of 0.5 and a minimum number of matched peaks of 4 was chosen for further analyses. The chosen parameters include mass tolerance for fragment peaks (0.5 Da), parent mass tolerance (2.0 Da), a minimum cluster size of 2 and a maximum cluster size of 250. These settings yielded the highest number of connected nodes with no standards having clustering with other standards. To facilitate network analysis, all nodes that contained ions that were present in the media controls were subtracted from the networks. The spectral networks were imported into Cytoscape 3.1.036 and visualized using the force-directed layout. Nodes represent parent masses and edge thickness corresponds to cosine score. Group and attributes files and Cumulative consensus curves were generated according to the GNPS documentations (https://bix-lab.ucsd.edu/display/Public/GNPS+Documentation+Page). To generate cumulative consensus curves, the network was rerun using the same parameters with input files being allocated to the spectrum file groups based on attribute. The data is publically accessible as MassIVE datasets MSV000078836 and MSV000078839. Ellipsoid area-proportional Venn diagrams were generated with the tool eulerAPE v3 (http://www.eulerdiagrams.org/eulerAPE).37 Bioinformatic genome, gene cluster and domain analysis was performed using the tools antiSMASH 3.0 (antismash.secondaymetabolites.org)38 and NaPDoS (napdos.ucsd.edu).39
Statistical Analysis
The intensity of the precursor ions of MS/MS clusters were exported through the “Create Cluster Buckets” option on GNPS (gnps.ucsd.edu) data analysis Advanced Output Options. The table was used to perform unsupervised and supervised analysis using R statistical environment40 and Qiime bioinformatics pipeline.41 The unsupervised analysis consisted of calculating Gower distance with the R package VEGAN42 and using the distance matrix to perform Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCoA) using Qiime and visualized using EMPeror.43 The supervised analysis consisted of training classifiers for different partitions of the data (e.g., classifying samples according to solvent extraction, growth media, or species labels based on whole metabolomics profile). The random forest classifier was used through randomForest package.29 The model accuracies were calculated subsampling the data in training and test datasets with the package caret.44 The random forest sample proximity values were used to calculate sample to sample dissimilarities and repeat the PCoA analysis for classification.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the NIH (R01-GM085770 to B.S.M. and P.R.J. and R01-GM097509 to B.S.M. and P.C.D.), the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP-2015/03348-3 to R.R.d.S. and a postdoctoral fellowship from the Deutsche Forschungs-gemeinschaft (CR 464-1 to M.C).
Footnotes
ASSOCIATED CONTENT
Tables S1-S3, Figures S1-S9
The Supporting Information is available free of charge on the ACS Publications website at DOI:.
Author Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
REFERENCES
- 1.Newman DJ, Cragg GM. J. Nat. Prod. 2012;75:311–335. doi: 10.1021/np200906s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.(a) Doroghazi JR, Metcalf WW. BMC Genomics. 2013;14 doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Cimermancic P, Medema MH, Claesen J, Kurita K, Wieland Brown LC, Mavrommatis K, Pati A, Godfrey PA, Koehrsen M, Clardy J, Birren BW, Takano E, Sali A, Linington RG, Fischbach MA. Cell. 2014;158:412–421. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Ziemert N, Lechner A, Wietz M, Millán-Aguiñaga N, Chavarria KL, Jensen PR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2014;111:E1130–E1139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1324161111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Hadjithomas M, Chen I-MA, Chu K, Ratner A, Palaniappan K, Szeto E, Huang J, Reddy TBK, Cimermančič P, Fischbach MA, Ivanova NN, Markowitz VM, Kyrpides NC, Pati A. mBio. 2015;6:e00932. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00932-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bode HB, Bethe B, Höfs R, Zeeck A. ChemBioChem. 2002;3:619–627. doi: 10.1002/1439-7633(20020703)3:7<619::AID-CBIC619>3.0.CO;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.(a) Yuan C, Guo YH, Wang HY, Ma XJ, Jiang T, Zhao JL, Zou ZM, Ding G. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:19350. doi: 10.1038/srep19350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Hewage RT, Aree T, Mahidol C, Ruchirawat S, Kittakoop P. Phytochemistry. 2014;108:87–94. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Wang QX, Bao L, Yang XL, Guo H, Ren B, Guo LD, Song FH, Wang WZ, Liu HW, Zhang LX. Fitoterapia. 2013;85:8–13. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2012.12.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.(a) Doroghazi JR, Albright JC, Goering AW, Ju KS, Haines RR, Tchalukov KA, Labeda DP, Kelleher NL, Metcalf WW. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014;10:963–968. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Hoffmann T, Krug D, Hüttel S, Müller R. Anal. Chem. 2014;86:10780–10788. doi: 10.1021/ac502805w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Krug D, Müller R. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014;31:768–783. doi: 10.1039/c3np70127a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Wu C, Kim HK, van Wezel GP, Choi YH. Drug Discovery Today: Technologies. 2015;13:11–17. doi: 10.1016/j.ddtec.2015.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Gaudencio SP, Pereira F. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015;32:779–810. doi: 10.1039/c4np00134f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.(a) Guthals A, Watrous JD, Dorrestein PC, Bandeira N. Mol. Biosyst. 2012;8:2535–2544. doi: 10.1039/c2mb25085c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Watrous J, Roach P, Alexandrov T, Heath BS, Yang JY, Kersten RD, van der Voort M, Pogliano K, Gross H, Raaijmakers JM, Moore BS, Laskin J, Bandeira N, Dorrestein PC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2012;109:E1743–E1752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203689109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nguyen DD, Wu C-H, Moree WJ, Lamsa A, Medema MH, Zhao X, Gavilan RG, Aparicio M, Atencio L, Jackson C, Ballesteros J, Sanchez J, Watrous JD, Phelan VV, van de Wiel C, Kersten RD, Mehnaz S, De Mot R, Shank EA, Charusanti P, Nagarajan H, Duggan BM, Moore BS, Bandeira N, Palsson BØ, Pogliano K, Gutiérrez M, Dorrestein PC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2013;110:E2611–E2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1303471110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.(a) Yang JY, Sanchez LM, Rath CM, Liu X, Boudreau PD, Bruns N, Glukhov E, Wodtke A, de Felicio R, Fenner A, Wong WR, Linington RG, Zhang L, Debonsi HM, Gerwick WH, Dorrestein PC. J. Nat. Prod. 2013;76:1686–1699. doi: 10.1021/np400413s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Winnikoff JR, Glukhov E, Watrous J, Dorrestein PC, Gerwick WH. J. Antibiot. 2014;67:105–112. doi: 10.1038/ja.2013.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.(a) Kleigrewe K, Almaliti J, Tian IY, Kinnel RB, Korobeynikov A, Monroe EA, Duggan BM, Di Marzo V, Sherman DH, Dorrestein PC, Gerwick L, Gerwick WH. J. Nat. Prod. 2015;78:1671–1682. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Liaw C-C, Chen P-C, Shih C-J, Tseng S-P, Lai Y-M, Hsu C-H, Dorrestein PC, Yang Y-L. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:12856. doi: 10.1038/srep12856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Henke MT, Soukup AA, Goering AW, McClure RA, Thomson RJ, Keller NP, Kelleher NL. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016 doi: 10.1021/acschembio.6b00398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.(a) Schorn M, Zettler J, Noel JP, Dorrestein PC, Moore BS, Kaysser L. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013;9:301–309. doi: 10.1021/cb400699p. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Crone WJK, Vior NM, Santos-Aberturas J, Schmitz LG, Leeper FJ, Truman AW. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016 doi: 10.1002/anie.201604304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Wu C, Medema MH, Lakamp RM, Zhang L, Dorrestein PC, Choi YH, van Wezel GP. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016;11:478–490. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.(a) Moree WJ, Phelan VV, Wu C-H, Bandeira N, Cornett DS, Duggan BM, Dorrestein PC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2012;109:13811–13816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206855109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Traxler MF, Watrous JD, Alexandrov T, Dorrestein PC, Kolter R. mBio. 2013;4 doi: 10.1128/mBio.00459-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Briand E, Bormans M, Gugger M, Dorrestein PC, Gerwick WH. Environ. Microbiol. 