Abstract
We analyzed 1,900 Turkish Behçet’s disease cases and 1,779 controls genotyped with the Immunochip. The most significantly associated single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) was rs1050502, a tag SNP for HLA-B*51. In the Turkish discovery set, we identified three novel loci, IL1A-IL1B, IRF8, and CEBPB-PTPN1, with genome-wide significance (P<5×10−8) by direct genotyping, and ADO-EGR2 by imputation. ADO-EGR2, IRF8, and CEBPB-PTPN1 replicated by genotyping 969 Iranian cases and 826 controls. Imputed data in 608 Japanese cases and 737 controls replicated ADO-EGR2 and IRF8 and meta-analysis additionally identified RIPK2 and LACC1. The disease-associated allele of rs4402765, the lead marker of the IL1A-IL1B locus, was associated with both decreased interleukin-1α and increased interleukin-1β production. ABO non-secretor genotypes of two ancestry-specific FUT2 SNPs showed strong disease association (P=5.89×10−15). Our findings extend shared susceptibility genes with Crohn’s disease and leprosy, and implicate mucosal factors and the innate immune response to microbial exposure in Behçet’s disease susceptibility.
Behçet’s disease is a systemic vasculitis that manifests with oral ulcers, uveitis, skin inflammation, genital ulcers, and inflammation in other organs1,2. Behçet’s disease is relatively common in modern-day countries located along the ancient Silk Routes3. The geographic distribution and the lack of consistency with expected patterns of Mendelian inheritance, despite a high sibling risk ratio (λs=11.4–52.5)4, suggest multiple genetic and environmental factors contribute to disease susceptibility. Although genetic studies have identified multiple susceptibility loci4–14, these genetic factors do not fully explain the apparent disease heritability.
To further clarify the genetic etiology of Behçet’s disease, we genotyped 2,014 Turkish cases and 1,826 population controls using the Immunochip15. After quality control filtering, 130,647 autosomal markers genotyped in 1,900 cases and 1,799 controls were subjected to association tests. Association analysis showed the strongest disease association within the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) region (Figure 1). Consistent with our previous findings using GWAS genotype data16, imputation of the MHC region showed the strongest association for HLA-B*51 (P=5.67×10−90, Table 1, Supplementary Fig. 1) among all markers. Other HLA alleles also showed significant association for Behçet’s disease (Supplementary Table 1), and regression analysis among MHC class I and II types confirmed independent disease protective association for HLA-A*03, and susceptibility for HLA-B*15 (Supplementary Table 2). Association analysis for SNPs showed the strongest disease association at rs1050502 (P=9.99×10−90, Table 1), a synonymous variant for isoleucine at position 47 of the HLA-B molecule, and a tag SNP for HLA-B*51 (r2=1).
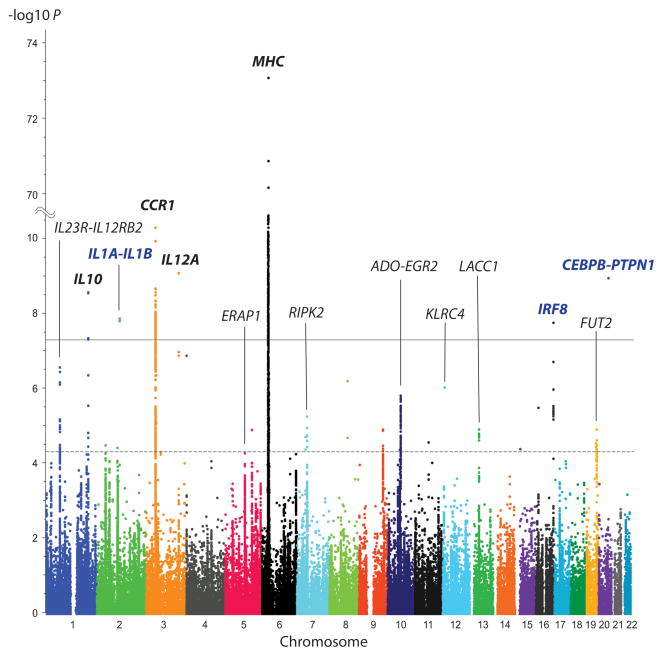
Figure 1. Association of Immunochip markers with Behçet’s disease in 1,900 cases and 1,779 controls from Turkey.
The disease association P-value of the genotyped Immunochip markers is shown according to their genomic location. Three new loci exceeding genome-wide significance are identified by bold blue typeface. Four confirmed reported loci that exceed genome-wide significance are identified by bold black typeface. The solid line indicates the threshold for genome-wide significance (P=5×10−8) and the broken line indicates the threshold for suggestive disease association (P=5×10−5). Twenty novel loci outside of the MHC region with P<5×10−5 were selected for further analysis by imputation and/or additional genotyping. SNP locations are from build 37/hg19.
Table 1.
Numeric association testing and conditional regression analysis for HLA-B*51, rs1050502 and four markers for which independent disease associations for Behçet’s disease were reported in a previous Immunochip study17.
| Marker | A1/A2 | OR | 95% CI | P |
PConditiona
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLA-B*51 | rs1050502 | rs116799036 | rs12525170 | HLA-Cw*16:02 | rs114854070 | |||||
| HLA-B*51 | +/− | 3.26 | 2.89–3.68 | 5.67×10−90 | - | - | 2.60×10−7 | 1.77×10−53 | 1.76×10−74 | 1.33×10−89 |
| rs1050502 | T/C | 3.25 | 2.88–3.66 | 9.99×10−90 | - | - | 2.60×10−7 | 1.77×10−53 | 1.76×10−74 | 1.33×10−89 |
| rs116799036 | A/G | 3.13 | 2.78–3.52 | 7.36×10−86 | 0.29 | 0.29 | - | 3.47×10−49 | 3.13×10−69 | 4.19×10−84 |
| rs12525170 | A/G | 2.42 | 2.13–2.76 | 2.07×10−43 | 0.0036 | 0.0036 | 1.64×10−4 | - | 1.03×10−25 | 1.04×10−41 |
| HLA-Cw*16:02 | +/− | 2.93 | 2.33–3.68 | 6.90×10−22 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.0015 | 1.96×10−4 | - | 1.40×10−21 |
| rs114854070 | A/G | 1.32 | 1.18–1.47 | 5.07×10−7 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.0013 | 1.57×10−4 | - |
PCondition indicates the residual P-value after conditioning on each marker and was determined from imputed data from 3,535 samples from Turkey with no missing genotype data for the six markers included in the regression analysis (Cases = 1,840, Controls = 1,735). P-value < 1×10−5 was considered independent association in the conditional regression analysis.
