Abstract
The epidemiology and clinical features of the Saffold cardiovirus (SAFV) remain ambiguous. The present study was designed to systematically and intensively investigate the epidemiological features of SAFV in pediatric patients in China. Three cohorts of pediatric patients were recruited from 2009 to 2012. Cohort 1 comprised patients with acute respiratory tract infections. Cohort 2 comprised patients with diarrhea. Cohort 3 comprised hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) patients. A total of 115 patients (1.6%) among 6052 (17/1647, 12/2013, and 86/2392 in cohorts 1, 2, and 3, respectively) were SAFV-positive. The samples from 82 SAFV-positive patients were successfully sequenced, and four genotypes were identified: 8 SAFV-1, 41 SAFV-2, 29 SAFV-3, and 4 SAFV-6. A significantly higher detection rate was found in the HFMD patients than in other two cohorts (both P <0.001). A higher frequency of severe clinical outcome and nervous system manifestation were also observed in the SAFV-positive HFMD patients. Additionally, 6 (3.5%) cerebrospinal fluid and 7 (2.2%) serum samples from the HFMD-associated encephalitis patients were SAFV-positive. Based on the VP1 sequences, all four genotypes displayed distinct geographical clustering. SAFV infection might be associated with a wide clinical spectrum and contribute to HFMD.
Picornaviruses (family Picornaviridae) are small non-enveloped viruses with a single-stranded positive-sense RNA genome that encodes a single polyprotein. Picornaviruses can cause numerous symptoms in animals, including respiratory, cardiac, hepatic, neurological, mucocutaneous, and systemic diseases of varying severities. The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses has recently classified the Picornaviridae family into 26 genera (including 46 species) based on genetic distance, six of which potentially infect humans (Enterovirus, Hepatovirus, Parechovirus, Kobuvirus, Cosavirus, and Cardiovirus) (www.picornaviridae.com). In the Cardiovirus genus, two distinct species, namely, Theilovirus and Encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV), were defined based on phylogenetic analysis. Cardioviruses can cause serious diseases such as myocarditis, diabetes, central nervous system conditions, and multiple sclerosis–like disease, which are mostly reported in animals1,2,3,4. Prior to 2007, only the Vilyuisk virus, a virus related to Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV), was associated with geographically restricted encephalitis-like illness in humans5,6,7.
Mounting evidence has recently been collected for the existence of a new human cardiovirus. In 2007, through DNase sequence-independent single-primer amplification, a previously undescribed cardiovirus was discovered from a stool sample collected from an 8-month-old child with fever of unknown origin8. Subsequent full-length viral genome sequencing and phylogenetic analysis showed that this new virus was a human cardiovirus and was closely related to but distinct from TMEV and EMCV. This virus was provisionally named Saffold virus (SAFV) and was classified into the Cardiovirus genus of the Picornaviridae family.
Since the discovery of SAFV, there has been an inspired interest in exploring the potential associations of SAFV with human diseases, particularly on its involvement in pediatric respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts infection. Several studies have detected the SAFV RNA in stool samples from children with gastroenteritis in Brazil, Germany, Thailand, Denmark, USA, Malaysia, and China as well as in the respiratory samples from children with influenza-like illnesses in Canada, Japan, and China9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19. SAFV has also been found in stools from South Asian children who either had non-polio acute flaccid paralysis (AFP) or were asymptomatic20. High sero-prevalences of SAFV-2 and SAFV-3 in children from different continents indicated that SAFVs are commonly exposed viruses in young children19,21,22,23,24. SAFV was recently found in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), blood, and myocardium of a previously healthy child who experienced sudden death, suggesting that the virus might cause serious invasive infection in children25.
All these aforementioned studies provided evidence that SAFV might have diverse pathogenicity that targets different tissues. However, given the insufficient systematic data, the epidemiological and genetic characteristics of SAFV infection remain ambiguous. The present study was designed to systematically and intensively investigate the epidemiological features of SAFV in pediatric patients in China.
Methods
Patient recruitment and sample collection
Three cohorts of pediatric patients were recruited from March 2009 to December 2012 in Chongqing Children's Hospital, Chongqing, China. Cohort 1 comprised hospitalized patients with acute respiratory tract infection (ARTI), which was determined based on cough, rhinorrhea, dyspnea, and/or acute fever>37.5°C. For recruited patients, nasopharyngeal aspirates (NPA) samples were collected upon hospital admission. Cohort 2 comprised outpatients with diarrhea, who had> 3 loose stools in the previous 24 hours. Patients who had confirmed inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, food intolerance, or patients who had any apparent clinical respiratory signs or symptoms were excluded. Stool samples were collected from the recruited patients. Cohort 3 consisted of patients who were diagnosed with hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD), according to the guidelines released by the Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China (http://www.moh.gov.cn/publicfiles/business/htmlfiles/mohyzs/s3586/201004/46884.htm). The outpatients were generally mild, with fever, and manifested at least one of the following features: maculopapular or vesicular rash on the palms, and/or soles, vesicles or ulcers in the mouth. Hospitalized patients were diagnosed with severe HFMD if they manifested one of the following additional complications: encephalitis, meningitis, AFP, or cardiorespiratory failure. For all HFMD patients, stool samples were collected, whereas for some cases, stool, throat swab, and serum samples were collected. In addition, CSF was additionally collected for some cases diagnosed with encephalitis. Healthy children who were recruited from the community during the same study period were used as controls, from whom stool, throat swab, and serum samples were also collected. None of the recruited healthy children exhibited ARTI, diarrhea, or HFMD-related symptoms during the recent one month of recruit.
