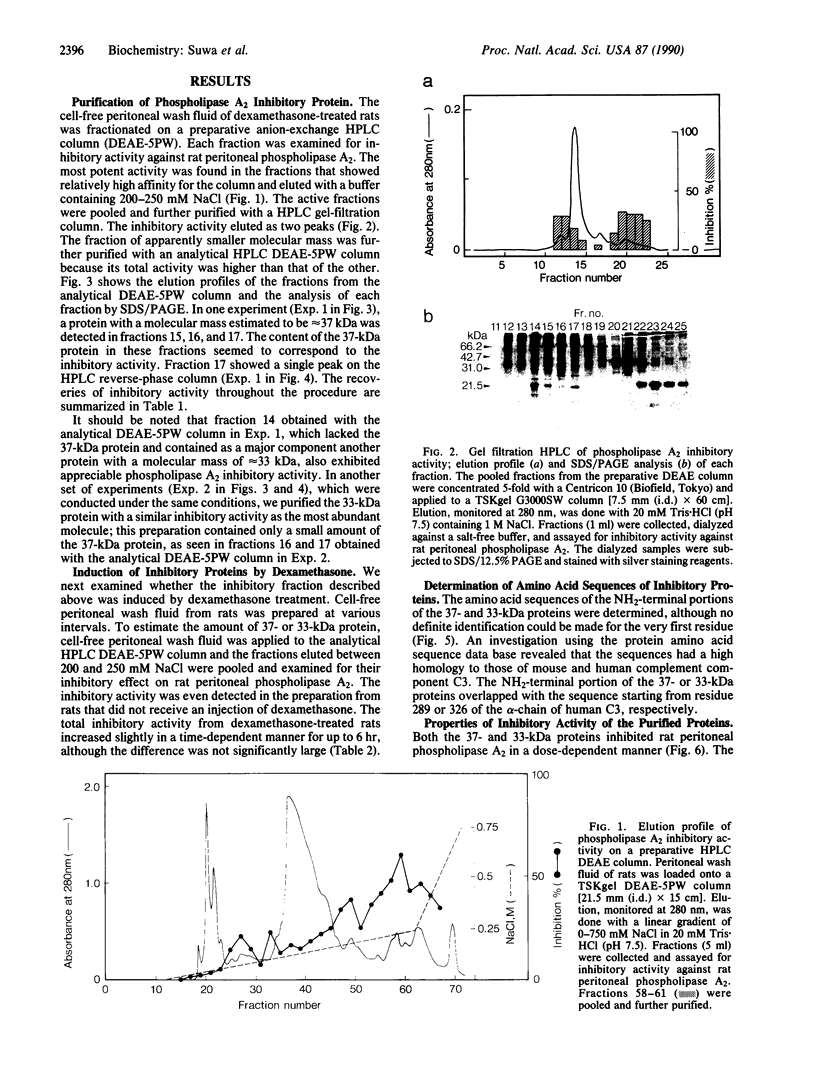
Abstract
We have purified two phospholipase A2 inhibitory proteins (37 and 33 kDa) from peritoneal fluid of dexamethasone-treated rats. The extracellular phospholipase A2 found in inflammatory sites differed from the exocrine phospholipase A2 in susceptibility to these endogenous inhibitors; both proteins inhibited the activity of the extracellular phospholipase A2 purified from sites of inflammation but did not affect appreciably the activity of either porcine pancreatic or Naja naja venom phospholipase A2. The amino acid sequence of the NH2-terminal portion of the purified proteins did not resemble that of lipocortins so far reported, but it was almost identical to that of parts of human or mouse complement component C3. These findings may indicate that degraded products of C3 are involved in the regulation of activity of a class of mammalian phospholipase A2.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basset-Seguin N., Dersookian M., Cehrs K., Yancey K. B. C3d,g is present in normal human epidermal basement membrane. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1273–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Carnuccio R., Di Rosa M., Flower R. J., Parente L., Persico P. Macrocortin: a polypeptide causing the anti-phospholipase effect of glucocorticoids. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):147–149. doi: 10.1038/287147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W., Kudo I., Hara S., Karasawa K., Inoue K. Extracellular phospholipase A2 activity in peritoneal cavity of casein-treated rats. J Biochem. 1986 Oct;100(4):1099–1101. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W., Kudo I., Tomita M., Inoue K. Purification and characterization of extracellular phospholipase A2 from peritoneal cavity of caseinate-treated rat. J Biochem. 1987 Jul;102(1):147–154. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloix J. F., Colard O., Rothhut B., Russo-Marie F. Characterization and partial purification of 'renocortins': two polypeptides formed in renal cells causing the anti-phospholipase-like action of glucocorticoids. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 May;79(1):313–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P., MEINERTZ H. Microdetermination of long-chain fatty acids in plasma and tissues. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2595–2599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danon A., Assouline G. Inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis by corticosteroids requires RNA and protein synthesis. Nature. 1978 Jun 15;273(5663):552–554. doi: 10.1038/273552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. E., 3rd, Harrison R. A., Lachmann P. J. Physiologic inactivation of fluid phase C3b: isolation and structural analysis of C3c, C3d,g (alpha 2D), and C3g. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1960–1966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forst S., Weiss J., Elsbach P., Maraganore J. M., Reardon I., Heinrikson R. L. Structural and functional properties of a phospholipase A2 purified from an inflammatory exudate. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 30;25(26):8381–8385. doi: 10.1021/bi00374a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Tack B., Powell M. A. Calpactins: two distinct Ca++-regulated phospholipid- and actin-binding proteins isolated from lung and placenta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):503–511. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara S., Kudo I., Matsuta K., Miyamoto T., Inoue K. Amino acid composition and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of human phospholipase A2 purified from rheumatoid synovial fluid. J Biochem. 1988 Sep;104(3):326–328. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman U., Eggertsen G., Engström A., Sjöquist J. Amino acid sequence of the trypsin-generated C3d fragment from human complement factor C3. Biochem J. 1985 Sep 1;230(2):353–361. doi: 10.1042/bj2300353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Schiffmann E., Venkatasubramanian K., Salomon D., Axelrod J. A phospholipase A2 inhibitory protein in rabbit neutrophils induced by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2533–2536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. L., Levine L. Stimulation of prostaglandin synthesis by bradykinin and thrombin and their mechanisms of action on MC5-5 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5814–5816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuth J. L., Morgan E. L., DiSipio R. G., Hugli T. E. Suppression of T lymphocyte functions by human C3 fragments. I. Inhibition of human T cell proliferative responses by a kallikrein cleavage fragment of human iC3b. