Significance
Cancer cells can be recognized and attacked by CD8+ cytolytic T cells, but tumor-infiltrating T cells often become functionally incompetent (“exhausted”) and fail to destroy tumor cells. We show that T-cell exhaustion requires antigen recognition by tumor-infiltrating T cells. By examining the transcriptional and chromatin accessibility profiles of antigen-reactive and -unreactive tumor-infiltrating cells, we confirm our previous conclusion that the transcription factor NFAT promotes CD8+ T-cell exhaustion and we identify Nr4a transcription factors as new targets for future investigation. We show that anti–PD-L1 treatment, a clinically relevant checkpoint blockade therapy that counteracts T-cell exhaustion, has modest but functionally important effects on gene expression in exhausted cells, without causing major changes in patterns of chromatin accessibility.
Keywords: T-cell exhaustion, chromatin accessibility, checkpoint blockade therapy, anti–PD-L1, ATAC-seq
Abstract
T-cell exhaustion is a progressive loss of effector function and memory potential due to persistent antigen exposure, which occurs in chronic viral infections and cancer. Here we investigate the relation between gene expression and chromatin accessibility in CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) that recognize a model tumor antigen and have features of both activation and functional exhaustion. By filtering out accessible regions observed in bystander, nonexhausted TILs and in acutely restimulated CD8+ T cells, we define a pattern of chromatin accessibility specific for T-cell exhaustion, characterized by enrichment for consensus binding motifs for Nr4a and NFAT transcription factors. Anti–PD-L1 treatment of tumor-bearing mice results in cessation of tumor growth and partial rescue of cytokine production by the dysfunctional TILs, with only limited changes in gene expression and chromatin accessibility. Our studies provide a valuable resource for the molecular understanding of T-cell exhaustion in cancer and other inflammatory settings.
Exposure of virus-specific or tumor-reactive CD8+ T cells to prolonged antigen stimulation in an inflammatory environment is associated with progressive loss of effector function, a phenomenon defined as T-cell exhaustion (1). Exhausted T cells show diminished cytokine production and decreased survival and express high levels of inhibitory receptors, including PD-1, LAG-3, TIM-3, and CTLA-4. Treatment with blocking antibodies against these inhibitory receptors—particularly CTLA-4 or the PD-1/PD-L1 axis (“checkpoint blockade”)—has proven remarkably efficacious in reversing exhaustion and promoting tumor regression in patients with metastatic melanoma and other cancers (2, 3). The clinical benefit of checkpoint blockade therapy correlates with the magnitude and diversity of intratumor CD8+ T-cell infiltrates (4, 5), indicating that antitumor immunity is naturally generated, especially in tumors such as cutaneous melanoma with high rates of mutation and consequent neoantigen generation (6). However, durable responses to checkpoint blockade therapies are observed in fewer than 50% of patients with melanoma (7, 8), pointing to the need for a more in-depth molecular characterization of T-cell exhaustion in cancer.
The transcriptional program that underlies T-cell exhaustion shares features with other states of reduced T-cell responsiveness, such as clonal anergy and adaptive tolerance (9). Although these states have been termed “dysfunctional,” we have suggested that they arise through the transcriptional activation of normal, physiological negative feedback loops initiated by the same transcription factors that were earlier involved in the initial antigen response. Specifically, we have shown that NFAT transcription factors not only initiate transcriptional programs characteristic of productive T-cell activation, but are also involved in anergy and functional exhaustion, depending on cell type, nature and duration of stimulation and whether there is concomitant activation of the NFAT transcriptional partner AP-1 (Fos-Jun) (10, 11). One proposed distinction is that anergy is induced by suboptimal stimulation of CD4+ T cells in the absence of costimulation (12), whereas CD8+ T-cell exhaustion occurs after an initial productive T-cell activation, as a consequence of continuous stimulation in an inflammatory environment (1). T cells subjected to chronic stimulation often retain significant effector function and express activation and costimulatory molecules, such as CD69 (13), CD25, 4-1BB, and OX40 (14, 15), alongside high levels of PD-1 and other inhibitory receptors. In addition to NFAT, other transcription factors implicated in T-cell exhaustion are Eomes, Blimp-1, Batf, HIF-1, FoxO1, and FoxP1 (16–21); with the exception of FoxP1, which is involved in maintenance of the naïve T-cell pool, these transcription factors are all important players in the regulation of effector versus memory T-cell differentiation (22). However, no “exhaustion-specific” transcription factors have been identified so far.
Gene transcription is modulated by a variety of epigenetic features, including nucleosome positioning and DNA and histone modifications. Several genomic loci associated with T-cell exhaustion, such as Pdcd1 (encoding PD-1), show epigenetic changes during antiviral responses (23, 24). Three recent studies have used ATAC-seq (assay for transposase-accessible chromatin using sequencing) (25) to evaluate genome-wide differences in chromatin accessibility in effector, memory, and exhausted CD8+ T cells during acute and chronic infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) (26–28). In contrast, there has not yet been a systematic evaluation of the epigenetic changes that accompany the switch from T-cell competence to T-cell exhaustion in tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells.
Here we combine RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and ATAC-seq to define transcriptional profiles and chromatin accessibility patterns in tumor-reactive and -nonreactive tumor-infiltrating T cells. ATAC-seq and DNase I hypersensitivity assays (29, 30) yield similar information about chromatin accessibility, but ATAC-seq can be performed with limiting cell numbers such as those available ex vivo (25). ATAC-seq data can be mined for enrichment of consensus binding motifs in different classes of accessible regions, providing clues as to which transcription factors might bind these accessible sites. Here we show that antigen-reactive tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells display distinct molecular features of activation as well as exhaustion, identify a set of regulatory regions specifically associated with the exhausted state, and highlight NFAT and Nr4a family members as likely drivers of T-cell exhaustion. Using mice treated with anti–PD-L1 under conditions that arrest tumor growth, we show that blocking PD-1/PD-L1 signaling enhances the function of cytolytic T cells (CTLs) by increasing granzyme and serpin gene levels, with minor genome-wide effects on chromatin accessibility and overall gene expression. We discuss our results in the context of recent studies of dysfunctional T cells in a different, autochthonous tumor model (31), as well as exhausted T cells during chronic viral infection (26–28).
Results
Phenotypic Comparison of Tumor-Reactive and Tumor-Ignorant Cytolytic T Cells Within the Tumor Environment.
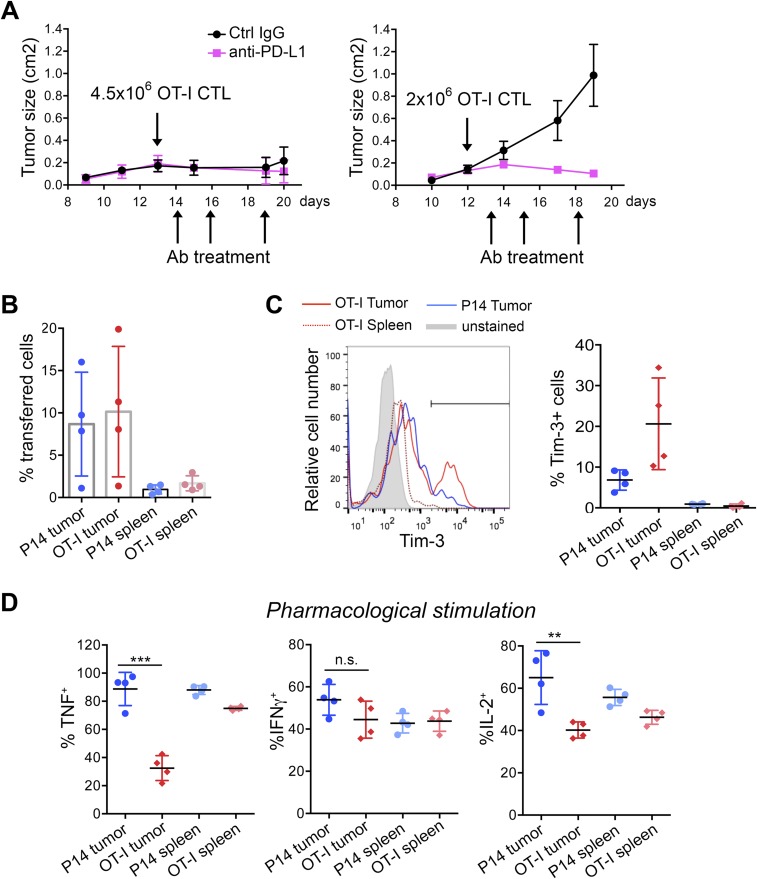
To study tumor-induced T-cell exhaustion, we intradermally injected C57BL/6 mice with B16-OVA, a melanoma cell line engineered to express the exogenous antigen chicken ovalbumin (OVA) (32) (Fig. 1A, Upper). In this widely established model, the aggressive growth of the B16-OVA melanoma tumor can be controlled by adoptive transfer of OT-I OVA-specific CTLs only at very early stages of the disease, or when CTLs transfer is combined with other forms of immunotherapy (33, 34). In preliminary experiments, injection of 4.5 × 106 in vitro-differentiated OT-I CTLs into mice with established intradermal tumors, with or without anti–PD-L1 treatment, led to a complete block in tumor growth (Fig. S1A, Left). To shift the balance in favor of tumor escape and induce functional exhaustion in the adoptively transferred T cells, we transferred lower numbers of OT-I CTLs (2 × 106 per mouse). In this setting, tumor growth was not arrested, and early administration of anti–PD-L1 blocked tumor growth (Fig. S1A, Right). For all subsequent experiments, we inoculated 2 × 106 OT-I CTLs per mouse.
Fig. 1.
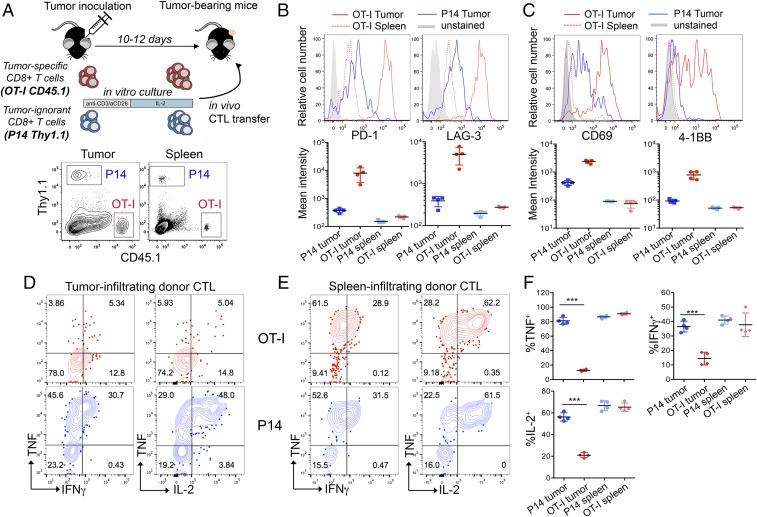
Tumor-specific CTLs become phenotypically and functionally exhausted, whereas tumor-ignorant bystander CTLs do not. (A, Upper) Flowchart of experiment: in vitro-generated OT-I and P14 CTLs were adoptively transferred into mice bearing subcutaneous B16-OVA tumors. (A, Lower) Flow cytometry plot showing the fraction of OT-I (CD45.1+) and P14 (Th1.1+) cells in the total CD8+ T-cell gate, in the tumor or spleen of a representative mouse, 8 days after in vivo transfer. (B and C, Upper), Expression of inhibitory receptors (PD-1 and LAG-3) and activation molecules (CD69 and 4-1BB) on tumor-infiltrating OT-I and P14 CD8+ T cells and on OT-I cells isolated from the spleen of a representative mouse. (B and C, Lower) Quantification (geometric mean of fluorescence intensity ± SD) of the expression levels of the cell-surface proteins indicated above each graph. Each dot represents one mouse. (D and E) Intracellular staining for the cytokines TNF, IFNγ, and IL-2, upon restimulation of OT-I and P14 cells isolated from the tumor (D) or spleen (E) with their cognate peptides. Data are from one representative experiment out of three. (F) Summary of cytokine production by P14 and OT-I cells infiltrating tumor or spleen upon restimulation with cognate peptides. Horizontal bars show averaged values ± SD (***P < 0.01, unpaired t test). Representative of three independent experiments. Each dot represents one mouse.