Laboratory detection
All collected samples were tested for SAFV using real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay targeting the 5′ untranslated region (UTR) as previously described11. All samples with positive reactions were further amplified using nested RT-PCR targeting the 5′-UTR, which generated a 540-bp amplicon11. A patient was considered to be infected with SAFV when positive detection was obtained in any type of the samples. The viral protein (VP) 1 gene of all positive samples were amplified using nested RT-PCR approach as previously described26.
The detection of other viral pathogens varied for three cohorts. For cohort 1, NPA samples were screened by RT-PCR or PCR for common respiratory viruses, which include influenza viruses A and B, respiratory syncytial viruses (RSV) A and B subtypes, parainfluenza viruses (PIV) types 1, 2, 3, and 4, metapneumovirus (MPV), human rhinovirus (HRV), coronavirus (COV), human adenovirus (HAdV), and human bocavirus (HBoV) as previously described27,28. In cohort 2, stool specimens were tested for the following viruses using the corresponding tools: rotaviruses A, IDEIA rotavirus direct antigen detection kit (IDEIA, Oxiod, UK); rotaviruses B and C, HAdV, sapovirus, and astrovirus, PCR or RT-PCR29; and noroviruses GI and GII and HBoV, real-time PCR30,31. In cohort 3, all collected stools, throat swabs, CSFs, and sera were subjected to detection of enterovirus (EV), and further classification of EV71 and coxsackievirus A16 (CVA16) was performed using real-time PCR using previously described primers32. To further identify the EV serotypes other than EV71 and CVA16, semi-nested RT-PCR, which is specific for a 5′ partial region of VP1, was performed for other EV-positive samples using previously reported primers33. The amplicons were subjected to sequencing and BLAST analysis.
This study was performed with the approval of the Ethical Committees of Chongqing Children's Hospital and Beijing Institute of Microbiology and Epidemiology. The methods were carried out in accordance with the approved guidelines. At recruitment, written informed consent was obtained from all guardians of participants.
SAFV strains accession numbers
The sequences obtained from the study were submitted to NCBI with the GenBank Accession Numbers KJ944637–KJ944718. The genomic sequences were assembled using Lasergene's DNA SeqMan software (version 7.1.0, DNA Star Inc. Madison, WI, USA). The MEGA program (version 6.0, Sudhir Kumar, Arizona State University) was used for alignments and phylogenetic tree construction by maximum likelihood method using 1000 bootstrap pseudo replicates. Nucleotide identities among strains were calculated using BioEdit (version 7.13, www.mbio.ncsu.edu/bioedit/bioedit.html).
Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics were performed, with continuous variables summarized as median and range, and categorical variables summarized as frequencies and proportions. The statistical significance between various groups was tested using the χ2-test or Fisher exact test for categorical variables and independent t test or nonparametric test for continuous variables. A two-sided P value of less than 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. Analyses were performed using SPSS version 11.5 (SPSS).
Results
Detection and genotyping of SAFV in three cohorts of patients
A total of 6052 patients (1647, 2013, and 2392 patients in cohorts 1, 2, and 3, respectively) were recruited into the study, 3810 (62.9%) of which were boys. Ages ranged from 26 days to 14 years (median, 12 months). More boys were included in cohort 1 (P = 0.044), and older age was presented in cohort 3 (P <0.001) (Table 1).
Table 1. The detection and genotyping of SAFV in three cohorts of patients.
| Cohort 3 (n = 2392) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort 1 (n = 1647) | Cohort 2 (n = 2013) | Subtotal | Mild HFMD (n = 1525) | Severe HFMD (n = 867) | Total | P value | |
| Age, months (median, range) | 9 (1–172) | 10 (1–163) | 24 (1–168) | 24 (1–156) | 24 (2–168) | 12 (1–172) | <0.001a |
| Sex, male (%) | 1096 (66.5) | 1252 (62.2) | 1462 (61.2) | 909 (59.6) | 553 (63.8) | 3810 (62.9) | 0.044b |
| Prevalence of SAFVs | 17 (1.0) | 12 (0.6) | 86 (3.6) | 40 (2.6) | 46 (5.3) | 115 (1.9) | <0.001b |
| No. of patients infected | |||||||
| SAFV-1 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 8 | |
| SAFV-2 | 9 | 4 | 28 | 13 | 15 | 41 | |
| SAFV-3 | 1 | 5 | 23 | 12 | 11 | 29 | |
| SAFV-6 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 4 | |
| Untyped | 4 | 3 | 26 | 11 | 15 | 33 | |
| Single-detection | 3 (17.6) | 3 (25.0) | 28 (32.6) | 10 (25.0) | 18 (39.1) | 34 (29.6) | 0.459c |
| Co-detection | 14 (82.4) | 9 (75.0) | 58 (67.4) | 30 (75.0) | 28 (60.9) | 81 (70.4) | |
NOTE: HFMD, Hand, foot, and mouth disease. The P value was calculated by comparing cohort 1, cohort 2 and cohort 3 as a general.
