Abstract
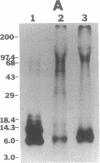
Rabbit antisera directed against a mixture of proteins solubilized from the wild-type adult Caenorhabditis elegans cuticle were used to isolate mutants, induced by ethyl methanesulfonate treatment, that exhibit alterations in surface antigenicity by immunofluorescence. Genetic mapping and complementation data for four such mutations define two genes, srf-2(I) and srf-3(IV). The mutant phenotypes observed by immunofluorescence appear to result from unmasking of antigenic determinants that are normally hidden in the wild-type cuticle. In support of this hypothesis, surface radioiodination experiments indicate that components labeled on the wild-type surface are missing or less readily labeled on the surface of srf-2 and srf-3 mutants.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambros V. A hierarchy of regulatory genes controls a larva-to-adult developmental switch in C. elegans. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambros V., Horvitz H. R. Heterochronic mutants of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 1984 Oct 26;226(4673):409–416. doi: 10.1126/science.6494891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambros V., Horvitz H. R. The lin-14 locus of Caenorhabditis elegans controls the time of expression of specific postembryonic developmental events. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):398–414. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974 May;77(1):71–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlow C. K., Franke E. D., Lowrie R. C., Jr, Partono F., Philipp M. Monoclonal antibody to a unique surface epitope of the human filaria Brugia malayi identifies infective larvae in mosquito vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6914–6918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. V., Rogalski T. M., Donati L. M., Baillie D. L. The unc-22(IV) region of Caenorhabditis elegans: genetic analysis of lethal mutations. Genetics. 1988 Jun;119(2):345–353. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. N., Kramer J. M., Hirsh D. Number and organization of collagen genes in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2389–2395. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. N., Kusch M., Edgar R. S. Cuticle of Caenorhabditis elegans: its isolation and partial characterization. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):7–17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. N., Laufer J. S., Kusch M., Edgar R. S. Genetic and Phenotypic Characterization of Roller Mutants of CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS. Genetics. 1980 Jun;95(2):317–339. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.2.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson E. L., Horvitz H. R. Identification and characterization of 22 genes that affect the vulval cell lineages of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1985 May;110(1):17–72. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grencis R. K., Crawford C., Pritchard D. I., Behnke J. M., Wakelin D. Immunization of mice with surface antigens from the muscle larvae of Trichinella spiralis. Parasite Immunol. 1986 Nov;8(6):587–596. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1986.tb00872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins B. J., Hirsh D. Roller mutants of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):63–72. doi: 10.1007/BF02425326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazura J. W., Grove D. I. Stage-specific antibody-dependent eosinophil-mediated destruction of Trichinella spiralis. Nature. 1978 Aug 10;274(5671):588–589. doi: 10.1038/274588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. M., Cox G. N., Hirsh D. Comparisons of the complete sequences of two collagen genes from Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):599–606. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. M., Johnson J. J., Edgar R. S., Basch C., Roberts S. The sqt-1 gene of C. elegans encodes a collagen critical for organismal morphogenesis. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90214-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusch M., Edgar R. S. Genetic studies of unusual loci that affect body shape of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans and may code for cuticle structural proteins. Genetics. 1986 Jul;113(3):621–639. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie C. D., Jungery M., Taylor P. M., Ogilvie B. M. Activation of complement, the induction of antibodies to the surface of nematodes and the effect of these factors and cells on worm survival in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):594–601. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moerman D. G., Baillie D. L. Formaldehyde mutagenesis in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Mutat Res. 1981 Feb;80(2):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(81)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipp M., Davis T. B. Biochemical and immunologic characterization of a major surface antigen of Dirofilaria immitis infective larvae. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2621–2627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipp M., Davis T. B., Storey N., Carlow C. K. Immunity in filariasis: perspectives for vaccine development. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:685–716. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.003345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipp M., Rumjaneck F. D. Antigenic and dynamic properties of helminth surface structures. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Mar;10(3):245–268. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Politz S. M., Chin K. J., Herman D. L. Genetic analysis of adult-specific surface antigenic differences between varieties of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1987 Nov;117(3):467–476. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanyam D., Rao Y. V., Menta K., Nelson D. S. Serum-dependent adhesion and cytotoxicity of cells to Litomosoides carinii microfilariae. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):529–530. doi: 10.1038/260529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent C., Tsuing N., Horvitz H. R. Egg-laying defective mutants of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1983 Aug;104(4):619–647. doi: 10.1093/genetics/104.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Mende N., Bird D. M., Albert P. S., Riddle D. L. dpy-13: a nematode collagen gene that affects body shape. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):567–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90215-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]