Hughes et al. reported in a previous Immunochip study of Behçet’s disease that rs116799036, a SNP in the HLA-B-MICA intergenic region, was more strongly associated with disease than HLA-B*51 and also reported three additional independent disease susceptibility markers in the MHC region, rs12525170, rs114854070, and HLA-Cw*16:0217. In our study, the P-value for rs116799036 was 1.3×105 fold higher (less significant) than the P-value for HLA-B*51 and regression analysis identified significant residual association of HLA-B*51 after conditioning on each of their markers (Table 1). In contrast, associations of their markers were completely abrogated by conditioning on HLA-B*51 (Table 1, Supplementary Fig. 1) and the associations of these markers were strongly correlated with their linkage disequilibrium (LD) with HLA-B*51 (Supplementary Fig. 2).
Outside of the MHC region, three novel loci, IL1A-IL1B (rs3783550, P-value corrected by genomic inflation [PGC]=2.12×10−8), IRF8 (rs11117433, PGC=2.73×10−8), and CEBPB-PTPN1 (rs913678, PGC=1.96×10−9), and three previously reported loci, IL10, CCR1, and IL12A, displayed genome-wide significant associations with Behçet’s disease based on Immunochip genotyping (Fig. 1, Supplementary Fig. 3, Table 2). We also replicated the disease association of markers in other loci previously reported for Behçet’s disease (IL23R-IL12RB2, ERAP1, KLRC4 and FUT2), but did not find evidence supporting an association of TNFAIP3 reported in a Han Chinese population10 or JRKL-CNTN5 recently reported in a Spanish population14 (Supplementary Table 3).
Table 2.
Genome-wide significant associations of markers genotyped on the Immunochip with Behçet’s disease determined in 1,900 cases and 1,779 controls from Turkey.
| Marker | Nearest gene(s) | Chr. | Position hg19 | A1/A2 | Allele Freq.
|
OR | 95% CI | P | PGC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Control | |||||||||
| New loci | ||||||||||
| rs3783550 | IL1A-IL1B | 2 | 113532885 | G/T | 0.360 | 0.298 | 1.33 | 1.20–1.46 | 1.29×10−8 | 2.12×10−8 |
| rs11117433 | IRF8 | 16 | 86019516 | C/G | 0.074 | 0.113 | 0.63 | 0.54–0.74 | 1.67×10−8 | 2.73×10−8 |
| rs913678 | CEBPB-PTPN1 | 20 | 48955424 | C/T | 0.474 | 0.404 | 1.33 | 1.21–1.46 | 1.10×10−9 | 1.96×10−9 |
| Reported loci | ||||||||||
| rs1518110 | IL10 | 1 | 206944861 | A/C | 0.368 | 0.302 | 1.34 | 1.22–1.48 | 2.63×10−9 | 4.55×10−9 |
| rs7616215 | CCR1 | 3 | 46205686 | C/T | 0.270 | 0.340 | 0.72 | 0.65–0.79 | 4.94×10−11 | 9.60×10−11 |
| rs17753641a | IL12A | 3 | 159647674 | G/A | 0.073 | 0.040 | 1.90 | 1.54–2.34 | 8.11×10−10 | 1.45×10−9 |
rs17753641 in IL12A was in moderate LD with the SNP (rs17810546) previously reported in a multiethnic study13 (r2=0.77, D′=0.99).
Four significant loci, IL1A-IL1B, IL12A, IRF8 and CEBPB-PTPN1, were not identified by our previous GWAS. Two loci (IL12A and IRF8) had no markers on the GWAS array in strong LD with the Immunochip lead SNP, and thus the associations were driven by the increased coverage on the Immunochip. The greater power provided by the larger sample size here also contributed to identification of disease associations in all four loci (Supplementary Table 4).
For 12 of the 20 novel loci with P<5×10−5 (Table 2 and Supplementary Table 5), imputation revealed a more significant association, including rs4402765 in the IL1A-IL1B locus (PGC=3.85×10−9) and a genome-wide significant association of rs7075773 in the ADO-EGR2 locus (PGC=2.96×10−9, Supplementary Fig. 3, Supplementary Table 6). Conditional regression analysis of the regions that exceeded genome-wide significance revealed an independent contribution to disease susceptibility at rs7203487 in the IRF8 locus after conditioning on the lead SNP, rs11117433 (Supplementary Table 7).
For replication, the 21 lead SNPs genotyped by the Immunochip in the 20 novel loci with P<5×10−5 in the Turkish population were genotyped in the Iranian population including 969 cases and 826 controls. Four of these loci, ADO-EGR2, LACC1, IRF8, and CEBPB-PTPN1 replicated in the Iranian population (Supplementary Table 8). In a meta-analysis of the Turkish and Iranian populations, ADO-EGR2, IRF8, and CEBPB-PTPN1 exceeded genome-wide significance (Table 3).
Table 3.