aMann-Whitney U test.
bχ2 test, two-sided.
cFisher exact test.
Among all the tested patients, 115 (1.9%) were SAFV-positive, [17 (1.0%), 12 (0.6%), and 86 (3.6%) from cohorts 1, 2, and 3, respectively (Table 1)]. A significantly higher detection rate was found in HFMD patients among the three cohorts (P <0.001). A total of 911 specimens (352 throat swab, 423 sera, and 136 stools) were collected from asymptomatic children. The age ranged from 4 months to 78 months (median, 29 months), and 553 (60.7%) were boys. No positive detection was found in any type of samples from asymptomatic children.
From the 115 SAFV-positive patients, 82 patients were successfully sequenced for VP1 nucleotide sequences, and four genotypes were identified: SAFV-1 (8, 9.8%), SAFV-2 (41, 50.0%), SAFV-3 (29, 35.4%), and SAFV-6 (4, 4.9%). For cohort 1, the SAFV determined from 13 of the 17 positive patients were successfully grouped into three genotypes: SAFV-1 (3, 23.1%), SAFV-2 (9, 69.2%), and SAFV-3 (1, 7.7%). In cohort 2, nine of the 12 detected SAFV were assigned to two genotypes: SAFV-2 (4, 44.4%) and SAFV-3 (5, 55.6%). In cohort 3, 60 of the 86 SAFV-positive patients were successfully sequenced, and four genotypes were identified: SAFV-1 (5, 8.3%), SAFV-2 (28, 46.7%), SAFV-3 (23, 38.3%), and SAFV-6 (4, 6.7%). The uncommonly seen SAFV-6 was only found in the HFMD patients (Table 1).
Co-detections with other viruses were found in 70.4% (81/115) of the SAFV-positive patients, including 77 co-detections with one virus, three with two viruses, and one with three viruses. The patients with SAFV single infection had a median age of 20 months (range, 9 months–108 months), and 13 (70.6%) were boys, which were comparable with co-detection patients (all P> 0.05). Three cohorts had comparable co-detection rates (82.4%, 75.0%, and 67.4%, P = 0.459) (Table 1). In cohort 1, the most frequent co-detection occurred between SAFV and PIV (5 patients), followed by SAFV and RSV-B (4), HAdV (2), HBoV (2), COV (2), influenza virus A (1), influenza virus B (1), and HRV-A (1). In cohort 2, nine patients were found to have co-detections, including co-detection with norovirus GII (6), rotavirus group A (2), and HAdV (2). In cohort 3, 58 patients were found to have co-detection of SAFV with EV71 (23), CVA16 (17), and other EVs (18).
Demographic and clinical characteristics of the SAFV-positive patients
The median age of the SAFV-positive patients was 24 months, and ranged from two months to 108 months. Of these patients, 70.4% were males. In cohort 1, the SAFV-positive patients were significantly older than the SAFV-negative patients (36.0 months vs. 9.0 months, P <0.001; Table 2). The infection rate increased significantly with age among children below 6 years old (Cochran-Armitage trend = −5.21, P <0.001). The highest positive rate (4.3%) was found in 4- to 5-year-old patients (Supplemental Table 1). In cohorts 2 and 3, the age and gender profiles were highly comparable between the SAFV-positive and SAFV-negative patients (all P> 0.05).
Table 2. The demographic and clinical characteristics of the SAFV infected patients.