Fig. S1.
Growth curves of B16-OVA tumors and phenotype of TILs. (A) Growth profile of B16-OVA tumors inoculated intradermally into C57BL/6 recipient mice. On days 12–13 after tumor inoculation, the indicated numbers of OT-I CTLs were adoptively transferred i.v. into tumor-bearing mice. Mice were treated with anti–PD-L1 or control IgG as indicated. The graphs show tumor progression upon transfer of 4.5 × 106 (Left) or 2 × 106 (Right) OT-I cells; n = 4 mice per group; average ±SE are shown; each experimental condition was tested once as part of the initial setup. (B) Percentages of OT-I and P14 TILs 8 days after in vivo transfer, measured after gating on total CD8+ TILs. Each dot represents a mouse; bars represent averages and SE; experiment is representative of three independent experiments. (C) Expression of Tim-3 in OT-I and P14 TILs, 8 days after transfer or in spleen-infiltrating OT-I cells (Left). One representative mouse out of four is shown. Gate indicates percentage of Tim-3+ cells. Average percentage of Tim-3+ cells (±SD) is shown on the Right, representative of at least three experiments. (D) Summary of cytokine production by P14 and OT-I cells infiltrating tumor or spleen, as indicated. Percentages of cells producing TNF, IFNγ, or IL-2 after ex vivo restimulation with PMA + thapsigargin are shown. Horizontal bars show averaged values ±SD (***P < 0.01, unpaired t test), representative of three independent experiments.
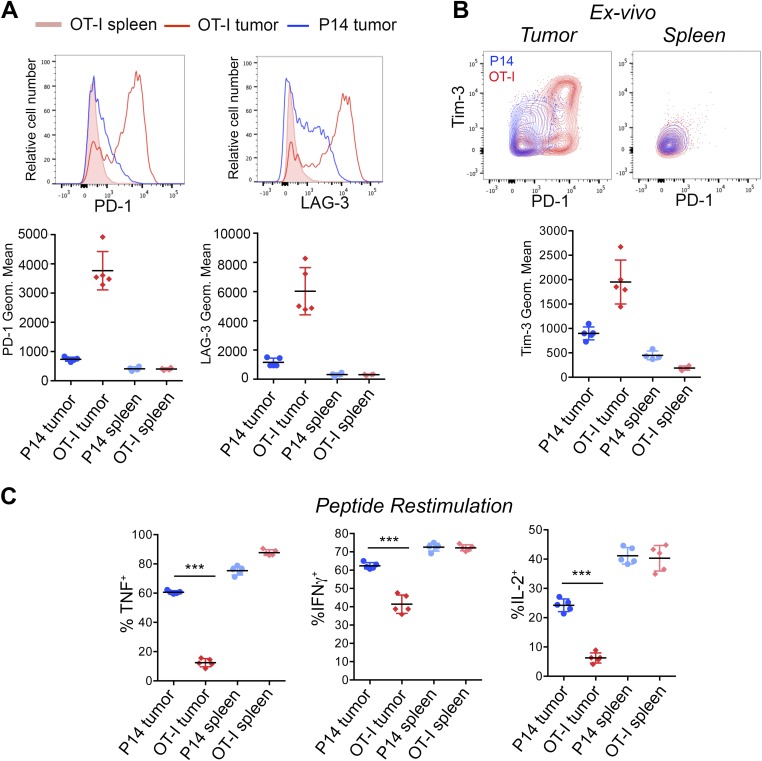
To discriminate between generic suppression imposed by the tumor environment in the absence of T-cell receptor (TCR) triggering, and exposure to the same environment with concomitant TCR engagement, we compared tumor-reactive OT-I and tumor-ignorant P14 CTLs (the P14 TCR recognizes an irrelevant peptide from LCMV). OT-I and P14 CD8+ T cells were obtained from TCR transgenic mice bearing different congenic markers (CD45.1 and Thy1.1, respectively), activated with anti-CD3 plus anti-CD28 and cultured in low dose IL-2 for 5 days (29), then transferred intravenously as a 1:1 mixture (2 × 106 cells of each specificity) into C57BL/6 recipient mice (CD45.2 and Thy1.2) with established subcutaneous B16-OVA tumors (Fig. 1A, Upper). Both OT-I and P14 CTLs infiltrated the tumors (Fig. 1A, Lower): 8 days after transfer, comparable percentages of P14 and OT-I cells were found in tumor and spleens of recipient mice (Fig. S1B). Notably, OT-I cells isolated from the tumors, either as early as day 3 (Fig. S2 A and B) or day 8 posttransfer (Fig. 1B and Fig. S1C), expressed high levels of PD-1 and LAG-3, and variable levels of Tim-3. By contrast, P14 cells isolated from the same tumors, and OT-I cells isolated from spleens of the same mice, expressed much lower levels of these markers, regardless of the time (3 or 8 days) after transfer into recipients (Fig. 1B and Figs. S1C and S2 A and B). OT-I but not P14 tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) also expressed the costimulatory molecule 4-1BB and the activation marker CD69 (Fig. 1C), both indicative of sustained TCR signaling. These activation molecules are also expressed in TILs in an autochthonous melanoma mouse model as well as in endogenous TILs in patients with cancer (15, 35, 36).
Fig. S2.
Phenotypic and functional analysis of OT-I and P14 TILs on day 3 after in vivo transfer. (A) PD-1 and LAG-3 expression in OT-I and P14 T cells isolated from B16-OVA tumors 3 days after in vivo T-cell transfer, as well as in splenic OT-I cells. (Upper) Expression of the indicated cell-surface proteins in a representative mouse out of four or five. (Lower) Quantification across different mice, including analysis of P14 cells from spleens of recipient mice (mean ± SD). Each dot indicates a mouse, representative of two independent experiments. (B, Upper) Expression of Tim-3 versus PD-1 in tumor-infiltrating and splenic P14 and OT-I cells 3 days after in vivo transfer in one representative mouse out of four or five. (Lower) Quantification of Tim-3 levels across different mice. (C) Intracellular staining for TNF, IFNγ, and IL-2 production by tumor-infiltrating and splenic OT-I and P14 cells, isolated 3 days after in vivo transfer, upon restimulation with cognate peptide ex vivo. Each dot represents a mouse, horizontal bars show averaged values (n.s., not significant; **P < 0.05; ***P < 0.01, unpaired t test). A single experiment, representative of two independent experiments, is shown.
To evaluate the functionality of OT-I TILs, we examined cytokine production in tumor- and spleen-infiltrating OT-I and P14 cells restimulated ex vivo with a mixture of their cognate peptides OVA (OVA257–264) and LCMV glycoprotein 33 (gp33–41). OT-I TILs recovered 8 days after transfer, showed severely reduced production of TNF, IFNγ, and IL-2 compared with P14 TILs, but the two cell types showed comparable cytokine production in the spleen (Fig. 1 D–F). Defective cytokine production upon peptide restimulation was observed as early as day 3 posttransfer in OT-I TILs (Fig. S2C). Pharmacological stimulation with a combination of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and thapsigargin, which bypass TCR signaling, normalized IFNγ production by OT-I TILs, whereas TNF and IL-2 production remained defective (Fig. S1D), suggesting that the decrease in IFNγ production reflects inefficient signaling proximal to the TCR, whereas the decrease in TNF and IL-2 production involves signaling steps occurring downstream of calcium entry and diacylglycerol-mediated activation of intracellular enzymes such as protein kinase C and RasGrp.
Transcriptional Profiles of OT-I and P14 TILs.
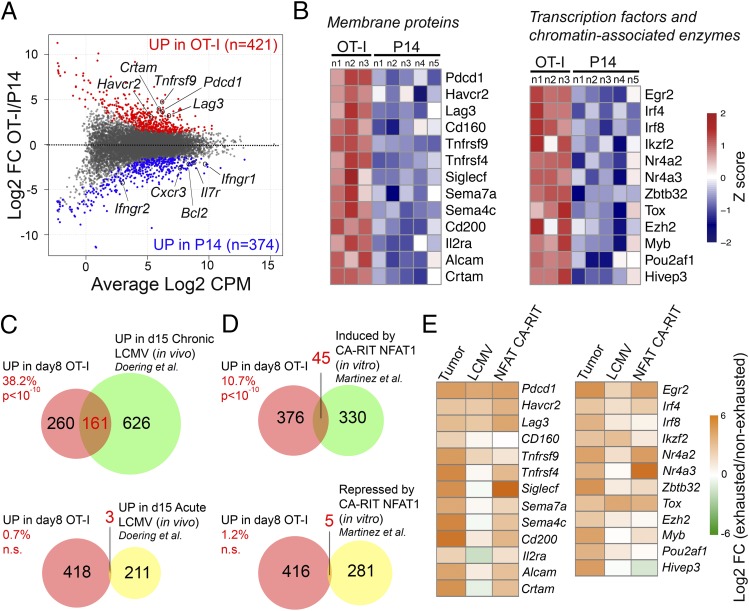
RNA-seq of sorted cells, 8 days after transfer into tumor-bearing recipient mice, identified 421 and 374 genes showing increased and decreased expression, respectively, in OT-I compared with P14 TILs (Fig. 2A). The genes fell into several categories based on biological function (Fig. 2B and Dataset S1). Genes encoding inhibitory receptors (Pdcd1, Lag3, Havcr2, Cd200, and Cd160), costimulatory molecules (Tnfrsf4 and Tnfrsf9), immunomodulatory semaphorins (Sema7a and Sema4c), cytokine receptors and adhesion molecules (Il2ra and Crtam) were up-regulated in OT-I TILs (Fig. 2 A, red and B, Left), whereas genes involved in CTLs persistence/survival and tissue homing (Il7r, Bcl2, and Cxcr3) and response to IFNγ (Ifngr1 and Ifngr2) were more highly expressed in P14 TILs (Fig. 2A, blue and Dataset S1). Among transcription factors and chromatin-associated enzymes, OT-I TILs displayed increased expression of genes encoding Egr2 and IRF- and Nr4a-family transcription factors as well as Ezh2, the enzymatic component of polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) (Fig. 2B, Right and Dataset S1). Overall, OT-I TILs displayed features of both in vivo activation and functional exhaustion.
Fig. 2.
Transcriptional profiles of OT-I and P14 TILs and comparison with other exhaustion models. (A) MA plot showing the log2-fold change of mRNA transcript levels and average counts per million (CPM) between OT-I and P14 TILs, isolated from B16-OVA tumors 8 days after in vivo transfer (averaged from three to five biological replicates). Each dot represents an expressed gene. Red and blue dots indicate genes significantly up-regulated [abs(log2 FC) ≥ 1 and FDR ≤ 0.05] in OT-I or P14 TILs, respectively. (B) Heat maps of expression of representative genes up-regulated in OT-I versus P14 TILs, showing individual replicates. (C) Venn diagrams showing the overlap between genes up-regulated in day 8 OT-I versus P14 TILs (red) and genes up-regulated (green) or down-regulated (yellow) in exhausted versus effector CTLs isolated from mice 15 days after LCMV infection (37). The percentage of genes up-regulated in OT-I TILs that are also differentially expressed in the indicated comparison is shown in red. The statistical significance of intersections is from Fisher’s exact tests (n.s. if P > 0.05). (D) Venn diagrams showing the overlap between genes up-regulated in OT-I TILs (red) and genes up-regulated (green) or down-regulated (yellow) in CA-RIT-NFAT1–transduced CTLs versus mock-transduced CTLs (38). (E) Heatmap of log2-fold changes of genes shown in B, in OT-I versus P14 TILs; in exhausted versus effector CTLs from mice infected with LCMV (37); or in CA-RIT-NFAT1–transduced CTLs versus control cells (38).