Results of association tests and meta-analysis of novel susceptibility loci identified in this study.
| Markera (Locus) | A1/A2 | Population | OR | 95% CI | P | PGC | I2 | Phet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3783550 (IL1A-IL1B) | G/T | Turkish | 1.33 | 1.20–1.46 | 1.29×10−8 | |||
| Iranian | 1.13 | 0.98–1.31 | 0.098 | |||||
| Japanese | 1.11 | 0.93–1.33 | 0.24 | |||||
| rs2230801 (RIPK2) | C/T | Turkish | 1.43 | 1.22–1.68 | 9.60×10−6 | |||
| Iranian | 1.11 | 0.84–1.46 | 0.47 | |||||
| Japanese | 3.41 | 1.80–6.47 | 6.39×10−5 | |||||
| TUR+JPN | 1.52 | 1.30–1.77 | 4.89×10−9 | 6.57×10−9 | 0.25b | 0.25b | ||
| rs224127 (ADO-EGR2) | A/G | Turkish | 1.26 | 1.15–1.39 | 1.56×10−6 | |||
| Iranian | 1.18 | 1.03–1.35 | 0.017 | |||||
| Japanese | 1.30 | 1.11–1.51 | 0.0011 | |||||
| TUR+JPN | 1.27 | 1.17–1.38 | 6.62×10−9 | 9.46×10−9 | 0 | 0.81 | ||
| rs1509966 (ADO-EGR2) | A/G | Turkish | 0.80 | 0.73–0.87 | 1.47×10−6 | |||
| Iranian | 0.79 | 0.69–0.90 | 5.09×10−4 | |||||
| Japanese | 0.91 | 0.77–1.07 | 0.24 | |||||
| TUR+IRN | 0.80 | 0.74–0.86 | 3.73×10−9 | 4.15×10−9 | 0 | 0.90 | ||
| rs2121033 (LACC1) | G/C | Turkish | 0.79 | 0.71–0.87 | 8.88×10−6 | |||
| Iranianc | 0.78 | 0.67–0.91 | 0.0012 | |||||
| Japanese | 0.69 | 0.58–0.83 | 4.68×10−5 | |||||
| TUR+IRN+JPN | 0.76 | 0.71–0.83 | 2.01×10−11 | 3.54×10−11 | 0 | 0.41 | ||
| rs7203487d (IRF8) | C/T | Turkish | 1.38 | 1.21–1.57 | 1.10×10−6 | |||
| Iranian | 1.42 | 1.17–1.72 | 4.13×10−4 | |||||
| TUR+IRN | 1.39 | 1.25–1.55 | 1.85×10−9 | 2.36×10−9 | 0 | 0.90 | ||
| rs142105922 (IRF8) | AAT/- | Turkish | 0.63 | 0.52–0.77 | 5.58×10−6 | |||
| Iraniane | 0.68 | 0.51–0.91 | 0.0088 | |||||
| Japanese | 0.59 | 0.43–0.82 | 0.0013 | |||||
| TUR+JPN | 0.62 | 0.53–0.74 | 3.01×10−8 | 4.14×10−8 | 0 | 0.65 | ||
| rs11117433 (IRF8) | C/G | Turkish | 0.63 | 0.54–0.74 | 1.67×10−8 | |||
| Iranian | 0.75 | 0.58–0.96 | 0.023 | |||||
| rs913678 (CEBPB-PTPN1) | C/T | Turkish | 1.33 | 1.21–1.46 | 1.10×10−9 | |||
| Iranian | 1.29 | 1.13–1.48 | 1.59×10−4 | |||||
| TUR+IRN | 1.32 | 1.22–1.42 | 9.44×10−13 | 1.43×10−12 | 0 | 0.72 |
Bold indicates genome-wide significance. Meta-analysis was performed for populations which exceeded the replication threshold (see methods).
Linkage disequilibrium between the listed marker and the lead Immunochip marker is detailed in Supplementary Table 11.
Although I2 and Phet did not exceed the heterogeneity limits (see Methods), the effect size of the low frequency variant, rs2230801, differs in two populations. Allele frequencies are shown in Supplementary Table 11.
rs9316059 for LACC1 failed in genotyping by TOF-MS in the Iranian population, therefore rs2121033, the lead SNP for LACC1 after imputation, was genotyped instead (r2=0.99 in Turkish).
rs7203487 showed independent disease association in conditional regression analysis for the lead SNP for IRF8, rs11117433.
rs142105922 for IRF8 failed in genotyping by TOF-MS. rs1401884 in high LD with rs142105922 was genotyped (r2=0.84).
TUR, Turks; IRN, Iranian; JPN, Japanese
We also evaluated replication of the novel markers in the Japanese population where possible using imputed data from the previous Japanese GWAS in 608 cases and 737 controls and replicated association of rs9316059 in LACC1 (Supplementary Table 9), which also exceeded genome-wide significance in a meta-analysis with Turkish data (Supplementary Table 10). Furthermore, disease association of rs2121033 in the LACC1 locus, which is in strong LD with rs9316059 (r2=0.99), was observed among all three populations and a combined meta-analysis found a highly significant association (PGC =3.54×10−11, Table 3).
With imputed data available from both the Turkish and the Japanese populations, a more comprehensive analysis of the novel suggestive regions could be performed, allowing identification of associations with alternate markers other than the lead one identified in the Turkish discovery collection. Meta-analysis of all markers with suggestive association (P<5×10−5) in the Turkish population that were also available in the Japanese dataset identified four loci with genome-wide significance, including rs2121033 in the LACC1 locus described above. New markers with moderate LD with the Immunochip lead marker were identified in ADO-EGR2 and IRF8 (Table 3, Supplementary Table 11) and conditional analysis of the Turkish genotypes suggested that these new markers were not independent of the lead SNPs (Supplementary Table 12). The Turkish and Japanese meta-analysis also identified a novel genome-wide significant association with rs2230801 (PGC=6.57×10−9), a missense variant of RIPK2 (p.Ile259Thr) (Table 3, Supplementary Table 11). In the Iranian collection, genotypes of the four markers that had achieved genome-wide significance in the Turkish and Japanese meta-analysis demonstrated at least nominal association evidence (P<0.05), except the rs2230801 RIPK2 variant (Supplementary Table 13), for which the power to replicate was low (0.32). All the novel Behçet’s disease susceptibility markers are located in putative functional regions with predicted functional effects, either altering protein structure or the expression of nearby genes (Supplementary Table 14).