| SAFV-positive | P value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Subtotal | Single-detection | Co-detection | SAFV-negative | SAFV-positive vs. SAFV-negative | Single-detection vs. co-detection |
| Cohort 1 | (n = 17) | (n = 3) | (n = 14) | (n = 1630) | ||
| Age, months (median, range) | 36 (8–108) | 45 (38–108) | 31 (8–77) | 9 (1–172) | <0.001a | 0.130a |
| Sex, boy (%) | 12 (70.6) | 2 (66.7) | 10 (71.4) | 1084 (66.5) | 0.723b | 1.00c |
| Clinical manifestation | ||||||
| Cough | 16 (94.1) | 3 (100) | 13 (92.9) | 1534 (94.1) | 1.000b | 1.00c |
| Pneumonia | 8 (47.1) | 3 (100) | 5 (35.7) | 1196 (73.4) | 0.015b | 0.082c |
| Bubble | 9 (52.9) | 0 (0) | 9 (64.3) | 1217 (74.7) | 0.051b | 0.082c |
| Asthma | 7 (41.2) | 0 (0) | 7 (50.0) | 231 (14.2) | 0.002b | 0.228c |
| Rhonchi | 6 (35.3) | 0 (0) | 6 (42.9) | 749 (46.0) | 0.380b | 0.514c |
| Rhinorrhoea | 3 (17.7) | 0 (0) | 3 (21.4) | 234 (14.4) | 0.701c | 1.00c |
| Dyspnea | 2 (11.8) | 0 (0) | 2 (14.3) | 299 (18.3) | 0.752c | 0.686c |
| Bronchitis | 2 (11.8) | 0 (0) | 2 (14.3) | 72 (4.4) | 0.176c | 0.686c |
| Sore throat | 1 (5.9) | 0 (0) | 1 (7.1) | 26 (1.6) | 0.246c | 0.823c |
| Cohort 2 | (n = 12) | (n = 3) | (n = 9) | (n = 2001) | ||
| Age, months (median, range) | 11 (2–38) | 13 (11–14) | 10 (2–37) | 10 (1–1630) | 0.774a | 0.266a |
| Sex, boy (%) | 9 (75.0) | 2 (66.7) | 7 (77.8) | 1246 (62.2) | 0.552b | 0.618c |
| Clinical manifestations | ||||||
| Diarrhea times ≥ 5 | 2 (25.0) | 1 (50.0) | 1 (11.1) | 974 (48.6) | 0.290c | 0.456c |
| Vomiting | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 928 (46.3) | 0.009c | NA |
| Cohort 3 | (n = 86) | (n = 28) | (n = 58) | (n = 2306) | ||
| Age, months (median, range) | 24 (6–55) | 20 (9–55) | 24 (6–52) | 24 (1–168) | 0.335a | 0.361a |
| Sex, boy (%) | 60 (69.8) | 20 (71.4) | 40 (69.0) | 1537 (66.7) | 0.547b | 0.816b |
| Outcome | <0.001b | 0.212b | ||||
| Mild HFMD | 39 (45.4) | 10 (35.7) | 29 (50.0) | 1450 (62.9) | ||
| Severe HFMD | 47 (54.7) | 18 (64.3) | 29 (50.0) | 856 (37.1) | ||
| Clinical manifestations | ||||||
| Respiratory system | 8 (9.3) | 2 (7.1) | 6 (20.3) | 199 (8.6) | 0.828b | 1.00c |
| Digestive system | 4 (4.7) | 3 (10.7) | 1 (1.7) | 134 (5.8) | 0.816c | 0.100c |
| Circulatory system | 4 (4.7) | 1 (3.6) | 3 (5.2) | 193 (8.4) | 0.218c | 0.607c |
| Nervous system | 45 (52.3) | 17 (60.7) | 28 (48.3) | 856 (37.1) | 0.004b | 0.279b |
Note: respiratory system syndromes were defined as the presence of at least one of the followings: cough, bronchitis or other upper respiratory tract disease, or pneumonia; digestive system syndromes were defined as the presence of at least one of the followings: diarrhea or vomit; circulatory system syndromes were defined as the presence of at least one of the followings: myocarditis or cardiac damage; nervous syndromes were defined as the presence of at least one of the followings: meningitis, encephalitis, brain myelitis, coma, acute flaccid paralysis or seizures. HFMD, Hand, foot, and mouth disease; NA, not applicable.
aMann-Whitney U test.
bχ2 test, two-sided.
cFisher exact test.
In cohort 1, seven (41.2%) of the SAFV-positive patients, which is significantly higher than that of the SAFV-negative patients (41.2% vs. 14.2%, P = 0.002), developed asthma that were related with this disease episode. By contrast, the opposite trend was found for pneumonia (47.1% vs. 73.4%, P = 0.015). Other clinical manifestations were highly comparable between SAFV-positive and SAFV-negative patients (all P> 0.05). In cohort 2, the diarrhea duration was comparable between SAFV-positive and SAFV-negative patients. No SAFV-positive patients exhibited symptoms of vomiting, but 928 (46.3%) SAFV-negative patients did (P = 0.009). Within cohort 3, the severe HFMD patients had significantly higher SAFV-positive rate than the mild HFMD patients (5.2% vs. 2.6%, P = 0.001). Furthermore, SAFV-positive patients presented with significantly higher frequency of nervous system manifestation than the SAFV-negative patients (52.3% vs. 37.1%, P = 0.004).
For all three cohorts, the clinical manifestations of patients with SAFV single detection were insignificantly different from those with SAFV co-detection (Table 2). We additionally analyzed whether the co-detection of SAFV might aggravate the clinical outcome of EV infected HFMD patients (Table 3). The results demonstrated that 18 out of 23 (78.3%) SAFV/EV71 co-detected patients developed severe HFMD, significantly higher than that of patients with EV71 single detection (78.3% vs. 42.6%, P = 0.001). By contrast, there was no significant difference between patients with CVA16 single detection and patients with SAFV/CVA16 co-detection (P> 0.05). Similarly, no difference was attained for other EVs co-detected patients either.
