Abstract
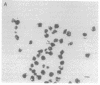
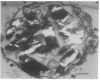
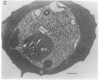
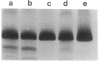
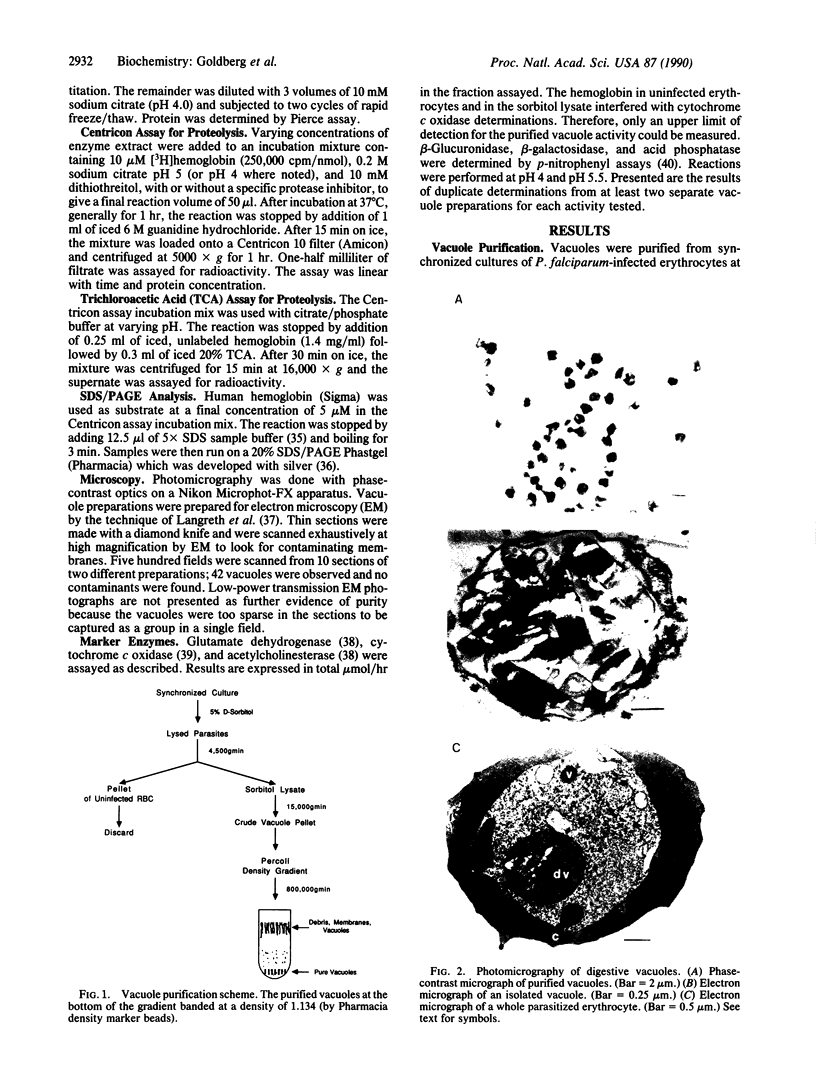
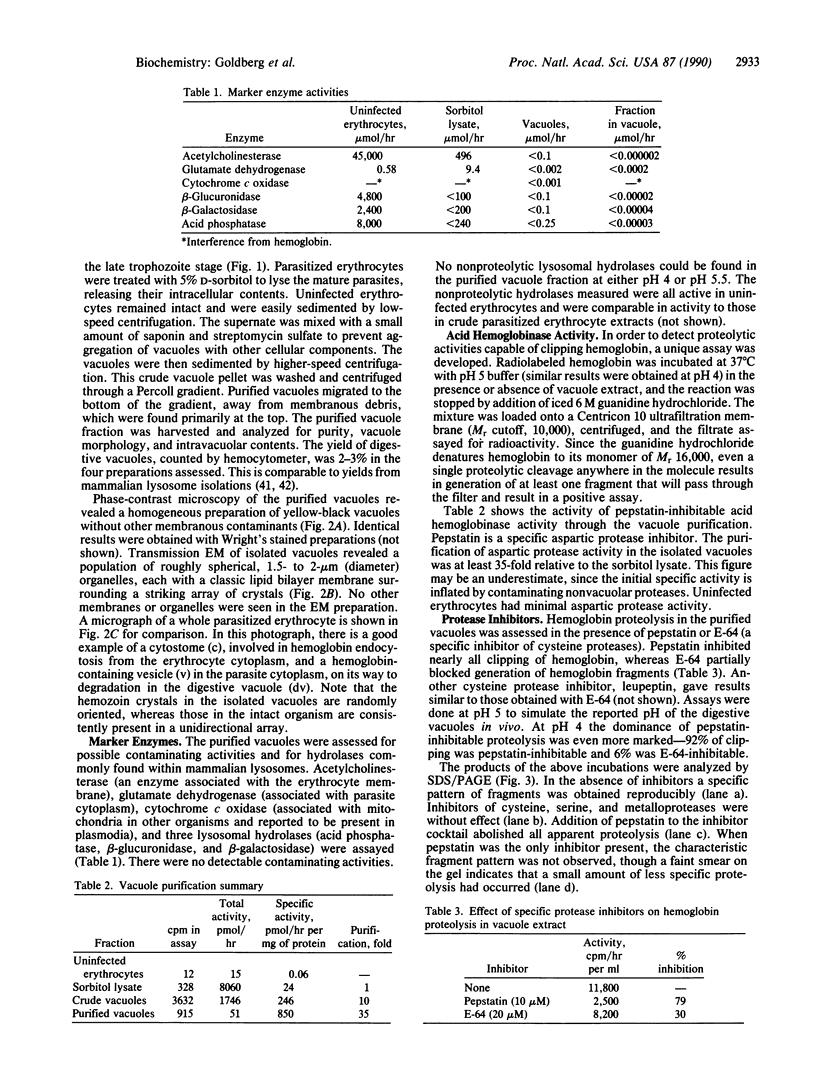
The malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum uses host erythrocyte hemoglobin as a major nutrient source. We report the purification of P. falciparum digestive vacuoles and characterization of the degradative process therein. Vacuoles were isolated by a combination of differential centrifugation and density gradient separation. The pure vacuoles were capable of degrading hemoglobin to small fragments with a pH optimum of 5-5.5. Proteolysis in the vacuoles appears to be an ordered process, requiring an aspartic protease to clip intact hemoglobin before other proteolytic activities can function efficiently. The vacuoles do not contain other hydrolases commonly found in lysosomes and therefore appear to be unique proteolytic organelles designed specifically to degrade hemoglobin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aikawa M., Hepler P. K., Huff C. G., Sprinz H. The feeding mechanism of avian malarial parasites. J Cell Biol. 1966 Feb;28(2):355–373. doi: 10.1083/jcb.28.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aikawa M. Parasitological review. Plasmodium: the fine structure of malarial parasites. Exp Parasitol. 1971 Oct;30(2):284–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(71)90094-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aissi E., Charet P., Bouquelet S., Biguet J. Endoprotease in Plasmodium yoelii nigeriensis. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1983;74(3):559–566. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(83)90229-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert K. A., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. The 87-kDa protein, a major specific substrate for protein kinase C: purification from bovine brain and characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK L., GRANT P. T., KERMACK W. O. Proteolytic enzymes of the erythrocytic forms of roden and simian species of malarial plasmodia. Exp Parasitol. 1961 Nov;11:372–379. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(61)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi I., Mego J. L. Purification of Plasmodium falciparum digestive vacuoles and partial characterization of the vacuolar membrane ATPase. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Oct;31(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua C. G., Carrell R. W., Howard B. H. The amino acid sequence of the alpha chain of the major haemoglobin of the rat (Rattus norvegicus). Biochem J. 1975 Jul;149(1):259–269. doi: 10.1042/bj1490259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan J. M., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. Red blood cells contain a pathway for the degradation of oxidant-damaged hemoglobin that does not require ATP or ubiquitin. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5705–5713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairlamb A. H., Paul F., Warhurst D. C. A simple magnetic method for the purification of malarial pigment. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Jul;12(3):307–312. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROMAN N. B. Dynamic aspects of the nitrogen metabolism of Plasmodium gallinaceum in vivo and in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1951 Mar-Apr;88(2):126–150. doi: 10.1093/infdis/88.2.