We compared our OT-I TILs RNA-seq data with a transcriptomics dataset from a different in vivo model, in which CD8+ T-cell exhaustion was driven by chronic LCMV infection (37). Of the genes up-regulated in OT-I compared with P14 TILs, 161 (38.2%) were also up-regulated in “exhausted” CTLs isolated on day 15 after chronic viral infection; this result was highly significant (P < 10−10; Fig. 2C, Top and Dataset S1). In contrast, only three genes overlapped with genes up-regulated in “effector” CTLs isolated from day 15 LCMV-infected mice, a number that did not reach statistical significance (Fig. 2C, Bottom and Dataset S1). Thus, the transcriptional profile of OT-I TILs showed a significant overlap with an independent in vivo exhaustion model (37). The relation to more recent data (26–28) is discussed below.
We previously showed that enforced expression of a constitutively active form of NFAT1, engineered to prevent interaction with its transcriptional partner AP-1 (CA-RIT-NFAT1), induced a genetic program that closely resembles T-cell exhaustion (38). Genes up-regulated in exhausted OT-I TILs showed a significant overlap (45 genes, 10.7%; P < 10−10) with genes up-regulated in in vitro-generated CA-RIT-NFAT1–expressing CTLs (Fig. 2D, Top); in contrast, there was no significant overlap between genes down-regulated by CA-RIT-NFAT1 and genes that showed increased expression in exhausted OT-I compared with P14 TILs (Fig. 2D, Bottom). The fold-induction of genes encoding membrane proteins, transcription factors, and chromatin-associated enzymes in exhausted OT-I over P14 TILs (Fig. 2B), exhausted over effector CTLs in the chronic LCMV model (37), and CA-RIT-NFAT–transduced versus control cells (38) is shown in Fig. 2E and Dataset S1. Together, these data support the notion that chronic NFAT activation contributes substantially to several features of CD8+ T-cell exhaustion (27, 28, 38).
Genome-Wide Changes in Chromatin Accessibility upon Restimulation of in Vitro-Generated CTLs.
To interrogate the role of NFAT and other transcription factors in the exhaustion program, we attempted to perform NFAT1 chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) on exhausted OT-I TILs. Although ChIP-seq for histone modifications can be performed on small numbers of cells (39), ChIP-seq for NFAT1 and other transcription factors in samples with limited cell numbers proved technically less feasible. We therefore used ATAC-seq (25), a technique that probes chromatin accessibility in small numbers of cells. Accessible regions identified by ATAC-seq can be mined to find enriched sequence motifs known to be bound by specific families of transcription factors (25). In combination with RNA-seq, this analysis provides an indication of which transcription factors might occupy accessible regions in vivo.
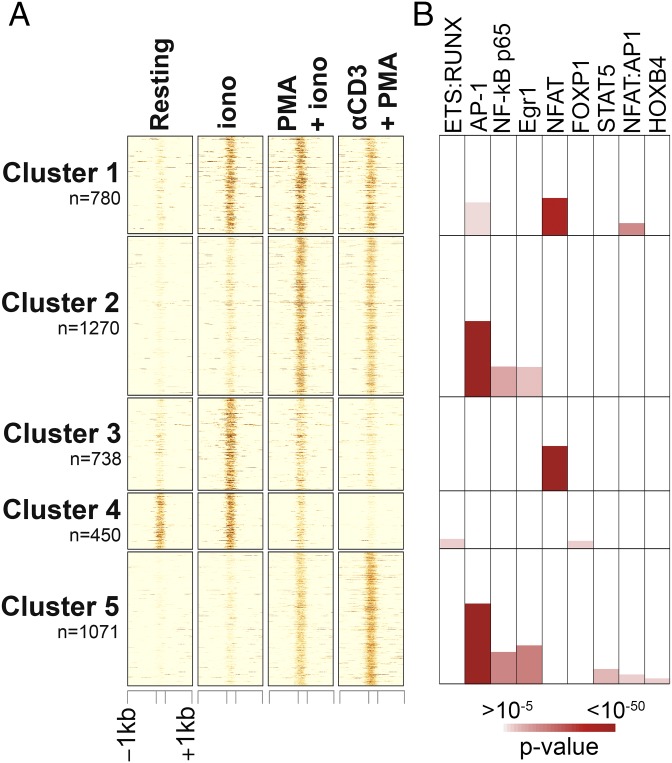
To validate our experimental strategy, we first performed ATAC-seq on in vitro-differentiated CTLs (29) that were left unstimulated (“resting”) or briefly restimulated for 2 h. Restimulation was performed with ionomycin alone (which at this early time point primarily activates NFAT transcription factors); PMA plus ionomycin (which activates NFAT, AP-1, and NFκB transcription factors, among others); or anti-CD3 + PMA (which activates AP-1 and NFκB, with less activation of NFAT). We identified a set of ∼4,300 genomic regions, which showed differential accessibility in at least one pairwise comparison, classified them into five major clusters by k-means clustering, and performed motif enrichment analysis for each cluster using Homer (40) (Fig. 3A). As expected, accessible regions in cluster 1 (high accessibility in all restimulated samples compared with resting CTLs) showed strong enrichment for consensus NFAT-binding motifs as well as NFAT:AP-1 composite sequences, whereas regions in cluster 3 (highest accessibility in CTLs restimulated with ionomcyin alone) were enriched for NFAT motifs without an AP-1 site in the immediate vicinity (Fig. 3B). Similarly, because of PMA stimulation, regions in both clusters 2 and 5 (higher accessibility in samples restimulated with PMA + ionomcyin and anti-CD3 + PMA compared with resting and ionomycin-stimulated cells) were enriched for AP-1, NFκB, and Egr consensus motifs (Fig. 3B and Dataset S2). Regions in cluster 4 (high accessibility in resting and ionomcyin-stimulated CTLs) showed enrichment for forkhead transcription factor motifs, consistent with a previously described role for FoxP1 in the maintenance of T-cell quiescence (41). Cluster 4 also showed enrichment for an unusual motif in which the AGGA[A] Ets binding site overlapped by one base pair with a [T]GTGGT Runt motif, consistent with the hypothesis that ETS and Runx proteins might have a general role in maintaining chromatin accessibility through recruitment of chromatin remodeling complexes (42).
Fig. 3.
Analysis of the chromatin accessibility landscape in acutely restimulated CTLs. (A) Heat map of ATAC-seq signal (averaged from two to three biological replicates) at ∼4,300 genomic regions whose accessibility was significantly altered in CTLs primed for 6 days and restimulated for 2 h with ionomycin (iono), anti-CD3 + PMA, PMA + iono, or left unstimulated (resting). Unsupervised clustering was used to identify patterns of chromatin accessibility across samples. (B, Top) Transcription factor-binding motifs associated with each cluster, color coded by enrichment P value. For significant motif enrichment (P value ≤10–5), the percentage of regions in the cluster with at least one motif occurrence is proportional to the colored area in each box. Therefore, the plot can be interpreted as for column charts.
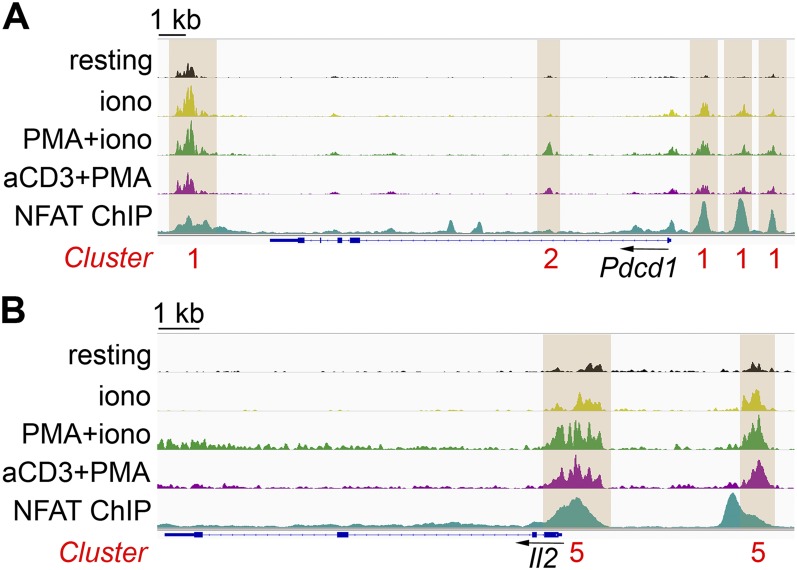
Fig. S3 shows representative genomic loci containing accessible regions belonging to the clusters identified in Fig. 3A. For instance, three regions in the promoter and one region downstream of the 3′-end of Pdcd1 gained accessibility under all three stimulation conditions tested (cluster 1); each of these regions corresponds to an endogenous NFAT1 ChIP-seq peak in in vitro-generated CTLs restimulated with PMA + ionomycin (38), consistent with the finding that Pdcd1 is a direct target of all three NFAT transcription factors, NFAT1, NFAT2, and NFAT4 (38, 43). The first intron of the Pdcd1 gene contains one region belonging to cluster 2 (accessibility induced by PMA + ionomycin and anti-CD3 + PMA but not by ionomycin alone, Fig. S3A); this region did not correspond to a site of NFAT binding. Similarly, the 5′-region of the Il2 locus contains peaks belonging to cluster 5 (Fig. S3B) showing low accessibility in resting cells or cells restimulated with ionomycin alone and high accessibility after stimulation with PMA + ionomycin and anti-CD3 + PMA. Of these two regions, the most proximal to the transcription start site (TSS) showed very strong binding to NFAT1 in ChIP-seq assays (38) and corresponds to the well-defined Il2 promoter, which harbors the ARRE2 element and cooperatively binds NFAT:AP-1 complexes (44, 45). A complete list of genomic regions and genes associated with each cluster can be found in Dataset S2.
Fig. S3.
Genome browser snapshots of ATAC-seq signal at representative regions modulated by acute restimulation in CTLs. Accessible regions at the representative genomic loci (A) Pdcd1 and (B) Il2 in acutely restimulated CTLs, as clustered in Fig. 3A. Peaks are highlighted by brown boxes, and cluster numbers are shown below in red. NFAT ChIP-seq signal in CTLs restimulated with PMA + ionomycin is from published datasets (38). The ATAC-seq signal is averaged from two to three biological replicates.
In summary, ATAC-seq experiments performed on restimulated CD8+ T cells led to the identification of distinct accessible regions depending on the stimulation condition, and motif enrichment analyses pointed to families of transcription factors known, expected, or predicted to drive gene transcription under those stimulation conditions. These studies set the stage for subsequent analysis of accessible regions in tumor-infiltrating CTLs.
Genome-Wide Chromatin Accessibility Profiles of Exhausted OT-I and Nonexhausted P14 TILs.