Table 3. The co-detection of other viruses with SAFV in HFMD patients.
| EV serotypes | SAFV and EV statuses | Mild HFMD | Severe HFMD | P valuea |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EV71 | Single detection (n = 1108) | 636 (57.4) | 472 (42.6) | 0.001 |
| Co-detection with SAFV (n = 23) | 5 (21.7) | 18 (78.3) | ||
| CA16 | Single detection (n = 500) | 354 (70.8) | 146 (29.2) | 0.984 |
| Co-detection with SAFV (n = 17) | 12 (70.6) | 5 (29.4) | ||
| Other EVs | Single detection (n = 222) | 159 (71.6) | 63 (28.4) | 0.655 |
| Co-detection with SAFV (n = 18) | 12 (66.7) | 6 (33.3) |
Note: HFMD, Hand, foot, and mouth disease; EV, enterovirus; CVA16, coxsackievirus A16.
aχ2 test, two-sided.
Genetic characterization of SAFVs
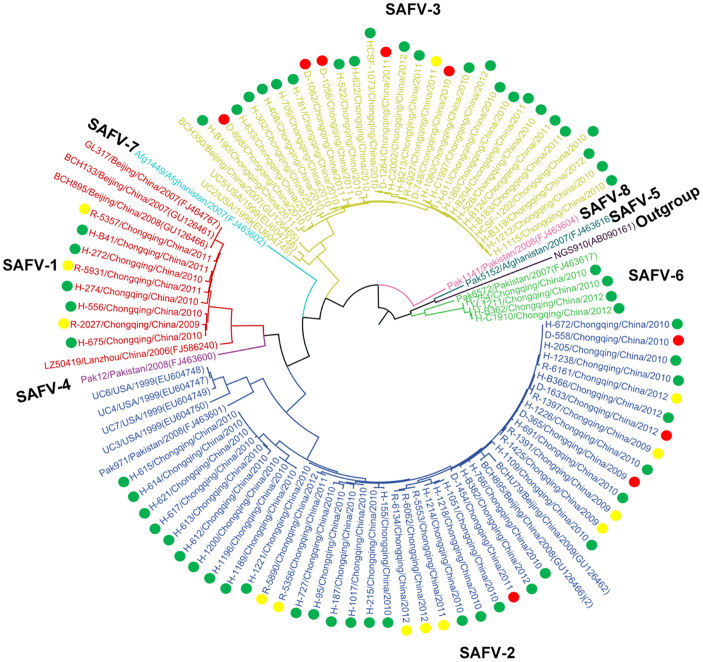
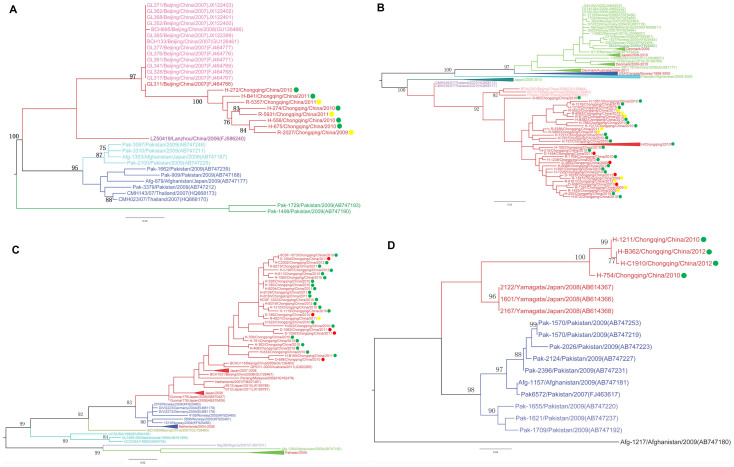
A phylogenetic tree was constructed based on the VP1 nucleotide sequences of Saffold cardiovirus detected in clinical samples of 82 patients in the current study, and sequences downloaded from GenBank by maximum likelihood method using MEGA 6.0 (Figure 1). A spatial pattern of the genetic clustering was identified for each genotype. For SAFV-1, four lineages were formed, and all the Chinese strains were grouped into one lineage (Figure 2A). For the Chinese lineage, an obvious geographic-specific distribution was observed, with strains from three locations grouped separately into three sublineages. All the SAFV-1 cases from the current study were grouped into the Chongqing sublineage, regardless of the cohort group. In SAFV-2, five lineages were constructed, which included European, North American, Middle-Eastern, Japanese, and East Asian lineages (Figure 2B). The strains from the present study were grouped into East Asian lineage, which, however, diverged from those from Beijing or Thai strains. In SAFV-3, six lineages were formed depending on the geographical origin. The Chongqing strains in this study were classified into the Asian lineages, forming a sublineage that was distinct from the strains of other regions (Figure 2C). In SAFV-6, the strains from three locations were classified into three clusters. The Chongqing strains formed a separate cluster, which is different from those of Japanese and Pakistani strains (Figure 2D).