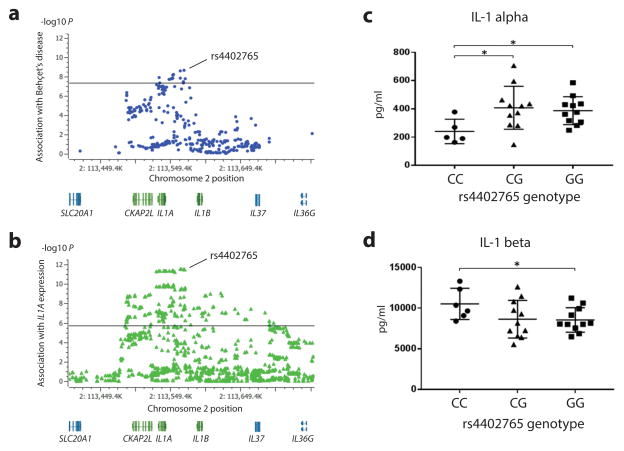
Although replication of the IL1A-IL1B region associations did not reach statistical significance in the Iranians or Japanese, there was a trend for association with a higher frequency of the risk allele in cases (Supplementary Tables 8 and 9). An expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) study shows the lead Behçet’s disease risk SNP rs4402765 is also the SNP most significantly associated with IL1A gene expression in lymphoblastoid cells and also shows that the disease risk allele is associated with reduced gene expression (Fig. 2a, b, Supplementary Fig. 3, Supplementary Table 14). Consistent with its effect on IL1A gene expression, we also found the amount of IL-1α protein in culture supernatants from healthy donor peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) stimulated with zymosan was reduced in homozygotes of the rs4402765 risk allele compared with homozygotes of the protective allele (Fig 2c). Although the published eQTL study did not show a significant association of rs4402765 genotype with IL1B gene expression, we found IL-1β protein was significantly increased in the cell culture supernatants of risk allele homozygotes compared to homozygotes of the protective allele (Fig 2d).
Figure 2. Expression analysis according to genotype of rs4402765, the lead SNP of the IL1A-IL1B locus.
(a) Disease association plot of the IL1A region from this study. The solid line indicates the threshold for genome-wide significance (P=5×10−8). rs4402765 is the lead SNP of the IL1A region for Behçet’s disease susceptibility (P=2.22×10−9) discovered by imputation of direct Immunochip and additional fine-mapped marker genotypes. (b) IL1A mRNA expression association plot of the IL1A region in 856 lymphoblastoid cell lines from MuTHER project data. The solid line indicates the threshold for statistical significance (P=2.12×10−6). rs4402765 is the lead SNP for IL1A mRNA expression (β=−0.22, P=3.31×10−12). SNP locations in (a) and (b) are from build 37/hg19. (c) IL-1α protein production by zymosan stimulated healthy PBMCs with different rs4402765 genotypes (disease risk allele: C). (d) IL-1β protein production by zymosan stimulated healthy PBMCs with different rs4402765 genotypes (disease risk allele: C). Means (horizontal bars) and standard deviations (error bars) are marked. *P<0.05
IL-1α is highly expressed in the epidermis and plays an important role in skin barrier functions against pathogens18. IL-1α is also required for effective host defense against disseminated candidiasis19. These findings suggest that genetically encoded reduced IL-1α expression may contribute to susceptibility to Behçet’s disease by weakening host response and defense against invading pathogens. Disease susceptibility may also be increased by the risk allele’s effect on IL-1β production in response to microbial pathogens. IL-1β is elevated in patients with Behçet’s disease20,21. Recently, effectiveness of IL-1 or IL-1β blockade in patients with Behçet’s disease has been reported22,23. This study raises the intriguing possibility that the decreased barrier function of IL-1α combines with the increased inflammatory response of IL-1β to increase Behçet’s disease risk.
FUT2 was recently reported to confer Behçet’s disease susceptibility in a meta-analysis of Iranian and Turkish GWAS data24. We have expanded this analysis to examine functionally relevant homozygous genotypes in a large sample size from three populations. FUT2 encodes alpha (1, 2) fucosyltransferase, which synthesizes secreted H antigen, the precursor of the ABO histo-blood group antigens in body fluids and the intestinal mucosa25. The rs601338 A allele (Turkish and Iranian) and the rs1047781 T allele (Japanese) are ancestry-specific FUT2 non-secretor mutations (p.Trp143Ter and p.Ile129Phe, respectively), for which homozygosity leads to an ABO non-secretor phenotype25. We found significant associations of rs601338 with disease in Turks (P=6.51×10−9) and in Iranians (P=1.65x10−5), and also significant association of rs1047781 in Japanese (P=6.50×10−4, Supplementary Table 15). These non-secretor genotypes are also associated with Crohn’s disease risk26,27 and with the gut microbiome composition28,29. The non-secretor phenotype has also been associated with increased predisposition to or resistance to different infectious agents30–32. Meta-analysis of the two common FUT2 non-secretor genotypes in Turks, Iranians and Japanese was highly significant (P=5.89×10−15, Supplementary Table 15), providing evidence that ABO non-secretion, particularly at mucosal surfaces, increases risk for Behçet’s disease and implicates the microbial-host interface in disease pathogenesis.
Our study has increased the number of susceptibility loci shared between Behçet’s disease and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which shares many clinical features, to eleven, adding four (ADO-EGR2, LACC1, IRF8, and CEBPB-PTPN1), thus indicating significant genetic similarity with IBD (Supplementary Table 16 and 17)26,33,34. In addition, markers within the reported susceptibility loci for IBD demonstrated a greater than expected by chance enrichment of associations with Behçet’s disease (Supplementary Fig. 4). Comparing between subgroups of IBD, our new findings emphasize higher genetic similarity of Behçet’s disease with Crohn’s disease (CD) (ADO-EGR2, RIPK2, LACC1, and IRF8) than with ulcerative colitis (ADO-EGR2 and CEBPB-PTPN1) (Supplementary Table 17)26,34.
A significant overlap in common susceptibility loci between Behçet’s disease and leprosy caused by infection with Mycobacterium leprae was also revealed by this study by adding three (RIPK2, ADO-EGR2 and LACC1) of the now four shared loci (Supplementary Table 17)35–37. The reported susceptibility loci for leprosy also showed relative enrichment of associations with Behçet’s disease (Supplementary Fig. 4).