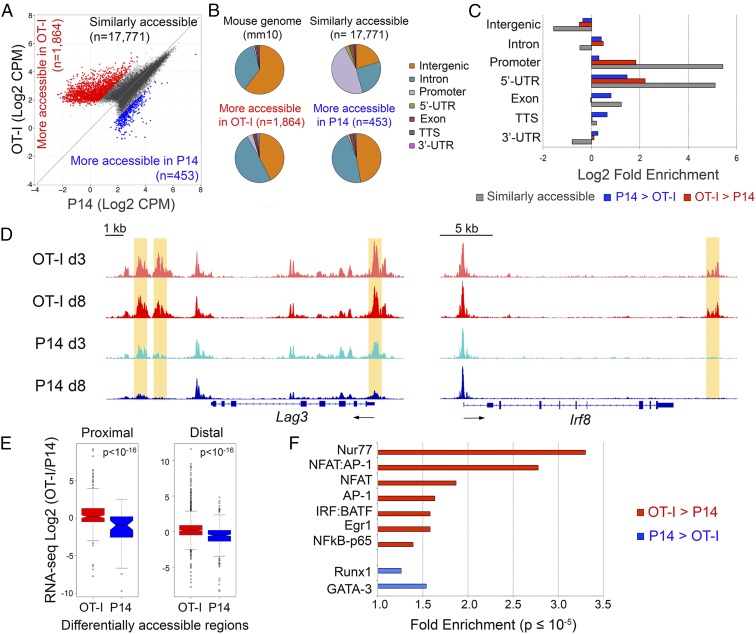
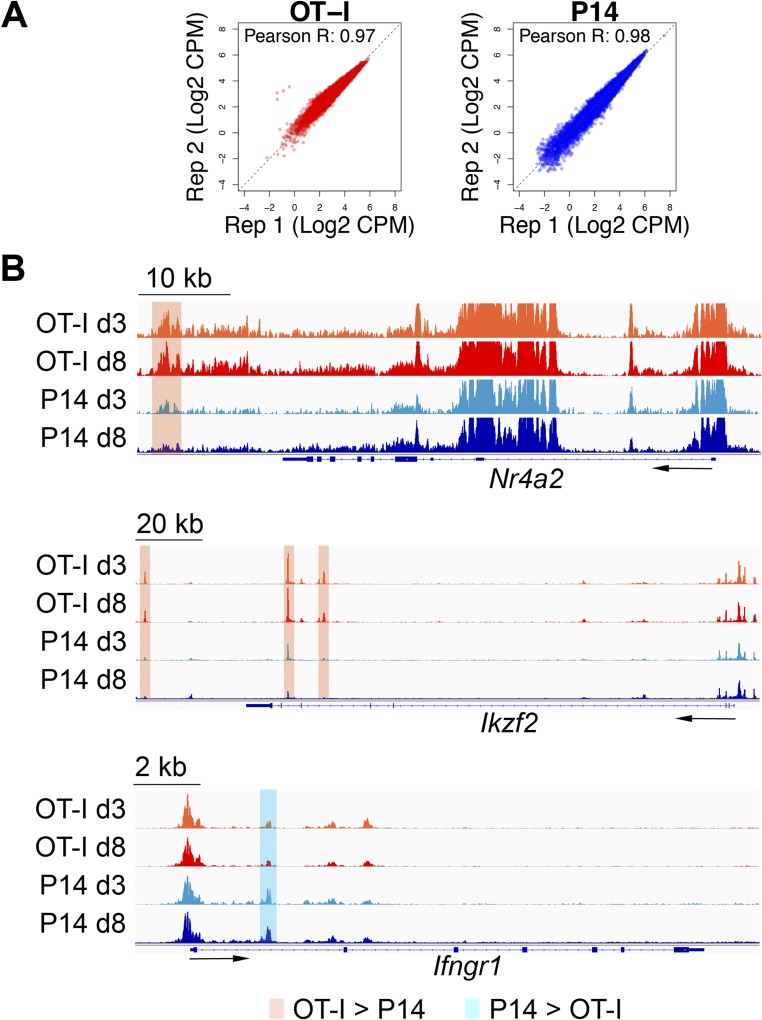
ATAC-seq on sorted P14 and OT-I TILs, performed on day 8 after transfer, identified 1,864 regions that were more accessible in OT-I than in P14 cells, compared with 453 regions more accessible in P14 than in OT-I cells (Fig. 4A and Fig. S4A and Dataset S3). Relative to the mouse genome, regions similarly accessible in OT-I and P14 cells (presumably regulatory regions of housekeeping or other commonly expressed T-cell lineage genes) were strongly enriched at promoters and 5′-UTRs, and depleted at intergenic and intronic elements (Fig. 4 B and C). In contrast, differentially accessible regions were enriched for introns and intergenic sequences compared with nondifferentially accessible regions. Genes up-regulated at the mRNA level in OT-I cells (Fig. 2B) exhibited increased chromatin accessibility within or in the vicinity of their transcribed regions, as illustrated for Lag3 and Irf8 in Fig. 4D and Nr4a2 and Ikzf2 in Fig. S4B. In all cases, increased accessibility was already obvious in OT-I cells isolated 3 days after in vivo transfer, correlating with early induction of a dysfunctional state in OT-I TILs (Fig. S2). Similarly, Ifngr1, which was more highly expressed in P14 cells (Fig. 2A), contained one region that was more accessible in P14 than in OT-I CTLs in its first intron (Fig. S4B). Genome-wide, genes close to regions more accessible in OT-I TILs were significantly up-regulated in these cells compared with P14 TILs, whether the accessible regions were proximal (−5 kb to +1 kb) or distal to the TSS (±50 kb, excluding the proximal window) (Fig. 4E).
Fig. 4.
Analysis of chromatin accessibility in OT-I and P14 TILs. (A) ATAC-seq signal (averaged from two biological replicates) in OT-I and P14 TILs, isolated 8 days after transfer. Each dot represents an ATAC-seq peak. The number of regions similarly accessible in both samples (dark gray), more accessible in OT-I than in P14 cells (red), and more accessible in P14 than in OT-I cells (blue) are indicated. (B) Pie chart showing the classification of ATAC-seq peaks from A compared with the mouse genome (mm10). (C) Log2-fold enrichment of the genomic classes shown in B relative to the whole genome. (D) Genome browser snapshots showing the ATAC-seq signal at two representative loci (Lag3 and Irf8). Regions more accessible in day 8 OT-I than P14 TILs are highlighted by orange boxes. (E) Correlation between ATAC-seq and RNA-seq data. Genes were associated with regions selectively accessible in day 8 OT-I (red) or P14 (blue) TILs by proximity to the TSS (proximal: −5 kb to +1 kb; distal: ±50 kb, with the exclusion of the proximal window). The distributions of log2-fold expression changes (as measured by RNA-seq) of the associated genes are shown in box plots and compared with a Mann–Whitney U test. (F) Transcription factor motifs associated with ATAC-seq regions more accessible in OT-I (red) or P14 (blue) TILs. The enrichment is relative to all accessible (both differential and nondifferential) regions of OT-I or P14 TILs, respectively. Only significant enrichment scores (P value ≤10–5) are shown.
Fig. S4.
Genome ATAC-seq in OT-I versus P14 TILs. (A) ATAC-seq signal from individual biological replicates in OT-I and P14 TILs. Dots represent the 20,088 regions shown in Fig. 4A. (B) Representative regions more accessible in OT-I than P14 day 8 TILs at the Nr4a2 and Ikzf2 loci (orange) or in P14 than OT-I day 8 TILs at the Ifngr1 locus (light blue). The ATAC-seq signal is averaged from two biological replicates.
To identify transcription factors that might drive exhaustion in OT-I TILs, we focused on regions more accessible in OT-I than in P14 cells. Consistent with the antigen-activated status of OT-I cells, these regions showed strong enrichment for consensus binding motifs for transcription factors associated with T-cell activation—AP-1, NFκB, and NFAT:AP-1 composite sites (Fig. 4F and Dataset S3). Consensus motifs for NFAT binding (without an adjacent AP-1 site) were also enriched in OT-I–specific accessible regions, in agreement with our hypothesis that NFAT binding in the absence of AP-1 drives T-cell exhaustion (Fig. 4F and Dataset S3). However, the strongest enrichment in OT-I–specific regions was for consensus Nur77 motifs (Fig. 4F and Dataset S3); indeed two members of this family, Nr4a2 (Nurr1) and Nr4a3 (Nor1), were strongly up-regulated in OT-I cells (Fig. 2B and Dataset S1). Genomic regions more accessible in OT-I TILs also showed enrichment for IRF:BATF and Egr motifs, consistent with previous findings implicating Batf in the regulation of effector CD8+ T-cell differentiation (46) and Egr2/Egr3 (both direct NFAT targets) (47, 48) in the induction of T-cell tolerance/anergy (49).
Identification of Exhaustion-Specific Accessible Regions in OT-I TILs.
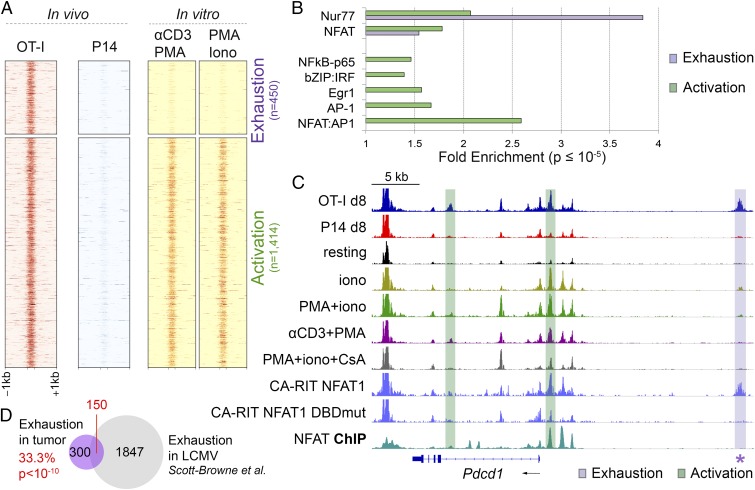
Because tumor-infiltrating OT-I cells are being continuously stimulated through the TCR, it was not surprising that OT-I–specific accessible regions were enriched for consensus binding motifs of transcription factors known to participate in T-cell activation. Functionally, however, tumor-infiltrating OT-I cells display a dysfunctional phenotype, because they show increased expression of inhibitory receptors and decreased ability to produce cytokines upon restimulation (Fig. 1). We therefore asked whether we could identify exhaustion-specific accessible regions in OT-I tumor-infiltrating cells by filtering out activation-related accessible regions. To this end, we subtracted the 1,414 regions highly accessible in CD8+ T cells acutely restimulated with PMA + ionomycin or PMA + anti-CD3 in vitro (Fig. 5A, yellow) from the 1,864 regions more accessible in day 8 OT-I than in P14 TILs (Figs. 4A and 5A, red). The remaining 450 regions were defined as exhaustion related (Fig. 5A, Top). By contrast, regions showing comparable accessibility between OT-I TILs and acutely restimulated CTLs samples were defined as activation related (Fig. 5A, Bottom; n = 1,414 regions).
Fig. 5.
Identification of accessible regions associated with exhaustion or activation in OT-I TILs. (A) Heat maps of ATAC-seq signal (averaged from two to three biological replicates) at regions more accessible in day 8 OT-I than P14 TILs and either more accessible (Top, exhaustion related) or similarly accessible (Bottom, activation related) in OT-I TILs versus CTLs acutely restimulated in vitro. (B) Transcription factor motifs associated with exhaustion- (purple) or activation-related (green) ATAC-seq regions. Only significant enrichment scores (P value ≤10–5) are shown. (C) Genome browser snapshot of ATAC-seq signal at the Pdcd1 locus, showing representative regions associated with exhaustion (purple) or activation (green) phenotypes. ATAC-seq tracks are shown for OT-I and P14 TILs 8 days after in vivo transfer, in vitro-generated CTL, resting and restimulated as indicated, and CTL transduced with CA-RIT-NFAT1 or a DNA-binding mutated NFAT (DBDmut) (28). The bottom track shows the NFAT ChIP-seq signal in CTLs restimulated in vitro with PMA + iono, taken from published datasets (38). The star highlights the exhaustion-associated Pdcd1 enhancer (−22.4 kb). (D) Overlap between exhaustion-associated open chromatin regions from OT-I TILs and from LCMV chronic infection in Scott-Browne et al. (28). Statistical significance is computed using the Fisher’s exact test.
A search for transcription factor motifs in the exhaustion-related regions revealed a highly significant enrichment for Nr4a (Nur77) (Fig. 5B), as well as significant enrichment for NFAT without an adjacent AP-1 site (Fig. 5B). By contrast, activation-related regions showed significant enrichment for AP-1, NFκB, NFAT, and NFAT:AP-1 composite sites (Fig. 5B). Egr motifs and bZIP:IRF composite motifs, were significantly enriched in activation-related, but not exhaustion-related accessible regions, suggesting that Egr factors and bZIP:IRF complexes are not drivers of the exhaustion program in our tumor model (Fig. 5B).