2016;11:384–400. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wang M, Carver J, Phelan V, Sanchez L, Garg N, Peng Y, Nguyen D, Watrous J, Kapono C, Luzzatto-Knaan T, Porto C, Bouslimani A, Melnik A, Meehan M, Liu W-T, Crüsemann M, Boudreau P, Esquenazi E, Sandoval-Calderón M, Kersten R, Pace L, Quinn R, Duncan K, Hsu C-C, Floros D, Gavilan R, Kleigrewe K, Northen T, Dutton R, Parrot D, Carlson E, Aigle B, Michelsen C, Jelsbak L, Sohlenkamp C, Pevzner P, Edlund A, McLean J, Piel J, Murphy B, Gerwick L, Liaw C-C, Yang Y-L, Humpf H-U, Mansson M, Keyzers R, Sims A, Johnson A, Sidebottom A, Sedio B, Klitgaard A, Larson C, P CB, Torres-Mendoza D, Gonzalez D, Silva D, Marques L, Demarque D, Pociute E, O'Neill E, Briand E, Helfrich E, Granatosky E, Glukhov E, Ryffel F, Houson H, Mohimani H, Kharbush J, Zeng J, Vorholt J, Kurita K, Charusanti P, McPhail K, Nielsen K, Vuong L, Elfeki M, Traxler M, Engene N, Koyama N, Vining O, Baric R, Silva R, Mascuch S, Tomasi S, Jenkins S, Macherla V, Hoffman T, Agarwal V, Williams P, Dai J, Neupane R, Gurr J, Rodríguez A, Lamsa A, Zhang C, Dorrestein K, Duggan B, Almaliti J, Allard P-M, Phapale P, Nothias L-F, Alexandrov T, Litaudon M, Wolfender J-L, Kyle J, Metz T, Peryea T, Nguyen D-T, Leer DV, Shinn P, Jadhav A, Müller R, Waters K, Shi W, Liu X, Zhang L, Knight R, Jensen P, Palsson B, Pogliano K, Linington R, Gutiérrez M, Lopes N, Gerwick W, Moore B, Dorrestein P, Bandeira N. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016;34:828–837. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nett M, Ikeda H, Moore BS. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009;26:1362–1384. doi: 10.1039/b817069j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.(a) Maldonado LA, Fenical W, Jensen PR, Kauffman CA, Mincer TJ, Ward AC, Bull AT, Goodfellow M. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005;55:1759–1766. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.63625-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Ahmed L, Jensen PR, Freel KC, Brown R, Jones AL, Kim BY, Goodfellow M. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2013;103:1069–1078. doi: 10.1007/s10482-013-9886-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Freel KC, Millán-Aguiñaga N, Jensen PR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013;79:5997–6005. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00880-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jensen PR, Moore BS, Fenical W. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015;32:738–751. doi: 10.1039/c4np00167b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jensen PR, Williams PG, Oh D-C, Zeigler L, Fenical W. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007;73:1146–1152. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01891-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.(a) Udwary DW, Zeigler L, Asolkar RN, Singan V, Lapidus A, Fenical W, Jensen PR, Moore BS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2007;104:10376–10381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700962104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Penn K, Jenkins C, Nett M, Udwary DW, Gontang EA, McGlinchey RP, Foster B, Lapidus A, Podell S, Allen EE, Moore BS, Jensen PR. ISME J. 2009;3:1193–1203. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2009.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Duncan KR, Crüsemann M, Lechner A, Sarkar A, Li J, Ziemert N, Wang M, Bandeira N, Moore BS, Dorrestein PC, Jensen PR. Chem. Biol. 2015;22:460–471. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.03.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Piel J, Hertweck C, Shipley PR, Hunt DM, Newman MS, Moore BS. Chem. Biol. 2000;7:943–955. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(00)00044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ray L, Yamanaka K, Moore BS. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016;55:364–367. doi: 10.1002/anie.201508576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.(a) Challis GL. ChemBioChem. 2005;6:601–611. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200400283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Roberts AA, Schultz AW, Kersten RD, Dorrestein PC, Moore BS. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012;335:95–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2012.02641.