FIG 1 .
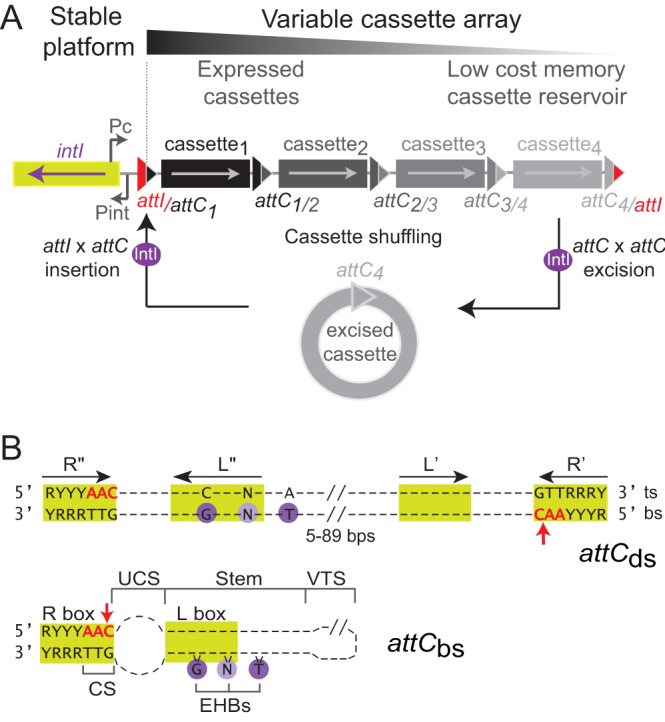
The integron system. (A) Organization of integrons. Functional platform composed of the intI gene encoding the integrase (green rectangle), the cassette promoter (PC) and the integrase promoter (Pint), as well as the primary attI recombination site (red triangle) are shown. Integrase (IntI; purple circle) catalyzes cassette excision (attC × attC) followed by insertion (attI × attC) of the excised cassette (gray circle). Hybrid att sites are indicated. Arrows inside the cassettes indicate the direction of their coding sequence (CDS), and the color intensity reflects the expression level of cassettes: only the first several cassettes of the array are expressed, while the subsequent ones can be seen as a low-cost cassette reservoir. (B) attC recombination sites. The double- and single-stranded attC sites (attCds and attCbs) are shown. Green boxes show putative IntI1 binding sites, and red arrows show the cleavage point. For the attCds, inverted repeats (R’’, L”, L’, and R’) are indicated by black arrows. The conserved nucleotides are indicated, and violet circles show the conserved G nucleotide and the other bases, which constitute the extrahelical bases (EHBs) in folded attC sites (see attCbs). The top strand (ts) and bottom strand (bs) are marked. The structure of attCbs was determined by the RNAfold program from ViennaRNA 2 package (Materials and Methods). Structural features, namely, the unpaired central spacer (UCS), the EHBs, the stem, and the variable terminal structure (VTS), as well as the conserved sequence (CS), are indicated. R, purine; Y, pyrimidine; N, any base.