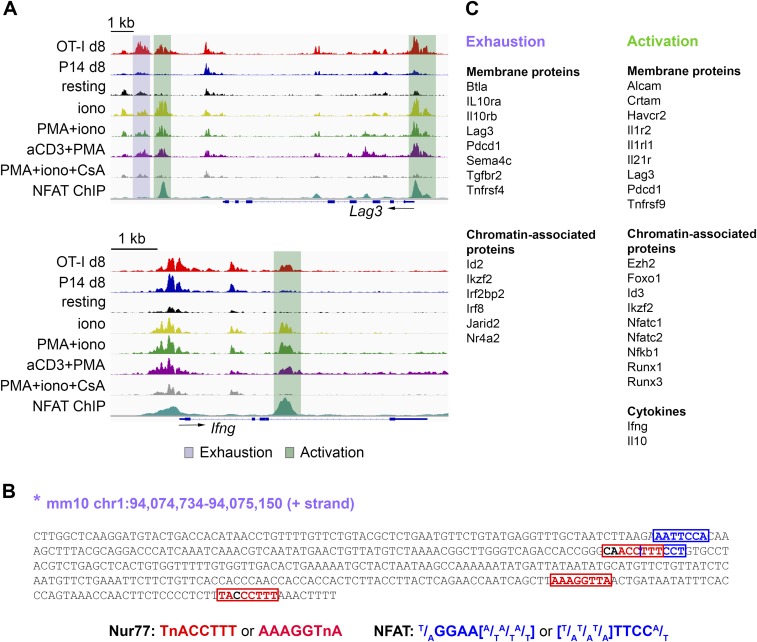
Notably, several loci known to be induced in both recently activated and exhausted T cells contained accessible regions associated with both exhaustion and activation, as shown for Pdcd1 (Fig. 5C) and Lag3 (Fig. S5A). A region near the Pdcd1 TSS, a region in the Lag3 promoter, a second region ∼2 kb 3′ of the Lag3 gene and an intronic region of the Ifng gene are selectively accessible in activated cells and show strong NFAT occupancy in in vitro-generated, restimulated CTLs (Fig. 5C and Fig. S5A), whereas a region further 3′ of the Lag3 gene (∼3 kb) and a region located −22.4 kb 5′ of the Pdcd1 TSS are selectively accessible in exhausted cells both in our model and in the LCMV model (26–28), and do not bind NFAT under these conditions (Fig. 5C and Fig. S5A). Notably, the −22 kb Pdcd1-accessible region, which is also accessible in cells transduced with CA-RIT-NFAT1 (Fig. 5C), was recently shown to be functionally active as an enhancer partly driving PD-1 expression in the EL-4 T-cell line (26). Sequence inspection of this region identified three potential Nur77 motifs and two NFAT motifs without an obvious adjacent AP-1 site (Fig. S5B); since neither NFAT1 nor CA-RIT-NFAT1 bind to this region in cells stimulated in vitro (Fig. 5C) (28, 38), NFAT may set up the accessibility of this region in exhausted cells, potentially paving the way for Nr4a and other transcription factors to bind the region and maintain its accessibility. Both the activation-associated and exhaustion-associated regions in the Pdcd1 locus fall within a domain bounded by CTCF sites (50).
Fig. S5.
Genome browser snapshots of ATAC-seq signal at representative exhaustion- or activation-associated regions. (A) ATAC-seq signal (averaged from two to three biological replicates) at representative genomic loci (Top, Lag3; Bottom, Ifng) highlighting accessible regions identified as either exhaustion- (purple) or activation-associated (green). NFAT ChIP-seq signal in CTLs restimulated with PMA + iono is from published datasets (38). (B) Sequence of the exhaustion-associated open-chromatin region in the Pdcd1 locus marked by a star in Fig. 5C, with manually curated Nur77 and NFAT motif occurrences. (C) Representative genes, categorized by function or localization, found within 200 kb from the exhaustion- or activation-related genomic regions identified in Fig. 5A.
We and others have recently defined the chromatin accessibility landscape of exhausted CTLs isolated from mice infected with LCMV (26–28). To interrogate the relation between exhausted T cells in our tumor model and a viral one, we intersected the exhaustion-related regions identified in OT-I cells (Fig. 5A) with regions more accessible in exhausted CTLs isolated from mice chronically infected with LCMV than in effector/memory/naïve CTLs (28) and found that 150 out of 450 exhaustion-related regions identified in OT-I TILs were also more accessible in exhausted CTLs from chronically LCMV-infected mice (Fig. 5D), indicating that common epigenetic mechanisms might underlie T-cell exhaustion in different settings.
Exhaustion-related accessible regions were associated with genes encoding immune-modulatory molecules (Btla, Il10ra/b, Tgbr2, Sema4c, and Tnfrsf4) and transcription factors whose binding motifs were enriched in OT-I–specific accessible regions (Irf8, Ikzf2, and Nr4a2) (Fig. S5C, Left). Activation-related accessible regions were found in genomic loci encoding cytokines (Ifng and Il10) (Fig. S5 A, Bottom, and C, Right), proteins known to be up-regulated as a consequence of either transient or sustained T-cell activation (Crtam, Tnfrsf9, and others); and numerous transcriptional regulators (Ezh2, Id3, Nfatc1/c2, Runx1/3, Foxo1, and Nfkb) (Fig. S5C, Right and Dataset S4).
In summary, our strategy of filtering out activation-related accessible regions allowed us to identify a set of regulatory genomic regions potentially involved in exhaustion and reinforced the notion of functional involvement of NFAT and Nr4a family members in establishing cancer-induced CD8+ T-cell exhaustion in tumor-infiltrating CTLs.
Effect of Anti–PD-L1 Treatment on RNA Expression and Chromatin Accessibility Profile of OT-I TILs.
PD-1 is a surface receptor containing an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM)/immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif (ITSM) that negatively regulates TCR responses (51, 52). Immunotherapy targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis has shown remarkable results in melanoma as well as other categories of solid tumors (8, 53), but only a few prior studies have investigated the transcriptional mechanisms associated with objective clinical responses to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade (27, 54). Blocking PD-1/PD-L1 signaling might reinvigorate the cytolytic activity of tumor-infiltrating CTLs at many levels, not mutually exclusive: reactivating cytoplasmic signaling downstream of the TCR, enhancing transcriptional responses in the nucleus, modulating mRNA or protein stability, and so on.
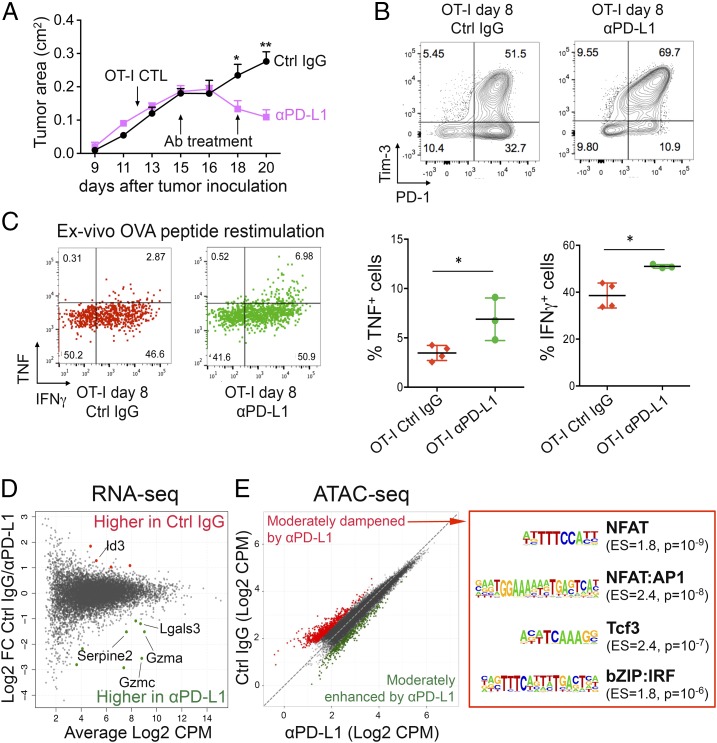
We asked whether blocking PD-1 signaling in tumor-infiltrating OT-I cells induced changes in gene expression and chromatin accessibility. Two injections of anti–PD-L1 (day 3 and day 6 after T-cell transfer) led to cessation of tumor growth (Fig. 6A), an increase in the percentage of OT-I tumor-infiltrating T cells expressing both PD-1 and Tim3 (Fig. 6B), and a small but significant increase in IFNγ and TNF production upon restimulation with OVA peptide ex vivo (Fig. 6C), together confirming that our conditions of anti–PD-L1 treatment led to reactivation of TCR signaling in the tumor-infiltrating OT-I cells. Under these conditions, OT-I TILs from anti–PD-L1–treated mice showed up-regulation of a very limited set of genes, including those encoding granzymes (Gzma, Gzmc, and others), which mediate cytolysis of target cells (55) and serpins, serine protease inhibitors that protect CTLs from damage induced by granzymes (56) (Fig. 6D and Dataset S5). Anti–PD-L1 treatment had a similarly moderate effect on chromatin accessibility (Fig. 6E). Indeed, we could identify regions showing differential accessibility in anti–PD-L1–treated cells only by using relaxed metrics (Fig. 6E, Left). Regions with decreased accessibility upon anti–PD-L1 treatment (Fig. 6E, red) contained consensus binding motifs for NFAT (including NFAT:AP1), a high-mobility group (HMG) motif assigned to Tcf family members and a composite IRF:BATF motif thought to be occupied by a cooperative IRF:Jun-Batf dimer complex in activated T cells (57, 58) (Fig. 6E, Right). These data are in agreement with a previous study examining CD8+ T-cell exhaustion in chronic LCMV infection before and after treatment with anti–PD-L1 (27). Overall, our results suggest that the effect of PD-1/PD-L1–targeted therapies are mainly exerted by modulating cytosolic signaling intermediates rather than through de novo changes in genome accessibility to transcription factors.
Fig. 6.
Effects of anti–PD-L1 treatment on phenotype and chromatin accessibility of OT-I TILs. Mice bearing s.c. B16-OVA tumors adoptively transferred with 2 × 106 OT-I CTLs on day 12 received two injections of anti–PD-L1 or control IgG as indicated (day 15 and day 18); n = 4–5 mice per group. (A) Tumor growth curves with average ± SEM. (B) Expression of PD-1 and Tim-3 on OT-I TILs 8 days after in vivo transfer; each plot corresponds to a pool of two to four mice. (C, Left) TNF and IFNγ intracellular staining of OT-I TILs from mice treated with control IgG or anti–PD-L1, after restimulation with OVA peptide. (C, Right) Quantification of TNF and IFNγ production; each dot represents a mouse; mean ± SD is shown (*P value <0.05, unpaired t test). (D) MA plot of gene expression changes in OT-I TILs isolated from mice treated with anti–PD-L1 versus Ctrl IgG (n = 2–3). Each dot represents a gene. Dots highlighted in color are significantly different [abs(log2 FC) ≥ 1 and FDR ≤ 0.1] between the two groups. (E, Left) Scatterplot showing the averaged ATAC-seq signal in OT-I TILs 8 days after transfer from mice treated with anti–PD-L1 or control IgG (n = 2–4). Each dot represents a peak. Regions more accessible in anti–PD-L1 than control or vice versa using a relaxed metric (fold changes exceeding 2 SDs from the mean) are highlighted in green and red, respectively. (E, Right) Transcription factor-binding motifs significantly enriched in regions dampened by anti–PD-L1 treatment. Enrichment scores (ES) and P values are shown.
Discussion
We used RNA-seq and ATAC-seq to distinguish the molecular features of activation and exhaustion in tumor-infiltrating T cells. We compared tumor-reactive OT-I TILs, which become unresponsive to restimulation as early as 3 days after in vivo transfer, with tumor-nonreactive P14 TILs, which remain antigen responsive despite exposure to the same tumor milieu. In previous papers, we documented NFAT involvement in CD4+ T-cell anergy and CD8+ T-cell exhaustion using NFAT-deficient cells and mice, as well as an engineered NFAT that lacks the ability to cooperate with AP-1 (38, 59). More recently, we defined the gene expression and chromatin accessibility profiles of CD8+ T cells during acute and chronic LCMV infection and identified common and distinct features of naïve, effector, memory, and exhausted cells (28). Together, our findings in the LCMV and tumor models extend our previous conclusion of NFAT involvement in CD8+ T-cell exhaustion (38) to in vivo models of antitumor and antiviral responses and identify several new players—including Nr4a2 (Nurr1) and Nr4a3 (Nor1)—as targets for future investigation (ref. 28 and this report). The potential involvement of NFAT and Nr4a was also noted in two other recent studies of T-cell exhaustion during chronic LCMV infection (26, 27). Our data are by and large concordant with these previous data; differences in interpretation are discussed below.
