Abstract
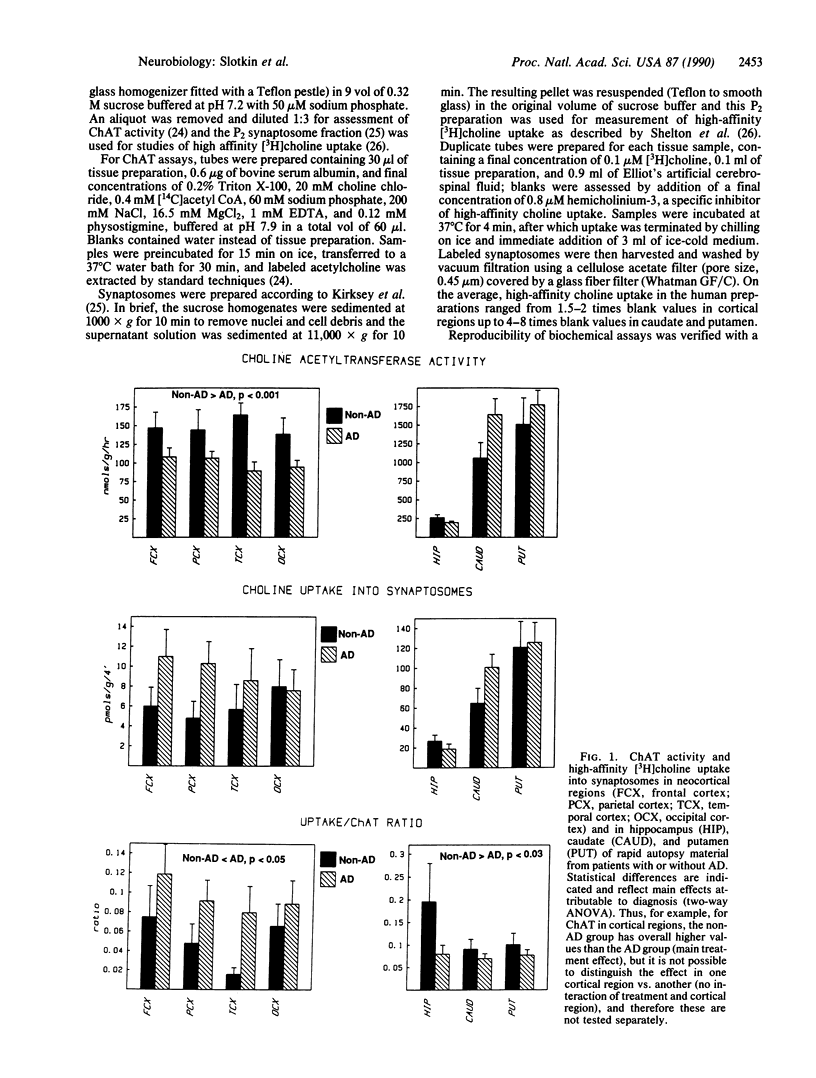
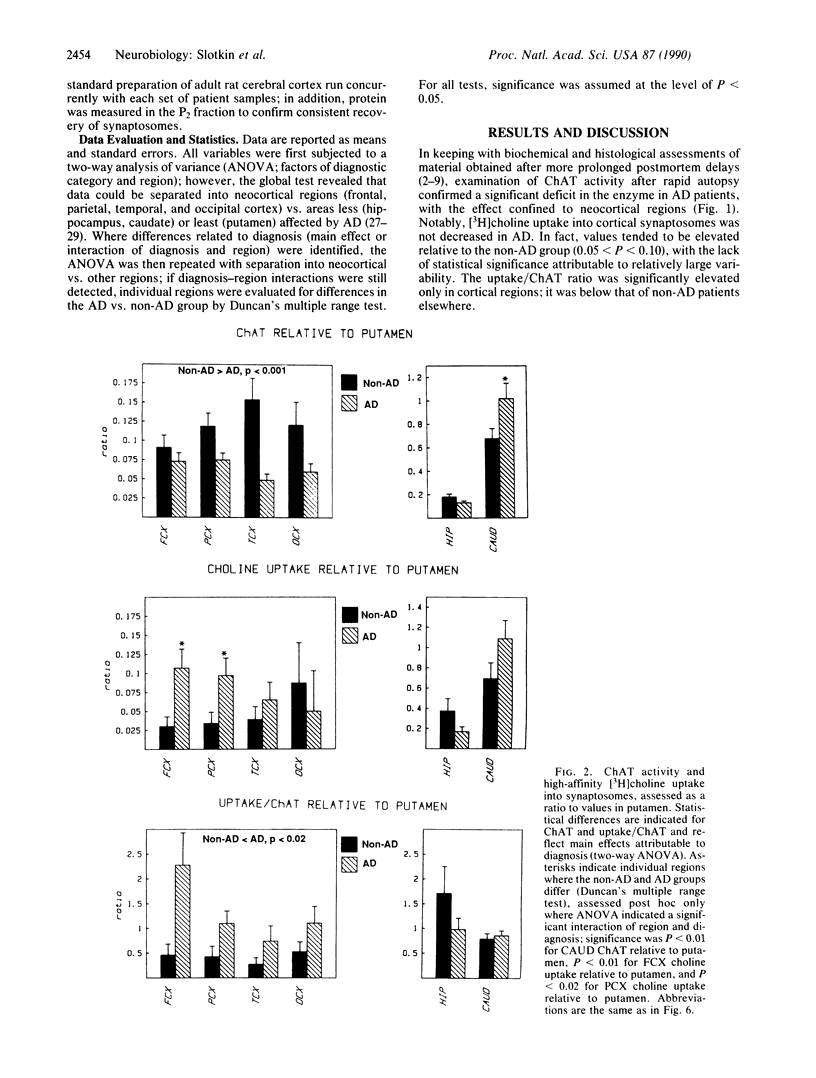
Brain regions from patients with or without Alzheimer disease (AD) were obtained within 2 hr of death and examined for indices of presynaptic cholinergic function. Consistent with loss of cholinergic projections, cerebral cortical areas involved in AD exhibited decreased choline acetyltransferase (acetyl-CoA:choline O-acetyltransferase, EC 2.3.1.6) activity. However, remaining nerve terminals in these regions displayed marked up-regulation of synaptosomal high affinity [3H]choline uptake, a result indicative of relative cholinergic hyperactivity. As choline uptake is also rate-limiting in acetylcholine biosynthesis, these findings have implications for both therapy and identification of causes contributing to neuronal death in AD.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bissette G., Reynolds G. P., Kilts C. D., Widerlöv E., Nemeroff C. B. Corticotropin-releasing factor-like immunoreactivity in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Reduced cortical and striatal concentrations. JAMA. 1985 Dec 6;254(21):3067–3069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen D. M., Allen S. J., Benton J. S., Goodhardt M. J., Haan E. A., Palmer A. M., Sims N. R., Smith C. C., Spillane J. A., Esiri M. M. Biochemical assessment of serotonergic and cholinergic dysfunction and cerebral atrophy in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 1983 Jul;41(1):266–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb11838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottfries C. G. Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia: biochemical characteristics and aspects of treatment. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1985;86(3):245–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00432208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985 Nov;42(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirksey D. F., Seidler F. J., Slotkin T. A. Ontogeny of (--)-[3H]norepinephrine uptake properties of synaptic storage vesicles of rat brain. Brain Res. 1978 Jul 14;150(2):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90287-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm N., Kuhar M. J. Post-mortem changes in high affinity choline uptake. J Neurochem. 1979 May;32(5):1487–1494. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb11089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau C., Ross L. L., Whitmore W. L., Slotkin T. A. Regulation of adrenal chromaffin cell development by the central monoaminergic system: differential control of norepinephrine and epinephrine levels and secretory responses. Neuroscience. 1987 Sep;22(3):1067–1075. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)92981-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordberg A., Alafuzoff I., Winblad B. Muscarinic receptor subtypes in hippocampus in Alzheimer's disease and mixed dementia type. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Sep 25;70(1):160–164. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90456-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry E. K., Perry R. H., Blessed G., Tomlinson B. E. Necropsy evidence of central cholinergic deficits in senile dementia. Lancet. 1977 Jan 22;1(8004):189–189. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91780-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossor M. N., Garrett N. J., Johnson A. L., Mountjoy C. Q., Roth M., Iversen L. L. A post-mortem study of the cholinergic and GABA systems in senile dementia. Brain. 1982 Jun;105(Pt 2):313–330. doi: 10.1093/brain/105.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylett R. J., Ball M. J., Colhoun E. H. Evidence for high affinity choline transport in synaptosomes prepared from hippocampus and neocortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 1983 Dec 19;289(1-2):169–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D. E., Goldgaber D., Burkhart D. S., Gilbert J. R., Gajdusek D. C., Roses A. D. Cellular localization of messenger RNA encoding amyloid-beta-protein in normal tissue and in Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1988;2(2):96–111. doi: 10.1097/00002093-198802020-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton D. L., Nadler J. V., Cotman C. W. Development of high affinity choline uptake and associated acetylcholine synthesis in the rat fascia dentata. Brain Res. 1979 Mar 16;163(2):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90354-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman K. A., Zigmond M. J., Hanin I. High affinity choline uptake in striatum and hippocampus: differential effects of treatments which release acetylcholine. Life Sci. 1978 Oct 30;23(17-18):1863–1870. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. R., Atweh S., Kuhar M. J. Sodium-dependent high affinity choline uptake: a regulatory step in the synthesis of acetylcholine. J Neurochem. 1976 May;26(5):909–922. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb06472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims N. R., Bowen D. M., Allen S. J., Smith C. C., Neary D., Thomas D. J., Davison A. N. Presynaptic cholinergic dysfunction in patients with dementia. J Neurochem. 1983 Feb;40(2):503–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb11311.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse P. J., Martino A. M., Antuono P. G., Lowenstein P. R., Coyle J. T., Price D. L., Kellar K. J. Nicotinic acetylcholine binding sites in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 1986 Apr 16;371(1):146–151. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90819-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