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrick L. M., Sloan R. L., Ryan T. W., Klonowski T. J., Garrick M. D. Primary structure of the major beta-chain of rat haemoglobins. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 1;173(1):321–330. doi: 10.1042/bj1730321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyang F. N., Poole B., Trager W. Peptidases from Plasmodium falciparum cultured in vitro. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1982 Apr;5(4):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(82)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempelmann E., Wilson R. J. Endopeptidases from Plasmodium knowlesi. Parasitology. 1980 Apr;80(2):323–330. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000000780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koldovský O., Palmieri M. Cortisone-evoked decrease of acid -galactosidase, -glucuronidase, N-acetyl- -glucosaminidase and arylsulphatase in the ileum of suckling rats. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(3):697–701. doi: 10.1042/bj1250697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Schlesinger P. H., Gluzman I. Y. Antimalarials increase vesicle pH in Plasmodium falciparum. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2302–2309. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambros C., Vanderberg J. P. Synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stages in culture. J Parasitol. 1979 Jun;65(3):418–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langreth S. G., Jensen J. B., Reese R. T., Trager W. Fine structure of human malaria in vitro. J Protozool. 1978 Nov;25(4):443–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1978.tb04167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy M. R., Chou S. C. Activity and some properties of an acid proteinase from normal and Plasmodium berghei-infected red cells. J Parasitol. 1973 Dec;59(6):1064–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy M. R., Siddiqui W. A., Chou S. C. Acid protease activity in Plasmodium falciparum and P. knowlesi and ghosts of their respective host red cells. Nature. 1974 Feb 22;247(5442):546–549. doi: 10.1038/247546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maunsbach A. B. Isolation of kidney lysosomes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:330–339. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polet H., Conrad M. E. Malaria: extracellular amino acid requirements for in vitro growth of erythrocytic forms of Plasmodium knowlesi. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jan;127(1):251–253. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal P. J., McKerrow J. H., Aikawa M., Nagasawa H., Leech J. H. A malarial cysteine proteinase is necessary for hemoglobin degradation by Plasmodium falciparum. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1560–1566. doi: 10.1172/JCI113766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth E. F., Jr, Brotman D. S., Vanderberg J. P., Schulman S. Malarial pigment-dependent error in the estimation of hemoglobin content in Plasmodium falciparum-infected red cells: implications for metabolic and biochemical studies of the erythrocytic phases of malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Sep;35(5):906–911. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudzinska M. A., Trager W., Bray R. S. Pinocytotic uptake and the digestion of hemoglobin in malaria parasites. J Protozool. 1965 Nov;12(4):563–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1965.tb03256.