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree was constructed from the VP1 nucleotide sequences of SAFVs using maximum likelihood method with 1000 bootstrap by MEGA 6.0.
The tree was based on the 285VP1 nucleotide sequences of SAFVs. The strains labeled with green dots were obtained from HFMD patients. The strains labeled with yellow dots were obtained from patients with ARTI. The strains labeled with red dots were obtained from patients with diarrhea.
Figure 2. Phylogenetic trees were constructed based on the VP1 nucleotide sequences using maximum likelihood method with 1000 bootstrap by MEGA 6.0 for SAFV-1 (A), SAFV-2 (B), SAFV-3 (C) and SAFV-6 (D).
The tree was based on the 285 VP1 nucleotide sequences of SAFVs. The strains labeled with yellow dots were obtained from patients with ARTI. The strains labeled with red dots were obtained from patients with diarrhea. The strains labeled with green dots were obtained from HFMD patients.
Detection of SAFV in sera and CSFs
Additional 171 CSFs were collected from patients with HFMD-associated encephalitis, and six (3.5%) were found to be SAFV-positive using real-time RT-PCR, and five were further confirmed by nested RT-PCR targeting the 5′-UTR. Two of six SAFV-positive CSFs were successfully sequenced for VP1, and only SAFV-3 was identified. Among 760 serum samples collected from HFMD patients (355 from mild HFMD patients and 328 from severe HFMD patients), eight HFMD patients (1.1%) were detected positive for SAFV, including seven patients with encephalitis and one patient with myocarditis. Among 328 sera from severe HFMD patients, 322 were collected from patients with HFMD-associated encephalitis, and seven (2.2%) were found to be SAFV-positive using real-time RT-PCR, and five were further confirmed by nested RT-PCR targeting the 5′-UTR. Two out of eight SAFV-positive sera were successfully identified to be SAFV-2 and all from patients with HFMD-associated encephalitis. From three of the six SAFV-positive CSFs and four of eight SAFV-positive sera, no HEV was detected.
Discussion
Information on the potential disease associations of SAFV has increased over the past six years, with data concentrated particularly on the involvement of SAFV in pediatric respiratory and gastrointestinal tract infections. In the current study, the prevalence of SAFV in pediatric patients in the recent four years in Chongqing, China was determined by performing molecular epidemiological investigation on three cohorts of patients. In addition to ARTI and diarrhea patients, an unexpected significantly higher prevalence of SAFV was found in HFMD patients, especially in patients with HFMD-associated encephalitis. Multiple genotypes of SAFV, which displayed geographic specific distribution pattern, were also found to be co-circulating in China. These data provided a reliable estimation based on a large sample size and long observation period, thereby expanding the understanding on the epidemiological features of SAFV.
One might query the higher frequency of SAFV in the HFMD patients was due to the old age and more sampling types of this cohort, in comparison with the ARTI and diarrhea cohorts. An increasing prevalence of SAFV was found in ARTI patients, but not in the HFMD patients. Thus, the age mismatch among the three cohorts might play minor roles in determining the detection rates. On the other hand, although the HFMD cohort was tested using stool, respiratory, blood, and CSF samples, an over-estimation of infection rate was not generated, because stool samples offered the highest diagnostic sensitivity. When we took no account of the patients with stool negative while other sample types are positive, a prevalence rate of 3.1% was still obtained. Thus, this effect alone might not explain the higher prevalence observed in HFMD.
Several lines of evidence indicate that SAFV might act as the agent responsible for the clinical syndromes, at least for some of the subjects. First, although co-detection with other viruses existed, SAFVs were the only pathogens identified in 34 (29.6%) SAFV-positive specimens in this study. The co-detection of SAFV with other viruses ranged from 0% to 100% in previous studies, and the variation in results is probably due to different diagnostic assays applied9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19. In the present study, 15 common respiratory viruses in ARTI patients, 9 common viruses in diarrhea patients, and all EVs in HFMD patients were detected. The current results might represent a higher probability of single infection than the previous studies. Still, single-infection by SAFV is only true relative to the list of viruses that are being tested. Second, this study also revealed the negative detection of SAFV in healthy children, indicating that SAFV is less likely to be present in asymptomatic subjects. This result is consistent with a previous study that was conducted among 39 asymptomatic patients in northern Germany11. Finally, more severe clinical outcome and manifestation of nervous system were exhibited by SAFV-positive HFMD patients than in SAFV-negative HFMD patients.
