Abstract
Mevalonate kinase [ATP:(R)-mevalonate 5-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.36] may be a regulatory site in the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway, and a mutation in the gene coding for this enzyme is thought to cause the genetic disease mevalonic aciduria. To characterize this enzyme, a rat liver cDNA library was screened with a monospecific antibody, and a 1.7-kilobase cDNA clone coding for mevalonate kinase was isolated. The complete DNA sequence was determined, and the longest open reading frame coded for a protein containing 395 amino acids with a deduced molecular weight of 41,990. Identification of the cDNA clone was confirmed by expression of enzyme activity in yeast and by protein sequence data obtained from sequencing purified rat mevalonate kinase. The deduced amino acid sequence of mevalonate kinase contained a motif for the ATP-binding site found in protein kinases, and it also showed sequence homology to the yeast RAR1 protein. The size of mevalonate kinase mRNA in rat liver was approximately 2 kilobases. Treatment with diets containing cholesterol-lowering agents caused an increase in both mevalonate kinase activity and mRNA levels, whereas diets containing 5% cholesterol lowered the levels of both enzyme activity and mRNA. These data indicate that long-term regulation of enzyme activity in rat liver is controlled by changes in the levels of mevalonate kinase mRNA.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P., Leberman R. Homologies and anomalies in primary structural patterns of nucleotide binding proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Nov 4;152(3):651–656. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby M. N., Edwards P. A. Identification and regulation of a rat liver cDNA encoding farnesyl pyrophosphate synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):635–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger R., Smit G. P., Schierbeek H., Bijsterveld K., le Coultre R. Mevalonic aciduria: an inborn error of cholesterol biosynthesis? Clin Chim Acta. 1985 Oct 31;152(1-2):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(85)90195-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergstrom J. D., Wong G. A., Edwards P. A., Edmond J. The regulation of acetoacetyl-CoA synthetase activity by modulators of cholesterol synthesis in vivo and the utilization of acetoacetate for cholesterogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14548–14553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Multivalent feedback regulation of HMG CoA reductase, a control mechanism coordinating isoprenoid synthesis and cell growth. J Lipid Res. 1980 Jul;21(5):505–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke C. F., Edwards P. A., Lan S. F., Tanaka R. D., Fogelman A. M. Regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase mRNA levels in rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3305–3308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke C. F., Tanaka R. D., Svenson K., Wamsley M., Fogelman A. M., Edwards P. A. Molecular cloning and sequence of a cholesterol-repressible enzyme related to prenyltransferase in the isoprene biosynthetic pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3138–3146. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsey J. K., Porter J. W. The inhibition of mevalonic kinase by geranyl and farnesyl pyrophosphates. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 25;243(18):4667–4670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Jarnagin A. S., McLean J., Henzel W., Kohr W., Fielding C., Lawn R. Cloning and sequencing of human cholesteryl ester transfer protein cDNA. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):632–634. doi: 10.1038/327632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Conjugation of antibodies with fluorochromes: modifications to the standard methods. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(3-4):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffey M. L., Stevens J. T., Terry B. J., Dorsky D. I., Crumpacker C. S., Wietstock S. M., Ruyechan W. T., Field A. K. Expression of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA polymerase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and detection of virus-specific enzyme activity in cell-free lysates. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4493–4498. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4493-4498.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann G., Gibson K. M., Brandt I. K., Bader P. I., Wappner R. S., Sweetman L. Mevalonic aciduria--an inborn error of cholesterol and nonsterol isoprene biosynthesis. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jun 19;314(25):1610–1614. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198606193142504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearsey S. E., Edwards J. Mutations that increase the mitotic stability of minichromosomes in yeast: characterization of RAR1. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(3):509–517. doi: 10.1007/BF00327205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz M. B., Cortelyou M. W., Kirsch D. R. Integrative transformation of Candida albicans, using a cloned Candida ADE2 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):142–149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
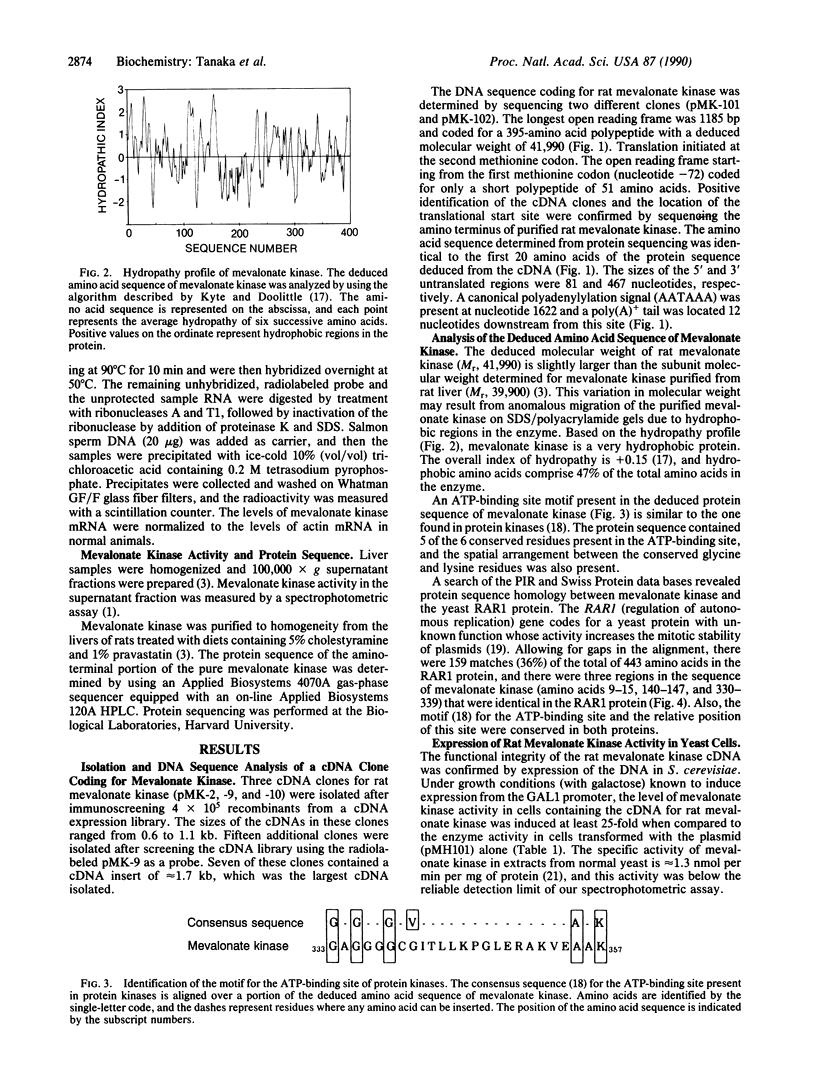
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabian M., Callaway K. A., Clarke C. F., Tanaka R. D., Greenspan M., Lusis A. J., Sparkes R. S., Mohandas T., Edmond J., Fogelman A. M. Regulation of rat liver 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A synthase and the chromosomal localization of the human gene. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):16249–16255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers E. W., Miller W. Optimal alignments in linear space. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Mar;4(1):11–17. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TCHEN T. T. Mevalonic kinase: purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1958 Nov;233(5):1100–1103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka R. D., Edwards P. A., Lan S. F., Knöppel E. M., Fogelman A. M. The effect of cholestyramine and Mevinolin on the diurnal cycle of rat hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. J Lipid Res. 1982 Sep;23(7):1026–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka R. D., Schafer B. L., Lee L. Y., Freudenberger J. S., Mosley S. T. Purification and regulation of mevalonate kinase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2391–2398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujita Y., Kuroda M., Shimada Y., Tanzawa K., Arai M., Kaneko I., Tanaka M., Masuda H., Tarumi C., Watanabe Y. CS-514, a competitive inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase: tissue-selective inhibition of sterol synthesis and hypolipidemic effect on various animal species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 11;877(1):50–60. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga R. K., Terpstra P., Hol W. G. Prediction of the occurrence of the ADP-binding beta alpha beta-fold in proteins, using an amino acid sequence fingerprint. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 5;187(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