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2605–2611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nydegger U. E., Zubler R. H., Gabay R., Joliat G., Karagevrekis C. H., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Circulating complement breakdown products in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation between plasma C3d, circulating immune complexes, and clinical activity. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):862–868. doi: 10.1172/JCI108708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Sinclair L. K., Browning J. L., Mattaliano R. J., Smart J. E., Chow E. P., Falbel T., Ribolini A., Garwin J. L., Wallner B. P. Purification and partial sequence analysis of a 37-kDa protein that inhibits phospholipase A2 activity from rat peritoneal exudates. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4239–4246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Sinclair L. K. Epidermal growth factor-dependent phosphorylation of lipocortin. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):81–84. doi: 10.1038/321081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pong S. S., Hong S. L., Levine L. Prostaglandin production by methylcholanthrene-transformed mouse BALB/3T3. Requirement for protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1408–1413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzanski W., Vadas P., Stefanski E., Urowitz M. B. Phospholipase A2 activity in sera and synovial fluids in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Its possible role as a proinflammatory enzyme. J Rheumatol. 1985 Apr;12(2):211–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., Tack B. F., Kristensen T., Glenney J. R., Jr, Hunter T. The cDNA sequence for the protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36 (calpactin I heavy chain) reveals a multidomain protein with internal repeats. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90737-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoman M. L., Meuth J. L., Morgan E. L., Weigle W. O., Hugli T. E. C3d-K, a kallikrein cleavage fragment of iC3b is a potent inhibitor of cellular proliferation. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2629–2633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurufuji S., Sugio K., Takemasa F., Yoshizawa S. Blockade by antiglucocorticoids, actinomycin D and cycloheximide of anti-inflammatory action of dexamethasone against bradykinin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Feb;212(2):225–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Pruzanski W. Role of secretory phospholipases A2 in the pathobiology of disease. Lab Invest. 1986 Oct;55(4):391–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Stefanski E., Pruzanski W. Characterization of extracellular phospholipase A2 in rheumatoid synovial fluid. Life Sci. 1985 Feb 11;36(6):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90640-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Hession C., Cate R. L., Tizard R., Sinclair L. K., Foeller C., Chow E. P., Browing J. L., Ramachandran K. L. Cloning and expression of human lipocortin, a phospholipase A2 inhibitor with potential anti-inflammatory activity. Nature. 1986 Mar 6;320(6057):77–81. doi: 10.1038/320077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetsel R. A., Lundwall A., Davidson F., Gibson T., Tack B. F., Fey G. H. Structure of murine complement component C3. II. Nucleotide sequence of cloned complementary DNA coding for the alpha chain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13857–13862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn M. H., Fey G. H. Human complement component C3: cDNA coding sequence and derived primary structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):708–712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]