In our study, we preactivated OT-I and P14 cells in vitro using polyclonal stimulation (anti-CD3 + anti-CD28), and transferred them into mice bearing B16-OVA melanoma. This was partly to shorten the overall time course of the experiments and partly because we wished to set the stage for targeting selected exhaustion-specific genes and regulatory regions in the transferred OT-I cells by CRISPR and RNAi. A different experimental design was used in a recent paper: naïve TCR-transgenic CD8+ T cells that did or did not recognize a tumor antigen were allowed to infiltrate premalignant liver lesions induced by oncogene expression (31). In both cases, the dysfunctional phenotype was observed only in antigen-reactive tumor-infiltrating cells. Thus, both studies connect exhaustion to antigen recognition rather than to residence in an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, regardless of whether the infiltrating cells are preactivated or naïve.
Functionally, the OT-I TILs in our system meet the classical definition of exhausted cells, because they are severely impaired in their ability to produce TNF or IL-2 upon restimulation. Nevertheless, these cells also display certain phenotypic features of activation, including expression of CD69 and 4-1BB. Similarly, many genes characteristically expressed by exhausted T cells (including those encoding Nr4a transcription factors and inhibitory receptors PD-1, Lag3, Tim3, and CTLA-4) are acutely but transiently up-regulated in effector cells in the LCMV model as well as in in vitro-activated cells (ref. 28 and this report). The observed overlap between activated and exhausted CD8+ T cells is not surprising, because it has been documented in mouse models of both chronic viral infections and cancer: CD8+ T cells exposed to persistent TCR stimulation in vivo are thought to undergo a process of functional adaptation and can retain effector phenotypes for long periods of time (60). Similar conclusions can be drawn from clinical experience with checkpoint blockade therapies (anti–PD-1/anti–PD-L1 and anti–CTLA-4) (60). However, experiments at the single-cell level will be needed to establish whether individual cells in the population simultaneously express features of both accessibility and exhaustion at the levels of gene expression and chromatin accessibility.
In our study of antitumor responses, we distinguished exhaustion-related accessible regions in OT-I TILs from those induced by TCR stimulation or exposure to the tumor environment. Of 1,864 regions differentially accessible in OT-I compared with P14 TILs, the majority (1,414 regions) were also represented in acutely activated CTLs, identifying the remaining 450 regions as exhaustion specific—selectively accessible only in OT-I TILs. In fact, most regions that become acutely accessible in activated T cells maintain accessibility stably for long periods after stimulation, even after activation-specific gene expression has declined (42). Thus the accessible regions shared between acutely activated T cells and OT-I TILs on the one hand (this report), and between effector and exhausted cells in the LCMV model on the other hand (28), may belong to this category of regions that are stably accessible in previously activated T cells (42). This hypothesis may also explain why chromatin accessibility patterns are stably maintained in exhausted T cells from anti–PD-1/anti–PD-L1–treated mice (ref. 27 and this report).
We previously used NFAT-deficient T cells as well as CA-RIT-NFAT1, a constitutively active NFAT unable to cooperate with AP-1 (38, 59), to confirm the involvement of NFAT transcription factors in CD8+ T-cell exhaustion. Indeed, both in this report and in the LCMV studies (26–28), exhaustion-specific accessible regions showed strong enrichment for the TGGAAA[A] motif (complement [T]TTTCCA) that binds NFAT, more so than observed for the composite NFAT:AP-1 motif. Genes selectively expressed in OT-I over P14 TILs, as well as regions selectively accessible in OT-I over P14 TILs (this report), showed substantial overlap with genes and accessible regions in CA-RIT-NFAT1–transduced CTLs; this finding was also true for genes and accessible regions in exhausted compared with effector LCMV-specific cells (28). The transcriptional program of CA-RIT-NFAT1–expressing cells reflects the constitutive nuclear localization and altered activity of a single NFAT transcription factor in a controlled in vitro environment (38, 59). Our data support the idea that sustained NFAT activation, under conditions that do not favor its interaction with AP-1, mediates a significant portion of the transcriptional program associated with T-cell dysfunction, during chronic viral infection, as well as in tumor-infiltrating cells.
Both in this and the LCMV studies (26–28), exhaustion-specific accessible regions were also strongly enriched for a consensus binding motif for nuclear receptors (TGACCTTT, annotated by Homer as a Nur77/Nr4a1 motif). Nr4a2 and Nr4a3 are both highly induced at the mRNA level in OT-I relative to P14 TILs, and Nr4a1 is a well-known TCR-inducible target gene in thymocytes (61). Furthermore, Nr4a2 is up-regulated in exhausted CD8+ T cells infiltrating autochthonous melanoma (31, 62), as well as in T cells from subsets of patients with metastatic melanoma (63). Taken together, the data suggest that Nr4a2 nuclear receptors are transcriptional regulators of CD8+ T-cell exhaustion, whose activity follows a standard paradigm: NFAT initiates the exhausted state by up-regulating the expression of Nr4a2 and Nr4a3 (as well as other transcription factors relevant to T-cell exhaustion); subsequently, Nr4a2 and Nr4a3 (and the other factors) maintain the exhausted state by acting either independently or cooperatively with NFAT.
We observed only modest changes in gene transcription in OT-I cells recovered from anti–PD-L1–treated mice. The anti–PD-L1 treatment was effective, because it resulted in tumor regression with a rapid time course. mRNAs selectively up-regulated in anti–PD-L1–treated OT-I TILs encoded proteins important for reversal of T-cell exhaustion, including granzymes that mediate target cell cytolysis (55) and serine protease inhibitors (serpins) that protect CTLs from bystander damage during this process (56). Up-regulation of granzyme mRNAs was also noted in two previous reports, which analyzed gene expression changes in exhausted virus- or tumor-reactive CD8+ T cells from PD-1/PD-L1–treated mice (27, 31).
Anti–PD-L1 treatment did not lead to major changes in chromatin accessibility in exhausted cells, as also noted in chronic viral infection (27). PD-1/PD-L1 engagement is primarily assumed to inhibit TCR-proximal signaling pathways, for instance through increased activity of phosphatases and transcriptional induction of E3 ligases that degrade the TCR (51, 52), thus interrupting these inhibitory signaling interactions with blocking antibodies might not have major effects on chromatin accessibility profiles, especially if the accessibility of many regions is stably maintained after activation, as discussed above (28, 42). It is plausible that the early stages of T-cell exhaustion reflect reversible signaling defects, whereas at later stages the hyporesponsive state is at least partly imposed through epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA methylation (23), that are less easily reversed (27, 64).
Indeed, it is clear that exhausted cells in tumor or viral models and in human patients are not always readily reactivated (27, 31, 54). The simplest explanation is that targeting only the PD-1 pathway might not be sufficient to fully reverse exhaustion, especially at time points where the balance is shifted in favor of tumor growth and immune escape (as is often true for patients with cancer enrolled in experimental immunotherapies). In the autochthonous tumor model discussed above (31), anti–PD1/PD-L1 treatment initiated 8 days after tumor induction led to increased granzyme expression with no rescue of cytokine production, but removal of tumor-reactive T cells from the exhaustion-inducing stimulus (tumor antigen) in the tumor environment, coupled with exposure to IL-2 and anti–PD-1 treatment in vitro, led to recovery of cytokine production in response to antigen. It will be interesting to determine whether similar treatment of OT-I TILs in our system also leads to functional recovery, and if so, whether such recovery is associated with major changes in patterns of chromatin accessibility, especially at the level of the exhaustion-associated accessible regions identified in our study.
Chronically stimulated T cells can effectively reject established tumors if critical negative signaling pathways, such as the PD-1/PD-L1/PD-L2 axis, are blocked. There is great interest in combination therapies that can at the same time antagonize inhibitory pathways and trigger costimulatory ones; for this reason, it is important to define the set of inhibitory receptors and costimulatory molecules expressed in each exhaustion model. When we focused on selected genes known to be associated with T-cell function, we found that genes encoding several cell-surface immunomodulatory receptors were up-regulated in our OT-I TILs and in CA-RIT-NFAT1–expressing cells [Tnfrsf4 (encoding OX40), Siglecf, Sema7a, Sema4c, and Cd200 family members, Alcam and Crtam]. Notably, CD200 family members and CD244 (2B4) are also highly expressed in exhausted T cells during chronic viral infection (28). It would be worth testing whether antibodies targeting some of these receptors, used either alone or in conjunction with checkpoint blockade therapies, would revive the cytolytic functions of exhausted CD8+ T cells during antitumor and antiviral responses.
Materials and Methods
Standard procedures for CD8+ T-cell isolation and culture, B16 tumor model, adoptive T-cell transfer, tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte manipulation, and anti–PD-L1 treatment are described in SI Materials and Methods. Detailed descriptions of RNA sequencing and ATAC-seq experiments and data analysis are also available in SI Materials and Methods. Mice were used according to protocols approved by the La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology animal care and use committee.
SI Materials and Methods
Mice.
P14 animals with a transgenic TCR recognizing the LCMV glycoprotein 33 (gp33–41) (65) were used. For in vitro experiments, P14 mice were additionally deficient for TCR α-chain. For in vivo experiments, P14 mice were additionally Thy1.1+ (a kind gift from R. Ahmed, Emory University, Atlanta, GA). OT-I animals with a transgenic TCR recognizing the ovalbumin (OVA257–264) peptide (a kind gift of S. Schoenberger, La Jolla Immunology Institute, La Jolla, CA) were backcrossed to CD45.1+ (B6.SJL-Ptprca Pepcb/BoyJ) mice (The Jackson Laboratory) and used for in vivo experiments. C57BL/6J male mice (The Jackson Laboratory), age 6–16 wk, were challenged with B16-OVA tumors and used as recipients in adoptive transfer experiments. All mice were maintained in specific pathogen-free barrier facilities and used according to protocols approved by the La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology animal care and use committees.
Isolation, Culture, and Restimulation of CD8+ T Cells.
Total CD8+ T cells, harvested from the spleen and lymph nodes of 6- to 12-wk-old P14 or OT-I mice by negative selection using Dynabeads (Invitrogen), were activated by anti-CD3 (clone 2C11) plus anti-CD28 (clone 37.51) (BD Biosciences) at 1 μg/mL on plates precoated with 50 μg/mL goat anti-hamster IgG (MP Biomedicals). On day 2, T cells were removed from the antibody-coated plate and recultured at 400,000 cells per milliliter with low dose (10 units/mL) recombinant IL-2 (Hoffmann-La Roche). Every day the concentration was adjusted to 400,000 cells per milliliter until days 5–6, when cells were either adoptively transferred (as described in B16 Tumor Model, Adoptive T-Cell Transfer, and Anti–PD-L1 Treatment) or restimulated in vitro for 2 h with the following agents (or combinations thereof): 10 nM PMA, 500 nM ionomycin, 2 μM Cyclosporin A (added 15 min before stimulation), or anti-CD3 (5 μg/mL, immobilized).
B16 Tumor Model, Adoptive T-Cell Transfer, and Anti–PD-L1 Treatment.