In our study, SAFVs were co-detected with other viruses in 14 (82.4%), 9 (75.0%), and 28 (32.6) specimens in ARTI, diarrhea and HFMD patients respectively. For ARTI and diarrhea cohorts, no differential clinical manifestations were inferred from the patients with SAFV single detection or SAFV co-detection, probably due to small sample size for comparison. However, for HFMD patients, we found the co-detection of SAFV could aggravate the clinical outcome of EV71 infection. We are uncertain whether SAFV/EV71 co-detection can lead to synergies in the HFMD pathogenic mechanism, and therefore responsible for the pathogenesis of severe HFMD, which need further investigation in the future.
Previous studies have demonstrated the existence of SAFV in CSF, but it was only limited to the case report25,34. In 2011, SAFV-3 was isolated from the CSF sample of a 9-year old boy with aseptic meningitis34. SAFV-2 was subsequently detected in the CSF and fecal samples of one child with cerebellitis as well as in the CSF, blood, and myocardium of another child who died suddenly with no history of illness25. In the current study, the existence of SAFV-3 was observed in the CSF and SAFV-2 was observed in serum samples from the patients with HFMD-associated encephalitis. Furthermore, among half of the SAFV-positive CSFs and sera, SAFV was the solely detected pathogen. This information provided the first valid estimation of SAFV in pediatric encephalitis.
Pediatric encephalitis caused by viral infection has always been of great public health concern worldwide because of its high morbidity and mortality. The common agents of viral encephalitis include herpes simplex virus 1, varicella zoster virus, EV, Epstein-Barr virus, human herpesvirus 6, and measles virus35,36. However, an etiological diagnosis was reached in less than 50% of the cases despite the use of modern microbiological and radiological methods35,37. The list of uncommonly observed etiological agents for pediatric encephalitis remained far from complete. Animal experiments have suggested that SAFV-2 and SAFV-3 can cause serious invasive infections and are neurotropic in mice38,39. Hertzler et al. reported that high doses of SAFV-2 intraperitoneally inoculated into adult mice resulted in paralysis and neuropathological changes consistent with acute encephalomyelitis, particularly in the limbic system38. Sorgeloss et al. showed that both SAFV-2 and SAFV-3 can infect the heart and the central nervous system of 129/Sv mice39. Furthermore, they found that SAFV-3 was more neurotropic than SAFV-2, and intracerebral inoculationof SAFV-3 into FVB/n mice caused acute encephalitis39. In the current study, the existence of SAFV-2 and SAFV-3 was observed in the patients with HFMD-associated encephalitis. The present results, together with those of the earlier studies, indicate that SAFV-2 and SAFV-3 might play a role in the pathogenesis of viral encephalitis. However, these results warrant further confirmation by independent studies.
To the best of the authors' knowledge, this study is the first to document SAFV in HFMD patients. The high frequency of SAFV in the stools, CSFs, and sera of children with HFMD and the absence of SAFV in healthy children suggest that this new virus might contribute to HFMD, especially in HFMD-associated encephalitis. This finding has important public health implication for HFMD disease control, especially among severe HFMD patients. Although with various patient types and large sample size, the major findings in the present study, especially the causal relationship between SAFV and the clinical disease, should be confirmed by serological study in the future.
Supplementary Material
Supplemental Table 1
Acknowledgments
The authors would like thank all the subjects, their families, and collaborating clinicians for their participation. This work was supported by grants from the China Mega-Project on Infectious Disease Prevention (No. 2013ZX10004202), the National Natural Science Foundation (No. 81222037) and the Military Medical and Technology Twelfth Five-Year Science and Research Key Plan (BWS11C073).
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author Contributions W.L., W.C.C., X.A.Z. and Q.B.L. designed the study. H.M.X. and E.M.L. were responsible for recruitment of subjects. X.A.Z., Q.B.L., Y.W., J.Z., D.D.H. and C.T.G. performed experiments. W.L., W.C.C., X.A.Z. and Q.B.L. conducted data management, performed statistical analyses, interpreted results and wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
References
- Craighead J. E., Huber S. A. & Haynes M. K. Diverse patterns of immune and non-immune-mediated disease in EMC M-variant-infected mice. J Autoimmun 3 Suppl 1, 27–29 (1990). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J. W. & Jun H. S. Viruses in type 1 diabetes: brief review. ILAR J 45, 343–348 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahic M., Bureau J. F. & Michiels T. The genetics of the persistent infection and demyelinating disease caused by Theiler's virus. Annu Rev Microbiol 59, 279–298 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleszak E. L., Chang J. R., Friedman H., Katsetos C. D. & Platsoucas C. D. Theiler's virus infection: a model for multiple sclerosis. Clin Microbiol Rev 17, 174–207 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L., Friedmann A., Sethi P. & Crowther J. R. Characterization of Vilyuisk virus as a picornavirus. J Med Virol 12, 195–203 (1983). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard A. E., Strom T. & Lipton H. L. Nucleotide sequence identifies Vilyuisk virus as a divergent Theiler's virus. Virology 191, 469–472 (1992). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L. Human Vilyuisk encephalitis. Rev Med Virol 18, 347–352 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. S., Lukashov V. V., Ganac R. D. & Schnurr D. P. Discovery of a novel human picornavirus in a stool sample from a pediatric patient presenting with fever of unknown origin. J Clin Microbiol 45, 2144–2150 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abed Y. & Boivin G. New Saffold cardioviruses in 3 children, Canada. Emerg Infect Dis 14, 834–836 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu C. Y. et al. Identification of cardioviruses related to Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus in human infections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105, 14124–14129 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drexler J. F. et al. Circulation of 3 lineages of a novel Saffold cardiovirus in humans. Emerg Infect Dis 14, 1398–1405 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren L. et al. Saffold cardiovirus in children with acute gastroenteritis, Beijing, China. Emerg Infect Dis 15, 1509–1511 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Z. Q. et al. New Saffold cardiovirus in children, China. Emerg Infect Dis 15, 993–994 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren L. et al. Saffold cardioviruses of 3 lineages in children with respiratory tract infections, Beijing, China. Emerg Infect Dis 16, 1158–1161 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khamrin P. et al. Three clusters of Saffold viruses circulating in children with diarrhea in Japan. Infect Genet Evol 13, 339–343 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khamrin P. et al. Saffold cardioviruses in children with diarrhea, Thailand. Emerg Infect Dis 17, 1150–1152 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen A. C., Gyhrs M. L., Holmes E. C. & Cui J. Co-circulation and persistence of genetically distinct saffold viruses, Denmark. Emerg Infect Dis 18, 1694–1696 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukagoshi H. et al. Sequencing and phylogenetic analyses of Saffold cardiovirus (SAFV) genotype 3 isolates from children with upper respiratory infection in Gunma, Japan. Jpn J Infect Dis 63, 378–380 (2010). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua K. B. et al. Saffold virus infection in children, Malaysia, 2009. Emerg Infect Dis 17, 1562–1564 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinkova O. et al. Cardioviruses are genetically diverse and cause common enteric infections in South Asian children. J Virol 83, 4631–4641 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoll J. et al. Saffold virus, a human Theiler's-like cardiovirus, is ubiquitous and causes infection early in life. PLoS Pathog 5, e1000416 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galama J., Lanke K., Zoll J., Roivainen M. & van Kuppeveld F. Seroepidemiology of Saffold cardiovirus type 2. Emerg Infect Dis 17, 1572–1573 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M. et al. Seroepidemiology of Saffold cardiovirus (SAFV) genotype 3 in Japan. J Infect 66, 191–193 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu C. Y. et al. Cultivation and serological characterization of a human Theiler's-like cardiovirus associated with diarrheal disease. J Virol 84, 4407–4414 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen A. C., Bottiger B., Banner J., Hoffmann T. & Nielsen L. P. Serious invasive Saffold virus infections in children, 2009. Emerg Infect Dis 18, 7–12 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itagaki T. et al. Sequence and phylogenetic analyses of Saffold cardiovirus from children with exudative tonsillitis in Yamagata, Japan. Scand J Infect Dis 42, 950–952 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiveljung-Lindell A. et al. Development and implementation of a molecular diagnostic platform for daily rapid detection of 15 respiratory viruses. J Med Virol 81, 167–175 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu W., McDonough M. C. & Erdman D. D. Species-specific identification of human adenoviruses by a multiplex PCR assay. J Clin Microbiol 38, 4114–4120 (2000). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohayem J. et al. A simple and rapid single-step multiplex RT-PCR to detect Norovirus, Astrovirus and Adenovirus in clinical stool samples. J Virol Methods 118, 49–59 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu X. W. et al. Human bocavirus infection, People's Republic of China. Emerg Infect Dis 13, 165–168 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stals A. et al. Multiplex real-time RT-PCR for simultaneous detection of GI/GII noroviruses and murine norovirus 1. J Virol Methods 161, 247–253 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstrepen W. A., Bruynseels P. & Mertens A. H. Evaluation of a rapid real-time RT-PCRassay for detection of enterovirus RNA in cerebrospinal fluid specimens. J Clin Virol 25, 2002 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nix W. A., Oberste M. S. & Pallansch M. A. Sensitive, seminested PCR amplification of VP1 sequences for direct identification of all enterovirus serotypes from original clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol 44, 2698–2704 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himeda T. et al. The preparation of an infectious full-length cDNA clone of Saffold virus. Virol J 8, 110 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S. et al. Viral Encephalitis: Etiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis and Management. The Open Infect Dis J 3, 1–12 (2009). [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L., Bennett J. E. & Dolin R. Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, Seventh Edition. Elsevier Inc 87, 1243–1263 (2010). [Google Scholar]
- Marcus T. T. S. Viral encephalitis. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 71, 703–709 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzler S., Liang Z., Treso B. & Lipton H. L. Adaptation of Saffold virus 2 for high-titer growth in mammalian cells. J Virol 85, 7411–7418 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorgeloss F., van Kuppeveld F. & Michiels T. Saffold virus infection of the mouse. Europic F-17, 104 (2010). [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental Table 1