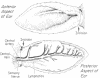
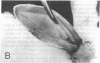
Abstract
Tissue injury resulting from ischemia and reperfusion forms the basis of several important disorders including myocardial infarction, stroke, and circulatory shock. To examine the role of neutrophils in this process and to determine the extent to which injury is a consequence of reperfusion, we utilized the monoclonal antibody 60.3, directed to CD18, the human leukocyte adherence glycoprotein, to block intravascular neutrophil aggregation and neutrophil adherence to endothelium in a rabbit model of tissue ischemia and reperfusion. Antibody treatment either before ischemia or after ischemia, but prior to reperfusion, resulted in the same degree of significant protection against endothelial, microvascular, and tissue injury. We conclude that neutrophils and increased neutrophil adhesiveness are important in the development of microvascular and tissue injury after ischemia and reperfusion and that under these circumstances, injury is primarily a consequence of reperfusion.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beatty P. G., Ledbetter J. A., Martin P. J., Price T. H., Hansen J. A. Definition of a common leukocyte cell-surface antigen (Lp95-150) associated with diverse cell-mediated immune functions. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2913–2918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunwald E., Kloner R. A. Myocardial reperfusion: a double-edged sword? J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1713–1719. doi: 10.1172/JCI112160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diener A. M., Beatty P. G., Ochs H. D., Harlan J. M. The role of neutrophil membrane glycoprotein 150 (Gp-150) in neutrophil-mediated endothelial cell injury in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):537–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler R. L., Dahlgren M. D., Morris D. D., Peterson M. A., Schmid-Schönbein G. W. Role of leukocytes in response to acute myocardial ischemia and reflow in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 2):H314–H323. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1986.251.2.H314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler R. Consequences of activation and adenosine-mediated inhibition of granulocytes during myocardial ischemia. Fed Proc. 1987 May 15;46(7):2407–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. N., Höllwarth M. E., Parks D. A. Ischemia-reperfusion injury: role of oxygen-derived free radicals. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1986;548:47–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisham M. B., Hernandez L. A., Granger D. N. Xanthine oxidase and neutrophil infiltration in intestinal ischemia. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):G567–G574. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.4.G567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M. Consequences of leukocyte-vessel wall interactions in inflammatory and immune reactions. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1987 Oct;13(4):434–444. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M. Neutrophil-mediated vascular injury. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1987;715:123–129. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1987.tb09912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez L. A., Grisham M. B., Twohig B., Arfors K. E., Harlan J. M., Granger D. N. Role of neutrophils in ischemia-reperfusion-induced microvascular injury. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 2):H699–H703. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.253.3.H699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitch J. H., Mendez L. Morphologic features of hepatic injury in cardiac disease and shock. J Hepatol. 1986;2(3):313–327. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(86)80043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchesi B. R., Mullane K. M. Leukocytes and ischemia-induced myocardial injury. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1986;26:201–224. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.26.040186.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx J. L. Oxygen free radicals linked to many diseases. Science. 1987 Jan 30;235(4788):529–531. doi: 10.1126/science.3810154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M. Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 17;312(3):159–163. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501173120305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M. Oxygen-derived radicals: a link between reperfusion injury and inflammation. Fed Proc. 1987 May 15;46(7):2402–2406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price T. H., Beatty P. G., Corpuz S. R. In vivo inhibition of neutrophil function in the rabbit using monoclonal antibody to CD18. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4174–4177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romson J. L., Hook B. G., Kunkel S. L., Abrams G. D., Schork M. A., Lucchesi B. R. Reduction of the extent of ischemic myocardial injury by neutrophil depletion in the dog. Circulation. 1983 May;67(5):1016–1023. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.67.5.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Schönbein G. W. Capillary plugging by granulocytes and the no-reflow phenomenon in the microcirculation. Fed Proc. 1987 May 15;46(7):2397–2401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. J., Todd R. F., 3rd, Fantone J. C., Mickelson J. K., Griffin J. D., Lucchesi B. R. Reduction of experimental canine myocardial reperfusion injury by a monoclonal antibody (anti-Mo1, anti-CD11b) that inhibits leukocyte adhesion. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):624–629. doi: 10.1172/JCI113364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedder N. B., Winn R. K., Rice C. L., Chi E. Y., Arfors K. E., Harlan J. M. A monoclonal antibody to the adherence-promoting leukocyte glycoprotein, CD18, reduces organ injury and improves survival from hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):939–944. doi: 10.1172/JCI113407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercellotti G. M., Wickham N. W., Gustafson K. S., Yin H. Q., Hebert M., Jacob H. S. Thrombin-treated endothelium primes neutrophil functions: inhibition by platelet-activating factor receptor antagonists. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Jun;45(6):483–490. doi: 10.1002/jlb.45.6.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis W. J., Hickstein D. D., Schwartz B. R., June C. H., Ochs H. D., Beatty P. G., Klebanoff S. J., Harlan J. M. Monoclonal antibody-defined functional epitopes on the adhesion-promoting glycoprotein complex (CDw18) of human neutrophils. Blood. 1986 Apr;67(4):1007–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J. Tissue destruction by neutrophils. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 9;320(6):365–376. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902093200606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]