Interestingly, the minor allele of the LACC1 lead SNP, rs2121033, confers protection for Behçet’s disease, but is in high LD with a common coding variant, rs3764147 (p.Ile254Val, r2=0.93), which increases risk for IBD and CD (Supplementary Table 17). Furthermore, a rare mutation in the laccase domain of the LACC1 protein, p.Cys284Arg, cosegregates with Mendelian systemic JIA and Crohn’s disease in consanguineous families38,39. A recent study reported that p.Ile254Val leads to impaired protein function and Lacc1−/ − mice produce decreased IL-1β in response to LPS treatment consistent with a role of IL-1β in Behçet’s disease pathogenesis40. The minor allele of rs913678 (C) in the CEBPB-PTPN1 locus also showed opposite direction effects between Behçet’s disease (risk) and IBD (protective) (Supplementary Table 17). This allele is associated with decreased gene expression (Supplementary Table 14) and C/EBPβ −/ − mice show increased susceptibility to pathogens41,42. These opposite effects suggest that different mechanisms involving these loci increase disease risk for Behçet’s disease compared with IBD.
A limitation of the Immunochip approach is that only selected genetic regions were explored in this study. In addition, the Immunochip has a potential problem in genotype calling accuracy because it is a custom array. To avoid miscalling, we applied strict quality control and cluster file preparation for the Turkish population (see methods). The peak genotyped markers of each disease-associated locus in the Turkish population showed robust clustering (Supplementary Fig. 5).
This Immunochip study in the largest discovery collection and with two additional populations in the replication phase provided robust evidence for HLA-B*51 in HLA-B as the primary genetic source of disease risk and identified multiple novel loci for Behçet’s disease. Genes in these loci contribute to the elucidation of disease pathogenesis by identifying significant disease-associated pathways including pathways involved in host defense, inflammation, and immune response (Supplementary Table 18). Although not yet proven, pathogenic infections have been proposed as an important environmental factor contributing to both the development and exacerbation of Behçet’s disease43. These pathways help to establish a link between genetic factors and environmental factors, such as microbial exposures that together contribute to disease susceptibility. Our current findings implicate genetic determinants of mucosal barrier function and the host response to pathogens in Behçet’s disease susceptibility, and draw important parallels and distinctions with other immune-related diseases.
METHODS
Subjects
We studied 2,014 Behçet’s disease cases and 1,826 genetically matched controls composed of the discovery and replication cohorts in previous GWAS and imputation studies7,9. We also included 969 Iranian cases and 826 controls recruited in a previous study24, and 608 Japanese cases and 737 controls recruited in a previous Japanese GWAS8 for replication. All Turkish and Iranian individuals affected with Behçet’s disease were diagnosed according to the International Study Group criteria for Behçet’s disease44 (Supplementary Table 19). All Japanese individuals affected with Behçet’s disease were diagnosed according to the Japanese Behçet’s disease criteria45 (Supplementary Table 20). Characteristics of each population are shown in Supplementary Table 21. All study participants provided written informed consent, and the study was approved by the ethics committee of each investigative institution.
Genotyping
We genotyped 2,014 Behçet’s disease cases and 1,826 healthy controls from the Turkish population on an Illumina iSelect HD custom genotyping array (Immunochip) according to Illumina’s protocols. All samples were genotyped at the National Institutes of Health (Bethesda, Maryland, USA). Genotypes were called by GenCall using GRCh build 37/hg19 mapping.
Data quality control
The cluster file was made from samples with initial call rate > 0.986 by the Illumina GenomeStudio GenTrain2.0 algorithm. Samples were excluded for a call rate < 0.85. After re-calculating, markers were excluded for call frequency < 0.95 and GenTrain score < 0.5. After data cleaning, the data of 3,737 samples across 185,548 markers were exported to Golden Helix SVS 8.3.3 software. Markers on chromosome X and Y were excluded. For further quality control, samples were excluded for call rate < 0.95 and markers were excluded for call rate < 0.95, minor allele frequency (MAF) < 0.01 and deviation from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE, P < 1×10−5).
A set of 38,256 LD-pruned markers with r2 < 0.5 was used to estimate identity by descent. For each pair or trio of individuals with pi-hat > 0.18, the sample with higher or highest call rate was included. Principal-component analysis was used to estimate population stratification (Supplementary Fig. 6). A set of LD-pruned markers after removing MHC region and long-range LD regions46 were used for estimation of genomic inflation factors, λGC and λ1000 (Supplementary Fig. 7). After quality control, a total of 1,900 cases, 1,779 controls, and 130,647 markers were included in the association analysis. This sample size provides greater than 83.6% power to detect a disease risk allele with effect size 1.25 and allele frequency 0.10 for a disease with 0.4% prevalence47.
Analysis of the MHC region
Immunochip genotyping data in the MHC region were imputed to type classical HLA alleles by SNP2HLA using the reference data collected by the Type I Diabetes Genetic Consortium48. Additional SNP genotypes from this region were also imputed by IMPUTE249 after phasing by SHAPEIT50 (see below). For quality control, markers with MAF < 0.01 and HWE P-value < 1×10−5 in controls were excluded. The concordance rate per allele in 2186 samples for which HLA-B*51 was directly typed was 98.6%.
Statistical association tests
Single marker associations were evaluated by basic allele tests comparing the allele frequencies between cases and controls using Golden Helix SVS 8.3.3 software. The correlation/trend test was performed and P < 5×10−8 was considered genome-wide significance. We also evaluated P-values corrected by genomic inflation of the Turkish population (PGC). Disease associations with markers reported in the previous studies were also evaluated. Conditional logistic regression analysis was performed to identify independently associated markers. After conditioning on a lead marker in each genome-wide significant locus, an additional marker was considered independently associated with Behçet’s disease when P < 5×10−5. Statistical power for the original GWAS collection, the Immunochip study, and the replication cohorts was calculated with CaTS51.