The B16-OVA mouse melanoma cell line expressing the ovalbumin protein (a kind gift of S. Schoenberger, La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology, La Jolla, CA) was previously described (32). Cells were cultured in Iscove's modified Dulbecco's medium (IMDM)/10% (vol/vol) FBS and passaged two to three times before inoculation. At the time of injection, cells were trypsinized and resuspended in Hanks balanced salt solution without Phenol Red at 5 million cells per milliliter C57BL/6J male mice (6–16 wk old) were injected intradermally with 250,000–300,000 B16-OVA cells (50 μL per injection). Tumor measurements were recorded with a manual caliper every 2–3 days and tumor area was calculated in centimeters squared (length × width). When the tumor reached a dimeter of 0.25–0.4 cm, Thy1.1+ P14 and CD45.1+ OT-I CTLs generated in vitro (as described in Isolation, Culture, and Restimulation of CD8+ T Cells) were collected, washed with PBS, and resuspended at a concentration of 20 million cells per milliliter in PBS, at a 1:1 P14:OT-I ratio. A total of 2–4.5 million CTLs were i.v. injected into the retroorbital vein in anesthetized mice bearing B16-OVA tumors. Mice were killed on day 3 or day 8 after adoptive T-cell transfer, or whenever tumors reached a diameter of 1.2 cm. In selected experiments, anti–PD-L1 Ab (clone no. 10F.9G2, BioXCell) or control anti-KLH rat IgG2b (BioXCell) were inoculated intraperitoneally (200 μg per mouse). Two injections of anti–PD-L1 or control IgG were performed, 3 and 6 days after adoptive transfer of OT-I CTLs. This regimen was optimized not to completely block the tumor growth, which would have prevented our investigation of infiltrating lymphocytes (Fig. S1). Randomization was performed such that each treatment group (anti–PD-L1 or control) comprised mice with comparable tumor sizes.
TILs Harvest, Sorting, and in Vitro Restimulation.
Mice were killed at specific time points (day 3 or 8 after adoptive T-cell transfer). Cell suspensions were prepared from spleens and tumors. Tumors were dissected, transferred to RPMI medium supplemented with TL Liberase Mixture (100 μg/mL; Roche) and incubated at 37 °C for 15 min. Then, additional Liberase was added, incubating with mixing for an additional 10 min. Tissue suspensions were passed through 70-μm strainers and washed with PBS/2% FBS. Samples were immediately processed for surface staining with the following Abs (BioLegend, eBioscience, or BD Biosciences): anti-CD8a (clone 53–6.7), anti-CD45.1 (clone A20), anti-Thy1.1 (clone OX-7), anti–PD-1 (clone 29F.1A12), anti–Tim-3 (clone RMT3-23), anti-LAG3 (clone C9B7W), anti–4-1BB (clone 17B5), anti-CD69 (clone HI.2F3), and Fixable Viability Dye eFluor 780.
For cytokine analysis upon ex vivo restimulation, whole spleen or tumor cell suspensions (1 × 106 cells per 500 μL) were plated in 48-well plates before adding 100 nM cognate peptides (OVA257–264 and LCMV gp33–41). Brefeldin A was added after incubating for 1 h at 37 °C. After an additional 3 h at 37 °C, cells were collected, stained with surface markers, and fixed with 3% PFA for 20 min at room temperature. Permeabilization and cytokine staining (anti-IFNγ, clone XMG1.2; anti-TNF, clone MP6-XT22; and anti-IL2, clone JES6-SH4) were performed in PBS/2% FBS plus 0.5% saponin. Data were acquired on Fortessa, FACSCanto, or LSRII cytometers (Becton Dickinson) and analyzed using FlowJo software (Tree Star).
For sorting of adoptively transferred OT-I and P14 cells, CD8+ T cells were preenriched from tumors using the Dynabeads FlowComp Mouse CD8 selection kit (Thermo Fisher) or from spleens using the Dynabeads Untouched Mouse CD8+ T-cell kit (Thermo Fisher). To ensure adequate cell yield, samples from multiple mice belonging to the same group were pooled before enrichment. Enriched CD8+ T cells were then stained with anti-CD8a (53-6.7), anti-CD45.1 (A20), anti-Thy1.1 (OX-7), anti–PD-1 (29F.1A12), anti–Tim-3 (RMT3-23), and Fixable Viability Dye eFluor 780. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes were isolated as live CD8+Thy1.1+ (P14) or CD8+CD45.1+ (OT-I) on BD FACSARIA III or FUSION sorters. PD-1 and Tim-3 expression on P14 and OT-I cells was checked in each sorting experiment before ATAC-seq or RNA-seq. For RNA-seq experiments, cells were sorted directly in lysis buffer and frozen at −80 °C before further processing.
ATAC-Seq.
ATAC-seq was performed according to Buenrostro et al. (25) with minor modifications: 30,000–50,000 sorted CD8+ T cells cells were lysed to extract nuclei. Nuclei were resuspended in 50 μL 1× TD buffer containing 2.5 μL transposase (Nextera, Illumina). The transposase reaction was conducted for 30 min at 37 °C, with mild shaking. Library amplification and barcoding were performed with the library amplification kit (KAPA Biosystems) using index primers, designed according to Buenrostro et al. (25) at a final concentration of 500 nM. PCR was conducted for 10–11 cycles. Library purification was performed with the MinElute PCR Purification Kit (Qiagen) and library size distribution was assessed using the Bioanalyzer High Sensitivity DNA Kit (Agilent). ATAC-seq libraries were quantified before pooling and sequencing using the real-time library quantification kit (KAPA Biosystems). Paired-end sequencing was performed on a HiSeq 2500 (Illumina) with 50 cycles for each read. Raw data from the sequencer was uploaded to Basespace (Illumina) for demultiplexing and FASTQ file generation.
ATAC-Seq Analysis.
Sequencing reads were mapped to the mouse genome (mm10) using bowtie2 with parameters --non-deterministic --mm --very-sensitive-local -X 2000. Unmapped reads, multimapping reads, and reads aligned to chrM, chrY, or unlocalized/unplaced scaffolds were removed with samtools and awk; duplicate reads were removed using picard MarkDuplicates; reads mapping to regions blacklisted by ENCODE (lifted over to mm10) were removed with bedtools. Reads were shifted by +4 bp (positive strand) or −5 bp (negative strand) so that the read start represents the center of the Tn5 transposon binding event (25). Each read was trimmed to 15 bp to account for the Tn5 steric hindrance (66). Peaks were called using a window-based approach using the R package csaw. Background signal was removed by discarding windows that did not reach 5 counts per million in at least one sample. Manually curated gender-associated regions on chrX were discarded, using the following coordinates: 103,410,000–103,490,000 (Xist), 50,549,000–50,638,000 (Firre), and 75,725,000–75,763,000 (intergenic). Libraries were normalized using the trimmed mean of M values (TMM) method computed using high-abundance regions separately for in vitro and in vivo samples. Batch effects were removed with the RemoveBatchEffect function from limma. Juxtaposed windows were merged in a single peak call up to a maximal chaining distance of 1,500 bp. For each peak call, the single 300-bp window with the highest abundance was retained as representative of that peak. Differential peaks were required to exhibit at least a 2.5-fold-change difference with false discovery rate (FDR) less than 0.05 using csaw’s Genewise negative binomial generalized linear models with quasi-likelihood tests. A more relaxed analysis was performed on the anti–PD-L1–treated samples: log2-fold changes of ATAC-seq peak signal between OT-I control and anti–PD-L1–treated samples were z-scored, and the regions deviating more than 2 SDs from the mean were considered differentially accessible. Clustering was performed using the partitioning around medoids (PAM) algorithm on peak counts per million z-scaled across samples. Heat maps of peak signals were generated using the computeMatrix and plotHeatmap scripts from the deepTools package. Genomic annotations of peaks and motif enrichment were computed with Homer (40) using the peak 300-bp-long windows. Foreground (or “test”) regions for each enrichment test are indicated: as a general rule, the subset of peaks of interest (for example, regions showing higher accessibility in a given sample compared with another sample) were used as foreground, whereas all of the accessible regions (both differentially and nondifferentially accessible) of that sample were used as background. Because all members of a transcription factor family tended to show similar enrichment due to motif similarity, to avoid redundancy one representative motif was shown in each figure (except for NFκB-p65 and NFAT, both belonging to the RHD family) but Datasets S1–S5 report the full Homer output. Motif occurrences in the Pdcd1 enhancer were manually curated using consensus motifs. Intersection of exhaustion-associated regions identified in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes with those identified in chronic LCMV infection (union of clusters 3 and 6 from figure 5B of Scott-Browne et al.) (28) were performed with bedtools, and the significance of the overlap was determined according to Fisher’s exact test. To generate tracks, BigWig files of coverage for individual replicates were computed with deepTools bamCoverage (--binSize 10 --normalizeUsingRPKM --smoothLength 30) and further rescaled using the TMM normalization coefficient calculated by csaw. The University of California Santa Cruz bigWigMerge utility was used to generate average coverage tracks for each biological condition.
RNA-Seq.
Total RNA was extracted from 5,000–30,000 sorted CD8+ T cells using the RNeasy micro kit or the miRNeasy micro kit. RNA quality was evaluated with the Bioanalyzer RNA pico kit (Agilent Technologies). Libraries were prepared from polyA+ RNA using either the Whole Transcriptome Amplification Sequencing Technology SEQR kit (Sigma-Aldrich) as previously described (67) (for OT-I vs. P14 TILs comparison) or the Smart-seq2 protocol (Clontech) (68) with minor modifications (for OT-I Ctrl vs. OT-I anti–PD-L1 comparison). Briefly, purified RNA was reverse transcribed using SuperScript II, Oligo dT30 VN primers, and template switching primers. A preamplification step of eight PCR cycles was performed using the Kapa HiFi Hotstart kit (Kapa Biosystems). The PCR product was purified using AMPureXP beads (Beckman Coulter) and 1 ng was further used for library preparation using the Nextera XT LibraryPrep kit (Illumina). Tagmented DNA was amplified with a 12-cycle PCR and again purified with AMPureXP beads. Library size distribution and yield were evaluated using the Bioanalyzer high-sensitivity DNA kit. Libraries were pooled at equimolar ratios and sequenced with the rapid run protocol on a HiSEq. 2500 (Illumina) with 50-nt single end cycling.
RNA-Seq Analysis.
Tumor-infiltrating OT-I vs. P14 CTLs.
Trimmed reads were mapped to the mouse genome (mm10) using STAR with the ENCODE parameters as per developer’s manual. Unmapped and multimapping reads were removed before counting using featureCounts with GENCODE vM6 annotations. Counts were analyzed using the R package edgeR and libraries were normalized using the TMM method. Differentially expressed genes were required to pass a linear fold change threshold of 2 and a FDR threshold of 0.05. The significance of the overlap between our transcriptomics data and microarray data from Doering et al. (37) or RNA-seq data from Martinez et al. (38) was determined by Fisher’s exact test upon gene matching using official gene symbols and aliases. To analyze the correlation between ATAC-seq signal and gene expression, differentially accessible ATAC-seq peaks were matched to genes by proximity to the TSS. Peaks were split between proximal (−5 kb to +1 kb from the TSS) and distal (within 50 kb from the TSS, excluding the proximal region) and the distribution of log2-fold changes was shown in boxplots.
Tumor-infiltrating OT-I Ctrl versus anti–PD-L1 treated.
Trimmed reads were mapped to the mouse genome (mm10) using TopHat. Uniquely mapping reads were counted using HTSeq count with RefSeq annotations. Counts were analyzed using the R package edgeR and libraries were normalized using the TMM method. Differentially expressed genes were required to pass a linear fold change threshold of 2 and a FDR threshold of 0.1.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Cheryl Kim, Kurt van Gunst, Lara Nosworthy, and Denise Hinz at the La Jolla Institute (LJI) Flow Cytometry Facility for help with cell sorting; Jason Greenbaum and Zheng “Alex” Fu of the Bioinformatics Core, and Jeremy Day of the Sequencing Core for help with next-generation sequencing (all at LJI); and Gregory Seumois and Brandie White from the LJI Sequencing Facility for help in preparing libraries for RNA-seq. This work was funded by NIH Grants R01 AI109842 and AI40127 (to A.R. and P.G.H.), and AI84167 (to P.G.H.). G.P.M. was supported by a Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Cientifico e Tecnologico (CNPq) Fellowship, Brazil. R.S. acknowledges support from a Quantitative and Computational Biosciences (QCB) Collaboratory Postdoctoral Fellowship and the QCB Collaboratory community directed by Matteo Pellegrini. V.W. was supported by a Pediatric Hematology–Oncology Fellowship from the University of California, San Diego. J.P.S.-B. was supported by the Fraternal Order of Eagles Fellow of the Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation, DRG-2069-11.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Data deposition: The data reported in this paper have been deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo (accession nos. GSE93014 and GSE88987).