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Fukabori Y., Suzuki M. Plasmodium berghei: a study of globinolytic enzyme in erythrocytic parasite. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 May;264(3-4):487–495. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheibel L. W., Miller J. Cytochrome oxidase activity in platelet-free preparations of Plasmodium knowlesi. J Parasitol. 1969 Aug;55(4):825–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W. Amino acid metabolism and protein synthesis in malarial parasites. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(2-3):265–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W. Biochemistry of Plasmodium (malarial parasites). Microbiol Rev. 1979 Dec;43(4):453–495. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.4.453-495.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W., Tanigoshi L. Purification of Plasmodium lophurae cathepsin D and its effects on erythrocyte membrane proteins. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Jul;8(3):207–226. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tentori L., Salvati A. M. Hemoglobinometry in human blood. Methods Enzymol. 1981;76:707–715. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)76152-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theakston R. D., Fletcher K. A., Maegraith B. G. The use of electron microscope autoradiography for examining the uptake and degradation of haemoglobin by Plasmodium berghei. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1970 Mar;64(1):63–71. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1970.11686664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Jensen J. B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.781840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander Jagt D. L., Hunsaker L. A., Campos N. M. Characterization of a hemoglobin-degrading, low molecular weight protease from Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Mar;18(3):389–400. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander Jagt D. L., Intress C., Heidrich J. E., Mrema J. E., Rieckmann K. H., Heidrich H. G. Marker enzymes of Plasmodium falciparum and human erythrocytes as indicators of parasite purity. J Parasitol. 1982 Dec;68(6):1068–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wattiaux R., Wattiaux-De Coninck S., Ronveaux-dupal M. F., Dubois F. Isolation of rat liver lysosomes by isopycnic centrifugation in a metrizamide gradient. J Cell Biol. 1978 Aug;78(2):349–368. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayon A., Cabantchik Z. I., Ginsburg H. Identification of the acidic compartment of Plasmodium falciparum-infected human erythrocytes as the target of the antimalarial drug chloroquine. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2695–2700. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02195.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayon A., Timberg R., Friedman S., Ginsburg H. Effects of chloroquine on the feeding mechanism of the intraerythrocytic human malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum. J Protozool. 1984 Aug;31(3):367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb02981.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarchin S., Krugliak M., Ginsburg H. Digestion of the host erythrocyte by malaria parasites is the primary target for quinoline-containing antimalarials. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Jul 15;35(14):2435–2442. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90473-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]