Additional genotyping, imputation
From the Immunochip association analysis, we selected the lead marker(s) with P < 5×10−5 from 20 novel loci (3 loci from Table 2 and 17 from Supplementary Table 5). Markers located within about ± 100 kb from these lead markers were selected for imputation. Since IL1A-IL1B and PTPN1 loci were sparsely genotyped by the Immunochip, fine mapping was performed for these loci before imputation with iPLEX assays (TOF-MS, Agena) using the same Turkish samples. The Tagger SNP selection tool from HapMap was used to select SNPs with the intent of obtaining 100% coverage of the HapMap phase 3 SNPs with greater than 1% minor allele frequency in the CEU HapMap population with pairwise r2 > 0.8. Although already tagged, additional SNPs with r2 > 0.8 with the most significantly associated SNP of the region were also included. After combining fine mapping and Immunochip data, we imputed these loci by IMPUTE249. The same loci were also imputed from Japanese GWAS data for the replication study. The 1000 Genomes Project Phase 1 integrated dataset52 was used as the reference panel for imputation. Markers with info score > 0.8 and genotypes with probability > 0.9 were included in analyses. For quality control, markers with MAF < 0.01 and HWE P-value < 1×10−5 in controls were excluded.
Replication
Disease associations of susceptibility markers previously reported from 11 loci outside of the MHC were analyzed for genotyped and imputed markers. The P-value <0.0045 (0.05 corrected for 11 loci) was considered replicated. Lead SNPs genotyped by Immunochip in the Turkish population for each novel suggestive locus with P < 5×10−5 were selected for genotyping in Iranian individuals by iPLEX assays (TOF-MS, Agena) for replication. Imputed Japanese GWAS data were also used for replication in the Japanese population. Meta-analysis in multiple populations was performed using META49. For a comprehensive assessment of the novel suggestive loci in imputed Turkish Immunochip and Japanese GWAS data, all the available markers with suggestive association in the Turkish population (P<5×10−5) were analyzed (n=215). The P-value threshold for replication in the Iranian and Japanese cohorts was corrected for the number of independent markers (n=37) after LD pruning to r2<0.8 (P<0.0014). The P-value of heterogeneity and I2 were calculated to evaluate heterogeneity between populations. Pheterogeneity < 0.05 and I2 > 0.5 were considered significant.
Association analysis for homozygous FUT2 non-secretor alleles
Turkish Immunochip data from the FUT2 locus was used to impute regional variants by the same methods as other loci to obtain genotyping data of rs601338, the common FUT2 non-secretor SNP. Genotyping of the common Asian non-secretor allele rs1047781 was performed in the Japanese population (594 cases and 692 controls) using the TaqMan 5′ exonuclease assay with validated TaqMan primer-probe sets (Applied Biosystems). The probe fluorescence signal was detected using the StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems) following the manufacturer’s protocol. Iranian genotype data of rs601338 from the previous study12 were used for the meta-analysis of homozygous non-secretor genotypes among the three populations.
Annotation
To develop mechanistic hypotheses, we investigated chromatin states, conservation, and regulatory motifs altered by SNPs identified in this study using Haploreg v4.153. Functional effects of non-synonymous coding variants were predicted by Polyphen-254. eQTL data were extracted from the Genevar55,56, Blood eQTL browser57 and GTEx58 to investigate the association between a disease susceptibility SNP and a target gene. P-value significance thresholds were applied as described in the original reports56–58.
Cytokine assays in PBMCs
Whole blood samples from healthy controls were collected in sodium heparin tubes. PBMCs were purified by Ficoll (Ficoll-Paque PLUS, GE Healthcare) using Leucosep tubes (Greiner Bio-One) by gradient centrifugation. Cells were then washed with PBS (Life Technologies) twice (400 x g for 10 minutes at room temperature then 250 x g for 12 minutes 4°C) and once with RPMI1640 medium (Life Technologies) with FBS (300 x g for 5 minutes at 4°C). The washed PBMCs were plated in triplicate into a 96-well plate (2×106 cells per ml) in RPMI1640 medium with FBS. Cells were left untreated or stimulated with zymosan (10mg/mL) at 37°C, 5% CO2 for 24 hrs. Supernatants of cultured PBMCs were collected after centrifugation and stored at −80° C. The concentrations of cytokines were detected using the Affymetrix eBioscience Human Simplex kits for IL-1α and IL-1β and a Bio-Rad Bio-Plex 200 Luminex system according to the manufacturer’s instructions. 50 μl of PBMC culture supernatants were used for the immunoassays. The data were analyzed for statistical significance using the two-tailed Mann-Whitney test (P<0.05).
Behçet’s disease susceptibility loci and overlap with other diseases
Susceptibility loci and lead SNPs that overlap Behçet’s disease susceptibility loci in other immune-related diseases and leprosy were extracted from ImmunoBase and the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) GWAS catalog. If the Behçet’s disease lead SNP or a SNP in strong LD (r2> 0.8) was associated with the other disease, concordance of allelic effect was ascertained. In diseases with susceptibility loci with no disease-associated markers in strong LD with the Behçet’s disease marker, concordant effects of disease-associated alleles were identified by their eQTL effects if available. LD data in CEU of the 1000 Genomes Project was applied. eQTL databases (Genevar55,56, Blood eQTL browser57 and GTEx58 and summary data from 12 studies available in HaploReg v4) were used to extract gene expression data. Permutation tests were performed to evaluate the number of disease risk loci shared between Behçet’s disease and IBD (CD and ulcerative colitis) or leprosy by a random selection of 1,000,000 sets of the same number of susceptibility loci for each disease from the Refseq gene list (22,345 genes). Associations with Behçet’s disease in this study for markers located in susceptibility loci for IBD or leprosy from previous studies were plotted to evaluate whether they are enriched for associations with Behçet’s disease.
