Thirty five year old female patient with complaints of chest pain, numbness in the left arm and presyncopy was admitted to the cardiology clinic. There were no significant findings on cardiac examination. Electrocardiography (ECG) revealed T negativity in leads aVL, D1 and V1-5. Her blood tests were creatinine: 1.1 mg/dL, BUN: 33, Na: 144 mmoL/L, K: 4.4 mmoL/L, glucose: 110 mg/dL, pro-BNP: 117 pg/mL, fT4: 14, TSH: 2.34, AST: 16 U/L, ALT: 14 U/L, LDH: 266 U/L, CRP: 3 mg/L, sedimentation rate: 32 mm/h, hs-troponin: 6 pg/mL (<13 pg/mL), Hgb: 12.6/dL, WBC 7,400/mm3, platelets: 296,000 mm3. Three dimensional transthoracic and transo-esophageal echocardigraphy of the patient revealed a cystic mass in size of 4.6 × 4.2 cm in the interventricular septum (Video 1, Fig. 1, 2).
Figure 1.
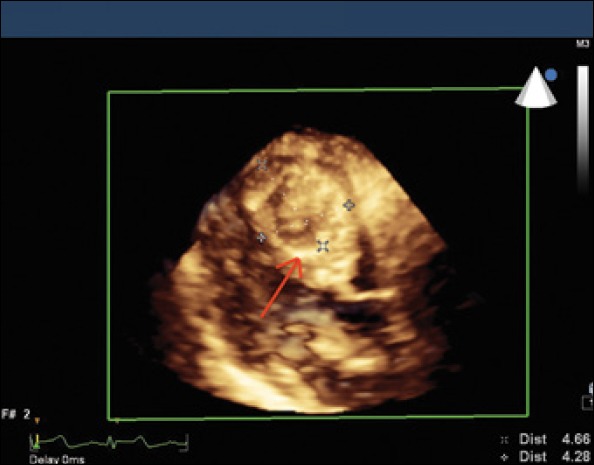
Parasternal long axis view of 3D transthoracic echocardiography revealed a cystic mass in size of 4.6 × 4.2 cm in the interventricular septum (Red arrow pointing cystic mass)
Figure 2.
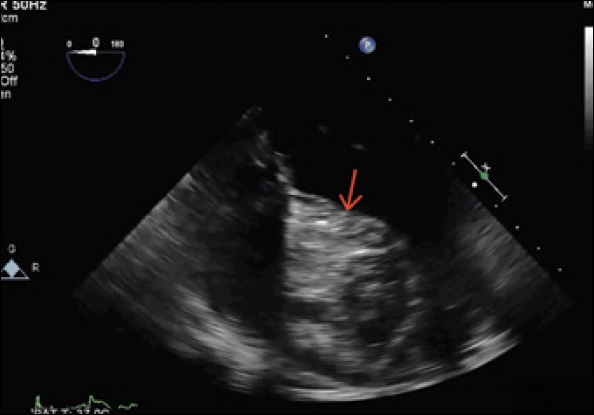
Mid oesophageal 0 degree view of transoesophageal echocardiography revealed a cystic mass in the interventricular septum (Red arrow pointing cystic mass)
A preliminary diagnosis of hydatid cyst was thought so indirect hemag-glutination test was requested and it resulted as positive. In Cardiac MRI, there was a cystic mass which was located in the interventricular septum and 5 × 4 × 3 cm in size. It was showing peripheral contrast enhancement and a few pieces of cystic spaces that had the largest 1.5 cm in size which was compatible with hydatid cysts (Fig. 3, 4).
Figure 3.