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sidebottom AM, Johnson AR, Karty JA, Trader DJ, Carlson EE. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013;8:2009–2016. doi: 10.1021/cb4002798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Park BS, Abdel-Azeem AZ, Al-Sanea MM, Yoo KH, Tae JS, Lee SH. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013;20:3872–3902. doi: 10.2174/09298673113209990176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Freel KC, Nam S-J, Fenical W, Jensen PR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011;77:7261–7270. doi: 10.1128/AEM.05943-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wilson MC, Gulder TAM, Mahmud T, Moore BS. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010;132:12757–12765. doi: 10.1021/ja105891a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Awakawa T, Crüsemann M, Munguia J, Ziemert N, Nizet V, Fenical W, Moore BS. ChemBioChem. 2015;16:1443–1447. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201500177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ramette A. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007;62:142–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2007.00375.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Liaw A, Wiener M. R News. 2002;2:18–22. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Barrabee EB, Horan AC, Gentile FA, Patel MG. USPTO. United States, Schering Corporation; 1997. Indolocarbazoles from Saccharothrix aerocolonigenes copiosa subsp. nov SCC 1951 ATCC 53856. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Esquenazi E, Jones AC, Byrum T, Dorrestein PC, Gerwick WH. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2011;108:5226–5231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1012813108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bose U, Hewavitharana AK, Vidgen ME, Ng YK, Shaw PN, Fuerst JA, Hodson MP. PLoS One. 2014;9:e91488. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Reen F, Romano S, Dobson A, Gara F. Mar. Drugs. 2015;13:4754–4783. doi: 10.3390/md13084754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wolfe AJ. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005;69:12–50. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.69.1.12-50.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.(a) Keller A, Eng J, Zhang N, Li Xj, Aebersold R. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2005;1 doi: 10.1038/msb4100024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Deutsch EW, Mendoza L, Shteynberg D, Farrah T, Lam H, Tasman N, Sun Z, Nilsson E, Pratt B, Prazen B, Eng JK, Martin DB, Nesvizhskii AI, Aebersold R. Proteomics. 2010;10:1150–1159. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200900375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cline MS, Smoot M, Cerami E, Kuchinsky A, Landys N, Workman C, Christmas R, Avila-Campilo I, Creech M, Gross B, Hanspers K, Isserlin R, Kelley R, Killcoyne S, Lotia S, Maere S, Morris J, Ono K, Pavlovic V, Pico AR, Vailaya A, Wang PL, Adler A, Conklin BR, Hood L, Kuiper M, Sander C, Schmulevich I, Schwikowski B, Warner GJ, Ideker T, Bader GD. Nat. Protoc. 2007;2:2366–2382. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Micallef L, Rodgers P. PLoS One. 2014;9:e101717. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Weber T, Blin K, Duddela S, Krug D, Kim HU, Bruccoleri R, Lee SY, Fischbach MA, Muller R, Wohlleben W, Breitling R, Takano E, Medema MH. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:W237–W243. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ziemert N, Podell S, Penn K, Badger JH, Allen E, Jensen PR. PLoS One. 2012;7:e34064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.R_Core_Team. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Austria: Vienna; 2013. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. URL http://www.R-project.org/. In. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R. Nat. Methods. 2010;7:335–336. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.f.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Dixon P. Journal of Vegetation Science. 2003;14:927–930. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Vazquez-Baeza Y, Pirrung M, Gonzalez A, Knight R. GigaScience. 2013;2:16. doi: 10.1186/2047-217X-2-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kuhn M. Journal of Statistical Software. 2008;28:26. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.