Pathway analysis
The pathways in which susceptibility genes are involved were analyzed in the GO database by DAVID v6.759. Twenty-one susceptibility genes including 9 novel genes from this study were included in the pathway analysis. P-values were corrected by Benjamini’s method. Pcorrected < 0.05 was considered significant.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Intramural Research Programs of the National Human Genome Research Institute and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Disease. We thank all the patients, the healthy controls and medical staff, for their enthusiastic support during this research study. M.T. is supported by a Fellowship for Japanese Biomedical and Behavioral Researchers at NIH from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science Research and a grant from the Japan Foundation for Applied Enzymology. Y.K. is supported by grants from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research [Grant No. 26713036], the Kanae Foundation for the Promotion of Medical Science, the Takeda Science Foundation, the SENSHIN Medical Research Foundation, and the Yokohama Foundation for Advancement of Medical Science. This research was also supported by the Portuguese Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia [Grant CMUP-ERI/TPE/0028/2013, Fellowship SFRH/BPD/70008/2010 to I.S., and an Investigator-FCT contract to S.A.O.], and the Research Committee of the Tehran University of Medical Sciences [Grant 132/714]. We thank Alexander F. Wilson for comments on this manuscript.
Footnotes
URLs.
GWAS Catalog, http://www.genome.gov/gwastudies/;
IMPUTE2, https://mathgen.stats.ox.ac.uk/impute/impute_v2.html;
SNP2HLA, https://www.broadinstitute.org/mpg/snp2hla/;
CaTS, http://csg.sph.umich.edu/abecasis/CaTS/;
META, https://mathgen.stats.ox.ac.uk/genetics_software/meta/meta.html;
Genevar, https://www.sanger.ac.uk/resources/software/genevar/;
Blood eQTL browser, http://genenetwork.nl/bloodeqtlbrowser/;
Haploreg, www.broadinstitute.org/mammals/haploreg/;
Polyphen-2, http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/;
GTEx, www.gtexportal.org/;
ImmunoBase, https://www.immunobase.org/;
DAVID, https://david.ncifcrf.gov/.
DATA AVAILABILITY
Statistical summary data for all markers genotyped with the Immunochip, for which the discovery cohort showed genome-wide significant or suggestive association (P<5×10−5) are provided in a Supplementary Data Set available in the Supplementary Materials.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
The study was designed by M.T., M.J.O., A.G., D.L.K. and E.F.R. Analysis was carried out by M.T., A.M., M.J.O., M.B., M.G., A.G., D.L.K. and E.F.R. Sample procurement and data generation were performed by M.T., N.M., A.M., M.J.O., Y.K., C.S., J.L., M.B., B.E., T.K., D.U., I.T-T., E.S., Y.O., I.S., F.D., V.F., F.S., B.S.A., A.N., N.M.S., F.G., S.O., A.U., Y.I., M.G., S.A.O., A.G., D.L.K. and E.F.R. The manuscript was written by M.T., M.J.O., M.B., M.G., A.G., D.L.K. and E.F.R. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- 1.Sakane T, Takeno M, Suzuki N, Inaba G. Behcet’s disease. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1284–91. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199910213411707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hatemi G, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of Behcet disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67:1656–62. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.080432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Verity DH, Marr JE, Ohno S, Wallace GR, Stanford MR. Behcet’s disease, the Silk Road and HLA-B51: historical and geographical perspectives. Tissue Antigens. 1999;54:213–20. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0039.1999.540301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gul A, Ohno S. HLA-B*51 and Behcet Disease. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2012;20:37–43. doi: 10.3109/09273948.2011.634978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ohno S, Aoki K, Sugiura S, Nakayama E, Itakura K. Letter: HL-A5 and Behcet’s disease. Lancet. 1973;2:1383–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93343-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.de Menthon M, Lavalley MP, Maldini C, Guillevin L, Mahr A. HLA-B51/B5 and the risk of Behcet’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control genetic association studies. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61:1287–96. doi: 10.1002/art.24642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Remmers EF, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants in the MHC class I, IL10, and IL23R-IL12RB2 regions associated with Behcet’s disease. Nat Genet. 2010;42:698–702. doi: 10.1038/ng.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mizuki N, et al. Genome-wide association studies identify IL23R-IL12RB2 and IL10 as Behcet’s disease susceptibility loci. Nat Genet. 2010;42:703–6. doi: 10.1038/ng.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kirino Y, et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies new susceptibility loci for Behcet’s disease and epistasis between HLA-B*51 and ERAP1. Nat Genet. 2013;45:202–7. doi: 10.1038/ng.2520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Li H, et al. TNFAIP3 gene polymorphisms confer risk for Behcet’s disease in a Chinese Han population. Hum Genet. 2013;132:293–300. doi: 10.1007/s00439-012-1250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kirino Y, et al. Targeted resequencing implicates the familial Mediterranean fever gene MEFV and the toll-like receptor 4 gene TLR4 in Behcet disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:8134–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1306352110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Xavier JM, et al. FUT2: filling the gap between genes and environment in Behcet’s disease? Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:618–24. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kappen JH, et al. Genome-wide association study in an admixed case series reveals IL12A as a new candidate in Behcet disease. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0119085. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ortiz-Fernandez L, et al. Genetic Analysis with the Immunochip Platform in Behcet Disease. Identification of Residues Associated in the HLA Class I Region and New Susceptibility Loci. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0161305. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cortes A, Brown MA. Promise and pitfalls of the Immunochip. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13:101. doi: 10.1186/ar3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ombrello MJ, et al. Behcet disease-associated MHC class I residues implicate antigen binding and regulation of cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:8867–72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1406575111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hughes T, et al. Identification of multiple independent susceptibility loci in the HLA region in Behcet’s disease. Nat Genet. 2013;45:319–24. doi: 10.1038/ng.2551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Barland CO, et al. Imiquimod-induced interleukin-1 alpha stimulation improves barrier homeostasis in aged murine epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 2004;122:330–6. doi: 10.1046/j.0022-202X.2004.22203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vonk AG, et al. Endogenous interleukin (IL)-1 alpha and IL-1 beta are crucial for host defense against disseminated candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 2006;193:1419–26. doi: 10.1086/503363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Liang L, et al. IL-1beta triggered by peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharide through TLR2/4 and ROS-NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pathways is involved in ocular Behcet’s disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013;54:402–14. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-11047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kim EH, Park MJ, Park S, Lee ES. Increased expression of the NLRP3 inflammasome components in patients with Behcet’s disease. J Inflamm (Lond) 2015;12:41. doi: 10.1186/s12950-015-0086-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Caso F, et al. Biological treatments in Behcet’s disease: beyond anti-TNF therapy. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:107421. doi: 10.1155/2014/107421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gul A, et al. Interleukin-1beta-regulating antibody XOMA 052 (gevokizumab) in the treatment of acute exacerbations of resistant uveitis of Behcet’s disease: an open-label pilot study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:563–6. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-155143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Xavier JM, et al. FUT2: filling the gap between genes and environment in Behcet’s disease? Ann Rheum Dis. 2013 doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ferrer-Admetlla A, et al. A natural history of FUT2 polymorphism in humans. Mol Biol Evol. 2009;26:1993–2003. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msp108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Franke A, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis increases to 71 the number of confirmed Crohn’s disease susceptibility loci. Nat Genet. 2010;42:1118–25. doi: 10.1038/ng.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hu DY, et al. Associations of FUT2 and FUT3 gene polymorphisms with Crohn’s disease in Chinese patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;29:1778–85. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wacklin P, et al. Secretor genotype (FUT2 gene) is strongly associated with the composition of Bifidobacteria in the human intestine. PLoS One. 2011;6:e20113. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rausch P, et al. Colonic mucosa-associated microbiota is influenced by an interaction of Crohn disease and FUT2 (Secretor) genotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:19030–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1106408108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sheinfeld J, Schaeffer AJ, Cordon-Cardo C, Rogatko A, Fair WR. Association of the Lewis blood-group phenotype with recurrent urinary tract infections in women. N Engl J Med. 1989;320:773–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198903233201205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Marionneau S, Airaud F, Bovin NV, Le Pendu J, Ruvoen-Clouet N. Influence of the combined ABO, FUT2, and FUT3 polymorphism on susceptibility to Norwalk virus attachment. J Infect Dis. 2005;192:1071–7. doi: 10.1086/432546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rupp C, et al. Fut2 genotype is a risk factor for dominant stenosis and biliary candida infections in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;39:873–82. doi: 10.1111/apt.12663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hatemi I, et al. Frequency of pathergy phenomenon and other features of Behcet’s syndrome among patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2008;26:S91–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jostins L, et al. Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2012;491:119–24. doi: 10.1038/nature11582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zhang FR, et al. Genomewide association study of leprosy. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:2609–18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0903753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Liu H, et al. Discovery of six new susceptibility loci and analysis of pleiotropic effects in leprosy. Nat Genet. 2015;47:267–71. doi: 10.1038/ng.3212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sales-Marques C, et al. NOD2 and CCDC122-LACC1 genes are associated with leprosy susceptibility in Brazilians. Hum Genet. 2014;133:1525–32. doi: 10.1007/s00439-014-1502-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wakil SM, et al. Association of a mutation in LACC1 with a monogenic form of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:288–95. doi: 10.1002/art.38877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Patel N, et al. Study of Mendelian forms of Crohn’s disease in Saudi Arabia reveals novel risk loci and alleles. Gut. 2014;63:1831–2. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Cader MZ, et al. C13orf31 (FAMIN) is a central regulator of immunometabolic function. Nat Immunol. 2016 doi: 10.1038/ni.3532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Screpanti I, et al. Lymphoproliferative disorder and imbalanced T-helper response in C/EBP beta-deficient mice. Embo j. 1995;14:1932–41. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tanaka T, et al. Targeted disruption of the NF-IL6 gene discloses its essential role in bacteria killing and tumor cytotoxicity by macrophages. Cell. 1995;80:353–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90418-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zierhut M, et al. Immunology and functional genomics of Behcet’s disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003;60:1903–22. doi: 10.1007/s00018-003-2333-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.International Study Group for Behçet’s Disease. Criteria for diagnosis of Behçet’s disease. Lancet. 1990;335:1078–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mizushima Y. Recent research into Behcet’s disease in Japan. Int J Tissue React. 1988;10:59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Price AL, et al. Long-range LD can confound genome scans in admixed populations. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;83:132–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.06.005. author reply 135–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Purcell S, Cherny SS, Sham PC. Genetic Power Calculator: design of linkage and association genetic mapping studies of complex traits. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:149–50. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/19.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jia X, et al. Imputing amino acid polymorphisms in human leukocyte antigens. PLoS One. 2013;8:e64683. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Marchini J, Howie B, Myers S, McVean G, Donnelly P. A new multipoint method for genome-wide association studies by imputation of genotypes. Nat Genet. 2007;39:906–13. doi: 10.1038/ng2088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Delaneau O, Marchini J, Zagury JF. A linear complexity phasing method for thousands of genomes. Nat Methods. 2012;9:179–81. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Skol AD, Scott LJ, Abecasis GR, Boehnke M. Joint analysis is more efficient than replication-based analysis for two-stage genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet. 2006;38:209–13. doi: 10.1038/ng1706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Abecasis GR, et al. A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature. 2010;467:1061–73. doi: 10.1038/nature09534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ward LD, Kellis M. HaploReg: a resource for exploring chromatin states, conservation, and regulatory motif alterations within sets of genetically linked variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:D930–4. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Adzhubei IA, et al. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods. 2010;7:248–9. doi: 10.1038/nmeth0410-248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Yang TP, et al. Genevar: a database and Java application for the analysis and visualization of SNP-gene associations in eQTL studies. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:2474–6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Grundberg E, et al. Mapping cis- and trans-regulatory effects across multiple tissues in twins. Nat Genet. 2012;44:1084–9. doi: 10.1038/ng.2394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Westra HJ, et al. Systematic identification of trans eQTLs as putative drivers of known disease associations. Nat Genet. 2013;45:1238–43. doi: 10.1038/ng.2756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Baran Y, et al. The landscape of genomic imprinting across diverse adult human tissues. Genome Res. 2015;25:927–36. doi: 10.1101/gr.192278.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dennis G, Jr, et al. DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 2003;4:P3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.