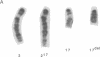Abstract
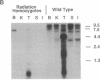
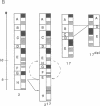
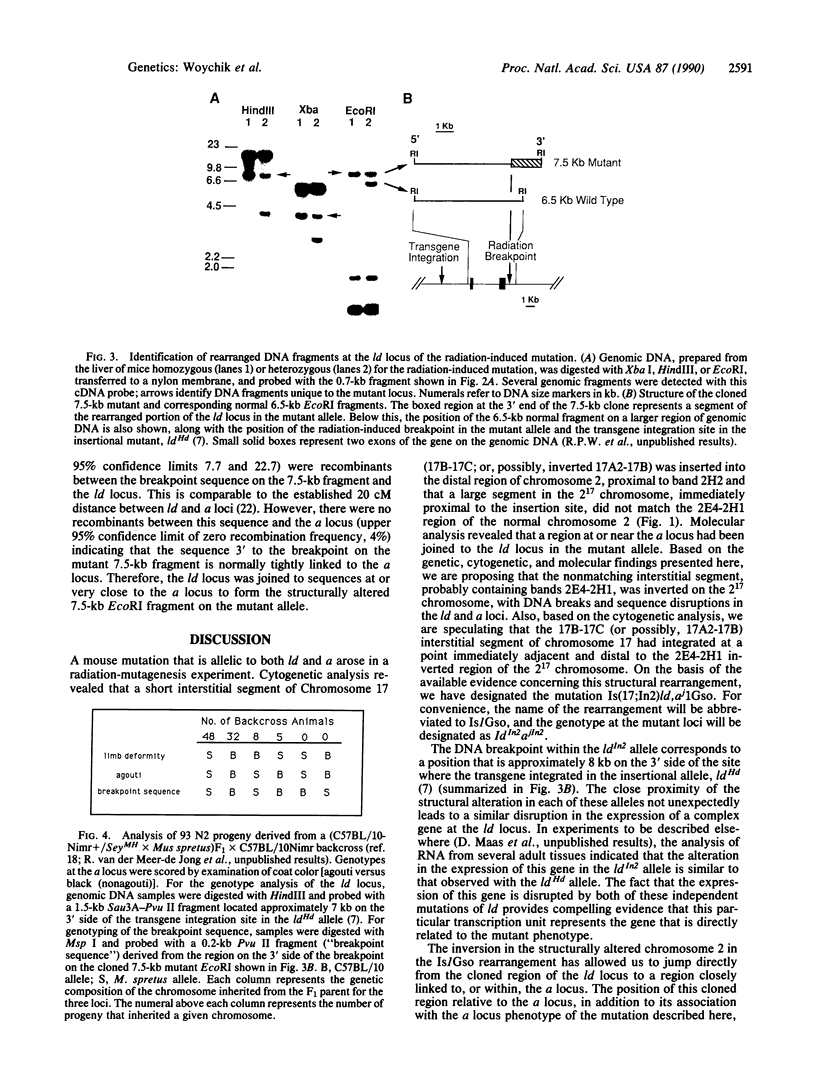
Molecular characterization of mutations in the mouse, particularly those involving agent-induced major structural alterations, is proving to be useful for correlating the structure and expression of individual genes with their function in the whole organism. Here we present the characterization of a radiation-induced mutation that simultaneously generated distinct alleles of both the limb deformity (ld) and agouti (a) loci, two developmentally important regions of chromosome 2 normally separated by 20 centimorgans. Cytogenetic analysis revealed that an interstitial segment of chromosome 17 (17B- 17C; or, possibly, 17A2-17B) had been translocated into the distal end of chromosome 2, resulting in a smaller-than-normal chromosome 17 (designated 17del) and a larger form of chromosome 2 (designated 2(17). Additionally, a large interstitial segment of the 2(17) chromosome, immediately adjacent and proximal to the insertion site, did not match bands 2E4-2H1 at corresponding positions on a normal chromosome 2. Molecular analysis detected a DNA rearrangement in which a portion of the ld locus was joined to sequences normally tightly linked to the a locus. This result, along with the genetic and cytogenetic data, suggests that the alleles of ld and a in this radiation-induced mutation, designated ldIn2 and ajIn2, were associated with DNA breaks caused by an inversion of an interstitial segment in the 2(17) chromosome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsh G. S., Epstein C. J. Physical and genetic characterization of a 75-kilobase deletion associated with al, a recessive lethal allele at the mouse agouti locus. Genetics. 1989 Apr;121(4):811–818. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.4.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Eustachio P., Jadidi S., Fuhlbrigge R. C., Gray P. W., Chaplin D. D. Interleukin-1 alpha and beta genes: linkage on chromosome 2 in the mouse. Immunogenetics. 1987;26(6):339–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00343701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davisson M. T., Roderick T. H. Status of the linkage map of the mouse. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):552–557. doi: 10.1159/000131022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. K., Hand R. E., Jr, Rinchik E. M. Molecular mapping within the mouse albino-deletion complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8862–8866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinebrecht J., Selow J., Winkler W. The mouse mutant limb-deformity (ld). Anat Anz. 1982;152(4):313–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett M., Cheng Z. Y., Lamela E. M., Yokoi T., Epstein C. J. Molecular markers for the agouti coat color locus of the mouse. Genetics. 1987 Apr;115(4):747–754. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.4.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak S., Stock A. D., Lusby A. A combination of sister chromatid differential staining and giemsa banding. Experientia. 1975 Aug 15;31(8):916–918. doi: 10.1007/BF02358850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinchik E. M., Carpenter D. A., Selby P. B. A strategy for fine-structure functional analysis of a 6- to 11-centimorgan region of mouse chromosome 7 by high-efficiency mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):896–900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell L. B. Functional and structural analyses of mouse genomic regions screened by the morphological specific-locus test. Mutat Res. 1989 May;212(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(89)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracusa L. D., Buchberg A. M., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Recombinant inbred strain and interspecific backcross analysis of molecular markers flanking the murine agouti coat color locus. Genetics. 1989 Jul;122(3):669–679. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracusa L. D., Russell L. B., Eicher E. M., Corrow D. J., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Genetic organization of the agouti region of the mouse. Genetics. 1987 Sep;117(1):93–100. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracusa L. D., Russell L. B., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Allelic variation within the Emv-15 locus defines genomic sequences closely linked to the agouti locus on mouse chromosome 2. Genetics. 1987 Sep;117(1):85–92. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik R. P., Stewart T. A., Davis L. G., D'Eustachio P., Leder P. An inherited limb deformity created by insertional mutagenesis in a transgenic mouse. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):36–40. doi: 10.1038/318036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeller R., Jackson-Grusby L., Leder P. The limb deformity gene is required for apical ectodermal ridge differentiation and anteroposterior limb pattern formation. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1481–1492. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]