Abstract
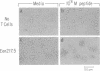
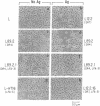
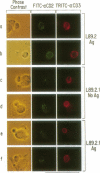
The role of the interaction of CD2 molecules with lymphocyte function-associated antigen 3 (LFA-3) in facilitating nominal antigen recognition by T lymphocytes was studied by utilizing an HLA-DR4-restricted CD4+ cytotoxic human T-cell clone specific for human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein gp120 as a responder and murine fibroblasts transfected with human class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and/or human LFA-3 molecules as antigen-presenting cells (APC). Although expression of the DR4 restriction element in fibroblasts is sufficient for T-cell recognition of a gp120 peptide as judged by induction of proliferation coexpression of human LFA-3 on DR4+ APC decreases the molar requirement of nominal antigen by greater than one order of magnitude. Both LFA-3 and the relevant class II MHC molecules are necessary for antigen-independent conjugate formation, but the binding is further enhanced by specific nominal antigen. CD2-LFA-3 interaction is independent of T-cell receptor-MHC interaction and contributes directly to the stabilized conjugate between the T cell and LFA-3-bearing APC; soluble CD2 and monoclonal antibodies to LFA-3 and CD2 reduce T-cell-APC binding to the level mediated by nominal antigen and MHC. During conjugate formation, CD2 but not CD3 molecules are reorganized into the cell-cell interaction site in an antigen-independent manner. Thus, reorganization and/or coassociation of CD2 with CD3 molecules is not essential for T-cell activation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen P. M., Matsueda G. R., Evans R. J., Dunbar J. B., Jr, Marshall G. R., Unanue E. R. Identification of the T-cell and Ia contact residues of a T-cell antigenic epitope. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):713–715. doi: 10.1038/327713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierer B. E., Peterson A., Gorga J. C., Herrmann S. H., Burakoff S. J. Synergistic T cell activation via the physiological ligands for CD2 and the T cell receptor. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):1145–1156. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. H., Cantrell D. A., Brattsand G., Crumpton M. J., Gullberg M. The CD2 antigen associates with the T-cell antigen receptor CD3 antigen complex on the surface of human T lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):551–553. doi: 10.1038/339551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Sette A., Colon S. M., Jenis D. M., Grey H. M. Isolation and characterization of antigen-Ia complexes involved in T cell recognition. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1071–1077. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90822-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton L. K., Sieh M., Pious D. A., Reinherz E. L. Identification of human CD4 residues affecting class II MHC versus HIV-1 gp120 binding. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):548–551. doi: 10.1038/339548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Bjorkman P. J. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):395–402. doi: 10.1038/334395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle C., Strominger J. L. Interaction between CD4 and class II MHC molecules mediates cell adhesion. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):256–259. doi: 10.1038/330256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussey R. E., Richardson N. E., Kowalski M., Brown N. R., Chang H. C., Siliciano R. F., Dorfman T., Walker B., Sodroski J., Reinherz E. L. A soluble CD4 protein selectively inhibits HIV replication and syncytium formation. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):78–81. doi: 10.1038/331078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klohe E. P., Watts R., Bahl M., Alber C., Yu W. Y., Anderson R., Silver J., Gregersen P. K., Karr R. W. Analysis of the molecular specificities of anti-class II monoclonal antibodies by using L cell transfectants expressing HLA class II molecules. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):2158–2164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfer A., Singer S. J., Janeway C. A., Jr, Swain S. L. Coclustering of CD4 (L3T4) molecule with the T-cell receptor is induced by specific direct interaction of helper T cells and antigen-presenting cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5888–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kappler J. The antigen-specific, major histocompatibility complex-restricted receptor on T cells. Adv Immunol. 1986;38:1–30. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Acuto O., Hercend T., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. The human T-cell receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:23–50. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.000323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moingeon P., Chang H. C., Wallner B. P., Stebbins C., Frey A. Z., Reinherz E. L. CD2-mediated adhesion facilitates T lymphocyte antigen recognition function. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):312–314. doi: 10.1038/339312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R. Molecular biology and function of CD4 and CD8. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:265–311. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60644-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson N. E., Chang H. C., Brown N. R., Hussey R. E., Sayre P. H., Reinherz E. L. Adhesion domain of human T11 (CD2) is encoded by a single exon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5176–5180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayre P. H., Hussey R. E., Chang H. C., Ciardelli T. L., Reinherz E. L. Structural and binding analysis of a two domain extracellular CD2 molecule. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):995–1009. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Luce G. E., Quinones R., Gress R. E., Springer T. A., Sanders M. E. Two antigen-independent adhesion pathways used by human cytotoxic T-cell clones. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):262–264. doi: 10.1038/323262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano R. F., Lawton T., Knall C., Karr R. W., Berman P., Gregory T., Reinherz E. L. Analysis of host-virus interactions in AIDS with anti-gp120 T cell clones: effect of HIV sequence variation and a mechanism for CD4+ cell depletion. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):561–575. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., van Schooten W., Keizer H., van Seventer G., van de Rijn M., Terhorst C., de Vries J. E. Alloantigen recognition is preceded by nonspecific adhesion of cytotoxic T cells and target cells. Science. 1986 Apr 18;232(4748):403–405. doi: 10.1126/science.3485822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallner B. P., Frey A. Z., Tizard R., Mattaliano R. J., Hession C., Sanders M. E., Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. Primary structure of lymphocyte function-associated antigen 3 (LFA-3). The ligand of the T lymphocyte CD2 glycoprotein. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):923–932. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]