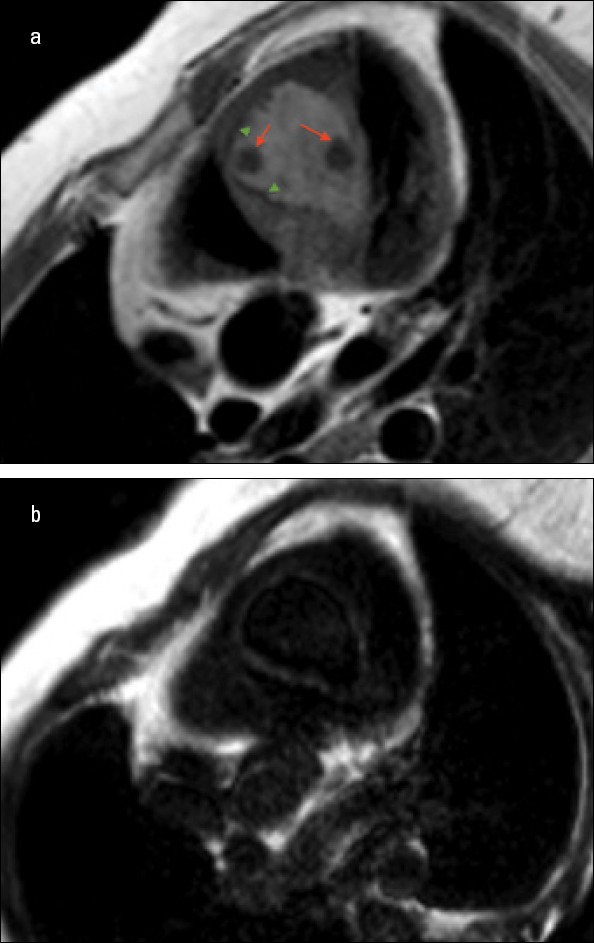
a, b. Cardiac MRI showed a cystic mass which was located in the interventricular septum and 5X4X3 cm in size. It was showing peripheral contrast enhancement and a few pieces of cystic spaces that had the largest 1.5 cm in size which was compatible with hydatid cysts (Red arrows pointing cystic spaces in cystic mass, green arrow heads pointing peripheral contrast enhancement)
Figure 4.
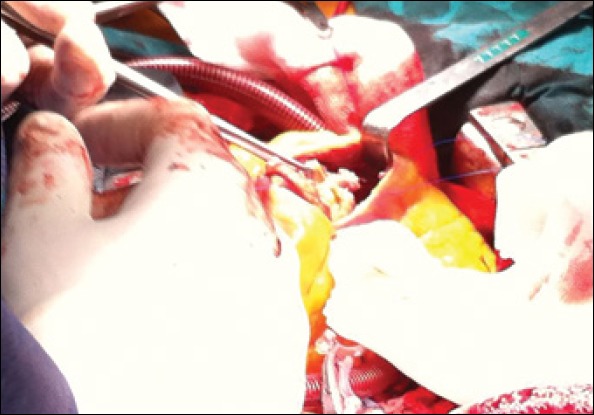
Peroperative view of cystic mass
The patient was given to the operation to get surgical excision. Postoperatively, patients had no problem and as pathological examination of the material removed with surgery (Fig. 5-7), cardiac hydatid cyst diagnosis was confirmed.
Figure 5.
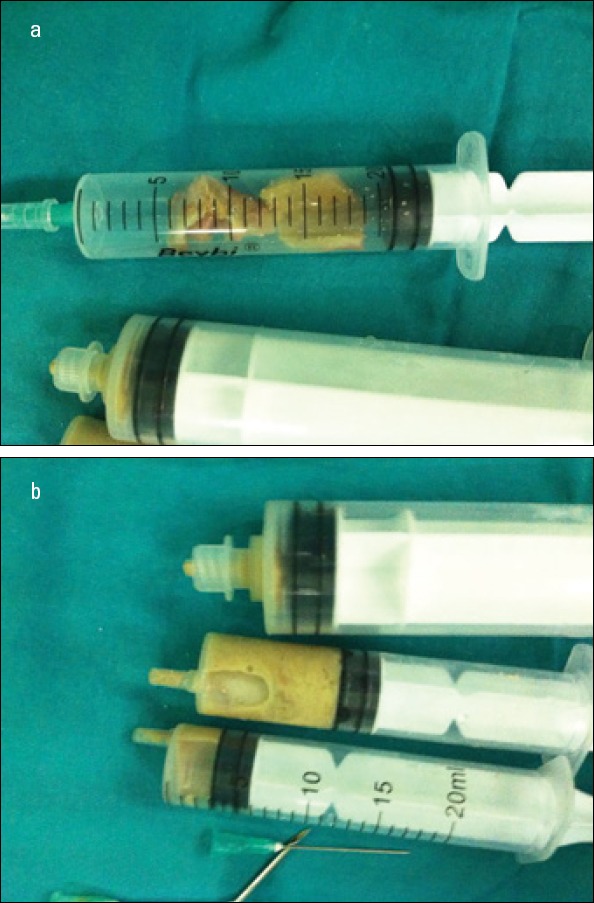
a, b. Resection materials in syringes were sent for pathological examination
Video 1
Parasternal long-axis view of transthoracic echocardiography revealed a cystic mass in the interventricular septum.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


