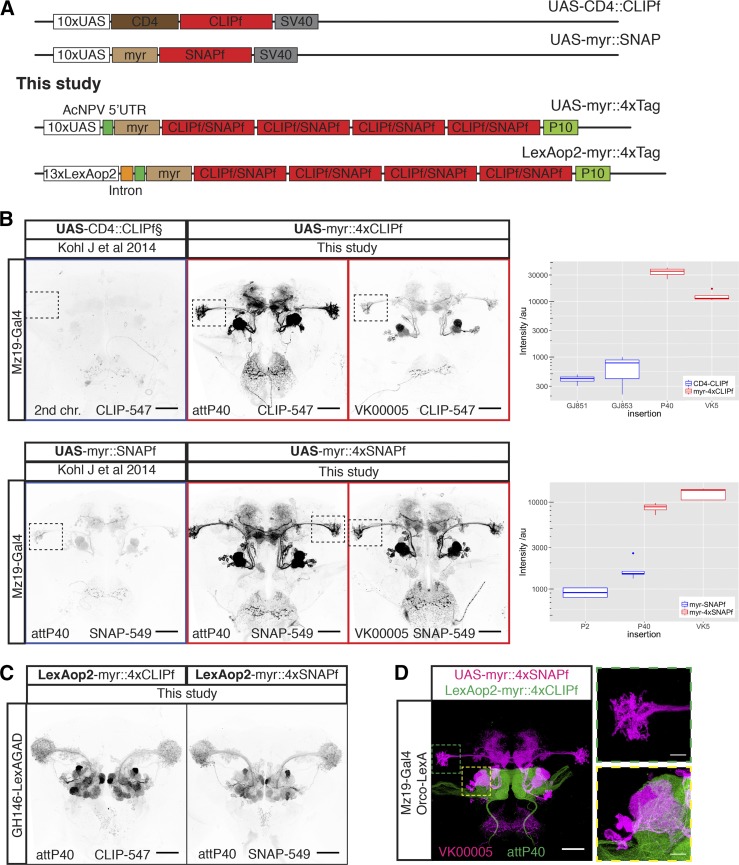
Figure 1.
New CLIPf and SNAPf reporters have increased sensitivity. (A) Schematic of previous CLIPf/SNAPf reporters from Kohl et al. (2014) and the new reporters from this study. (B) Labeling of Mz19-Gal4 neurons using the old and new reporters. Each panel contains information on the dye used and insertion sites. Dotted boxes in images highlight the Lateral Horn region used for quantification. Boxplots show the quantification of fluorescence intensity of the axonal terminals of projection neurons in the lateral horn (arbitrary units). Boxplot n numbers were: GJ853 CD4::CLIPf on the second chromosome n = 3, GJ851 CD4::CLIPf on the third chromosome n = 4, P40 myr::4xCLIPf n = 4, VK00005 myr::4xCLIPf n = 4, P40 myr::4xSNAPf n = 4, VK00005 myr::4xSNAPf n = 5, P2 myr::SNAPf n = 4, and P40 myr::SNAPf n = 5. (C) New LexAop2-myr::4xCLIPf/4xSNAPf reporters labeling olfactory projection neuron using the weak GH146-LexA::GAD driver. (D) Orthogonal labeling of olfactory sensory neurons (green) and projection neurons (magenta) using new tags. Shown is the max intensity projection of a confocal stack after deconvolution. Images in B and C were acquired using the same microscope settings. Bars, 50 μm in whole brain images and 10 μm in higher magnification images of the boxed areas in D.