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1620498114/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Wherry EJ, Kurachi M. Molecular and cellular insights into T cell exhaustion. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15(8):486–499. doi: 10.1038/nri3862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Brahmer JR, et al. Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(26):2455–2465. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1200694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Robert C, et al. Nivolumab in previously untreated melanoma without BRAF mutation. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(4):320–330. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1412082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tumeh PC, et al. PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Nature. 2014;515(7528):568–571. doi: 10.1038/nature13954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.van Rooij N, et al. Tumor exome analysis reveals neoantigen-specific T-cell reactivity in an ipilimumab-responsive melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(32):e439–e442. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.47.7521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pleasance ED, et al. A comprehensive catalogue of somatic mutations from a human cancer genome. Nature. 2010;463(7278):191–196. doi: 10.1038/nature08658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Larkin J, et al. Efficacy and safety of Nivolumab in patients with BRAF V600 mutant and BRAF wild-type advanced melanoma: A pooled analysis of 4 clinical trials. JAMA Oncol. 2015;1(4):433–440. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.1184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hamid O, et al. Safety and tumor responses with lambrolizumab (anti-PD-1) in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(2):134–144. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1305133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schietinger A, Greenberg PD. Tolerance and exhaustion: Defining mechanisms of T cell dysfunction. Trends Immunol. 2014;35(2):51–60. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2013.10.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rao A, Luo C, Hogan PG. Transcription factors of the NFAT family: Regulation and function. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:707–747. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.15.1.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hogan PG, Chen L, Nardone J, Rao A. Transcriptional regulation by calcium, calcineurin, and NFAT. Genes Dev. 2003;17(18):2205–2232. doi: 10.1101/gad.1102703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Choi S, Schwartz RH. Molecular mechanisms for adaptive tolerance and other T cell anergy models. Semin Immunol. 2007;19(3):140–152. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.02.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zajac AJ, et al. Viral immune evasion due to persistence of activated T cells without effector function. J Exp Med. 1998;188(12):2205–2213. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.12.2205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ladányi A, et al. T-cell activation marker expression on tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes as prognostic factor in cutaneous malignant melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(2):521–530. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-1161-03. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gros A, et al. PD-1 identifies the patient-specific CD8+ tumor-reactive repertoire infiltrating human tumors. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(5):2246–2259. doi: 10.1172/JCI73639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Stephen TL, et al. Transforming growth factor β-mediated suppression of antitumor T cells requires FoxP1 transcription factor expression. Immunity. 2014;41(3):427–439. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.08.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Shin H, et al. A role for the transcriptional repressor Blimp-1 in CD8(+) T cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection. Immunity. 2009;31(2):309–320. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.06.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Buggert M, et al. T-bet and Eomes are differentially linked to the exhausted phenotype of CD8+ T cells in HIV infection. PLoS Pathog. 2014;10(7):e1004251. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Quigley M, et al. Transcriptional analysis of HIV-specific CD8+ T cells shows that PD-1 inhibits T cell function by upregulating BATF. Nat Med. 2010;16(10):1147–1151. doi: 10.1038/nm.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Doedens AL, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factors enhance the effector responses of CD8(+) T cells to persistent antigen. Nat Immunol. 2013;14(11):1173–1182. doi: 10.1038/ni.2714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Staron MM, et al. The transcription factor FoxO1 sustains expression of the inhibitory receptor PD-1 and survival of antiviral CD8(+) T cells during chronic infection. Immunity. 2014;41(5):802–814. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.10.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chang JT, Wherry EJ, Goldrath AW. Molecular regulation of effector and memory T cell differentiation. Nat Immunol. 2014;15(12):1104–1115. doi: 10.1038/ni.3031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Youngblood B, et al. Cutting edge: Prolonged exposure to HIV reinforces a poised epigenetic program for PD-1 expression in virus-specific CD8 T cells. J Immunol. 2013;191(2):540–544. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bally AP, Austin JW, Boss JM. Genetic and epigenetic regulation of PD-1 expression. J Immunol. 2016;196(6):2431–2437. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Buenrostro JD, Giresi PG, Zaba LC, Chang HY, Greenleaf WJ. Transposition of native chromatin for fast and sensitive epigenomic profiling of open chromatin, DNA-binding proteins and nucleosome position. Nat Methods. 2013;10(12):1213–1218. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sen DR, et al. The epigenetic landscape of T cell exhaustion. Science. 2016;354(6316):1165–1169. doi: 10.1126/science.aae0491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Pauken KE, et al. Epigenetic stability of exhausted T cells limits durability of reinvigoration by PD-1 blockade. Science. 2016;354(6316):1160–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf2807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Scott-Browne JP, et al. Dynamic changes in chromatin accessibility occur in CD8(+) T cells responding to viral infection. Immunity. 2016;45(6):1327–1340. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.10.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pipkin ME, et al. Interleukin-2 and inflammation induce distinct transcriptional programs that promote the differentiation of effector cytolytic T cells. Immunity. 2010;32(1):79–90. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.11.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Thurman RE, et al. The accessible chromatin landscape of the human genome. Nature. 2012;489(7414):75–82. doi: 10.1038/nature11232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schietinger A, et al. Tumor-specific T cell dysfunction is a dynamic antigen-driven differentiation program initiated early during tumorigenesis. Immunity. 2016;45(2):389–401. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.07.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Falo LD, Jr, Kovacsovics-Bankowski M, Thompson K, Rock KL. Targeting antigen into the phagocytic pathway in vivo induces protective tumour immunity. Nat Med. 1995;1(7):649–653. doi: 10.1038/nm0795-649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schüler T, Blankenstein T. Cutting edge: CD8+ effector T cells reject tumors by direct antigen recognition but indirect action on host cells. J Immunol. 2003;170(9):4427–4431. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.9.4427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gerner MY, Heltemes-Harris LM, Fife BT, Mescher MF. Cutting edge: IL-12 and type I IFN differentially program CD8 T cells for programmed death 1 re-expression levels and tumor control. J Immunol. 2013;191(3):1011–1015. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Liu X, et al. Endogenous tumor-reactive CD8(+) T cells are differentiated effector cells expressing high levels of CD11a and PD-1 but are unable to control tumor growth. OncoImmunology. 2013;2(6):e23972. doi: 10.4161/onci.23972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Geissler K, et al. Immune signature of tumor infiltrating immune cells in renal cancer. OncoImmunology. 2015;4(1):e985082. doi: 10.4161/2162402X.2014.985082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Doering TA, et al. Network analysis reveals centrally connected genes and pathways involved in CD8+ T cell exhaustion versus memory. Immunity. 2012;37(6):1130–1144. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.08.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Martinez GJ, et al. The transcription factor NFAT promotes exhaustion of activated CD8+ T cells. Immunity. 2015;42(2):265–278. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.01.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Seumois G, et al. Epigenomic analysis of primary human T cells reveals enhancers associated with TH2 memory cell differentiation and asthma susceptibility. Nat Immunol. 2014;15(8):777–788. doi: 10.1038/ni.2937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Heinz S, et al. Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. Mol Cell. 2010;38(4):576–589. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.05.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wei H, et al. Cutting edge: Foxp1 controls naive CD8+ T cell quiescence by simultaneously repressing key pathways in cellular metabolism and cell cycle progression. J Immunol. 2016;196(9):3537–3541. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bevington SL, et al. Inducible chromatin priming is associated with the establishment of immunological memory in T cells. EMBO J. 2016;35(5):515–535. doi: 10.15252/embj.201592534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Oestreich KJ, Yoon H, Ahmed R, Boss JM. NFATc1 regulates PD-1 expression upon T cell activation. J Immunol. 2008;181(7):4832–4839. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.7.4832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Shaw JP, et al. Identification of a putative regulator of early T cell activation genes. Science. 1988;241(4862):202–205. doi: 10.1126/science.3260404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Jain J, et al. The T-cell transcription factor NFATp is a substrate for calcineurin and interacts with Fos and Jun. Nature. 1993;365(6444):352–355. doi: 10.1038/365352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kurachi M, et al. The transcription factor BATF operates as an essential differentiation checkpoint in early effector CD8+ T cells. Nat Immunol. 2014;15(4):373–383. doi: 10.1038/ni.2834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Rengarajan J, et al. Sequential involvement of NFAT and Egr transcription factors in FasL regulation. Immunity. 2000;12(3):293–300. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Safford M, et al. Egr-2 and Egr-3 are negative regulators of T cell activation. Nat Immunol. 2005;6(5):472–480. doi: 10.1038/ni1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zheng Y, et al. Egr2-dependent gene expression profiling and ChIP-Seq reveal novel biologic targets in T cell anergy. Mol Immunol. 2013;55(3–4):283–291. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.03.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Austin JW, Lu P, Majumder P, Ahmed R, Boss JM. STAT3, STAT4, NFATc1, and CTCF regulate PD-1 through multiple novel regulatory regions in murine T cells. J Immunol. 2014;192(10):4876–4886. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sheppard KA, et al. PD-1 inhibits T-cell receptor induced phosphorylation of the ZAP70/CD3zeta signalosome and downstream signaling to PKCtheta. FEBS Lett. 2004;574(1–3):37–41. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.07.083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Xiao Y, et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 modulates T cell responses by controlling Cbl-b degradation. J Immunol. 2015;195(9):4218–4227. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Topalian SL, et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(26):2443–2454. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1200690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hugo W, et al. Genomic and transcriptomic features of response to anti-PD-1 therapy in metastatic melanoma. Cell. 2016;165(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Chowdhury D, Lieberman J. Death by a thousand cuts: Granzyme pathways of programmed cell death. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:389–420. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ashton-Rickardt PG. Serine protease inhibitors and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunol Rev. 2010;235(1):147–158. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2010.00892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Li P, et al. BATF-JUN is critical for IRF4-mediated transcription in T cells. Nature. 2012;490(7421):543–546. doi: 10.1038/nature11530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Glasmacher E, et al. A genomic regulatory element that directs assembly and function of immune-specific AP-1-IRF complexes. Science. 2012;338(6109):975–980. doi: 10.1126/science.1228309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Macián F, García-Rodríguez C, Rao A. Gene expression elicited by NFAT in the presence or absence of cooperative recruitment of Fos and Jun. EMBO J. 2000;19(17):4783–4795. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.17.4783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Speiser DE, et al. T cell differentiation in chronic infection and cancer: Functional adaptation or exhaustion? Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(11):768–774. doi: 10.1038/nri3740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Moran AE, et al. T cell receptor signal strength in Treg and iNKT cell development demonstrated by a novel fluorescent reporter mouse. J Exp Med. 2011;208(6):1279–1289. doi: 10.1084/jem.20110308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Giordano M, et al. Molecular profiling of CD8 T cells in autochthonous melanoma identifies Maf as driver of exhaustion. EMBO J. 2015;34(15):2042–2058. doi: 10.15252/embj.201490786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Tirosh I, et al. Dissecting the multicellular ecosystem of metastatic melanoma by single-cell RNA-seq. Science. 2016;352(6282):189–196. doi: 10.1126/science.aad0501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Turner SJ, Russ BE. Can T cells be too exhausted to fight back? Science. 2016;354(6316):1104–1105. doi: 10.1126/science.aal3204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Pircher H, Bürki K, Lang R, Hengartner H, Zinkernagel RM. Tolerance induction in double specific T-cell receptor transgenic mice varies with antigen. Nature. 1989;342(6249):559–561. doi: 10.1038/342559a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Adey A, et al. Rapid, low-input, low-bias construction of shotgun fragment libraries by high-density in vitro transposition. Genome Biol. 2010;11(12):R119. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-12-r119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Arlehamn CL, et al. Transcriptional profile of tuberculosis antigen-specific T cells reveals novel multifunctional features. J Immunol. 2014;193(6):2931–2940. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Picelli S, et al. Full-length RNA-seq from single cells using Smart-seq2. Nat Protoc. 2014;9(1):171–181. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2014.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.